Abstract
Abstract 412
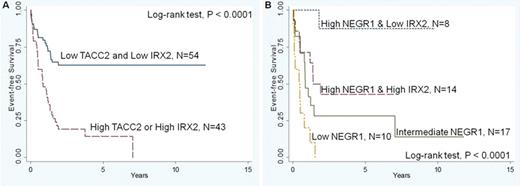
ALL arising in infants is a highly refractory disease. Overall event-free survival (EFS) remains poor and infants with MLL rearrangements (MLL-R) or those <90 days of age are known to have particularly poor outcomes. To identify genes predictive of event-free survival (EFS) that might serve as new diagnostic and therapeutic targets, we completed gene expression profiling (Affymetrix HG_U133Plus2) in 97 infant ALL cases registered to COG Clinical Trial P9407. Of these 97 infants, 78 were most recently uniformly treated on P9407 cohort 3. In the 97 cases, median age at diagnosis was 166 days (range 1–365) and increased age at diagnosis was significantly associated with improved EFS (P = 0.001). 89/97 infants had MLL-R, of which 49 had an AF4 partner gene (MLL-AF4 (AFF1)). Infants <90 days of age (P=.0001) and those with MLL-R (MLL-AF4, MLL-ENL (MLLT1), MLL-Other) had a significantly decreased EFS, while infants with MLL-AF9 (MLLT3) or cases lacking MLL-R had a significantly better EFS (P=0.014). From modeling expression profiles and multivariate analyses, a number of genes were identified that had a significant effect on EFS and were independent of patient age or MLL-R status, including: TACC2 and IRX2 (from modeling the entire cohort of 97 cases); RORA, IGJ, ZEB1, YES1 (cohort 3 modeled alone); and IRX1, IRX2, ST3GAL6, HLA-DQB1, STAB1, NEGR1, IRX5 (MLL-AF4 cases modeled alone). The significant effect of MEIS1 and KCNK12 expression on EFS was lost after consideration of MLL-R status, while the significance of many genes (particularly in the HOXA family) was not independent of patient age in multivariate analyses. Assessment of the expression levels of two genes alone at diagnosis: TACC2 and IRX2 in the entire cohort of 97 cases (P<0.0001; Fig. A), or, NEGRI and IRX2 in the MLL-AF4 cases (P<0.0001; Fig. B), were highly predictive of outcome on current treatment regimens. Distinctive and strikingly different gene expression profiles were also seen in infant ALL cases <90 days of age vs. >90 days of age (in the overall cohort and in the MLL-AF4 cases). Specifically evaluating the impact of patient age treated as a continuous variable revealed a striking transition in expression profiles at 90 days with a differential expression pattern involving many genes encoding histone-related, heat shock family, or immune response regulators (including HLA-DRB4, IL1R2, HSPA1A///1B). These distinctive profiles may reflect different transformed stem/precursor cells or susceptibilities to leukemic transformation at different patient ages, altered marrow microenvironments, or altered immune status; high expression of the heat shock proteins in particular among the youngest infants may reflect a more limited immune surveillance capacity. Given the rarity of infant ALL, this study represents one of the largest uniformly treated groups of infant leukemia to undergo gene expression profiling. In these studies we have identified genes that are highly predictive of outcome at diagnosis, in all infant ALL and in MLL-AF4 cases. Further analysis of these expression profiles, coupled with validation studies in other infant ALL cohorts, may allow for the identification of novel therapeutic targets among the genes discovered herein and ultimately for the development of more effective therapies.
Felix:None: Patent not licensed.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal