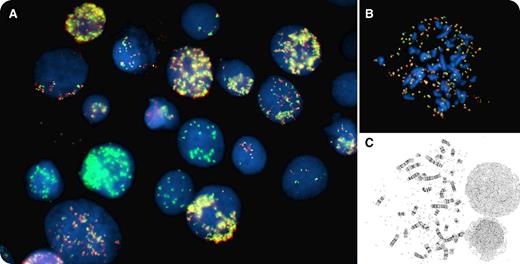
Pancytopenia with circulating blasts was identified in a 79-year-old man. Cytogenetic analysis of unstimulated cultured bone marrow cells revealed a complex karyotype including a variable number of double-minute chromosomes, from 10 to >100 (panel C). Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis, performed with the Vysis MYC break-apart probe set, showed a signal pattern reminiscent of fireworks with bright green and yellow peonies on a black sky (panel A), due to the presence of multiple MYC amplicons. The MYC probe set showed heterogeneity in both the number and the composition of the amplicons, with some cells showing combined amplification of the 5′ and 3′ probes in the form of fused, yellow fluorescent signals, while others presented with only the 3′ MYC probe signal (green) amplification. FISH metaphases showed tens to hundreds of MYC amplicons (panel B). The final morphologic diagnosis was acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes (WHO classification).
Double-minute chromosomes are rarely but recurrently found in acute myeloid leukemias. They represent gene amplification, and MYC is the gene most frequently involved. The number of double minutes is variable and can reach hundreds as seen in this case.
Pancytopenia with circulating blasts was identified in a 79-year-old man. Cytogenetic analysis of unstimulated cultured bone marrow cells revealed a complex karyotype including a variable number of double-minute chromosomes, from 10 to >100 (panel C). Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis, performed with the Vysis MYC break-apart probe set, showed a signal pattern reminiscent of fireworks with bright green and yellow peonies on a black sky (panel A), due to the presence of multiple MYC amplicons. The MYC probe set showed heterogeneity in both the number and the composition of the amplicons, with some cells showing combined amplification of the 5′ and 3′ probes in the form of fused, yellow fluorescent signals, while others presented with only the 3′ MYC probe signal (green) amplification. FISH metaphases showed tens to hundreds of MYC amplicons (panel B). The final morphologic diagnosis was acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes (WHO classification).
Double-minute chromosomes are rarely but recurrently found in acute myeloid leukemias. They represent gene amplification, and MYC is the gene most frequently involved. The number of double minutes is variable and can reach hundreds as seen in this case.
For additional images, visit the ASH IMAGE BANK, a reference and teaching tool that is continually updated with new atlas and case study images. For more information visit http://imagebank.hematology.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal