Abstract
Imatinib mesylate treatment markedly reduces the burden of leukemia cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients. However, patients remain at risk for relapse on discontinuing treatment. We have previously shown that residual BCR-ABL+ progenitors can be detected in CML patients within the first 2 years of imatinib treatment. However, reduced rates of relapse and continued decline of BCR-ABL levels with prolonged treatment, together with the ability of selected patients to maintain remission after discontinuing treatment, led us to investigate whether prolonged imatinib exposure resulted in reduction or elimination of BCR-ABL+ stem cells. We evaluated BCR-ABL expression in CD34+CD38+ (38+) committed progenitors and CD34+CD38− (38−) stem/primitive progenitor cells in samples from CML patients on imatinib treatment for at least 4 years with cytogenetic and molecular response. High levels of BCR-ABL expression were maintained over time in the 38− stem cell fraction. The absolute frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells as determined by limiting dilution analysis was consistently higher in 38− compared with 38+ cells. Transplantation into NOD/SCID-IL2Rγ-chain knockout mice demonstrated that BCR-ABL+ cells had long-term in vivo repopulating capacity. These results directly demonstrate that BCR-ABL+ stem cells persist in CML patients despite prolonged treatment with imatinib, and support ongoing efforts to target this population.
Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) results from HSC transformation by the BCR/ABL gene.1 Treatment with the BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate (Novartis) results in sustained clinical remissions in CML patients with major reduction in BCR-ABL transcript levels on quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) analysis.2 However, the majority of patients achieving remission with imatinib mesylate continue to have molecular evidence of persistent disease.3 Mathematical modeling of the kinetics of reduction of BCR-ABL levels in imatinib mesylate–treated CML patients suggest that imatinib mesylate has increased activity against progenitors and mature cells and limited activity against stem cells.4,5 Laboratory studies confirm heterogeneity of response of different cell types to imatinib mesylate, with quiescent CML stem cells being the most resistant to imatinib mesylate–induced apoptosis.6,7 We and others have shown that CML stem cells are also insensitive to the second-generation ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) nilotinib and dasatinib.8-12 There is a high likelihood of leukemia relapse on discontinuation of treatment, and it is currently recommended that patients receive imatinib mesylate indefinitely to prevent relapse, with associated risk of side effects and considerable expense.
We have previously shown that residual BCR-ABL expressing CD34+ cells, colony forming cells (CFCs), and long-trem culture intiating cells (LTCICs) can be detected in the BM of patients in remission with imatinib mesylate treatment.3 These earlier studies were carried out in patients who had been treated with imatinib mesylate for < 2 years. Other groups have reported that BCR-ABL–expressing CML progenitors were eradicated within a year of starting imatinib mesylate treatment whereas BCR-ABL positivity continued to be seen in the stem cell compartment, although at reduced levels.13 On the other hand, BCR-ABL levels continue to slowly decline over time in CML patients with prolonged imatinib mesylate treatment.14 In addition, the rate of disease relapse in patients receiving imatinib mesylate treatment decreases with ongoing treatment.15 Finally, a proportion of imatinib mesylate–treated patients who achieve undetectable levels of BCR-ABL on Q-PCR analysis maintain sustained remissions after discontinuation of imatinib mesylate treatment.16-18 These observations raise the possibility that prolonged imatinib mesylate treatment may be associated with reduction or elimination of CML stem cells. The ability to directly measure residual leukemia stem cells in CML patients would considerably assist assessment of the effects of treatments against this population.
In the current study, we evaluated residual leukemia stem cell levels in patients who had been treated with imatinib mesylate for at least 4 years and who were followed at our center. Our results directly demonstrate the persistence of BCR-ABL+ stem cells in the BM of CML patients in prolonged remission on imatinib mesylate treatment.
Methods
Patients and samples
CML patients followed at City of Hope (n = 20) treated with imatinib mesylate for 4 or more years from whom cryopreserved BM samples were available were studied. Patients were in complete cytogenetic response (CCR) and 19 patients were reported to be in complete molecular response by the clinical laboratory at time of study. Of these, 12 patients were consistently negative on PCR evaluation. The Q-PCR assay used by the clinical laboratory detects BCR-ABL transcripts corresponding to a BCR-ABL: BCR ratio of 0.1%, or a 3-log reduction on the international scale, but does not detect lower levels of BCR-ABL transcripts. Mononuclear cells were isolated using Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient separation. Cells were cryopreserved in DMSO-containing medium in liquid nitrogen tanks (vapor phase). Frozen cells were thawed and incubated in IMDM supplemented with 20% FBS and DNAse I (Sigma-Aldrich) for 3 hours at 37°C before further processing. CD34+ cells were isolated from BM mononuclear cells (MNCs) by immunomagnetic column separation (Miltenyi Biotec; StemCell Technologies). Column-selected CD34+ cells were labeled with anti-CD34–APC (clone 8G12) and anti-CD38–PE (clone HB7) Abs (BD Biosciences), and CD34+CD38+ (38+) committed progenitors and CD34+CD38− (38−) stem or primitive progenitor cells were isolated by flow cytometric sorting.
Real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from MNCs, CD34+CD38+ cells, and CD34+CD38− cells using RNeasy mini or micro kits (QIAGEN). First-strand cDNA was synthesized using the Superscript III first strand kit (Life Technologies). Reactions were performed in a total volume of 20 μL. Quantitative PCR analysis for detection of BCR/ABL and BCR transcripts was performed using a TaqMan universal PCR master mix kit and the ABI Prism 7900 sequence detector (Applied Biosystems). Primer and probe sequences for B3A2 and BCR were as previously described.19 Quantitation standards for Q-PCR were prepared by PCR amplification of B3A2, B2A2, and BCR sequences from K562 (B3A2), Meg01 (B2A2), and HL60 (BCR) cell lines, respectively. The primer sequences used for amplifying the standards were: BAFw 5′-aga agc ttc tcc ctg aca tc-3′; BARe 5′-aga tgc tac tgg ccg ctg aa-3′; BCR Fw 5′-tca cca aga gag aga ggt cca a-3′; BCRRe 5′-ggt cag aaa gag cga tgc cct c-3′. The purified PCR product was cloned into the pCRII-TOPO vector (Life Technologies). Serial dilutions of each standard were made and a 6-log series of BCR-ABL and BCR standards were processed with every PCR. The amounts of BCR-ABL and BCR mRNA were calculated based on standard curves and expressed as ratio of BCR-ABL to BCR. The quantitative PCR assay could detect as low as one copy of BCR-ABL per reaction. The sensitivity of this assay relative to the international scale was determined using K562:HL60 dilutions corresponding to reference reagents used by the WHO International Panel. This Q-PCR assay could consistently detect BCR-ABL:BCR ratios at and below 0.01%, corresponding to complete molecular response (CMR)4.0.
To test the accuracy of the Q-PCR with small amounts of RNA, total RNA extracted from K562 cells was diluted 1:100 into HL60 cells. Ten-fold logarithmic serial dilutions were performed to yield 200 ng, 20 ng, 2 ng, and 0.2 ng per reaction, equivalent to 20 000, 2000, 200, and 20 cells, respectively. First-strand cDNA was synthesized using Superscript III first-strand kit and PCR reactions for BCR-ABL and BCR were performed.
Limiting dilution analysis
To measure the absolute frequency of BCR-ABL–expressing cells, a limiting dilution assay was developed. CD34+38+ and CD34+38− cells selected by flow cytometry were deposited in wells of 96-well plates in serial dilutions of 4 different concentrations with 12 replicates for each concentration. CD34+38+ cells were plated at 900, 300, 100, and 33 cells/well, and CD34+38− cells at 300, 100, 33, and 11 cells/well. Cells were washed with PBS and lysed in 12 μL of cell-to-signal buffer (Life Technologies). Total RNA was extracted using cell-to-signal buffer and 1-step RT-PCR was performed on 11 μL of cell lysate using primers designed to specifically detect transcripts from the breakpoint region of the p210 BCR-ABL fusion gene. Initially, 35 cycles of PCR amplification were carried out using the BCR68 (5′-AGAAGCTTCTCCCTGACATCCG-3′) and ABL3 (5′-GGTACCAGGAGTGTTTCTCCAGACTG-3′) primers. Subsequently, a fraction of the first-stage product was subjected to an additional 35 cycles of PCR amplification using internal nested primers, BCRfwd (5′-TGAAACTCCAGACTGTCC-3′) and ABLrev (5′-TCAGACCCTGAGGCTCAAAG-3′). Amplified samples were size separated by gel electrophoresis, and stained with ethidium bromide. Wells were scored as positive or negative for presence of BCR/ABL. The frequency of BCR/ABL-positive cells was calculated using L-CALC software (StemCell Technologies) based on the reciprocal of the concentration of test cells that resulted in 37% negative wells.
FISH
FISH was performed with the Vysis LS1 Bcr-Abl dual-color, dual-fusion translocation probe (Abbott Molecular).
Transplantation of human cells into immunodeficient mice
All animal studies were reviewed and approved by Research Animal Care Committee (RACC) at the City of Hope. NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid IL2rgtm1Wjl /SzJ mice (NSG mice) from 6 to 8 weeks of age were used for experiments. Animals were housed in a pathogen-free environment with autoclaved food and acidified water. CD34+ cells from CML patients were transplanted via tail vein injection into sublethally irradiated (300 cGy) mice (3-4 mice per sample). Mice were euthanized after 11-12 weeks and marrow contents of femurs and spleen cells obtained at necropsy. Human cell engraftment in BM, peripheral blood (PB), and spleen was analyzed by labeling with anti–human CD45-FITC, CD34-PerCP, CD33-allophycocyanin, CD19–Pacific Blue, CD3-APC–Cy7, CD14-PE and CD11b-PE–Cy7 Abs (eBioscience) and analysis on an LSRII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). BCR-ABL mRNA expression in human cells engrafted in BM and spleen was evaluated by PCR. Total cellular RNA was extracted from human CD45+ cells isolated from BM. PCR analysis for BCR/ABL was performed as described “Real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis.”
Statistical analysis
Data for Q-PCR analysis obtained from multiple experiments were reported as the median, quartiles, and range. Significance levels were determined using the Mann-Whitney test. Data for limiting dilution analyses and engraftment were reported as mean and SEM.
Results
CML patients who had been treated with imatinib mesylate for at least 4 years and had achieved CCR and molecular response (undetectable BCR-ABL on Q-PCR analysis in the clinical laboratory) were studied, with the exception of one patient whose samples were used in murine engraftment studies. The clinical characteristics of these patients are listed in Table 1. All patients were in chronic phase at start of imatinib mesylate treatment. The median age of patients was 54 years (range, 25-68 years). Eight patients (40%) had received IFN or IFN + Ara-C before starting imatinib mesylate. The median time to starting imatinib mesylate was 1.5 months (range, 0-31 months) and from starting imatinib mesylate to CCR was 6 months (range, 3-34 months). Twelve patients were consistently in complete molecular response whereas 7 patients were intermittently in molecular response.
Patient characteristics
| Patient ID . | Age, y . | Sex . | Phase at IM start . | Prior treatment . | Time from diagnosis to IM start, mo . | Time to CCyR after starting IM, mo . | PCR-negative sample studied . | Consistently PCR negative . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 144 | 47 | M | CP | IFN + Ara-C | 7 | 9 | Y | Y |
| 177 | 50 | F | CP | IFN | 21 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 202 | 56 | F | CP | IFN | 15 | 3 | Y | N |
| 222 | 64 | F | CP | IFN | 30 | 9 | Y | N |
| 232 | 58 | M | CP | IFN + Ara-C | 20 | 9 | Y | Y |
| 238 | 62 | M | CP | IFN | 25 | 6 | Y | N |
| 248 | 68 | M | CP | None | 1 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 256 | 40 | M | CP | None | 0.25 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 273 | 41 | F | CP | None | 0.75 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 292 | 41 | F | CP | None | 0.5 | 3 | Y | Y |
| 296 | 66 | M | CP | IFN | 13 | 5 | Y | Y |
| 299 | 59 | F | CP | None | 4 | 6 | Y | N |
| 327 | 37 | M | CP | None | 0.75 | 9 | Y | N |
| 347 | 35 | M | CP | None | 2 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 397 | 44 | F | CP | None | 0.1 | 10 | Y | N |
| 469 | 25 | M | CP | None | 0.1 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 476 | 56 | F | CP | None | 0.1 | 5 | Y | N |
| 833 | 67 | F | CP | IFN | 31 | 34 | N | N |
| 902 | 52 | F | CP | None | 0.0 | 4 | Y | Y |
| 924 | 57 | M | CP | None | 0.1 | 5 | Y | Y |
| Patient ID . | Age, y . | Sex . | Phase at IM start . | Prior treatment . | Time from diagnosis to IM start, mo . | Time to CCyR after starting IM, mo . | PCR-negative sample studied . | Consistently PCR negative . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 144 | 47 | M | CP | IFN + Ara-C | 7 | 9 | Y | Y |
| 177 | 50 | F | CP | IFN | 21 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 202 | 56 | F | CP | IFN | 15 | 3 | Y | N |
| 222 | 64 | F | CP | IFN | 30 | 9 | Y | N |
| 232 | 58 | M | CP | IFN + Ara-C | 20 | 9 | Y | Y |
| 238 | 62 | M | CP | IFN | 25 | 6 | Y | N |
| 248 | 68 | M | CP | None | 1 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 256 | 40 | M | CP | None | 0.25 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 273 | 41 | F | CP | None | 0.75 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 292 | 41 | F | CP | None | 0.5 | 3 | Y | Y |
| 296 | 66 | M | CP | IFN | 13 | 5 | Y | Y |
| 299 | 59 | F | CP | None | 4 | 6 | Y | N |
| 327 | 37 | M | CP | None | 0.75 | 9 | Y | N |
| 347 | 35 | M | CP | None | 2 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 397 | 44 | F | CP | None | 0.1 | 10 | Y | N |
| 469 | 25 | M | CP | None | 0.1 | 6 | Y | Y |
| 476 | 56 | F | CP | None | 0.1 | 5 | Y | N |
| 833 | 67 | F | CP | IFN | 31 | 34 | N | N |
| 902 | 52 | F | CP | None | 0.0 | 4 | Y | Y |
| 924 | 57 | M | CP | None | 0.1 | 5 | Y | Y |
M indicates male; F, female; CP, chronic phase; IFN, IFN-α; Ara-C, cytosine arabinoside; and IM, imatinib mesylate.
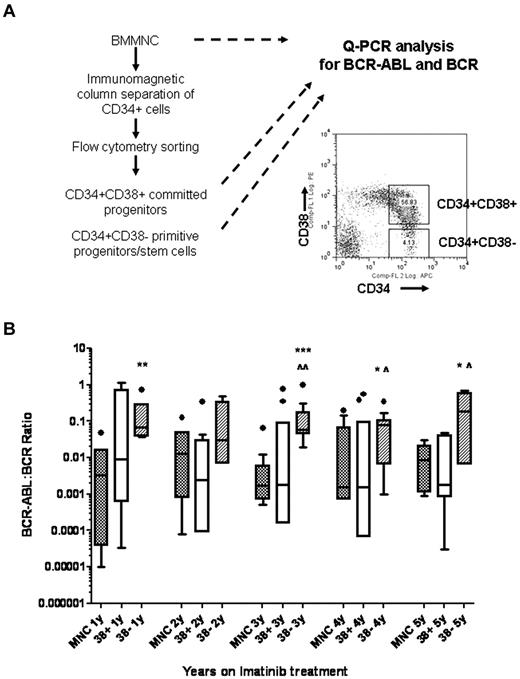
BM samples collected 1 to 5 years after starting imatinib mesylate treatment were analyzed for BCR-ABL expression in MNCs, CD34+CD38+ committed progenitors and CD34+CD38− primitive progenitors/stem cells. CD34+ cells were selected from MNCs using immunomagnetic selection and CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− cells were further selected using flow cytometry. A total of 53 samples from 13 patients were studied. The average numbers of CD34+CD38+ cells obtained were 26 612 ± 5103 and CD34+CD38− cells were 1338 ± 169. MNCs and selected cell populations were analyzed using Q-PCR analysis for detection of BCR/ABL and BCR. The reliability of BCR-ABL measurement in these small samples was confirmed using serial dilutions of RNA from cell lines as shown in Figure 1. BCR-ABL measurements were comparable using RNA dilutions ranging from 200 ng to 0.2 ng, equivalent to a range of 20 000 cells to 20 cells. Two or more serially collected cryopreserved samples were studied for each patient. The cumulative results for Q-PCR analysis for BCR-ABL in MNCs (n = 47), CD34+CD38+ (n = 45), and CD34+CD38− cells (n = 40) are shown in Figure 2. The Q-PCR assay used in our laboratory was more sensitive than the clinical assay and detected BCR-ABL expression in MNC samples from all patients. Our results indicated that 7 of 13 patients had achieved CMR, 3 patients had achieved MMR, and 3 patients less than MMR, based on the international scale. Higher level of BCR-ABL were maintained in CD34+CD38− cells, compared with levels in MNC and CD34+CD38+ cells, over 5 years of imatinib mesylate treatment. Differences between MNC and CD38− cells were significant in years 1 and 3 (P < .01 and P < .001, respectively), and trended toward significance in years 4 and 5 (P = .09). Differences between CD38+ and CD38− cells were significant at year 3 (P < .05), and trended toward significance in years 4 and 5 (P = .07 and .1). We did not observe significant differences in BCR-ABL mRNA levels in CD38+ and CD38− cells between patient groups with different levels of response. These results indicate that BCR-ABL+ stem or primitive progenitor cells can persist in the BM of patients receiving prolonged imatinib mesylate treatment.
Reliability of BCR-ABL measurement with a small number of cells. RNA extracted from K562 cells was diluted 1:100 into RNA from HL60 cells. Ten-fold serial dilutions were performed to obtain 200 ng, 20 ng, 2 ng, and 0.2 ng, equivalent to 20 000, 2000, 200, and 20 cells, respectively, which were then used for Q-PCR analysis of BCR-ABL and BCR. (A) BCR-ABL and BCR measurements following Q-PCR of different dilutions of RNA are shown. (B) The ratio of BCR-ABL to BCR at the different dilutions is shown.
Reliability of BCR-ABL measurement with a small number of cells. RNA extracted from K562 cells was diluted 1:100 into RNA from HL60 cells. Ten-fold serial dilutions were performed to obtain 200 ng, 20 ng, 2 ng, and 0.2 ng, equivalent to 20 000, 2000, 200, and 20 cells, respectively, which were then used for Q-PCR analysis of BCR-ABL and BCR. (A) BCR-ABL and BCR measurements following Q-PCR of different dilutions of RNA are shown. (B) The ratio of BCR-ABL to BCR at the different dilutions is shown.
Persistence of BCR-ABL+ cells in primitive progenitor/stem cells in CML patients in CCR with imatinib mesylate treatment for 5 years. (A) Experimental procedures for isolating CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− cells by flow cytometry sorting followed by Q-PCR for BCR-ABL and BCR are shown. (B) The cumulative results for Q-PCR analysis for BCR-ABL levels in MNC, CD34+CD38+, and CD34+CD38− cells in CML patients after 1 to 5 years of imatinib mesylate treatment are shown using box and whisker (Tukey) plots. Significance values comparing MNC and CD34+CD38− cells are *.05 > P < .1, **P < .01, ***P < .001; comparing CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− cells are ^.05 > P < .1, ^P < .05.
Persistence of BCR-ABL+ cells in primitive progenitor/stem cells in CML patients in CCR with imatinib mesylate treatment for 5 years. (A) Experimental procedures for isolating CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− cells by flow cytometry sorting followed by Q-PCR for BCR-ABL and BCR are shown. (B) The cumulative results for Q-PCR analysis for BCR-ABL levels in MNC, CD34+CD38+, and CD34+CD38− cells in CML patients after 1 to 5 years of imatinib mesylate treatment are shown using box and whisker (Tukey) plots. Significance values comparing MNC and CD34+CD38− cells are *.05 > P < .1, **P < .01, ***P < .001; comparing CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− cells are ^.05 > P < .1, ^P < .05.
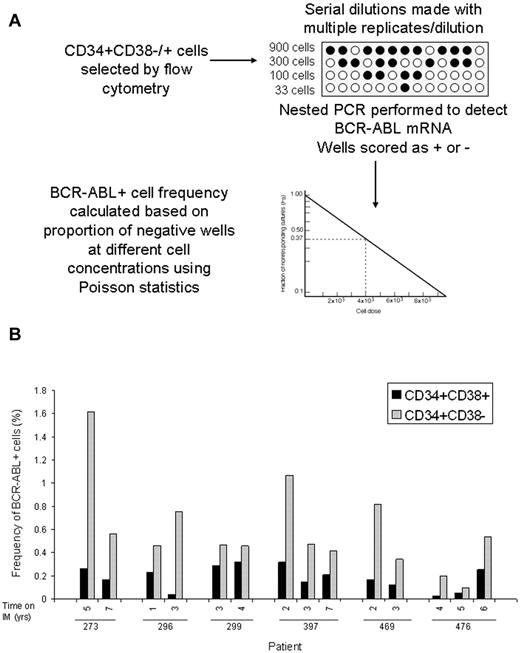
BCR-ABL levels measured using Q-PCR analysis represent the average expression level for the cell population analyzed. However, BCR-ABL expression may vary between individual cells and average BCR-ABL expression levels could be disproportionately affected by a minority of cells with high expression levels. Therefore, BCR-ABL levels measured by Q-PCR may not necessarily represent the frequency of BCR-ABL–positive cells in the population analyzed. Limiting dilution analyses are a well established approach to estimating frequencies of specific cells in a mixed population.20,21 We adapted the limiting dilution assay format to estimate the frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in CD34+38+ and CD34+38− populations. Selected cells were distributed into 96-well plates at 4 different concentrations per well with multiple replicates per concentration. Nested PCR was performed and wells scored as positive or negative for BCR-ABL. The frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in different subpopulations was calculated using Poisson statistics (Figure 3). Because frequency is calculated on the basis of the proportion of negative wells rather than positive wells, it is not affected by the level of BCR-ABL expression per cells. The estimated frequencies of BCR-ABL+ cells in the CD34+CD38+ and CD34+CD38− subpopulations in serial samples (n = 14 samples, 28 assays) from 6 patients is shown in Figure 3 and Table 2. These results confirm that the limiting dilution analysis is a robust approach to measure the frequency of BCR-ABL–expressing cells and clearly demonstrate that there is increased frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells within the CD34+CD38− population (0.59 ± 0.1%) compared with the CD34+CD38+ population (0.19 ± 0.03%; P < .001) in patients on long-term imatinib mesylate treatment. The kinetics of BCR-ABL+ CD34+CD38− stem cells over time shows interpatient variability. Three patients showed reduction in frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in the CD34+CD38− cell fraction in serial samples, whereas 3 patients showed stable or increasing frequency of BCR-ABL cells. FISH analysis performed on a subset of samples where sufficient cells were available detected low levels of BCR-ABL–positive cells (0.5%-1%) in the CD34+CD38− population in 2 of 6 samples obtained from 3 patients. BCR-ABL–positive cells were not detected in CD34+CD38+ cells from the same samples or in normal CD34+ cells (Table 2). These results are consistent with the frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells within the CD34+CD38− fraction observed using limiting dilution analysis (0.59%), which is at the limit of detection of the FISH assay.
Frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in CD34+38+ or CD34+38− populations. (A) A schematic of experimental and analytical procedures for measurement of the frequency of BCR-ABL–positive cells within flow cytometry selected CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ cells using limiting dilution analysis is shown. (B) The frequencies of BCR-ABL+ cells within the CD34+CD38+ (black bars) and CD34+CD38− (grey bars) subpopulations in 14 samples obtained at different time points from 6 patients is shown (2-3 serial samples per patient).
Frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in CD34+38+ or CD34+38− populations. (A) A schematic of experimental and analytical procedures for measurement of the frequency of BCR-ABL–positive cells within flow cytometry selected CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ cells using limiting dilution analysis is shown. (B) The frequencies of BCR-ABL+ cells within the CD34+CD38+ (black bars) and CD34+CD38− (grey bars) subpopulations in 14 samples obtained at different time points from 6 patients is shown (2-3 serial samples per patient).
Frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells on limiting dilution and FISH analysis
| Patient . | Years on IM treatment . | Frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells, % . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limiting dilution analysis . | FISH . | ||||
| CD34+CD38+ . | CD34+CD38− . | CD34+CD38−* . | CD34+CD38+* . | ||
| 476 | 4 | 0.03 | 0.20 | ||
| 4.5 | 0.05 | 0.09 | |||
| 5.5 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 0 (200) | ||
| 469 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.81 | ||
| 3 | 0.12 | 0.34 | |||
| 397 | 2 | 0.32 | 1.06 | 0 (50) | 0 (233) |
| 3 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 0 (200) | 0 (206) | |
| 6.5 | 0.21 | 0.41 | 1 (200) | 0 (216) | |
| 273 | 4.5 | 0.27 | 1.61 | 0.5 (200) | 0 (246) |
| 6.5 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 1 (98) | 0 (220) | |
| 296 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.46 | ||
| 3 | 0.04 | 0.75 | |||
| 299 | 3 | 0.29 | 0.47 | ||
| 4 | 0.32 | 0.45 | |||
| Patient . | Years on IM treatment . | Frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells, % . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limiting dilution analysis . | FISH . | ||||
| CD34+CD38+ . | CD34+CD38− . | CD34+CD38−* . | CD34+CD38+* . | ||
| 476 | 4 | 0.03 | 0.20 | ||
| 4.5 | 0.05 | 0.09 | |||
| 5.5 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 0 (200) | ||
| 469 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.81 | ||
| 3 | 0.12 | 0.34 | |||
| 397 | 2 | 0.32 | 1.06 | 0 (50) | 0 (233) |
| 3 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 0 (200) | 0 (206) | |
| 6.5 | 0.21 | 0.41 | 1 (200) | 0 (216) | |
| 273 | 4.5 | 0.27 | 1.61 | 0.5 (200) | 0 (246) |
| 6.5 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 1 (98) | 0 (220) | |
| 296 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.46 | ||
| 3 | 0.04 | 0.75 | |||
| 299 | 3 | 0.29 | 0.47 | ||
| 4 | 0.32 | 0.45 | |||
Numbers in parentheses represent number of cells analyzed.
To determine whether residual BCR-ABL+ cells in imatinib mesylate-treated patients retain functional long-term engrafting capacity, CD34+ cells from 6 patients were transplanted into immunodeficient NSG mice. Patients had been on imatinib mesylate treatment from 4 to 9 years (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). Cells from each patient were injected into 3-4 mice (total of 20 mice). The number of cells and mice injected are shown in supplemental Table 1. Mice were evaluated for engraftment with human cells and presence of BCR-ABL–expressing cells in BM, spleen, and PB at 11-12 weeks after transplantation (Figure 4A). The level of engraftment of human CD45+ cells was consistent in mice receiving samples from a single patient, and ranged from 25% to 50% for individual patients (Figure 4B). Immunophenotypic characterization of engrafted human CD45+ cells demonstrated multilineage engraftment of myeloid and lymphoid cells (Figure 4C). BCR-ABL expression was detected by Q-PCR in human cells engrafted in the BM of mice receiving transplants from each patient (Figure 4D). These results indicate that BCR-ABL+ cells with functional in vivo repopulating capacity are retained in patients in remission on imatinib mesylate treatment.
Engraftment of NOD/SCID-IL2Ry-chain knockout (NSG) mice with CD34+ BM cells from CML patients treated with imatinib mesylate. (A) The schematic for these experiments is shown. BM CD34+ cells from CML patients in remission (n = 6) were transplanted via tail vein injection into sublethally irradiated NSG mice (3-4 mice per sample, total of 20 mice). Mice were evaluated for human cell engraftment and BCR-ABL status of engrafted cells after 11-12 weeks. (B) The percentage of human CD45+ cell engraftment in BM, spleen and PB of mice transplanted with CD34+ cells are shown. Results represent the mean ± SEM of human CD45+ cells engrafted in BM, spleen, and PB for each BM sample transplanted. (C) The percentage of human CD45+ cells expressing different surface markers in mouse BM, spleen, and PB are shown (n = 20). (D) The BCR-ABL status of engrafted cells was evaluated using Q-PCR. BCR-ABL expression in human cells engrafted in BM of individual mice is shown (n = 15). Horizontal bars represent median values. Samples from the 5 mice that were excluded also expressed BCR-ABL, but BCR values were too low to allow quantitation.
Engraftment of NOD/SCID-IL2Ry-chain knockout (NSG) mice with CD34+ BM cells from CML patients treated with imatinib mesylate. (A) The schematic for these experiments is shown. BM CD34+ cells from CML patients in remission (n = 6) were transplanted via tail vein injection into sublethally irradiated NSG mice (3-4 mice per sample, total of 20 mice). Mice were evaluated for human cell engraftment and BCR-ABL status of engrafted cells after 11-12 weeks. (B) The percentage of human CD45+ cell engraftment in BM, spleen and PB of mice transplanted with CD34+ cells are shown. Results represent the mean ± SEM of human CD45+ cells engrafted in BM, spleen, and PB for each BM sample transplanted. (C) The percentage of human CD45+ cells expressing different surface markers in mouse BM, spleen, and PB are shown (n = 20). (D) The BCR-ABL status of engrafted cells was evaluated using Q-PCR. BCR-ABL expression in human cells engrafted in BM of individual mice is shown (n = 15). Horizontal bars represent median values. Samples from the 5 mice that were excluded also expressed BCR-ABL, but BCR values were too low to allow quantitation.
Discussion
In this study, we show that BCR-ABL+ stem and primitive progenitor cells are retained in CML patients in remission on prolonged imatinib mesylate treatment. We observed an increased frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells in the CD34+CD38− stem/primitive progenitor population compared with CD34+CD38+ committed progenitors, with no decrease in BCR-ABL levels within the CD34+CD38− population from one to 5 years after treatment. Residual BCR-ABL+ cells retained functional long-term repopulating capacity as assessed by their ability to generate BCR-ABL+ cells after transplantation to immunodeficient mice. These results are of considerable importance because they directly demonstrate the selective retention of leukemia stem cells in the BM of imatinib mesylate–treated CML patients. Moreover, they show that residual leukemia stem cells can be accurately enumerated and evaluated for functional capacity. These results may have important implications not only for the assessment of the effects of different TKIs against leukemia stem cells, but also for studies of discontinuation of TKI treatment, and for evaluation of treatments directed against leukemia stem cells.
Discontinuation of imatinib mesylate treatment is usually associated with disease relapse, and it is currently recommended that patients continue to receive imatinib mesylate treatment indefinitely to maintain remission.18,22 However, prolonged imatinib mesylate treatment may be associated with risks of long-term complications, reduced compliance, drug resistance, and considerable ongoing costs. Ongoing clinical trials of imatinib mesylate discontinuation indicate that ∼ 40% of a select group of patients who achieve sustained BCR-ABL–negative state on Q-PCR analysis do not relapse after discontinuation of imatinib mesylate.16-18 However, there is evidence that the original leukemic clone persists in CML patients who are in CMR after allogeneic transplantation or imatinib mesylate treatment.23 Even patients who maintain sustained CMR after imatinib mesylate discontinuation show evidence of persistent BCR-ABL–positive cells when evaluated using more sensitive assays such as DNA PCR.17 These results indicate that BCR-ABL+ cells are retained in virtually all CML patients treated with imatinib mesylate if sensitive-enough tests are used, and that CMR needs to be defined on the basis of the sensitivity of the assay used. There is an evolving consensus to report BCR-ABL levels based on assay sensitivity, such as CMR4.0 or CMR4.5 (complete molecular response 4 logs reduction, molecular response 4.5 logs reduction).24 Despite showing persistence of BCR-ABL+ cells in patients in molecular remission, previous studies have not clarified the nature of the cells contributing to continued BCR-ABL expression. It is not known whether residual cells are BCR-ABL+ stem cells or some other long-lived populations. The current studies are of significance because they clearly show that CD34+CD38− stem cells represent a major reservoir of residual BCR-ABL+ cells in patients in remission on imatinib mesylate treatment. In addition, these studies provide the first measurements of the relative frequency of BCR-ABL+ cells within this population, and demonstrate for the first time that residual BCR-ABL+ stem cells have the capacity to generate BCR-ABL+ cells after transplantation to immunodeficient mice.
At present, it is not possible to predict which patients will or will not relapse after discontinuation of TKI treatment. The risk of disease regeneration and relapse may be related to the numbers of leukemia stem cells within the residual BCR-ABL–positive cells, variability in leukemogenic capacity of residual BCR-ABL+ cells, and heterogeneity of immune or microenvironmental factors that regulate leukemia cell growth. Selection of stem cell populations enhances the sensitivity of detection of residual BCR-ABL+ cells, and allows direct evaluation of BCR-ABL expression in stem cell as opposed to other long-lived populations. The limiting dilution assay described here makes it possible to perform quantitative assessment of leukemic stem cells. Information regarding the frequency of residual leukemia stem cells could potentially impact treatment of CML patients by providing a measurement of the depth of response. Alternatively the capacity of residual stem cells to proliferate and regenerate leukemia cells may be more important in determining risk of disease regeneration and relapse. Although the patients evaluated in the current study may differ from those enrolled in imatinib mesylate discontinuation trials, it will be of interest to determine whether the assays described here can provide a better predictor of recurrence on discontinuing treatment compared with analysis of bulk mononuclear cells. These assays may also provide a surrogate end point for evaluating other treatments designed to reduce leukemia stem cells and enhance the proportion of patients in whom treatment can be discontinued without disease recurrence. It will be of great interest to perform assessment of residual stem cells as described in the current study in a cohort of patients who have discontinued imatinib mesylate treatment, to determine whether the frequency of leukemia stem cells can predict for risk of recurrence after imatinib mesylate discontinuation.
The number of patients who maintain molecular remission after stopping imatinib mesylate treatment represents only a small fraction of patients initially started on treatment with imatinib mesylate. There is considerable interest in developing new treatment approaches to improve the proportion of patients in whom imatinib mesylate treatment can be discontinued without disease relapse. Several strategies to target residual leukemia stem cells are in various stages of clinical development.25-27 However, these approaches are limited by the lack of methods for evaluating the effects of treatments on CML stem cells. Enumeration of CML stem cells and assessment of leukemia-initiating capacity using the methods described here could be of great value for evaluating the ability of different treatments to target, reduce, or eliminate CML stem cells. Obstacles to the clinical application of these methodologies include their relatively cumbersome nature and the limited number of cells available for analysis from patient samples that could limit the sensitivity or result in failure of the assay. Modifications that can be used to enhance sensitivity of the assays include the use of improved methodologies for RNA extraction from small samples and addition of a preamplification step to enhance the robustness and reliability of the procedure. The use of newer technologies using microfluidic devices and sensitive molecular detection techniques may be particularly helpful for efficient, quantitative evaluation of small samples.28
The current studies also have implications to other leukemias and solid tumors that arise from malignant stem cell populations. Recently rare leukemia stem cells resistant to therapeutic targeting were detected in patients with del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome at the time of complete clinic cytogenetic remission.29 Improved approaches to directly assess and enumerate residual cancer stem cells will be of increasing importance to determine the effect of available treatments, and guide the development and application of new strategies to target these important populations. The current studies demonstrate the feasibility of such approaches and provide a framework for development of strategies to enumerate residual cancer stem cells and study their functional capacity.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the patients and physicians who participated in this study. They thank the City of Hope Analytical Cytometry Core for their excellent technical assistance.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant R01 CA 95684 and a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Translational Research Grant (R.B.).
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: S. Chu designed and performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; T.M. performed experiments and reviewed the manuscript; A.L. performed research and reviewed the manuscript; S. Chakraborty performed experiments and reviewed the manuscript; Q.H. performed research and reviewed the manuscript; D.S.S. provided material and reviewed the manuscript; and R.B. designed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: R.B. has been on the advisory boards for, and has received honoraria from, Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb. D.S.S. has been on the advisor boards and speakers bureaus of, and has received honoraria from, Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Ravi Bhatia, MD, Division of Hematopoietic Stem Cell and Leukemia Research, City of Hope National Medical Center, 1500 E Duarte Rd, Duarte, CA 91010; e-mail: rbhatia@coh.org.