Abstract
Abstract 3454
Multivariable analysis for EFS according to RUNX1-mut status in all CN-AML pts
| . | HR . | EFS . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUNX1, mut v wt | 2.27 | 1.65–3.12 | <.001 |
| FLT3-ITD, ITD v no ITD | 1.57 | 1.27–1.95 | <.001 |
| WT1, mut v wt | 1.44 | 1.02–2.01 | .04 |
| WBC, continuous 50 unit increase | 1.13 | 1.04–1.23 | .006 |
| Age group, ≥60y v <60y | 1.80 | 1.46–2.22 | <.001 |
| . | HR . | EFS . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUNX1, mut v wt | 2.27 | 1.65–3.12 | <.001 |
| FLT3-ITD, ITD v no ITD | 1.57 | 1.27–1.95 | <.001 |
| WT1, mut v wt | 1.44 | 1.02–2.01 | .04 |
| WBC, continuous 50 unit increase | 1.13 | 1.04–1.23 | .006 |
| Age group, ≥60y v <60y | 1.80 | 1.46–2.22 | <.001 |
Note: A hazard ratio (HR) >1 corresponds to a higher risk for higher values of continuous variables and the 1st level listed of a dichotomous variable.
To gain biological insight, RUNX1 mut-associated gene and miR expression signatures were derived in CN-AML for the first time. Older, NPM1-wt pts were analyzed since RUNX1 muts are more common in this age group and are nearly exclusive from NPM1 muts, which have their own characteristic gene-expression signature. This yielded 484 probe sets representing 278 named genes differentially expressed between RUNX1-mut (n=31) and RUNX1-wt (n=45) pts (P<.001). Genes normally expressed in hematopoietic stem (HSC) and early progenitor cells, including DNTT, BAALC, MN-1, CD109, P2RY14, FOXO1 and FLT-3 were upregulated in RUNX1-mut pts, as were components of the Wnt-signaling pathway, LRP6 and TCF4, that promote self-renewal and proliferation of HSCs. Genes upregulated (SETBP1, RBPMS, and SLC37A3) and downregulated (CCNA1 and RNASE3) in AML stem cells relative to AML progenitors were similarly deregulated in the RUNX1-mut signature. B cell lineage genes BLNK, IGHM, IRF8 and several class II MHC molecules were upregulated in RUNX1-mut pts while CEBPA, a key promoter of granulopoiesis, was downregulated. Genes implicated in chemoresistance, GAS6, PRKCE, and PTK2, were upregulated and MYCN, a promoter of both proliferation and apoptosis of myeloid cells, was downregulated in RUNX1-mut pts. Seven miRs were differentially expressed between RUNX1-mut and RUNX1-wt pts. Two members of the let-7 tumor suppressor family, which represses self-renewal and promotes differentiation of stem cells, were downregulated, as was miR-223, a positive regulator of granulopoiesis. MiRs -99a and -100 were also downregulated and miRs -211 and -595 upregulated in association with RUNX1 muts.
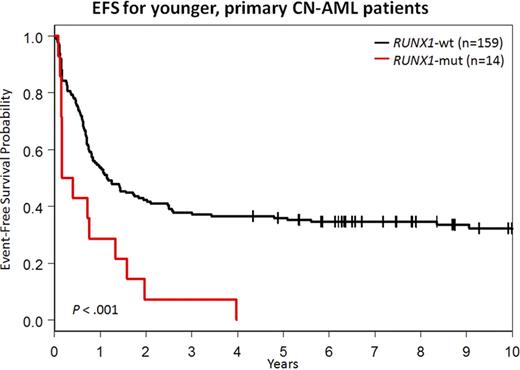
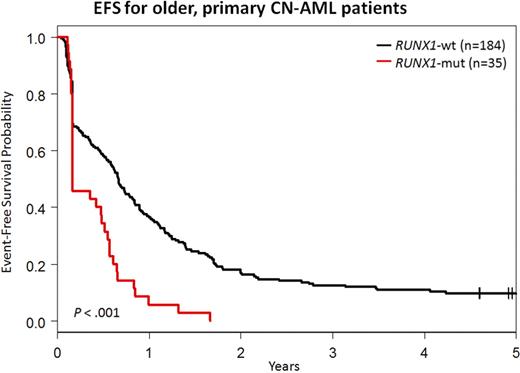
In summary, RUNX1 muts are twice as common in older CN-AML pts than younger. They negatively impact on outcome in both younger and older pts not receiving alloSCT in CR1. RUNX1-mut blasts have molecular features of normal/malignant stem cells and B cells, which may explain their chemoresistance and guide novel therapeutic approaches.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal