Abstract
Abstract 3345
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is frequently complicated by venous thromboembolism (VTE). The reported incidence varies from 2% to 37%, with the highest risk arising in the first weeks after treatment initiation. VTE leads to morbidity, mortality and premature termination of therapy. Prevention of VTE in ALL is complicated, as thrombotic and bleeding factors need to be balanced. The efficacy of prophylactic antithrombotic measures is not clear yet, and standardized guidelines are lacking. We assessed the effect of various prevention protocols on the VTE risk in adults treated for ALL.
Between April 1999 and November 2005, 240 consecutive patients aged 16–59 years with newly diagnosed ALL were treated with the same anti-leukemic protocol in a Dutch-Belgian multicenter study, which included L-asparaginase in cycle 1 (5000 U/m2/day, day 15–28). All VTE events during treatment were prospectively recorded. VTE prophylaxis was applied only in cycle 1 during asparaginase administration, and varied between different centers: no prophylaxis, fresh frozen plasma (FFP), or antithrombin (AT) concentrate. A centers' prevention protocol was used as a proxy for all patients treated in that center. AT plasma levels were assessed of patients with VTE and 22 controls without VTE. We determined VTE incidence in cycle 1, the impact of the various prophylactic measures, and VTE incidence during the total treatment period for ALL. Secondly, we assessed the clinical relevance of VTE on ALL outcome.
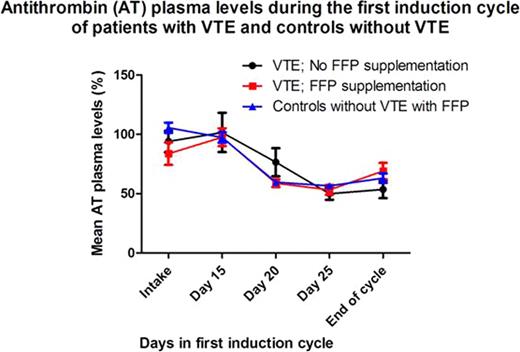
25 of 240 patients (10.4%; 95% CI 6.6–14.3) experienced objectively diagnosed, symptomatic VTE in cycle 1 (10 cerebral thromboses of which 8 in the sagittal sinus, 11 upper limb vein thromboses (10 central venous catheter (CVC)-related), 3 deep vein thromboses of the leg, 1 pulmonary embolism). VTE incidence in patients receiving FFP prophylaxis was reduced by 70% as compared to patients without prophylactic measures (7.2% vs. 23.9%; RR 0.3; 95% CI 0.1–0.6; Table 1). Age, sex, ALL-type and CVC-placement did not differ significantly between patients with and without FFP prophylaxis. The effect of prophylactic AT concentrate could not be properly assessed as it was only rarely given in two centers. Mean AT plasma levels did not differ significantly between VTE patients with or without FFP, neither between patients with VTE and controls without VTE (Figure 1). During the total treatment period, VTE occurred in 36 of 240 patients (15.0%; 95% CI 10.5–19.5). Patients with VTE in cycle 1 were less likely to obtain complete remission after cycle 1 (HR 0.5; 95% CI 0.3–0.9), but did not have a significantly decreased overall survival (HR 1.5; 95% CI 0.9–2.6).
Effect of FFP prophylaxis on VTE incidence during ALL treatment cycle 1
| . | ALL patients with VTE in cycle 1 . | Total number of ALL patients . | VTE incidence . |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFP prophylaxis | 14 | 194 | 7.2% |
| No FFP prophylaxis | 11 | 46 | 23.9% |
| Total | 25 | 240 | 10.4% |
| RR = 0.3 (95% CI 0.1 – 0.6) | |||
| . | ALL patients with VTE in cycle 1 . | Total number of ALL patients . | VTE incidence . |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFP prophylaxis | 14 | 194 | 7.2% |
| No FFP prophylaxis | 11 | 46 | 23.9% |
| Total | 25 | 240 | 10.4% |
| RR = 0.3 (95% CI 0.1 – 0.6) | |||
ALL = acute lymphoblastic leukemia; FFP = fresh frozen plasma; VTE = venous thromboembolism; RR = relative risk
FFP significantly reduced VTE incidence by 70% during ALL treatment, without reversing the AT deficiency induced by asparaginase. Our observation is in contrast with two previous studies on the effect of FFP on VTE in ALL. The mechanisms by which FFP accomplishes this antithrombotic effect are not clear yet and require further investigation. Since this was a retrospective, observational study, the effect of prophylactic FFP on VTE risk in adults treated for ALL should be confirmed by a randomized controlled trial.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal