Abstract
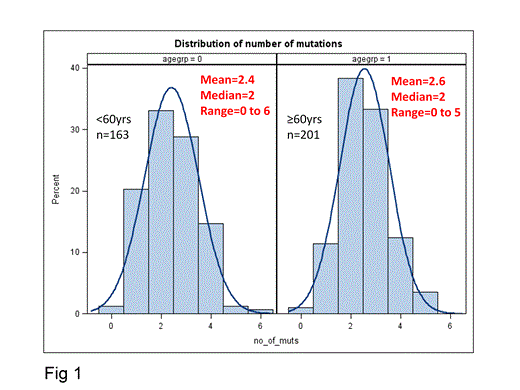
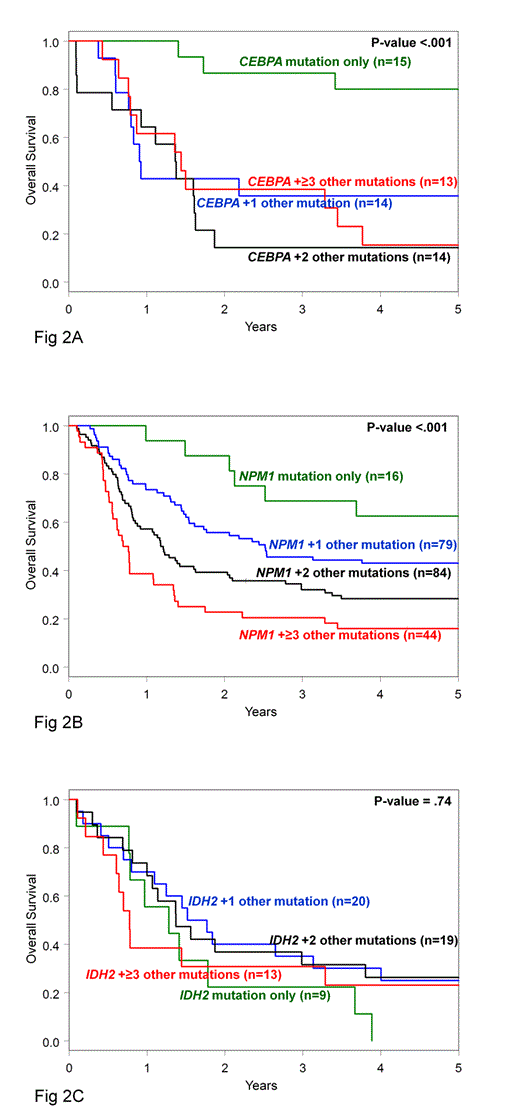
In CN-AML, mutations of specific genes have prognostic significance and are used for treatment guidance. However, these mutations are in general not mutually exclusive and CN-AML patients (pts) frequently harbor mutational combinations with unclear prognostic significance because of the concurrent presence of mutations with favorable (CEBPA, NPM1) and unfavorable (ASXL1, DNMT3A, IDH1, IDH2, FLT3-ITD, MLL-PTD, RUNX1, TET2, WT1) impact on outcome. Here, we report the frequency and clinical significance of isolated mutations and their combinations in 364 CN-AML pts. Younger [<60 years (y); n=163] and older (≥60 y; n=201) pts were intensively treated on frontline CALGB/Alliance protocols and, per protocol, did not undergo allogeneic stem cell transplantation in first complete remission (CR). Median follow-up for pts alive was 8.7 y. Pts were analyzed centrally for mutations in the ASXL1, CEBPA, DNMT3A, IDH1, IDH2, NPM1, RUNX1, TET2, and WT1 genes and the presence of FLT3-ITD, FLT3-TKD and MLL-PTD. We found that 99% of pts had ≥1 and 88% ≥2 of the 12 mutations. Specifically, 11% of pts had 1 gene mutated (n1), 40% had 2 (n2), 31% 3 (n3), and 18% harbored ≥4 mutated genes (n4). The distribution of the different n groups in younger and older pts was similar (Fig 1). The expected frequency of each mutated gene in every numerical (n) group was calculated as follows: [no. of pts with the mutated gene] x [total no. of mutations in the n group] / [total no. of mutations in all pts], and compared with the observed frequency. CEBPA, IDH2, NPM1, and RUNX1 mutations were overrepresented in the n1 and n2 groups (P<.001, P<.001, P=.002, P=.02, respectively) and thus likely represent “early” events in leukemogenesis. In contrast, DNMT3A, FLT3-ITD, and TET2 mutations were more frequent in the n3 and n4 groups (P=.008, P<.001, P=.02, respectively) suggesting that they are likely “late” events. The distribution among age groups and clinical impact of the “early” mutations (i.e., CEBPA, NPM1, IDH2) presenting as isolated mutations or in combination with other mutations were then investigated. Isolated RUNX1 mutations could not be evaluated due to small sample size. Younger pts were more likely to harbor an isolated “early” mutated gene than older pts (21% v 12%, P=.03). Specifically, isolated CEBPA and NPM1 mutations were more frequent in younger pts compared with the older (7% v 2%, P=.007; 7% v 3%, P=.07, respectively). In pts with isolated CEBPA mutations, these were always bi-allelic. Single “early” mutated genes varied in their impact on CR achievement (CEBPA: 100%, NPM1: 94%, IDH2: 67%), and overall survival (OS; 3-y OS: CEBPA: 87%, NPM1: 69%, IDH2: 22%). Acquisition of additional mutations adversely modified the prognostic significance of favorable “early” mutations in the CEBPA (Fig 2A) and NPM1 (Fig 2B) genes, but left unchanged the unfavorable effect of IDH2 mutations (Fig 2C). Two mutational combinations were exceptions to this: younger pts with both NPM1 and DNMT3A mutations (8 pts) had an excellent prognosis with 3-y OS of 100%; and older pts with concurrent NPM1 and IDH2 mutations (9 pts; all IDH2 mutations were in codon R140) had a high 3-y OS rate of 67%. We conclude that CEBPA and NPM1 mutations mainly define pts with favorable prognosis when they present as single markers, whereas mutated IDH2 predominantly associates with adverse outcome. The NPM1+DNMT3A and NPM1+IDH2 mutational patterns may define novel favorable molecular subtypes in younger and older CN-AML pts, respectively, but these results require corroboration in larger pt cohorts.
Disclosures:
Mrózek:AMERICAN SOCIETY OF HEMATOLOGY: I will review abstracls submitted for presentation at the 55th ASH Annual Meeting in the 611 category Other. Eisfeld:AMERICAN SOCIETY OF HEMATOLOGY: I will review abstracls submitted for presentation at the 55th ASH Annual Meeting in the 608 category Other.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2013 by The American Society of Hematology
2013

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal