Abstract
Platelets are activated on increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity ([Ca2+]i), accomplished by store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) involving the pore-forming ion channel subunit Orai1. Here, we show, for the first time, that the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) is expressed in platelets and megakaryocytes. SOCE and agonist-induced [Ca2+]i increase are significantly blunted in platelets from SGK1 knockout mice (sgk1−/−). Similarly, Ca2+-dependent degranulation, integrin αIIbβ3 activation, phosphatidylserine exposure, aggregation, and in vitro thrombus formation were significantly impaired in sgk1−/− platelets, whereas tail bleeding time was not significantly enhanced. Platelet and megakaryocyte Orai1 transcript levels and membrane protein abundance were significantly reduced in sgk1−/− mice. In human megakaryoblastic cells (MEG-01), transfection with constitutively active S422DSGK1 but not with inactive K127NSGK1 significantly enhanced Orai1 expression and SOCE, while effects reversed by the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM). Transfection of MEG-01 cells with S422DSGK1 significantly increased phosphorylation of IκB kinase α/β and IκBα resulting in nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunit p65. Treatment of S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells with the IκB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM) abolished SGK1-induced increase of Orai1 expression and SOCE. The present observations unravel SGK1 as novel regulator of platelet function, effective at least in part by NF-κB–dependent transcriptional up-regulation of Orai1 in megakaryocytes and increasing platelet SOCE.
Introduction
Platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation are essential for primary hemostasis at sites of vascular injury but are also critically important for the development of acute thrombotic occlusion at regions of atherosclerotic plaque rupture, the major pathophysiologic mechanism underlying myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.1
Platelet activation is triggered by various agonists, including subendothelial collagen, ADP released from activated platelets, thrombin generated by the coagulation cascade, or the collagen receptor glycoprotein VI (GPVI)–specific agonists convulxin (CVX) and collagen-related peptide (CRP).2 The agonists lead to platelet granule release, integrin αIIbβ3 activation, phosphatidylserine exposure, aggregation, and thrombus formation.2 All those platelet responses depend on an increase of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i),3,4 which is accomplished by inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release from intracellular stores triggering subsequent stimulation of store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) across the plasma membrane.5 Two key players in platelet SOCE have recently been identified: The 4-transmembrane-spanning pore-forming calcium release-activated channel moiety Orai1, which mediates entry of extracellular Ca2+, and stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1), an Orai1 regulating Ca2+ sensor expressed predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum.6-8 Regulators of Orai1 in other cell types include receptor for activated protein kinase C-1,9 reactive oxygen species,10 and lipid rafts.11
However, regulation of Orai1 in platelets is poorly understood. Platelet activation has been shown to be regulated in vitro and in vivo by the PI3K/Akt signaling cascade.12,13 Interference with PI3K signaling has previously been shown to compromise Ca2+ influx into platelets.14,15
Signaling molecules regulated by PI3K signaling include the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1), a kinase belonging to the AGC family of serine/threonine protein kinases.16,17 SGK1 has originally been cloned as a glucocorticoid-sensitive gene but later shown to be regulated by a variety of hormones and other triggers, including thrombin, growth factors IGF-1 and TGF-β, oxidative stress, and ischemia.17
SGK1 has previously been reported to regulate a wide variety of carriers and ion channels, including the epithelial Ca2+ channels TRPV5 and TRPV6.17 Most recently, SGK1 has been shown to be critically important for the Ca2+ entry into mast cells after activation of the IgE receptor,18 an effect mediated by regulation of Orai1.19 Furthermore, SGK1 participates in the regulation of renal tubular Na+ reabsorption, salt appetite, and thus blood pressure.17 A gain-of-function SGK1 gene variant, the combined presence of single nucleotide polymorphism in intron 6 (rs1743966) and in exon 8 (rs1057293), is associated with enhanced blood pressure.20 The same genetic SGK1 variants are associated with ischemic stroke, an association partially independent of blood pressure, and thus the result of additional SGK1-dependent mechanisms.21
SGK1 has been shown to foster coagulation by up-regulation of tissue factor expression.22 But prothrombotic activity is in addition critically dependent on the function of platelets, key players in the initiation of arterial thrombosis and vascular occlusion resulting in ischemic diseases.23 Surprisingly, nothing is hitherto known about the influence of SGK1 on platelet function.
Thus, the present study explored the role of SGK1 in the regulation of platelet function. We could show, for the first time, that SGK1 is strongly expressed in platelets and megakaryocytes, acts as an important regulator of NF-κB–dependent Orai1 expression in megakaryocytes, and thus influences Ca2+ response, activation, and thrombus formation of released platelets.
Methods
Chemicals and antibodies
Platelets were activated using ADP (Sigma-Aldrich), thrombin (Roche Diagnostics), CVX (Enzo), collagen (Nycomed), CRP (Richard Farndale, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom), and thrombin receptor agonist PAR-4 activating peptide (NH2-AYPGKF, JPT Peptide Technologies). Fluorophore-labeled antibodies anti–P-selectin-FITC (Wug.E9-FITC; Emfret Analytics), anti–integrin αIIbβ3-PE (JON/A-PE; Emfret Analytics), and annexin V–Fluos (Roche Diagnostics) were used for flow cytometric analysis.
Preparation of human platelets
Blood from healthy volunteers was collected in ACD buffer and centrifuged at 200g for 20 minutes. The obtained platelet-rich plasma was added to modified Tyrode-HEPES buffer (137mM NaCl, 2.8mM KCL, 12mM NaHCO3, 5mM glucose, 0.4mM Na2HPO4, 10mM HEPES, 0.1% BSA, pH 6.5). After centrifugation at 900g for 10 minutes and removal of the supernatant, the resulting platelet pellet was resuspended in Tyrode-HEPES buffer (pH 7.4, supplemented with 1mM CaCl2).
Cell culture and transfection
The human megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line MEG-01 (DSMZ) was cultured in RPMI 1640 medium with Glutamax (Invitrogen), 10% FBS (Invitrogen), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen) in a humidified atmosphere at 37°C and 5% CO2. MEG-01 and human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells were transiently transfected for 48 hours with the constitutively active SGK1 mutant S422DSGK1 (hSGK1SD in pCDNA3.1), which does not require activation by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase PDK1,19 or the inactive mutant K127NSGK1 (hSGK1KN in pCDNA3.1), which lacks catalytic activity.19 Transfections were performed as described previously24 using FuGENE HD transfection reagent (Roche Diagnostics) according to the manufacturer's instructions. For experiments with pharmacologic inhibition of SGK1 or IκB kinase (IKK), 1μM GSK650394 (Solvay) or 10μM BMS-345541 (Sigma-Aldrich) was added.
Mice
Gene-targeted mice lacking functional SGK1 (sgk1−/−) and the corresponding wild-type littermate mice (sgk1+/+) were generated and bred as described by Wulff et al.25 Animals were genotyped by PCR. All animal experiments were conducted according to German law for the welfare of animals and were approved by local authorities.
Preparation of mouse platelets
Platelets were obtained from 10- to 12-week-old sgk1−/− mice and sgk1+/+ mice of either sex. The mice were anesthetized with ether, and blood was drawn from the retro-orbital plexus into heparinized tubes. Blood parameters were analyzed with pocH-100iv automatic hematology analyzer (Sysmex). Platelet-rich plasma was obtained by centrifugation at 260g for 5 minutes. Afterward, platelet-rich plasma was centrifuged at 640g for 5 minutes to pellet the platelets. To ease platelets, apyrase (0.02 U/mL, Sigma-Aldrich) and prostaglandin I2 (0.5μM, Calbiochem) were added to the platelet-rich plasma. After 2 washing steps, the pellet of washed platelets was resuspended in modified Tyrode-HEPES buffer (pH 7.4, supplemented with 1mM CaCl2).
Isolation and culture of murine megakaryocytes
For the isolation of murine sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ megakaryocytes, bone marrow cells were harvested by flushing the femurs and tibiae with PBS as described by Shivdasani and Schulze.26 The obtained cells were separated over Percoll (GE Healthcare) and cultured in specific growth medium (MethoCult; StemCell Technologies) containing 50 ng/mL thrombopoietin (Invitrogen) as described previously.27 After 5 to 7 days, differentiation into megakaryocytes was tested by microscopy and glyocoprotein Ib (GPIb) staining.
RT-PCR analysis
To determine SGK1 and Orai1 mRNA abundance in platelets and megakaryocytes from sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ mice as well as in MEG-01 cells, mRNA was extracted and quantitative real-time PCR was performed as described in supplemental Methods (available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
Flow cytometry
Two-color analysis of mouse platelet activation was conducted using fluorophore-labeled antibodies for P-selectin expression (Wug.E9-FITC) and the active form of αIIbβ3 integrin (JON/A-PE). Heparinized whole blood was diluted 1:20 in modified Tyrode buffer and washed twice. After adding 1mM CaCl2, blood samples were mixed with antibodies and subsequently stimulated with agonists for 15 minutes at room temperature. For analysis of phosphatidylserine exposure, washed platelets were diluted in Tyrode buffer containing 2mM CaCl2 and activated with CVX and/or thrombin for 15 minutes and stained with annexin V–Fluos at room temperature. For measuring Orai1 surface expression, washed platelets were incubated for 60 minutes (37°C) with Orai1 rabbit anti–mouse antibody (Proteintech), washed once in PBS, and stained in 1:500 diluted FITC-labeled goat anti–rabbit secondary antibody (Invitrogen) for 30 minutes (37°C). In all approaches, reaction was stopped by addition of PBS and samples were immediately analyzed on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (BD Biosciences).
Platelet aggregometry
Aggregation experiments were performed in diluted whole blood with electrode impedance aggregometry (Model 700; Chrono-Log). Citrate-anticoagulated whole blood was diluted with physiologic saline. After calibration, agonists were added at the indicated concentrations and aggregation was measured for 10 minutes with a stir speed of 1000 rpm at 37°C. The extent of aggregation was quantified in ohms (Ω) by comparing the deflection of the trace with the calibration mark representing 20 Ω. The data analysis was performed with AGGRO/LINK8 software (Chrono-Log).
Calcium measurements
Washed murine platelets were suspended in Tyrode buffer without calcium and loaded with 5μM Fura-2 acetoxymethylester (Invitrogen) in the presence of 0.2 μg/mL Pluronic F-127 (Biotium) at 37°C for 30 minutes. Loaded platelets, washed once and resuspended in Tyrode buffer containing 0.5mM EGTA (Roth) or 1mM Ca2+, were activated with agonists. Calcium responses were measured under stirring with a spectrofluorimeter (LS 55, PerkinElmer), at alternate excitation wavelength of 340 and 380 nm (37°C). The 340/380 nm ratio values were converted into nanomolar concentrations of [Ca2+] by lysis with Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich) and a surplus of EGTA. Harvested MEG-01 cells were centrifuged at 530g for 5 minutes and then resuspended in RPMI medium (Invitrogen) and stained as described above. Measurements were performed in Ca2+ free Tyrode buffer. After incubation with 5μM thapsigargin (Invitrogen) for 10 minutes, 1mM Ca2+ was added. Isolated human platelets were incubated 60 minutes before measurement with the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM; Solvay), the SOCE inhibitor 2-APB (50μM; Sigma-Aldrich) or DMSO as solvent control at 37°C.
Western blot analysis
MEG-01 or HEK293 cells, freshly isolated human platelets, or pooled mouse platelets were centrifuged for 5 minutes at 240g, and the pellet was resuspended in lysis buffer (50mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 1% Trion-X, 0.5% Na2HPO4, 0.4% β-mercaptoethanol) containing protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich). After centrifugation for 30 minutes at 20 000g and 4°C, the supernatant was taken and the protein concentration was measured with Bradford (Bio-Rad). For immunoblotting, proteins were electrotransferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and blocked with 5% nonfat milk or 5% BSA at room temperature for 1 hour. Then, the membrane was incubated with the primary antibody against SGK1 (1:100; Pineda), Orai1 (1 μg/mL; Abcam), phospho-IKKα/β (Ser176/180; 1:1000, Cell Signaling), or phospho-IκBα (Ser32/36 1:1000; Cell Signaling) at 4°C overnight. After washing with TBST, the blots were incubated with secondary antibody conjugated with HRP (1:2000; Cell Signaling) for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing, antibody binding was detected with the ECL detection reagent (GE Healthcare). Bands were quantified with Quantity One Software (Bio-Rad). Membrane protein extraction was performed as described in supplemental Methods.
Immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy
Washed platelets were allowed to adhere to a fibrinogen surface (20 μg/mL) on a chamber slide; MEG-01 cells and murine megakaryocytes were adhered to poly-L-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich). Adherent platelets, megakaryocytes, and MEG-01 or HEK293 cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (2%), washed and blocked with 2% BSA for 30 minutes, followed by incubation with the primary antibody for 2 hours at room temperature. Primary antibodies against SGK1 (1:100; Pineda), Orai1 (1:1000; Millipore), NF-κB p65 (1:250; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and GP1bα (1:200; Emfret) were used. Chamber slides were washed and incubated with a FITC- or Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). The actin cytoskeleton was stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (Invitrogen); nuclei were stained with DRAQ-5 dye (1:2000; Biostatus). The slides were mounted with ProLong Gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen). Confocal microscopy was performed using a Zeiss LSM5 EXCITER Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (Carl Zeiss Micro Imaging) with a A-Plan 63× ocular.
Flow chamber
Heparinized whole mouse blood was diluted 1:3 in modified Tyrode buffer and perfused through a transparent flow chamber (slit depth, 50 μm) over a collagen-coated surface (200 μg/mL) with a wall shear rate of 1700s−1 for 5 minutes. After perfusion, the chamber was rinsed for 5 minutes by perfusion with Tyrode buffer, and pictures were taken from 5 or 6 different microscopic areas (×20, Carl Zeiss). Analysis was done with AxioVision (Carl Zeiss), and the mean percentage value of the covered area was determined.
Bleeding time
Mice were anesthetized, and a 3-mm segment of the tail tip was removed with a scalpel. Tail bleeding was monitored by gentle absorption of the blood with filter paper at 20-second intervals without making contact with the wound site. When no blood was observed on the paper, bleeding was determined to have ceased. Experiments were stopped after 20 minutes.
Statistical analysis
Data are given as mean ± SD or SEM; n represents the number of experiments. All data were tested for significance using paired or unpaired Student t test and 1-way ANOVA with Dunnet posthoc test.
Results
In an initial experiment, expression of the SGK1 was analyzed in human as well as in murine platelets and megakaryocytes. RT-PCR analysis, confocal microscopy, and Western blot analysis of human platelets revealed strong expression of SGK1 in platelets both at mRNA and protein levels (Figure 1A-B). The expression level was comparable with that in HEK293 cells.
SGK1 mRNA and protein expression in human as well as in murine platelets and megakaryocytes. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR of mRNA encoding SGK1 in human platelets and HEK293 cells. (B) Western blot and confocal microscopy of SGK1 abundance in human platelets, nontransfected and S422DSGK1-transfected HEK293 cells. Red represents actin; and green, SGK1. Bar represents 5 μm. (C) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding SGK1 in platelets from sgk1−/− mice expressed in percentage of the respective value in platelets from sgk1+/+ mice. ***P < .001. (D) Representative Western blot analysis of SGK1 protein abundance in platelets from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice. (E) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding SGK1 in megakaryocytes from sgk1−/− mice expressed in percentage of the respective value in megakaryocytes from sgk1+/+ mice. ***P < .001. (F) Confocal microscopy of SGK1 protein abundance in megakaryocytes from sgk1+/+ (top) and sgk1−/− (bottom) mice. Red represents glycoprotein Ib; green, SGK1; and blue, nuclei. Bar represents 10 μm.
SGK1 mRNA and protein expression in human as well as in murine platelets and megakaryocytes. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR of mRNA encoding SGK1 in human platelets and HEK293 cells. (B) Western blot and confocal microscopy of SGK1 abundance in human platelets, nontransfected and S422DSGK1-transfected HEK293 cells. Red represents actin; and green, SGK1. Bar represents 5 μm. (C) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding SGK1 in platelets from sgk1−/− mice expressed in percentage of the respective value in platelets from sgk1+/+ mice. ***P < .001. (D) Representative Western blot analysis of SGK1 protein abundance in platelets from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice. (E) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding SGK1 in megakaryocytes from sgk1−/− mice expressed in percentage of the respective value in megakaryocytes from sgk1+/+ mice. ***P < .001. (F) Confocal microscopy of SGK1 protein abundance in megakaryocytes from sgk1+/+ (top) and sgk1−/− (bottom) mice. Red represents glycoprotein Ib; green, SGK1; and blue, nuclei. Bar represents 10 μm.
To study the functional role of SGK1 in regulating platelet function, platelets and megakaryocytes were isolated from mice lacking SGK1 (sgk1−/−) and respective wild-type littermates (sgk1+/+). RT-PCR analysis, immunofluorescence staining, and Western blotting confirmed the absence of sgk1 mRNA and SGK1 protein in sgk1−/− platelets (Figure 1C-D) and megakaryocytes (Figure 1E-F).
Sgk1−/− mice appeared healthy and did not exhibit spontaneous bleeding. Blood platelet counts and mean platelet volume were similar in sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice (Table 1), indicating that SGK1 is not essential for platelet generation. In addition, no differences were found in other hematologic parameters (Table 1) or platelet-specific glycoproteins (supplemental Figure 1).
Blood count of sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice
| . | sgk1+/+ . | sgk1−/− . |
|---|---|---|
| Platelets, × 103/μL | 1023 ± 175 | 1020 ± 99 |
| Mean platelet volume, fL | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.3 |
| Erythrocytes, × 106/μL | 9.7 ± 1.2 | 9.7 ± 1.2 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.3 ± 1.3 | 14.0 ± 1.0 |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.4 ± 3.9 | 40.6 ± 2.9 |
| Mean corpuscular volume, fL | 42.7 ± 2.2 | 42.0 ± 1.6 |
| . | sgk1+/+ . | sgk1−/− . |
|---|---|---|
| Platelets, × 103/μL | 1023 ± 175 | 1020 ± 99 |
| Mean platelet volume, fL | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.3 |
| Erythrocytes, × 106/μL | 9.7 ± 1.2 | 9.7 ± 1.2 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.3 ± 1.3 | 14.0 ± 1.0 |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.4 ± 3.9 | 40.6 ± 2.9 |
| Mean corpuscular volume, fL | 42.7 ± 2.2 | 42.0 ± 1.6 |
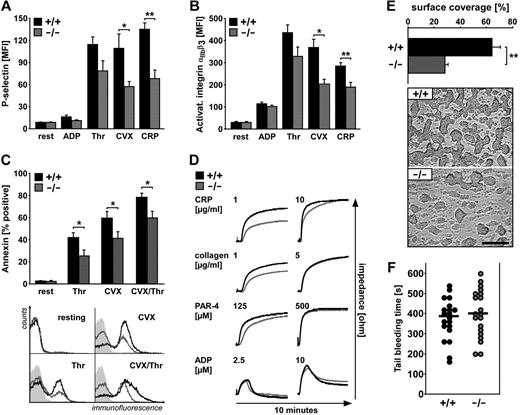
To elucidate the impact of SGK1 on platelet activation, platelet degranulation, integrin αIIbβ3 activation, and phosphatidylserine exposure flow cytometric measurements were performed. Degranulation-dependent P-selectin surface exposure was quantified before and after activation with ADP (10μM), thrombin (0.02 U/mL) as well as the specific agonists of the collagen receptor GPVI, CVX (1 μg/mL), and CRP (5 μg/mL). As illustrated in Figure 2A, P-selectin abundance at the platelet surface was significantly lower in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets after stimulation with CVX and CRP. Degranulation after stimulation with thrombin tended to be lower in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets, a difference, however, not reaching statistical significance.
Activation-dependent platelet degranulation, αIIbβ3integrin activation, phosphatidylserine exposure, and aggregation as well as in vitro thrombus formation and tail bleeding time. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of degranulation-dependent P-selectin exposure in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 10μM ADP, 0.02 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 5 μg/mL CRP. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6). *P < .05. **P < .01. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of αIIbβ3 integrin activation in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 10μM ADP, 0.02 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 5 μg/mL CRP. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6). *P < .05. **P < .01. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 1.0 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 0.05 U/mL thrombin + 0.5 μg/mL CVX. (Top) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 9). *P < .05. (Bottom) Representative overlays of annexin-positive sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets. Light gray panels represent isotype controls. (D) Impedance aggregometry after stimulation with different concentrations of CRP (1 and 10 μg/mL), collagen (1 and 5 μg/mL), PAR-4 activating peptide (125 and 500μM), and ADP (2.5 and 10μM). Representative aggregation tracings of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) mice (n = 4). (E) Thrombus formation in vitro. Whole blood from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice was perfused over a collagen-coated surface for 5 minutes at a shear rate of 1700s−1. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6; top) and representative phase-contrast images (bottom) of surface coverage. **P < .01. Bar represents 50 μm. (F) Tail bleeding time measured after amputating the tail tip of sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse; black bar represents the mean value.
Activation-dependent platelet degranulation, αIIbβ3integrin activation, phosphatidylserine exposure, and aggregation as well as in vitro thrombus formation and tail bleeding time. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of degranulation-dependent P-selectin exposure in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 10μM ADP, 0.02 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 5 μg/mL CRP. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6). *P < .05. **P < .01. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of αIIbβ3 integrin activation in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 10μM ADP, 0.02 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 5 μg/mL CRP. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6). *P < .05. **P < .01. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice in response to 1.0 U/mL thrombin, 1 μg/mL CVX, and 0.05 U/mL thrombin + 0.5 μg/mL CVX. (Top) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 9). *P < .05. (Bottom) Representative overlays of annexin-positive sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets. Light gray panels represent isotype controls. (D) Impedance aggregometry after stimulation with different concentrations of CRP (1 and 10 μg/mL), collagen (1 and 5 μg/mL), PAR-4 activating peptide (125 and 500μM), and ADP (2.5 and 10μM). Representative aggregation tracings of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) mice (n = 4). (E) Thrombus formation in vitro. Whole blood from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice was perfused over a collagen-coated surface for 5 minutes at a shear rate of 1700s−1. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6; top) and representative phase-contrast images (bottom) of surface coverage. **P < .01. Bar represents 50 μm. (F) Tail bleeding time measured after amputating the tail tip of sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse; black bar represents the mean value.
After stimulation with CVX and CRP, surface expression of activated integrin αIIbβ3 was significantly lower in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets (Figure 2B). After low-dose concentrations of thrombin or ADP, the activation of integrin αIIbβ3 was not significantly different between sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets.
For examination of activation-dependent phosphatidylserine exposure, platelets were stimulated with thrombin (1.0 U/mL), CVX (1 μg/mL), or thrombin/CVX (0.05 U/mL/0.5 μg/mL) and annexin-positive cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. After stimulation with thrombin, CVX or the combination (thrombin/CVX), surface exposure of phosphatidylserine was significantly lower in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets (Figure 2C).
To determine whether impaired degranulation, integrin αIIbβ3 activation, and phosphatidylserine exposure would translate into functional deficits in sgk1−/− platelets, we performed impedance measurements of platelet aggregation before and after activation with low or high concentrations of CRP (1 and 10 μg/mL), collagen (1 and 5 μg/mL), PAR-4 activating peptide (125 and 500μM), and ADP (2.5 and 10μM). As illustrated in Figure 2D, platelet aggregation after stimulation with low-dose concentrations of the GPVI-acting ligands collagen or CRP was significantly less pronounced in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets. Only a slight difference was found after stimulation with low-dose PAR-4 activating peptide, an agonist of the principal murine thrombin receptor. The aggregation defect found in sgk1−/− platelets was overcome by increasing the agonist concentration.
To elucidate the relevance of SGK1 in pathologic thrombus formation, we examined platelet adhesion to collagen-coated surfaces under flow at high arterial shear rates (1700s−1). As illustrated in Figure 2E, sgk1+/+ platelets formed massive and dense thrombi after 5 minutes of perfusion, whereas sgk1−/− platelets formed only some smaller single thrombi with a significantly reduced thrombus surface coverage. To test whether the defect in sgk1−/− platelets impaired hemostasis, we measured tail bleeding time. As shown in Figure 2F, the bleeding time was not significantly different in sgk1−/−mice compared with sgk1+/+ mice.
Platelet activation, including integrin αIIbβ3 activation, granule release, phosphatidylserine exposure, aggregation, and thrombus formation, are directly dependent on an increase in the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i). Spectrofluorimetric measurements were thus used to elucidate the impact of SGK1 on the increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity after platelet activation by thrombin (0.02 U/mL), CVX (1 μg/mL), CRP (10 μg/mL), and ADP (10μM).
To discriminate between intracellular Ca2+ store release and Ca2+ influx from extracellular space, we performed measurements of activation-dependent changes in [Ca2+]i in the presence (1mM Ca2+) and absence (0.5mM EGTA) of extracellular Ca2+ (Figure 3A-B). Before stimulation, the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration was similar in sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. In the presence of extracellular Ca2+ all agonists triggered an increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity in sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. The increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity was, however, less pronounced in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets, a difference reaching statistical significance after stimulation with CVX and CRP (Figure 3A-B). In the absence of extracellular Ca2+, the increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity after stimulation with either agonist was similar in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets.
Agonist-induced Ca2+ response and impaired SOCE in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets. (A) Representative tracings of Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets before and after stimulation with thrombin (0.02 U/mL), CVX (1 μg/mL), CRP (10 μg/mL), and ADP (10μM) in the absence (0.5mM EGTA, left) or presence (1mM Ca2+, right) of extracellular Ca2+. (B) Arithmetic mean of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 4 per group). **P < .01. (C) Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 6 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01.
Agonist-induced Ca2+ response and impaired SOCE in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets. (A) Representative tracings of Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets before and after stimulation with thrombin (0.02 U/mL), CVX (1 μg/mL), CRP (10 μg/mL), and ADP (10μM) in the absence (0.5mM EGTA, left) or presence (1mM Ca2+, right) of extracellular Ca2+. (B) Arithmetic mean of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 4 per group). **P < .01. (C) Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 6 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01.
The impaired agonist induced Ca2+ response in the presence of extracellular Ca2+ pointed to an impaired SOCE in SGK1-deficient platelets. To test this hypothesis, SOCE was induced in sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets with saroplasmatic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ ATPase pump inhibitor thapsigargin. In the absence of extracellular Ca2+, thapsigargin (5μM) triggered a Ca2+ release from intracellular stores (store release) that was similar in sgk1+/+ platelets and in sgk1−/− platelets (Figure 3C). The subsequent addition of extracellular Ca2+ in the continued presence of thapsigargin triggered an SOCE, which was significantly less pronounced in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets. These results demonstrate, for the first time, that SGK1 is a regulator of platelet SOCE contributing to the regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ activity in platelets and platelet activation.
To test whether the decreased SOCE in sgk1−/−could have been the result of a decreased cell membrane protein abundance of the major platelet SOCE-mediating channel Orai1, we compared the Orai1 protein expression in sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. As shown in Figure 4A-D, Western blotting, immunofluorescence/confocal microscopy, and FACS analysis all disclosed that Orai1 protein (membrane) abundance was significantly lower in sgk1−/− platelets than in sgk1+/+ platelets, whereas STIM1 expression was not significantly different.
Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets and megakaryocytes. (A) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 protein abundance in platelets from sgk1+/+ (left panels) and sgk1−/− (right panels) mice. Red represents actin; and green, Orai1. Bar represents 10 μm. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of Orai1 surface expression in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice. (Bottom) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 7). **P < .01. (Top) Representative overlays of Orai1-positive sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets; light gray panel represents isotype control. (C) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysate protein of Orai1 and STIM1 from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) platelets. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of isolated membrane protein and cytosolic fraction of Orai1 from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1+/+ (black bars) and sgk1−/− (gray bars) platelets. **P < .01. (E) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 protein abundance in megakaryocytes cultivated from bone marrow of sgk1+/+ (left panels) and sgk1−/− (right panels) mice (top). Red represents GPIb; green, Orai1; and blue, nuclei. Bar represents 10 μm. Statistical analysis of Orai1 immunofluorescence abundance (bottom). **P < .01. n = 4.
Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets and megakaryocytes. (A) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 protein abundance in platelets from sgk1+/+ (left panels) and sgk1−/− (right panels) mice. Red represents actin; and green, Orai1. Bar represents 10 μm. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of Orai1 surface expression in platelets from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) mice. (Bottom) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 7). **P < .01. (Top) Representative overlays of Orai1-positive sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets; light gray panel represents isotype control. (C) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysate protein of Orai1 and STIM1 from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− (gray bar) platelets. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of isolated membrane protein and cytosolic fraction of Orai1 from sgk1+/+ and sgk1−/− platelets. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1+/+ (black bars) and sgk1−/− (gray bars) platelets. **P < .01. (E) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 protein abundance in megakaryocytes cultivated from bone marrow of sgk1+/+ (left panels) and sgk1−/− (right panels) mice (top). Red represents GPIb; green, Orai1; and blue, nuclei. Bar represents 10 μm. Statistical analysis of Orai1 immunofluorescence abundance (bottom). **P < .01. n = 4.
Immunofluorescence/confocal microscopy revealed that Orai1 protein abundance was again significantly lower in sgk1−/− megakaryocytes compared with sgk1+/+ megakaryocytes (Figure 4E). Further experiments were performed in the human megakaryocytic cell line MEG-01, an extensively used model of human megakaryocytes.28 According to confocal microscopy and Western blot analysis, the protein abundance of Orai1 in the plasma membrane of MEG-01 cells was significantly increased after transfection with the constitutively active mutant S422DSGK1 but not after transfection with the inactive mutant K127NSGK1 (Figure 5A-B). Addition of the store-depleting SR/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin (5μM) in nominally Ca2+-free solution was followed by rapid, transient increase in cytosolic Ca2+ in MEG-01 cells (Figure 5C). Subsequent addition of Ca2+ to the extracellular medium resulted in a rapid and sustained increase in cytosolic Ca2+ because of SOCE. Both slope and peak of MEG-01 SOCE were significantly enhanced by transient expression of the constitutively active mutant S422DSGK1 but not of the inactive mutant K127NSGK1 (Figure 5C).
SGK1-dependent Orai1 membrane abundance and SOCE in megakaryocytic cell line MEG-01. (A) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells (left). Red represents actin; green, Orai1; and blue, nuclei. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Statistical analysis of Orai1 immunofluorescence membrane abundance (right). *P < .05. **P < .01. n = 4. (B) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 7) of Orai1 protein abundance. *P < .05. **P < .01. (C) SOCE in SGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1 (black), or K127NSGK1 (red) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 15 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid) MEG-01 cells and in S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM) or DMSO as solvent control. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance. **P < .01. (E) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the specific SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394. Fura-2 fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control plasmid (gray) or S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells after treatment with GSK650394 (1μM, red) or DMSO (black) as solvent control. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 9 per group) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. **P < .01.
SGK1-dependent Orai1 membrane abundance and SOCE in megakaryocytic cell line MEG-01. (A) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells (left). Red represents actin; green, Orai1; and blue, nuclei. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Statistical analysis of Orai1 immunofluorescence membrane abundance (right). *P < .05. **P < .01. n = 4. (B) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 7) of Orai1 protein abundance. *P < .05. **P < .01. (C) SOCE in SGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1 (black), or K127NSGK1 (red) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 15 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid) MEG-01 cells and in S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM) or DMSO as solvent control. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance. **P < .01. (E) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the specific SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394. Fura-2 fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control plasmid (gray) or S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells after treatment with GSK650394 (1μM, red) or DMSO (black) as solvent control. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 9 per group) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. **P < .01.
The basal Fura-2 fluorescence ratio, reflecting resting intracellular Ca2+ concentration, was similar in MEG-01 cells transfected with control plasmid, in MEG-01 cells transfected with S422DSGK1 and in MEG-01 cells transfected with K127NSGK1. Moreover, the Ca2+ release from intracellular stores after thapsigargin (5μM) treatment was not significantly different between MEG-01 cells transfected with control plasmid, MEG-01 cells transfected with S422DSGK1, and MEG-01 cells transfected with K127NSGK1 (Figure 5C). The specific SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM) abolished the S422DSGK1-induced up-regulation of Orai1 expression and SOCE (Figure 5D-E).
Quantitative RT-PCR revealed that Orai1 mRNA levels were significantly lower in sgk1−/− platelets and megakaryocytes than in sgk1+/+ platelets and megakaryocytes (Figure 6A). Transfection of MEG-01 cells with S422DSGK1, but not with K127NSGK1, significantly increased Orai1 mRNA levels (Figure 6B). Those observations pointed to SGK1-sensitive transcriptional regulation of Orai1 in megakaryocytes.
SGK1-sensitive NF-κB–dependent transcription in MEG-01 cells und primary megakaryocytes. (A) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in platelets (left) and megakaryocytes (right) from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− mice (gray bar). **P < .01. (B) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells of Orai1 mRNA abundance. **P < .01. (C) Western blot analysis of phospho-IKKα/β in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IKKα/β phosphorylation. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of phospho-IκBα in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IκBα phosphorylation. **P < .01. (E) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid) and S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells incubated with SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM), IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM), or DMSO as solvent control. **P < .01. (F) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the highly specific IKK inhibitor BMS-345541. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM, red), or DMSO as solvent control (black) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 8 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (G) Confocal microscopy of nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65 (RelA) in murine megakaryocytes cultivated from bone marrow of sgk1+/+ (top) and sgk1−/− (bottom) mice. Red represents GPIb; green, p65; and blue, nuclei. White arrows point to nuclear translocated p65. Bar represents 10 μm.
SGK1-sensitive NF-κB–dependent transcription in MEG-01 cells und primary megakaryocytes. (A) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in platelets (left) and megakaryocytes (right) from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− mice (gray bar). **P < .01. (B) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells of Orai1 mRNA abundance. **P < .01. (C) Western blot analysis of phospho-IKKα/β in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IKKα/β phosphorylation. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of phospho-IκBα in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IκBα phosphorylation. **P < .01. (E) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid) and S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells incubated with SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM), IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM), or DMSO as solvent control. **P < .01. (F) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the highly specific IKK inhibitor BMS-345541. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM, red), or DMSO as solvent control (black) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 8 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (G) Confocal microscopy of nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65 (RelA) in murine megakaryocytes cultivated from bone marrow of sgk1+/+ (top) and sgk1−/− (bottom) mice. Red represents GPIb; green, p65; and blue, nuclei. White arrows point to nuclear translocated p65. Bar represents 10 μm.
Further experiments aimed to disclose the underlying mechanism of SGK1-dependent transcriptional regulation of Orai1. Transfection with S422DSGK1, but not transfection with K127NSGK1, significantly increased phosphorylation of the NF-κB regulating kinases IKKα/β (Figure 6C) and IκBα (Figure 6D) in MEG-01 cells. The up-regulation of Orai1 mRNA 48 hours after S422DSGK1 transfection was abrogated after a 24-hour incubation with the highly selective IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM) or the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM; Figure 6E). Furthermore, the S422DSGK1-induced up-regulation of SOCE could be inhibited by treatment with BMS-345541 (10μM; Figure 6F). Finally, as evident from immunofluorescence/confocal microscopy, the nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65 reflecting transcriptional activity was significantly less pronounced in sgk1−/− megakaryocytes than in sgk1+/+ megakaryocytes (Figure 6G). Consistent with that finding, we found an increased expression of p65 in isolated nuclear fractions of MEG-01 cells transfected with S422DSGK1 compared with untransfected MEG-01 cells or to cells transfected with K127NSGK1 (supplemental Figure 5).
Discussion
Platelets play a central role in the pathogenesis of arterial thrombosis and the mechanisms regulating the adhesive functions of platelets are thus of pivotal importance for occlusive cardiovascular disease.1,23 The present study unravels a novel regulator of platelet function, the PI3K pathway downstream effector SGK1. SGK1 belongs to the AGC family of serine-threonine kinases and shares a relatively high degree of homology with Akt in its catalytic domain.16,17 Previous work has identified a critical role for PI3K13-15 and some of its downstream effectors (eg, the AGC family members Akt12,29 and protein kinase C30 ) in promoting and maintaining platelet activation, including activation-dependent Ca2+ signaling. But the molecular targets of the products of PI3K in their respective functions have been incompletely defined.29 In this study, we could show, for the first time, that SGK1 is a novel important regulator of cytosolic Ca2+ and function of platelets and megakaryocytes.
Similar to observations in platelets completely lacking Orai17 or expressing a functional inactive Orai1 mutant (R93WOrai1),6 the impact of SGK1 deficiency on activation-dependent degranulation or integrin αIIbβ3 activation is more pronounced after application of GPVI agonists than after administration of thrombin or ADP. Possibly, thrombin or ADP stimulates in addition Orai1 independent Ca2+ entry, whereas Orai1-mediated Ca2+ entry is particularly important for GPVI-ITAM-mediated cell activation.31
The decreased activation of integrin αIIbβ3 in platelets lacking SGK1 paralleled a deficit in the ability of these platelets to undergo aggregation at low-dose concentrations of agonists. Increasing the agonists concentrations dissipated the differences between sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets, indicating that SGK1 deficiency enhances the sensitivity of platelets to activating agonists but does not modify the maximal effect after full activation. Apparently, the abundance of Orai1 is limiting after moderate but not after full platelet activation. Clearly, SGK1 deficiency does not abrogate SOCE and Ca2+-sensitive platelet function but decreases the sensitivity of the platelets to stimulators of Ca2+ entry. In the absence of SGK1, apparently other signaling molecules, such as Akt, maintain basic platelet function. Thus, in contrast to the severe phenotype of Orai1-deficient mice,7 the phenotype of sgk1−/− mice is mild.
Rupture of an atherosclerotic lesion leads to endothelial denudation and exposure of the thrombogenic subendothelial collagen to circulating platelets, initiating platelet recruitment to the injured vessel wall.32 According to the present study, lack of SGK1 decreases collagen-triggered thrombus formation under high shear stress. Platelet responses, including degranulation, integrin αIIbβ3 activation, thrombus formation, and especially phosphatidylserine exposure, which collectively accomplish platelet procoagulant activity, critically depend on an increase in [Ca2+]i.3,33 An increase of [Ca2+]i may result from release of intracellular Ca2+ compartmentalized in endoplasmic reticulum and entry of extracellular Ca2+ triggered by the depletion of SR Ca2+ stores, the SOCE.2
SGK1 deficiency markedly decreased platelet SOCE. Although the filling and release of the intracellular Ca2+ stores were unaffected in sgk1−/− platelets, SOCE was markedly reduced in platelets of SGK1-deficient mice. Furthermore, sgk1−/− platelets and megakaryocytes expressed less Orai1 Ca2+ channel protein in their cell membrane. Orai1 is a plasma membrane protein and the pore-forming unit for the SOCE.34 Orai1 is regulated by STIM1.35 STIM1 senses the Ca2+ content of the intracellular stores in platelet endoplasmic reticulum (dense tubular system) and activates the plasma membrane Orai1 on store depletion.8 Both Orai1 and STIM1 have previously been shown to be critically important for proper function of platelets.7,8 Besides the decreased Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1−/− platelets, SGK1 sensitivity of Orai1 expression was apparent from transfections with the constitutively active mutant (S422DSGK1) or the inactive mutant (K127NSGK1) of SGK1 in the human megakaryoblastic cell line MEG-01, cells with many properties in common with normal human megakaryocytes at an early stage of maturation.36 MEG-01 cells regulate the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in response to activation or store depletion via the same mechanisms, which are operative in platelets and megakaryocytes.37 Furthermore, MEG-01 cells highly express the store-operated Ca2+ channel Orai1 as well as the store Ca2+ sensor STIM138 and thus represent an ideal model for studying mechanisms regulating SOCE in human megakaryocytes. Transfection with the constitutively active mutant S422DSGK1, but not transfection with the inactive mutant K127NSGK1, significantly increased Orai1 membrane abundance and SOCE, an effect abrogated in the presence of GSK650394 (1μM), a specific SGK1 inhibitor.39 Accordingly, SGK1 regulates membrane expression of Orai1 and SOCE in megakaryocytes.
The decreased Orai1 protein abundance in sgk1−/− platelets could have resulted from decreased Orai1 transcription or accelerated degradation of Orai1 protein. As sgk1−/− platelets and megakaryocytes contain significantly less Orai1 mRNA than sgk1+/+ platelets and megakaryocytes, SGK1 is at least partially effective by up-regulating Orai1 transcription. Similarly, Orai1 mRNA levels in MEG-01 cells were increased by transfection with S422DSGK1 but not by transfection with K127NSGK1. Apparently, SGK1 does not directly influence SOCE, agonist-induced Ca2+ entry, or Ca2+-dependent platelet activation, as degranulation or integrin αIIbβ3 activation was not directly modified by SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (supplemental Figures 2 and 3).
Further experiments addressed the mechanism mediating SGK1-dependent Orai1 transcription. SGK1 is known to regulate transcription by up-regulating NF-κB activity through phosphorylation and activation of IKKα/β.16,40 Thus, SGK1 enhances the ability of IKKα/β to phosphorylate endogenous IκBα.41 The majority of NF-κB components, including the regulatory IκB and IKK, are expressed in both MEG-01 cells and human megakaryocytes.42 Functionally, NF-κB has been shown to regulate megakaryocytic differentiation.43 Thus, there is evolving evidence pointing to a decisive role of NF-κB in regulating gene expression in megakaryocytes. Nevertheless, megakaryocytic proteins, which are under transcriptional control of NF-κB and NF-κB–activating mechanisms in megakaryocytes, remain to be clarified. In the present study, transfection with S422DSGK1 but, not with K127NSGK1, significantly increased IKKα/β and IκBα phosphorylation in megakaryocytic MEG-01 cells. NF-κB activation could be disrupted by small-molecule inhibitors of IKKβ.44 Accordingly, the highly selective IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM), which shows greater than 10-fold selectivity for IKKβ than for IKKα,45 abrogated the up-regulation of Orai1 mRNA induced by transfection of MEG-01 cells with S422DSGK1 and abolished the SGK1-induced increase of SOCE (Figure 6F).
NF-κB is held latent in the cytoplasm as a complex bound with unphosphorylated IκB, thereby blocking the nuclear translocation of NF-κB.46 Phosphorylation of IκB by IKK leads to proteosomal degradation of IκB, liberating the NF-κB dimers (mostly p50-p65 dimers) to translocate into the nucleus and initiate transcription of target genes.47 Accordingly, nuclear translocation of p65 was less pronounced in sgk1−/− megakaryocytes than in sgk1+/+ megakaryocytes, and transfection of MEG-01 cells with S422DSGK1 increased nuclear expression of p65.
IKKβ-dependent NF-κB activation plays a key role in inflammation and inflammatory signaling pathways in metabolic diseases48 as diabetes or the metabolic syndrome, which are classically associated with platelet hyper-responsiveness and atherothrombotic complications, such as myocardial infarction or ischemic stroke.49 Hyperglycemia, glucose-induced AGEs, and oxidative stress are powerful stimulators of SGK117 and its downstream target NF-κB.48 Platelets from patients with type 2 diabetes show increased degranulation, adhesion, and aggregation of platelets,49 which could be a result of an increased Orai1 expression and SOCE found in these platelets.50 As SGK1 is strongly up-regulated in diabetic hyperglycemia,17 we speculate that an increased stimulation of SGK1 in these patients could contribute to megakaryocytic NF-κB induction, stimulation of Orai1 expression resulting in enhanced SOCE, and increased activation-dependent responsiveness of their platelets. In view of the present observations, gain-of-function SGK1 polymorphisms could increase platelet responsiveness, thus predisposing the carriers to thrombotic complications. In a recent study, a common gain-of-function SGK1 gene variant indeed has been identified to be associated with ischemic stroke.21
As a result of the strong effect of SGK1 on Orai1 expression and the similarity between the phenotype of Orai1-deficient and SGK1-deficient platelets, it appears safe to conclude that the SGK1-dependent regulation of Orai1 protein abundance substantially contributes to SGK1-sensitive platelet function. However, it must be kept in mind that SGK1 regulates a variety of further carriers and channels, enzymes, and transcription factors,17 which, at least in theory, could participate in the modulation of platelet function independently of regulating Orai1.
In conclusion, the present observations identify SGK1 as a novel transcriptional regulator of Orai1 in megakaryocytes which is at least partially effective through activation of NF-κB. Thus, SGK1-dependent Orai1 regulation in megakaryocytes can influence SOCE and activation-dependent Ca2+ entry as well as Ca2+-dependent mechanisms, such as degranulation, aggregation, and thrombus formation in released platelets.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tanja Hildenbrandt and Yvonne Riexinger for providing outstanding technical assistance.
This work was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB TR19 and KFO 274) and the Fortüne program (1934-0-0). This study was supported by the DFG Klinische Forschergruppe 274.
Authorship
Contribution: O.B. performed experiments, analyzed data, designed research, and wrote the manuscript; E.-M.S., P.M., T.S., S.T.T., M.E., C.L., E.S., and A.E. performed experiments and analyzed data; and A.E.M., D.K., M.G., and F.L. analyzed data, designed research, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Florian Lang, Department of Physiology, University of Tübingen, Gmelinstr 5, 72076 Tübingen, Germany; e-mail: florian.lang@uni-tuebingen.de.


![Figure 3. Agonist-induced Ca2+ response and impaired SOCE in sgk1−/− and sgk1+/+ platelets. (A) Representative tracings of Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets before and after stimulation with thrombin (0.02 U/mL), CVX (1 μg/mL), CRP (10 μg/mL), and ADP (10μM) in the absence (0.5mM EGTA, left) or presence (1mM Ca2+, right) of extracellular Ca2+. (B) Arithmetic mean of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 4 per group). **P < .01. (C) Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of sgk1+/+ (black line) and sgk1−/− (gray line) platelets after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SD (n = 6 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/119/1/10.1182_blood-2011-06-359976/4/m_zh89991183130003.jpeg?Expires=1770991657&Signature=DeoNoVWVe2aTxinb8HgJCPFa2OsfBINF1P2YTf7JJVSVQbqid-j5eFZ2bjCPDD5bpDQuP5pMgF~Outj0Adgm6HrbnXALC-1g78r9JKJPZT7qic2s8l5urRLUOUD5gw~Rjfk4vqqtFnJFcp5xq5mv3tJ4DdFztJRCotkU-fd5hhklJCJS1uGBbjfyZCjQo4QtovRnDMs-Rq4oAVaFnxAxystBqzsNIAvZSbRV2atooaAfbdJGWrx1o-ABnnAW-mFM0jlK2rjlLENHt7tQEPg~t8nz9zC92-7y8e~LiYSKGiKJnXA3mcreHF1I53rK9EBMnv0i61NewS9ND83K9kMU9w__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

![Figure 5. SGK1-dependent Orai1 membrane abundance and SOCE in megakaryocytic cell line MEG-01. (A) Confocal microscopy of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells (left). Red represents actin; green, Orai1; and blue, nuclei. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Statistical analysis of Orai1 immunofluorescence membrane abundance (right). *P < .05. **P < .01. n = 4. (B) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 7) of Orai1 protein abundance. *P < .05. **P < .01. (C) SOCE in SGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1 (black), or K127NSGK1 (red) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 15 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of Orai1 membrane abundance in nontransfected (control plasmid) MEG-01 cells and in S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM) or DMSO as solvent control. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of Orai1 protein abundance. **P < .01. (E) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the specific SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394. Fura-2 fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control plasmid (gray) or S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells after treatment with GSK650394 (1μM, red) or DMSO (black) as solvent control. Representative tracings (top) and arithmetic mean (bottom) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 9 per group) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. **P < .01.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/119/1/10.1182_blood-2011-06-359976/4/m_zh89991183130005.jpeg?Expires=1770991657&Signature=dDqeVxbstcm8duv2jCbONOCi3vaHKmr-N9PUR9vL8X22KvxUoHJL9YABMCrZrhZqs93E2FvM3xIDp7nGRbl-kbBB1HVVrrwTEUeF-UCH2w3PpJOy5mni-NpyseRpTu6~2BQh4aOXIERXpTQsALq2y5elQ4LmqUjtoAX92atqPihl9xBr-HFZReHHji1iTbeWfcAlo~b~ZAh~~0Ptcae~hxdu7TQHUz0jbJFQy~v7rGg~5IzYQmTtmjcZAnkzLKAiYWQdNS5iJQ1BIAFVDNLnfgK-OtOlk~ywx7FB26YLg1trIRFamKCyiDxqHeiWHbIj9MGv5jQTFMf9k-hcqelgfA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 6. SGK1-sensitive NF-κB–dependent transcription in MEG-01 cells und primary megakaryocytes. (A) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 4) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in platelets (left) and megakaryocytes (right) from sgk1+/+ (black bar) and sgk1−/− mice (gray bar). **P < .01. (B) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells of Orai1 mRNA abundance. **P < .01. (C) Western blot analysis of phospho-IKKα/β in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IKKα/β phosphorylation. **P < .01. (D) Western blot analysis of phospho-IκBα in nontransfected (control plasmid), S422DSGK1-transfected, and K127NSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells. Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 5) of IκBα phosphorylation. **P < .01. (E) Arithmetic mean ± SEM (n = 6) of mRNA encoding Orai1 in nontransfected (control plasmid) and S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells incubated with SGK1 inhibitor GSK650394 (1μM), IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM), or DMSO as solvent control. **P < .01. (F) SOCE in MEG-01 cells treated with the highly specific IKK inhibitor BMS-345541. Fura-2-fluorescence reflecting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i of MEG-01 cells transfected with control-plasmid (gray), S422DSGK1-transfected MEG-01 cells treated with the IKK inhibitor BMS-345541 (10μM, red), or DMSO as solvent control (black) after exposure to 5μM thapsigargin (Ca2+ store depletion) in the nominal absence of extracellular Ca2+ for 10 minutes and subsequent addition of 1mM extracellular Ca2+. Representative tracings (left) and arithmetic mean (right) of maximal Δ[Ca2+]i ± SEM (n = 8 per group) before and after addition of 1mM Ca2+. **P < .01. (G) Confocal microscopy of nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65 (RelA) in murine megakaryocytes cultivated from bone marrow of sgk1+/+ (top) and sgk1−/− (bottom) mice. Red represents GPIb; green, p65; and blue, nuclei. White arrows point to nuclear translocated p65. Bar represents 10 μm.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/119/1/10.1182_blood-2011-06-359976/4/m_zh89991183130006.jpeg?Expires=1770991657&Signature=M~mt65xx32BmTe7SaPE2TtbnrSHkEyru1A2GVIin0kjgF114mQ5gwmhaJvdKTb5Vjot6jp5y-hbZHPkDmMbHYD-RdZyX61id5JBn2Wn8p6kBWIlYvc~Zgg1u0~xrqC9DXLc4CF74CYF7HjKW1gCN~yYBOhNBTMHVLk0-dvC5NJUgnXHMnbJ2mODbQ~z9BLVt54eMFHRzYDRiIUT2D5~fNNq84EdZju6hnYvxX5mQXN8eNAEFiYLGZpeBLhGTE3u7Bxd64LF1~SwAjqE1o7Q2gb28JqimLJ9SFfdzwNaU7XpAQaXpnqAIwVORnOpUmQR4Wt2RwYlnZRRyCVAJWmjuzA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)