Abstract
Abstract 4798
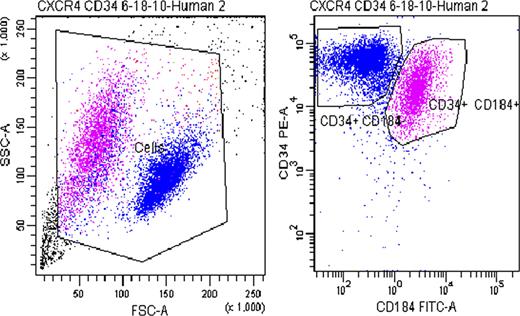
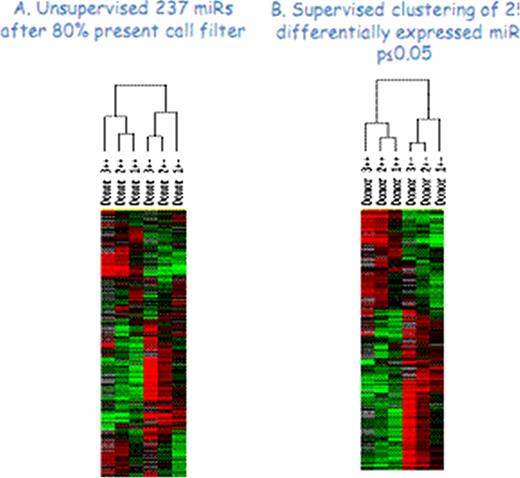
Although CD34+ cells represent a small population of phenotypically defined cells within the bone marrow and peripheral blood circulation, they remain a very heterogeneous population of cells which contain hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. CXC Chemokine Receptor 4 (CXCR4) is an α-chemokine receptor specific for stromal-derived-factor-1 (SDF-1 also called CXCL12) and is found on CD34+ cells. Plerixafor (also known as Mozobil® or AMD3100) is currently used as a mobilizing agent for CD34+ cells by interfering with the binding of CXCR4 to SDF-1. To explore differences between CD34+CXCR4+ and CD34+CXCR4- populations, gene and microRNA signatures were determined using microarray analysis. Three healthy human donors were cytokine mobilized with G-CSF, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected by apheresis, and CD34+ cells were immunoselected using the Miltenyi CliniMACS® system and cryopreserved. These cells were then thawed and allowed to sit overnight at 37°C in X-Vivo-10. The following day the cells were stained and sorted on a BD FACSAria III® cell sorter. All three individuals CD34+CXCR4+ and CD34+CXCR4- fell within two rather restrictive populations based on forward and side scatter gating with CD34+CXCR4+ cells routinely being smaller in size than the CD34+CXCR4- populations (Figure 1). Total RNA was isolated from the sorted cells and amplified to cRNA. Control cRNA was labeled with Cy3 dye and experimental cRNA was labeled with Cy5 dye and co-hybridized to a custom-made 17.5K cDNA (UniGene cluster) microarray. Using unsupervised and supervised Eisen's hierarchical clustering and Array Class Comparison analysis relationships were determined. Hierarchical cluster analysis demonstrated that the CD34+CXCR4+ and CD34+CXCR4- had different gene expression patterns (Figure 2). Ingenuity Pathway Analysis revealed that genes up-regulated in the CD34+CXCR4+ population were related to TREM-1 signaling (innate immunity), dendritic cell maturation, NFAT-regulation of the immune response, and T-cell receptor and NK cell signaling. In contrast, the CD34+CXCR4- population expressed more primitive genes such as those related to IGF-1, ERK/MAPK, IL-3, and Nitric Oxide signaling as well as transcription factors such as N-myc and HOX-A9. MicroRNA profiling of the CD34+CXCR4- population also express the miR-17-92 polycistron cluster (miR17, 18a, 19a, 19b, 20a, 92) (Figure 3). These results are consistent with the CD34+CXCR4- population being more primitive than the CD34+CXCR4+ population. It is interesting to speculate whether the CD34+CXCR4+ population includes a progenitor for T cell and innate immune responses while progenitors for hematopoietic stem cells and adaptive immune responses are within the CD34+CXCR4- populations.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal