Abstract
Abstract 526
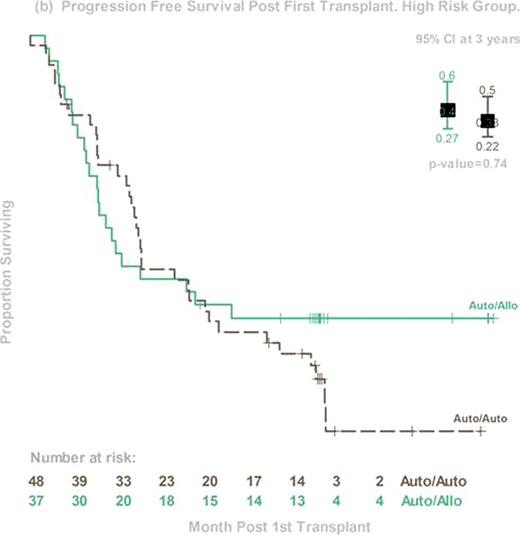
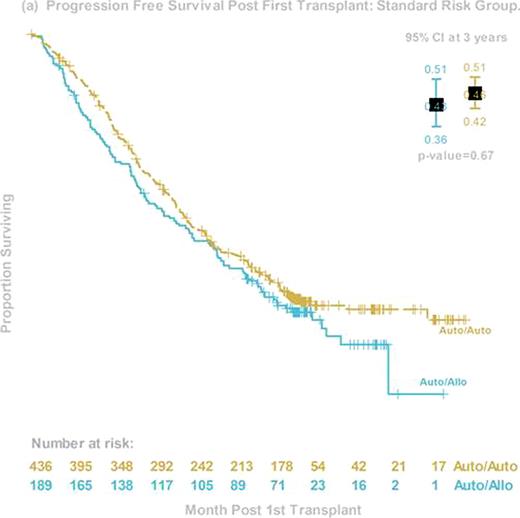
The prognosis of patients with high-risk myeloma (HR MM) continues to be dismal, despite the early incorporation of novel agents. Early phase trials of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHCT) suggest the possibility of an immunologic graft-versus-myeloma effect that might favorably affect survival. Less toxic reduced-intensity HCT preparative regimens now allow more widespread use of alloHCT in the MM population. BMT CTN 0102 is a phase III multicenter clinical trial that biologically assigned patients to either melphalan 200mg/m2 (MEL 200) auto-auto without (obs) or with 1 year of thalidomide and dexamethosone (ThalDex), or an auto-allo approach using MEL 200 followed by alloHCT using 2 Gy total body irradiation. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis was cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil. Patients were stratified by biological prognostic factors that were considered to be high risk at the time of the trial design: chromosome 13 deletions by metaphase karyotype and beta-2 microglobulin ≥4 mg/dl. The primary endpoint was 3-year progression free survival (PFS). Between December 2003 and March 2007, 710 patients from 43 US centers were enrolled, and 85 fulfilled the criteria of HR MM. Among them, 48 were assigned to auto-auto (24 Thal-Dex and 24 obs) and 37 to auto-allo. Groups differed in age (median 57 y and 51y, p=0.02) but were otherwise balanced. Compliance with second transplant was 65% for auto-auto and 78% for auto-allo. Compliance with ThalDex was poor, so the two auto-auto arms were pooled for the primary analysis. Three-year PFS was 33% (95% Confidence Interval (CI), 22–50%) and 40% (95% CI, 27–60%, p=0.74) and 3-year OS was 67% (95% CI, 54–82%) and 59% (95% CI, 49–78%, p=0.46) for auto-auto and auto-allo, respectively. Corresponding probabilities for 3-year progression/relapse was 53% and 33% (p=0.09), and 3 year treatment-related mortality was 8% and 20% (p=0.3). Among auto-allo patients, probabilities of grade 3–4 acute and chronic GVHD were 9% and 48%, respectively. Among the 59 (31 auto-auto, 28 auto-allo) patients who received second transplant, 3 year PFS was 35% and 46% (p=0.6). Disease response at day 56 after second transplant was 57% for very good partial response (VGPR) or better and 37% for complete response (CR) and near CR (nCR) in the auto-auto group; and 48% (VGPR or better) and 41% (CR+nCR) in the auto-allo group. In conclusion, this planned secondary analysis of a cohort of HR MM patients demonstrated equivalent 3-year PFS and OS for auto-auto and auto-allo in both intention-to-treat and as-treated analyses. However, trends in late PFS and time to progression/relapse suggest further follow-up is needed before final conclusions regarding the utility of auto-allo in this HR cohort can be made. Finally, this study shows the feasibility of an alloHCT approach for HR MM patients and may serve as a platform for future studies seeking to enhance graft-versus-myeloma effects.
Disclosures:
Stadtmauer:Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Krishnan:Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Qazilbash:Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Vesole:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Giralt:Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Millenium: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2010 by The American Society of Hematology
2010

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal