Abstract
Abstract 3976
International guidelines for identifying monoclonal gammopathies now include serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) and serum free light chain (FLC) immunoassays with derived kappa/lambda (κ/λ) ratios. Compared with the absolute FLC concentration, the use of the (κ/λ) ratio is a more sensitive marker of monoclonal FLC production because it also includes suppression of the non tumor FLC in its calculation and also has prognostic implications in multiple myeloma (MM). Following this rationale, pilot studies have indicated that novel paired immunoassays, called Hevylite (HLC) assay, enables the measurement of isotype matched immunoglobulin pairs (IgGκ/IgGλ, IgAκ/IgAλ) and offer a sensitive alternative to immunofixation. We examined the performance of HLC assay on stored samples from newly diagnosed MM patients treated on two successive Total Therapy 3 trials (TT3A & TT3B).
The details of the TT3A and TT3B clinical trials have been previously published. The IgA and IgG k/λ HLC reagent kits, provided by The Binding Site, Inc, have been used to run the test on a subset of TT3A patients where the stored serum samples were still available. UAMS Clinical Laboratory tested samples for IgA k/λ and IgG k/λ HLC nephelometrically using BNII. Chi-square and Fisher's exact tests were used to compare baseline characteristics between protocols patients with and without available serum samples. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression were used to model associations between baseline covariates and HLC assay. Kaplan and Meier method was used to model progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
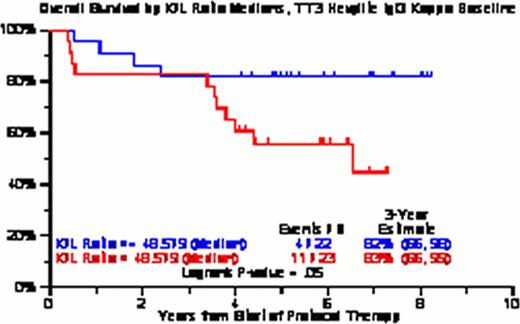
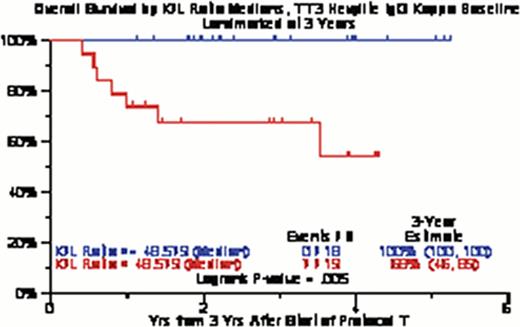
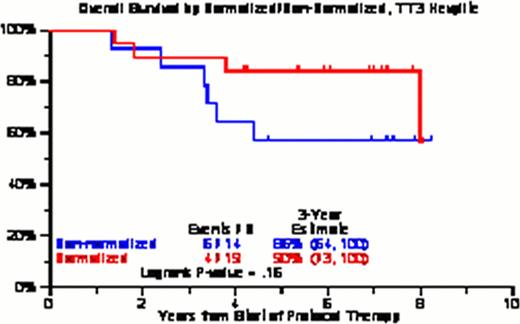
101 baseline serum samples were available (TT3A=67, TT3B=34) for patients with IgGκ (n=45), IgGλ (n=22), IgAκ (n=17) and IgAλ (n=17) isotype MM. Patient characteristics between the patients with and without available samples were comparable except a higher proportion of IgA isotype, higher baseline serum CRP and higher baseline serum LDH in patients without available samples (Table 1). There were no differences in PFS or OS amongst the 4 heavy chain isotypes. Whether evaluating by optimal cut-point or by tertiles, there were no differences in PFS/OS for the IgAκ, IgAλ or IgGλ MM. There was an OS benefit observed for IgGκ MM subset (Figure 1) by baseline samples, even when landmarked at 3 years (Figure 2). Comparing post-therapy HLC ratio normalization in 33 paired samples (IgG k/λ =25, IgA k/λ =8), there was a trend for improved OS in patients who had normalized the ratio after autologous stem cell transplantation (Figure 3).
These data provide early evidence of pre- and post-therapeutic prognostic utility of the HLC assay. Although our study was conducted on a small subset of TT3 patients, these data support the prospective evaluation of the HLC assay in upfront MM clinical trials.
KM curves for OS by Kappa/Lambda ratio medians for IgGκ TT3 samples
KM curves for OS by Kappa/Lambda ratio medians for IgGκ TT3 sample (3-year landmark)
KM curves for OS by Kappa/Lambda ratio medians for IgGκ TT3 sample (3-year landmark)
KM curves for OS for normalized versus non-normalized TT3 paired samples (baseline and post-transplant)
KM curves for OS for normalized versus non-normalized TT3 paired samples (baseline and post-transplant)
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal