Abstract
Abstract 3327
Adult immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an isolated low platelet count. Options for initial therapy in children and adults include corticosteroids (CS), intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and anti-D. Second-line treatments include splenectomy, rituximab, and the thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-A) eltrombopag and romiplostim. Treatments are usually effective in raising platelet counts, but there are often associated toxicities. We designed and administered a patient survey to compare side effects reported with different ITP therapies to an off treatment control group.
A literature search identified 56 distinct side effects reported by patients on medical therapy for ITP. A self-report questionnaire was designed that asked patients how frequently (never, occasionally, regularly, almost always, always) they had experienced each side effect during the last 30 days. If a respondent had experienced the side effect, he/she was also asked to indicate the level of distress associated with the symptom on a rating scale. Adult non-pregnant patients with ITP were eligible for the IRB-approved study if they were currently taking one of the following therapies, and had done so for at least 30 days: CS, rituximab plus pulse high dose dexamethasone [Dex-Ritux], eltrombopag, IVIG, romiplostim, or no therapy (control group). Clinical details were obtained from patient records. Side effects in the treatment groups were compared to the control sample using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (alpha = .05).
Ninety-one eligible patients completed the survey. Eleven (12%) were on CS (9 patients on prednisone [median dose 20mg/day] and 2 on pulse high dose dexamethasone), 11 (12%) on Dex-Ritux, 21 (23%) on eltrombopag, 9 (10%) on IVIG, 22 (24%) on romiplostim, and 17 (19%) on no therapy. Sixty-two percent overall and 71% of control patients were female (n=56, n=12). One hundred percent of patients reported experiencing at least one side effect. The most commonly reported side effects were fatigue (n= 78; 86%), stress (n=70; 77%), anxiety (n=56; 62%), joint pain (n=55; 60%), and muscle pain (n=55; 60%).
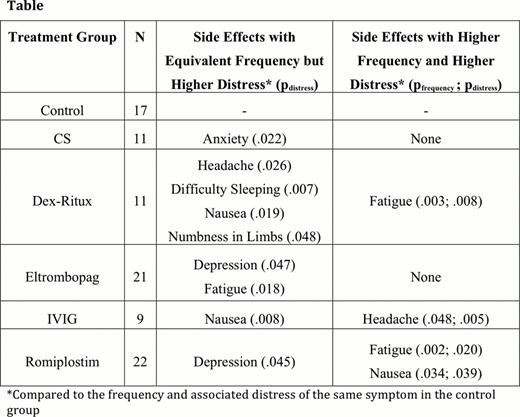
Most side effects reported by patients on treatment did not occur with significantly greater frequency or distress than in the control sample. Side effects that occurred with significantly greater frequency compared to the control sample were found in every treatment group except eltrombopag. Most of these symptoms were mild and not associated with greater distress compared to control patients who experienced the same side effect. The number of side effects occurring with greater frequency was 15 with romiplostim, 5 with Dex-Ritux, 3 with CS, and 2 with IVIG. Side effects that occurred with significantly greater distress compared to the control sample were found in every treatment group. Greater distress was not necessarily associated with greater frequency (see Table).
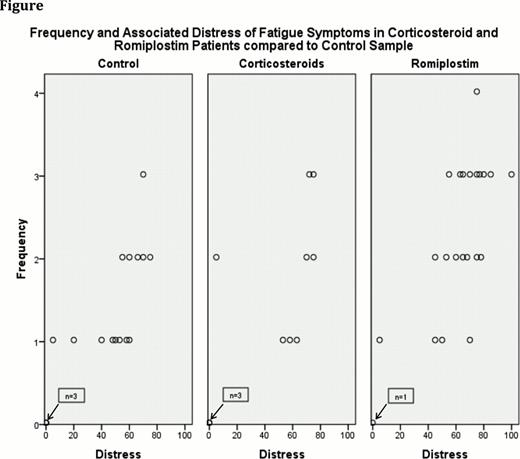
Many unwanted effects, such as fatigue, insomnia, dyspepsia, and skin irritation, that have traditionally been associated with CS treatment did not occur with greater frequency or distress in that group; however, few patients were on long term or high dose CS therapy. Surprisingly, unlike published series, we found that romiplostim patients experienced fatigue with significantly greater frequency and more distress than the control group (see Figure).
These results suggest that, while unwanted effects of ITP treatment in adults are common, the great majority are not associated with significant patient distress. Patients who participated in this study were being treated at a clinic where treatment guidelines for adult ITP favored TPO-As over CS. Thus our findings may not reflect general experience.
Bussel:Amgen: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cangene: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding; IgG of America: Research Funding; Immunomedics: Research Funding; Ligand: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Eisai, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Shinogi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Symphogen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sysmex: Research Funding; Portola: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal