Abstract
Abstract 4132
Although precise matching of the donor/recipient pairs has been made easier by HLA typing at the allelic level, several issues with respect to unrelated transplantation remain to be addressed. In particular, the impacts of allelic HLA matching in patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and myelodysplasic syndrome (MDS) who receive allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem cells (PBSC) after a reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) regimen is still unclear. In the present study, we aim to compare the impact of the donor type in this setting: HLA identical sibling versus HLA matched 10/10 (high resolution) unrelated donor (MUD).
From 01/2001 to 12/2010, 108 consecutive patients with AML (n=63) and MDS (n=45) received PBSC after RIC in our center, either from HLA identical sibling (n=69) or MUD (n=39). Conditioning regimen was fludarabine based in 95% of patients and GvHD prophylaxis consisted in cyclosporine plus mycophenolate in 79% of patients. Engraftment, acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), transplantation-related mortality (TRM), relapse rate and overall survival (OS) at 3 years were compared according to type of donor: HLA identical sibling donor and MUD.
WHO classification for MDS at time of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) was RAEB1 (24%), RAEB2 (36%), MDS transformed into secondary AML (20%), CMML2 (9%), RA (4%), or other (7%). Disease risk was assumed by cytogenetic (MRC for AML, IPSS for MDS) and EBMT score (good risk: CR1 for AML or MDS or untreated MDS, intermediate risk: CR2 for AML, CR2 or partial remission for MDS, poor risk: all other status). Cytogenetic (no missing data) was poor, intermediate or good for 21, 74 and 5% of AML and 24, 36 and 40% of MDS, respectively. EBMT score at time of HSCT was poor, intermediate or good for 29, 7, 64% of MDS and 11, 21, 68% of AML, respectively.
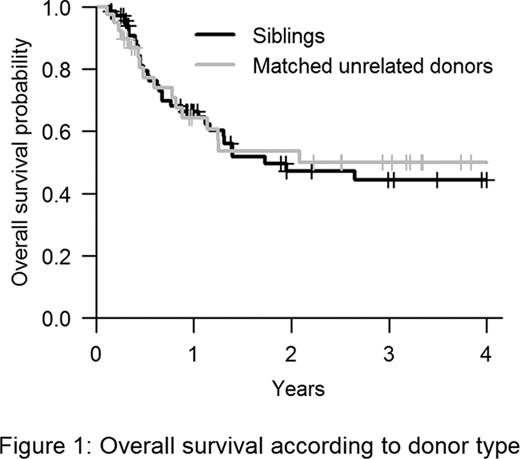
Patients characteristics according to type of donor were similar for age (median 57 years), gender and disease distribution. Particularly, disease risks were comparable in 2 groups. Conversely, conditioning regimen (more ATG in MUD: 69 vs. 43%, p=0.016), donor age (younger for MUD: 30 vs. 52 years, p<0.0001) and number of CD34+ cells infused (higher in MUD: 7 vs. 6.5 × 106/kg, p=0.022) were different. The median follow-up was 36 months (range 2 to 72). All patients engrafted. The cumulative incidence of acute GvHD was 40% with HLA matched sibling donor and 44% for MUD (p=0.58). The cumulative incidence of chronic GvHD at 3 years was 49% with HLA matched sibling donor and 45% with MUD (p=0.66). No risk factor was associated with acute GvHD but chronic GvHD was less frequent in patients with AML vs. MDS (41% vs. 59%, p=0.077) and in those patients who received ATG in conditioning regimen (54% vs. 43%, p=0.067). During follow-up, 47 patients died. The 3-year cumulative incidence of TRM was 17% and 22% with HLA matched sibling donor and MUD, respectively (p=0.55). Adjusting for age, MDS was the only factor increasing TRM (HR 3.4; 95% CI 1.2 to 9.5; p=0.02). The 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse was 46% with HLA matched sibling donor and 30% with MUD (p=0.28) knowing that there was no difference between both groups regarding disease risk (cytogenetic and EBMT score). The 3-year OS was 44% with HLA matched sibling donor (95%CI: 33–61) and 50% with MUD (95%CI: 35–71) (Figure 1).
Fenaux:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Peffault de Latour:Alexion: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal