Abstract
Dysregulated JAK-STAT signaling is a key feature in MF, which is characterized by splenomegaly, debilitating symptoms, poor quality of life (QoL), cytopenias, and shortened survival. Ruxolitinib is a selective JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor with clinical activity in MF. COMFORT-I is a Phase III, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study of ruxolitinib in patients with MF. At wk 24, 41.9% of patients receiving ruxolitinib reached the protocol-defined threshold of a ≥35% reduction in spleen volume (SV) compared to 0.7% in the placebo group (p<0.0001). The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the relationship between SV reduction achieved with ruxolitinib treatment and changes in symptoms and QoL.
309 patients were randomized to receive ruxolitinib (n=155) or placebo (n=154). Initial dosing was based on baseline platelet counts: 15 mg BID for counts of 100–200 x109/L and 20 mg BID for >200 x109/L. SV was measured by blinded imaging (MRI or CT scan) every 12 wks. Via electronic diary, patients reported MF symptoms daily using the modified Myelofibrosis Symptom Assessment Form (MFSAF) v2.0. The Total Symptom Score (TSS) from the MFSAF represents a combined score for the individual symptoms of abdominal discomfort, pain under ribs on left side, early satiety, itching, night sweats, and bone/muscle pain. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality-of-Life 30 (EORTC QLQ-C30) and Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement System (PROMISE) Fatigue questionnaires were administered at each visit; Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) was administered at every visit beginning at wk 4. The PGIC rates a patient's overall sense of whether a treatment has been beneficial or not on a 7-point scale, ranging from 1 = very much improved to 7 = very much worse, with 4 = no change.
Baseline QoL scores reflected debilitating disease, and were similar to scores for similar-aged patients with other cancers (Scott NW, Fayers PM, Aaronson NK, et al. EORTC QLQ-C30 Reference Values Manual, July 2008). The impact on patients was particularly evident on the PROMIS Fatigue scale and QLC-C30 Global Health, Physical Functioning, Role Functioning, and Social Functioning subscales.
Baseline Symptom and QoL Measures*
| Parameter Measured . | Ruxolitinib (mean) . | Placebo (mean) . | Maximum Score Possible . |
|---|---|---|---|
| MFSAF - TSS | 18.0 | 16.5 | 60 (worst possible) |
| PROMIS Fatigue | 43.4 | 43.2 | 100 (worst possible) |
| EORTC QLQ C-30 Subscales | |||
| EORTC Global Health | 52.6 | 54.5 | 100 (best possible) |
| Physical Functioning | 69.5 | 67.6 | 100 (best possible) |
| Role Functioning | 64.6 | 65.1 | 100 (best possible) |
| Emotional Functioning | 73.7 | 76.3 | 100 (best possible) |
| Cognitive Functioning | 81.1 | 79.3 | 100 (best possible) |
| Social Functioning | 68.0 | 65.9 | 100 (best possible) |
| Parameter Measured . | Ruxolitinib (mean) . | Placebo (mean) . | Maximum Score Possible . |
|---|---|---|---|
| MFSAF - TSS | 18.0 | 16.5 | 60 (worst possible) |
| PROMIS Fatigue | 43.4 | 43.2 | 100 (worst possible) |
| EORTC QLQ C-30 Subscales | |||
| EORTC Global Health | 52.6 | 54.5 | 100 (best possible) |
| Physical Functioning | 69.5 | 67.6 | 100 (best possible) |
| Role Functioning | 64.6 | 65.1 | 100 (best possible) |
| Emotional Functioning | 73.7 | 76.3 | 100 (best possible) |
| Cognitive Functioning | 81.1 | 79.3 | 100 (best possible) |
| Social Functioning | 68.0 | 65.9 | 100 (best possible) |
Baseline measures for patients with both baseline and wk 24 data.
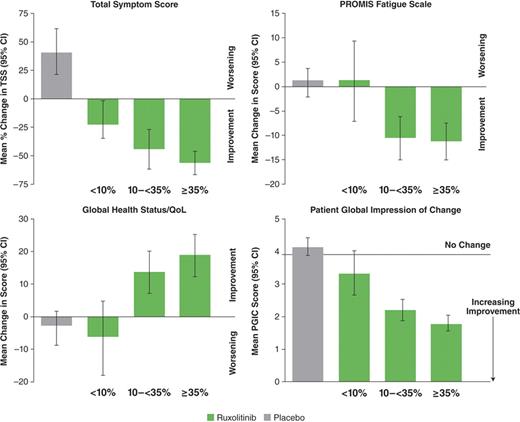
Associations between changes in symptoms and QoL with the objectively measured changes in SV were evaluated. Patients receiving ruxolitinib were grouped according to SV reduction at 24 wks of treatment: ≥35% reduction in SV (n=65), 10-<35% (n=51), and <10% (n=23). Symptom and QoL responses were evaluated among the various subgroups (of the SV reduction percentage strata) and comparisons were made across these and the total placebo group (n=106). Shown in the Figure are mean changes at wk 24 relative to baseline for TSS, QoL indicators, and PGIC scores.
Changes in SV as low as 10% in ruxolitinib-treated patients were associated with improvements on EORTC QLQ-C30 Global Health subscale, PROMISE Fatigue scale, and the MFSAF v2.0 diary TSS. Moreover, commensurate improvements in these outcomes were observed as the SV reduction increased. Importantly, the simple PGIC questionnaire allowed patients to characterize a meaningful change in their condition that was consistent with more comprehensive measures of MF symptoms and quality of life, reflecting a doctor-patient assessment easily applied to clinical practice.
Change from Baseline to Wk 24 in TSS, QoL (PROMIS Fatigue Scale and QLQ-C30 Global Health Status), and PGIC by Reductions in SV (<10%, 10-<35%, and ≥35%)
Change from Baseline to Wk 24 in TSS, QoL (PROMIS Fatigue Scale and QLQ-C30 Global Health Status), and PGIC by Reductions in SV (<10%, 10-<35%, and ≥35%)
Mesa:Incyte: Research Funding; Lilly: Research Funding; SBio: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Gotlib:Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding. Gupta:Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Catalano:Incyte: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Deininger:BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding. Shields:Incyte: Consultancy. Miller:Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Winton:Incyte: Consultancy. Hare:Incyte: Employment. Erickson-Viitanen:Incyte: Employment. Sun:Incyte: Employment. Sandor:Incyte: Employment. Levy:Incyte: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kantarjian:Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Verstovsek:Incyte: Research Funding.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal