Abstract
In vertebrates, endothelial cells form 2 hierarchical tubular networks, the blood vessels and the lymphatic vessels. Despite the difference in their structure and function and genetic programs that dictate their morphogenesis, common signaling pathways have been recognized that regulate both vascular systems. ALK1 is a member of the transforming growth factor-β type I family of receptors, and compelling genetic evidence suggests its essential role in regulating blood vascular development. Here we report that ALK1 signaling is intimately involved in lymphatic development. Lymphatic endothelial cells express key components of the ALK1 pathway and respond robustly to ALK1 ligand stimulation in vitro. Blockade of ALK1 signaling results in defective lymphatic development in multiple organs of neonatal mice. We find that ALK1 signaling regulates the differentiation of lymphatic endothelial cells to influence the lymphatic vascular development and remodeling. Furthermore, simultaneous inhibition of ALK1 pathway increases apoptosis in lymphatic vessels caused by blockade of VEGFR3 signaling. Thus, our study reveals a novel aspect of ALK1 signaling in regulating lymphatic development and suggests that targeting ALK1 pathway might provide additional control of lymphangiogenesis in human diseases.
Introduction
Lymphatic vessels are a network of endothelial-lined vessels that are critical for the collection and transport of interstitial fluid, absorption of lipids in the intestine, and the transport of lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells to the lymph nodes. Malformation or dysfunction of lymphatic vasculature contributes to the pathogenesis of many human diseases. For instance, loss of lymphatic function caused by genetic deficiency or damage of lymphatic vessels causes lymphedema. However, solid tumors can hijack the lymphatic vasculature to spread tumor cells to distant sites. A better understanding of the signaling pathways that regulate the lymphangiogenesis will assist the design of novel therapeutics for human diseases that can better control the growth and differentiation of lymphatic vessels.
Several important lymphatic endothelial regulators and markers have been identified, such as Sox18, Prox1, VEGFR3, VEGFC/D, podoplanin, and LYVE1. In the mouse, lymphatic development is characterized by the induction of Sox18 expression at embryonic day (E) 9.0, followed by Prox1 expression at E10.5 in a subset of endothelial cells populating the dorsal cardinal vein.1,2 The Prox1-expressing cells bud-off the cardinal vein and form the primary lymphatic sacs and subsequently through the process of lymphangiogenesis, a functional lymphatic network is established.3 VEGFR3–VEGFC/D signaling is essential for the lymphatic development. It promotes migration, proliferation, and survival of lymphatic cells. For instance, inactivation of VEGFR3 results in the failure of Prox1-positive cells to bud-off from the cardinal vein.4 In addition, sustained VEGFR3–VEGFC/D signaling is required for lymphatic vessel stability as its inhibition results in the regression of preexisting lymphatic vessels.5 Another critical regulator of lymphatic development is Prox1, a homeobox transcription factor that regulates expression of the lymphatic phenotype genes podoplanin and LYVE1 and is referred to as a master regulator of lymphatic identity.6,7 Podoplanin is a membrane mucoprotein, and podoplanin-deficient mice die at birth as the result of respiratory failure and have defects in lymphatic development.8,9 LYVE1 is a hyaluronan receptor, and LYVE1-deficient mice are viable but have defects in lymphatic development.10
The blood vessels and the lymphatic vessels differ in their functional and structural characteristics. During morphogenesis the 2 vascular systems are regulated by apparently distinct genetic programs. Despite these differences, accumulating evidences also support that common molecular pathways are used during angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. For instance, in addition to its well-established role in the development of lymphatic vasculature, VEGFR3 is also essential for the early blood vessel development in embryos and contributes to tumor angiogenesis.11,12 Angiopoiteins and their receptor Tie2 are known to be important for the remodeling of endothelium and vascular stability during angiogenesis. The same signaling system also plays a role in lymphangiogenesis.13 EphrinB2 is essential for the angiogenic remodeling of blood vessels in early embryo, and interestingly deletion mutation of EphrinB2 causes abnormal development of lymphatic vessels.14,15
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) is a member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) type I family of receptors. The TGF-β family of receptors elicits diverse tissue-specific responses, including regulating proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival.16-18 ALK1 is primarily expressed in the developing vascular system and plays a critical role in arteriogenesis and arterial endothelial cell development.19,20 In addition, mutations in ALK1 or its coreceptor endoglin are associated with the human vascular disorder hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia,21,22 a vascular disorder that leads to telangiectases and arteriovenous malformations in skin, mucosa, and viscera. ALK1 signals through a heteromeric complex that includes ALK1 and the TGF-β type II receptors BMPR2, ACVR2A, or ACVR2B. Potential ALK1 ligands include bone morphogenic protein 9 (BMP9) and BMP10, which directly bind and activate ALK1.23 Ligand binding results in activation of ALK1 through transphosphorylation by the type II receptor. Activated ALK1 in turn phosphorlyates Smad1 and Smad5, which subsequently translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene expression.24 In the mouse, ALK1 deficiency results in embryonic lethality at E11.5 as the result of defects in the remodeling of the primary capillary plexus into a functional network of arteries, capillaries, and veins.19 In addition, ALK1-deficient embryos have decreased smooth muscle cell recruitment to the developing dorsal aorta.19 As ALK1-deficent embryos die at the onset of lymphatic vessel development the role of ALK1 in lymphatic development is unknown.
Here we show that ALK1 signaling is functionally active in cultured lymphatic endothelial cells. In vivo, blockade of ALK1 signaling with the use of decoy receptors or ALK1-specific antibody results in defective lymphatic development in early postnatal mice. Our data demonstrate that, unlike VEGFR3 signaling, which is essential for the proliferation and survival of lymphatic endothelial cells, ALK1 signaling regulates the differentiation of lymphatic endothelial cells to influence the lymphatic vascular development and remodeling. Furthermore, we show that inhibition of ALK1 signaling enhances the apoptosis of lymphatic endothelial cells upon depletion of VEGFR3 ligands.
Methods
Reagents
hALK1Fc (aa. 1-118), hVEGFR3Fc (aa. 1-329), mALK1Fc (aa. 23-119), mALK2 (aa. 1-123), and mALK7 (aa. 1-113) were purified from transient transfection of 293T cells. mALK3Fc, mALK4Fc, mALK5Fc, and mALK6Fc were purchased from R&D Systems. Goat anti-LYVE1 (AF2125) and rabbit anti–active Caspase3 (AF835) were purchased from R&D Systems. Cy3-anti–smooth muscle actin (C6198) and FITC-isolectin-B4 (L2895) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Rat anti-CD31 (553370) was purchased from BD Pharmingen. Hamster anti-podoplanin (CMV010) was purchased from Cell Sciences. Secondary antibodies were all chicken anti–(species on interest) Alexa-594 or Alexa-488, purchased from Invitrogen. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs; CC-2517) and human microvascular dermal neonatal lymphatic endothelial cells (CC-2505) and required media were purchased from Lonza. Detroit 551 fibroblast cells (CCL-110) were purchased from ATCC. The rabbit anti-ALK1 neutralizing antibody was generated by immunization with His-tagged recombinant protein of the extracellular domain of murine ALK1. Immune serum was purified by affinity chromatography by the use of a mouse ALK1Fc.
Tissue harvest
Tail dermis was collected by first removing the bone from the tail, followed by incubation in 20mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and separation of the dermis and epidermis. Dermis was then fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and used in a standard immunofluorescence protocol. Retina was isolated from the eye after overnight fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde. Retinas were then stained as previously described.25
RNA extraction and real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
For stimulation of HUVEC and lymphatic endothelial cell assay, 13 000 cells per well were plated into 96-well plates in growth media. Sixteen hours later cells were serum starved (EGM2) for 3 hours and stimulated with rhBMP9 or rhBMP10 for 3 hours. RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis was performed by the use of TaqMan Gene Expression Cells-to-CT kit (Applied Biosystems) according to manufacturer's protocol. Gene expression was analyzed by the use of TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix (Applied Biosystems), GAPDH (Hs00266705_g1)–, and Smad6 (Hs00178579_m1)–specific TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems) and analyzed on an Applied Biosystems 7500 reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) system. Primers used in RT-PCR include the following: hAlk1 (L-AGCAGGCCTGTCTCAGGA, R-CCTGGGAGGTAGACGTTGC), hAlk2 (L-CCCAGCTGCCCACTAAAG, R-CGCCTTTTAAATTTTCGGAGA), hAlk3(L-GGACGAAAGCCTGAACAAAA, R-GCAATTGGTATTCTTCCACGA), hAlk4 (L-CTCAGGGTCTGGC-TCAGG, R-ACATCACCACCCCTCCAG), hAlk5 (L-AACGTCAGGTTCTGGCTCA, R-GAATATCTTAACAGCAACTTCTTCTCC), hAlk6 (L-ATCAGGCCTCCCTCTGCT, R-CACTTTCACAGCTACCTTTTCG), hAlk7 (L-GGAAGATGTGGCTGTGAAAAT, R-GTTGAGTCCAAGTTCCATTATCTTT), hAVCR2B (L-GAGGCCTCTCATACCTGCAT, R-GGTCGCTCTTCAGCAATACA), hBMPR2 (L-GAAGCCTGGAAAGAAAATAGCC, R-AATCATCATAAGTTCAGCCATCC), hENG (L-TCCCCAAGACCCAGATCC, R-GCATGCAGAAGGACAGTGAC), hTGFβRII (L-CCAATATCCTCGTGAAGAACG, R-GTATCTTGCAGTTCCCACCTG), and hGAPDH (L-GAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCAC, R-GTTCACACCCATGACGAACA).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Mouse ALK1-7Fc binding assay.
We coated 96-well plates with donkey anti–human Fc (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories). Plates were then washed and blocked with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), 0.5% BSA. hIgG or Fc fusion proteins were captured in PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then washed 3 times with PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20, and the rabbit anti-ALK1 neutralizing antibody was added. Plates were washed 3 times with PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20 and then probed with anti–rabbit HRP (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories). HRP activity was developed by the use of Sure Blue Reserve TMP Microwell Peroxidase Substrate (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories Inc), and absorbance was measured at 450 nm.
BMP9 binding assay.
We coated 96-well plates with mouse Alk1Fc. Plates were then washed and blocked with PBS and 0.5% BSA. Immobilized mALK1 was incubated with preimmune rabbit serum, ALK1-immunized rabbit serum, or affinity-purified rabbit anti-ALK1. Plates were then washed 3 times with PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20, and vehicle control or mouse BMP9-HIS was added to the plate. Plates were washed 3 times with PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20 and then probed with mouse anti-HIS antibody (Roche). Plates were washed 3 times with PBS, 0.5% BSA, and 0.05% Tween-20 and then probed with anti–mouse AP (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories). AP activity was developed by the use of 1-Step PNPP substrate (Thermo Scientific), and absorbance was measured at 405 nm.
Animal studies
All studies were conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. An Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all animal protocols.
Results
ALK1 signaling in lymphatic endothelial cells
Analysis of ALK1 mRNA expression in HUVECs and human microvascular dermal neonatal lymphatic endothelial cells revealed that both cell types express ALK1 (Figure 1A). In addition to ALK1, lymphatic endothelial cells also express ACVR2B, BMPR2, and endoglin, which are involved in ALK1 signaling (Figure 1A).26,27 To test whether lymphatic endothelial cells are responsive to the ALK1 ligands BMP9 or BMP10, HUVECs and lymphatic endothelial cells were stimulated with rhBMP9 or rhBMP10, and the expression of Smad6, an ALK1 target gene, was assessed. Both HUVECs and the lymphatic cells robustly responded to BMP9 and BMP10 stimulation (Figure 1B). Phosphorylation of Smad1 and induction of the ALK1 target gene Id1 also correlated with Smad6 induction; however, Smad6 was the most sensitive readout of BMP9 stimulation (data not shown). rhBMP9 or rhBMP10 activity was effectively neutralized by pretreatment with a soluble decoy receptor of ALK1 extracellular domain fused to Fc portion of human IgG1 (ALK1Fc; Figure 1B). Furthermore, we found that siRNA targeting ALK1, compared with other type I receptors, had the most significant effect on BMP9 stimulation of lymphatic endothelial cells (Figure 1C). siRNA targeting downstream signaling components of ALK1 signaling, including Endoglin, Smad1, Smad4, and Smad5, also reduced BMP9-induced Smad6 up-regulation (Figure 1C). Target gene knockdown was verified for each siRNA (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). These data raise an interesting possibility that ALK1 signaling may also be involved in lymphatic endothelial cell biology.
Lymphatic endothelial cells express ALK1. (A) RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in HUVECs and human microvascular dermal neonatal lymphatic endothelial cells. RNA from a mixture of human cell lines with (+) and without (−) reverse transcriptase enzyme was used as a positive and negative control. Sizes of PCR products are indicated. (B) Expression level of Smad6 in HUVECs and lymphatic endothelial cells stimulated with 50 pg/mL rhBMP9 or 500 pg/mL rhBMP10 for 3 hours. Inhibition of rhBMP9 and rhBMP10 induced up-regulation of Smad6 expression by pretreatment with 10 μg/mL ALK1Fc. Quantitative RT-PCR results are normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and then to the untreated (UT) sample. Gray squares represent individual data points (n = 3). (C) Expression level of Smad6 in lymphatic endothelial cells stimulated with rhBMP9 150 pg/mL and transfected with siRNA targeting the Alk1-7, Smad1, 4, 5, or endoglin (Eng). Gray squares represent individual data points (n = 3).
Lymphatic endothelial cells express ALK1. (A) RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in HUVECs and human microvascular dermal neonatal lymphatic endothelial cells. RNA from a mixture of human cell lines with (+) and without (−) reverse transcriptase enzyme was used as a positive and negative control. Sizes of PCR products are indicated. (B) Expression level of Smad6 in HUVECs and lymphatic endothelial cells stimulated with 50 pg/mL rhBMP9 or 500 pg/mL rhBMP10 for 3 hours. Inhibition of rhBMP9 and rhBMP10 induced up-regulation of Smad6 expression by pretreatment with 10 μg/mL ALK1Fc. Quantitative RT-PCR results are normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and then to the untreated (UT) sample. Gray squares represent individual data points (n = 3). (C) Expression level of Smad6 in lymphatic endothelial cells stimulated with rhBMP9 150 pg/mL and transfected with siRNA targeting the Alk1-7, Smad1, 4, 5, or endoglin (Eng). Gray squares represent individual data points (n = 3).
ALK1Fc disrupts both blood vessel and lymphatic vessel development in vivo
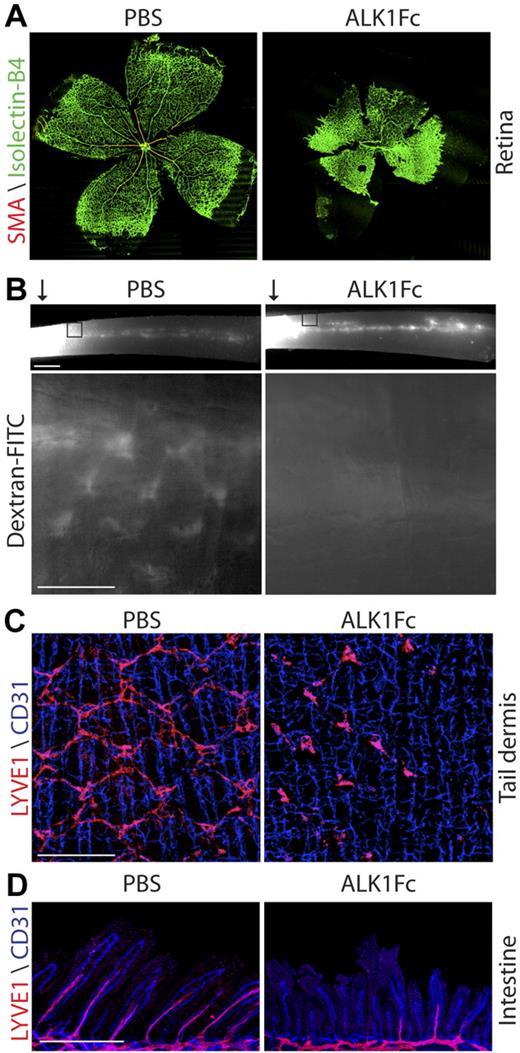
To circumvent the embryonic lethality of ALK1 deficiency that prevents the assessment of its role during lymphatic development, we decided to block the ALK1 signaling using ALK1Fc in neonatal mice. Analysis of P8 mouse retinas revealed that systemic treatment of neonatal mice with ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, at P1, P3, and P5) resulted in a dramatic increase in retinal vascular density, failed remodeling of the primary retinal capillary plexus into a mature vascular pattern, and defective arteriogenesis as indicated by the loss of smooth muscle actin (SMA) staining (Figure 2A). These findings are reminiscent of the vascular defects associated with ALK1 deficiency during embryogenesis19 and suggest that ALK1Fc is able to block ALK1 signaling in vivo. Interestingly, similar treatment also resulted in prominent accumulation of chyle in the abdominal cavity by P7 (supplemental Figure 2), which is indicative of a possible defect in the intestinal lymphatics. To directly investigate the impact of ALK1Fc on lymphatic function, P5 neonatal mice treated with ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) or PBS were injected subcutaneously with dextran–fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) into the tail tip. Drainage of the dextran–FITC through the lymphatic network was analyzed 5 minutes after injection. In the PBS-injected pups, a dextran–FITC-positive lymphatic collecting vessel was readily visible running the length of the tail (Figure 2B). In addition, the stereotypic honeycomb pattern of capillary lymphatic vessels in the tail dermis was highlighted by the injected dextran–FITC (Figure 2B). By comparison, ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) had similar dextran–FITC-positive staining in the collecting vessel (Figure 2B top); however, the honeycomb lymphatic vessels were completely absent (Figure 2B bottom). These data suggest that ALK1Fc treatment results in the defective development of lymphatic microvessels, whereas it has little effect on the lymphatic collecting vessels that have already formed before birth. LYVE1 staining of P6 tail dermis further confirmed the impaired development of the honeycomb pattern of lymphatic vessels. Individual LYVE1-positive cells were still present in ALK1Fc-treated tail dermis; however, the cells failed to make the necessary connections to form the honeycomb structure (Figure 2C). In addition to lymphatic vessels the tail dermis has an extensive network of blood vessel capillaries. Unlike the lymphatic microvessels that form postnatally, the preexisting blood capillaries were unaffected (Figure 2C).
ALK1Fc causes vascular and lymphatic defects. (A) Isolectin-B4 (green) and SMA (red) staining of P8 retina from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg; P1 P3, P5). (B) Analysis of lymphatic function by dextran–FITC injection into the tail tip () of a P5 pup treated with PBS or ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3). Images were captured 5 minutes after injection. (Top) Drainage of dextran–FITC into the collecting lymphatic vessel that extends the length of the tail. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (Bottom) “Honeycomb” lymphatic vessels in the dermis adjacent to the injection site (box). Scale bar represents 250 μm. (C) CD31 (blue, vasculature) and LYVE1 (red, lymphatic) staining of the tail dermis from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) at P6. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (D) CD31 (blue, vasculature) and LYVE1 (red, lymphatic) staining of the intestine from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) at P6. Scale bar represents 250 μm.
ALK1Fc causes vascular and lymphatic defects. (A) Isolectin-B4 (green) and SMA (red) staining of P8 retina from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg; P1 P3, P5). (B) Analysis of lymphatic function by dextran–FITC injection into the tail tip () of a P5 pup treated with PBS or ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3). Images were captured 5 minutes after injection. (Top) Drainage of dextran–FITC into the collecting lymphatic vessel that extends the length of the tail. Scale bar represents 1 mm. (Bottom) “Honeycomb” lymphatic vessels in the dermis adjacent to the injection site (box). Scale bar represents 250 μm. (C) CD31 (blue, vasculature) and LYVE1 (red, lymphatic) staining of the tail dermis from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) at P6. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (D) CD31 (blue, vasculature) and LYVE1 (red, lymphatic) staining of the intestine from PBS- or ALK1Fc-treated pups (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) at P6. Scale bar represents 250 μm.
Because the first observation of lymphatic dysfunction was chyle accumulation in the abdomen of ALK1Fc-treated pups, the lymphatic network in the intestine was further investigated. ALK1Fc treatment resulted in shorter villous length of the P6 neonates, where the extension of villus lacteals into the villi was greatly reduced and in many cases was completely stalled (Figure 2D). Because further lymphatic capillary extension into the villi accompanies the continuing growth of intestinal villi in early postnatal mice (supplemental Figure 3), the observed defect is likely attributable to a blockade of lymphatic development rather than a regression of preexisting villus lacteals. However, the preexisting lymphatic vascular network on the outer surface of the intestine28 appeared largely unaffected, except for apparent vessel dilation (data not shown). Similar to the tail dermis the blood vessels within the intestine villi appeared normal in the ALK1Fc-treated pups (Figure 2D). These data demonstrate that ALK1Fc affects neovascular development of both lymphatic and blood vessels, whereas it has little effect on existing vessels.
The signaling axis of ALK1–ACVR2B/BMPR2–BMP9/10 regulates early postnatal lymphatic development
Similar to ALK1Fc we found ACVR2BFc and BMPR2Fc were able to block both BMP9- and BMP10-induced Smad6 expression (supplemental Figure 4), suggesting that ACVR2B and BMPR2 are potential type II receptors for BMP9/10 signaling. Genetic deletion of ACVR2B has been demonstrated to result in postnatal death associated with cardiac and vertebral patterning defects.29 Genetic deletion of BMPR2 results in embryonic lethality, and mice with hypomorphic allele of BMPR2 die before birth as a result of skeletal and cardiac defects.30,31 Mutations in BMPR2 are also associated with pulmonary hypertension.32 However, the effect of postnatal inhibition of BMPR2- or ACVR2B-dependent signaling on vascular or lymphatic development has not been established.
As demonstrated in Figure 3A, treatment of neonatal mice with either ACVR2BFc or BMPR2Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) resulted in increased retinal vascular density and decreased SMA staining at P6, which resembled the effect of ALK1Fc. Importantly, injection of ACVR2BFc or BMPR2Fc also resulted in lymphatic vessel defects in P6 neonates, which were similar, yet to a less extent, to those observed with ALK1Fc (Figure 3A). These findings demonstrated that the effect on lymphatic vessel is a pathway specific effect rather than being unique to one reagent.
The ALK1 pathway is directly involved in lymphatic vessel development. (A) Analysis of lymphatic and vascular development at P6, after treatment with ALK1Fc, ACVR2BFc, BMPR2Fc, or VEGFR3Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis. Vascular development is visualized by isolectin-B4 (green) and SMA (red) staining of the retina. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (B) Inhibition of rhBMP9 induced up-regulation of Smad6 expression by the ALK1 immunized serum (α-ALK1-s) or affinity purified antibody (α-ALK1-a), whereas preimmune serum (Pre) has no effect. Red boxes represent each data point (n = 3). (C) Inhibition of rhBMP9 binding to ALK1 protein by treatment with the ALK1 immunized serum (α-ALK1-s) or affinity purified antibody (α-ALK1-a), whereas preimmune serum (Pre) has no effect. Red boxes represent each data point (n = 2). (D) ALK1-neutralizing antibody binds mouse ALK1 but not ALK2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7. (E) Analysis of lymphatic development at P6 after treatment with the ALK1 neutralizing antibody (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) in the tail dermis. (F) Analysis of lymphatic development at P6 after treatment with the ALK1-neutralizing antibody (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) in the ear. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis and ear. Scale bar represents 250 μm.
The ALK1 pathway is directly involved in lymphatic vessel development. (A) Analysis of lymphatic and vascular development at P6, after treatment with ALK1Fc, ACVR2BFc, BMPR2Fc, or VEGFR3Fc (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis. Vascular development is visualized by isolectin-B4 (green) and SMA (red) staining of the retina. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (B) Inhibition of rhBMP9 induced up-regulation of Smad6 expression by the ALK1 immunized serum (α-ALK1-s) or affinity purified antibody (α-ALK1-a), whereas preimmune serum (Pre) has no effect. Red boxes represent each data point (n = 3). (C) Inhibition of rhBMP9 binding to ALK1 protein by treatment with the ALK1 immunized serum (α-ALK1-s) or affinity purified antibody (α-ALK1-a), whereas preimmune serum (Pre) has no effect. Red boxes represent each data point (n = 2). (D) ALK1-neutralizing antibody binds mouse ALK1 but not ALK2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7. (E) Analysis of lymphatic development at P6 after treatment with the ALK1 neutralizing antibody (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) in the tail dermis. (F) Analysis of lymphatic development at P6 after treatment with the ALK1-neutralizing antibody (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) in the ear. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis and ear. Scale bar represents 250 μm.
The results of in vivo experiments with ALK1Fc, ACVR2BFc, and BMPR2Fc all suggest a role for ALK1 signaling during lymphatic development. Because the ligands of TGF-β family oftentimes engage more than one receptor system, in principle the effect of a decoy soluble receptor, which functions by sequestering ligands, might not be limited to its own signaling system.33 To demonstrate that the observed lymphatic defects are directly attributed to blocked ALK1 signaling, we took advantage of an ALK1-specific neutralizing antibody. The ALK1 antibody can inhibit the binding of BMP9 to immobilized mALK1 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Figure 3C) and to block the up-regulation of SMAD6 expression after BMP9 stimulation in endothelial cells (Figure 3B). In addition, this antibody is highly selective and does not bind other TGF-β type I receptors in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Figure 3D). Importantly, treatment of neonates with the ALK1-neutralizing antibody (10 mg/kg, P1 and P3) resulted in lymphatic defects similar to those as observed with ALK1Fc treatment (Figure 3E-F). ALK1-neutralizing antibody treatment resulted in a failure of the lymphatic endothelial cells to make the necessary connections to form the honeycomb structure in the tail (Figure 3E). In the ear the treatment with ALK1-neutralizing antibody resulted in decreased branching of the lymphatic vessels and lymphatic vascular density (Figure 3F). Collectively, these data suggest that ALK1 pathway plays an essential role in regulating the postnatal development of lymphatic vasculature.
Despite the dramatic effect of ALK1 inhibition on lymphatic development in vivo, inhibition or activation of ALK1 signaling had no significant effect on the proliferation and migration of lymphatic endothelial cells in 2-dimensional culture (data not shown). However, lymphatic endothelial cells cultured in 3-dimensional fibrin matrix exhibited increased spouting and proliferation upon treatment with ALK1Fc, BMPR2Fc, and ACVR2BFc, whereas treatment with other TGF-β type I-Fc and type II-Fc receptors had no affect (supplemental Figure 5 and data not shown). These results are consistent with the notion that blockade of ALK1 signaling disrupts the balance of proliferation and differentiation of endothelial cells.
ALK1 is involved in multiple stages of lymphatic development
When ALK1Fc treatment was started at P1, the lymphatic and vascular defects were very dramatic and severe (Figures 2B,3A), and in many cases very few lymphatic structures were present. We next sought to examine the effects of delaying treatment on lymphatic development to determine at what stage of lymphatic development ALK1 signaling is required. When ALK1Fc treatment was started at P3 (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5), a time point when lymphatic vessels are present but the honeycomb structure is not well established, the lymphatic defect was still dramatic, with many missing connections, when analyzed at P8 (Figure 4A). The blood vascular defect associated with ALK1Fc was significantly decreased if the initiation of the treatment was delayed (Figure 4A). When ALK1Fc treatment was started at P8 (10 mg/kg, P8 and P10), a time point when the honeycomb pattern is well established, ALK1Fc failed to cause regression of the preexisting lymphatic vessels, when analyzed at P12 (Figure 4B). By comparison, treatment with VEGFR3Fc (10 mg/kg, P8 and P10) resulted in significant regression of the honeycomb structure (Figure 4B). A closer examination of the lymphatic vessels in the PBS- and ALK1Fc-treated pups at P8 and P12 suggests a possible impairment in the maturation or remodeling of the lymphatic vessels. In comparison with the control P8, the control P12 tail contained fewer “ringed structures” in the honeycomb network, which apparently have been remodeled into discreet vessels. In contrast, the ringed structures were much more prevalent (arrows) in the P12 ALK1Fc-treated pups, reminiscent of the P8 control tails, suggesting that ALK1Fc blocked the remodeling process (Figure 4C). Therefore, our data suggest ALK1 signaling is required for the formation of initial lymphatic plexus as well as further remodeling into mature network.
ALK1 is involved in multiple stages of lymphatic development. (A) Analysis of vascular and lymphatic development in P8 pups when ALK1Fc treatment is started when the honeycomb pattern is being established (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis, whereas vascular development is visualized by isolectin-B4 (green) staining of the retina. Scale bar represents 500 μm (retina) and 250 μm (tail). (B) Analysis of lymphatic development in P12 pups when ALK1 treatment is started when the honeycomb structure is fully established (10 mg/kg, P8 and P10). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (C) High-magnification images demonstrate the remodeling process that occurs from P8 to P12 and the “ringed” structures that fail to be remodeled in ALK1Fc-treated pups.
ALK1 is involved in multiple stages of lymphatic development. (A) Analysis of vascular and lymphatic development in P8 pups when ALK1Fc treatment is started when the honeycomb pattern is being established (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis, whereas vascular development is visualized by isolectin-B4 (green) staining of the retina. Scale bar represents 500 μm (retina) and 250 μm (tail). (B) Analysis of lymphatic development in P12 pups when ALK1 treatment is started when the honeycomb structure is fully established (10 mg/kg, P8 and P10). Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 (green) staining in the tail dermis. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (C) High-magnification images demonstrate the remodeling process that occurs from P8 to P12 and the “ringed” structures that fail to be remodeled in ALK1Fc-treated pups.
Distinct roles of ALK1 and VEGFR3 during lymphatic development
Previous reports and Figure 4B have demonstrated that the VEGFR3–VEGFC/D pathway is critically required for lymphatic vessel development and survival.4,5 We sought to explore the effect of ALK1 blockade on the dependence of lymphatic vessels on VEGFR3-VEGFC/D signaling. At P4, a time point, when the honeycomb pattern is being established, single-agent treatment of ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P2) or VEGFR3Fc (1 mg/kg, P1) significantly inhibited lymphatic vessel development (Figure 5A). The combination of both agents had a much more dramatic effect, with almost a complete loss of lymphatic vessels (Figure 5A). We next analyzed the effect of combined treatment on preexisting lymphatic vessels at P8, when the honeycomb pattern is well established. Defects in lymphatic development became evident 24 hours after administration of VEGFR3Fc, the defect was much more dramatic with a treatment of 48 hours (Figure 5B). ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5) treatment results in a moderate lymphatic defect by P8 (Figure 5B). However, the combination of ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc resulted in a more profound effect on the lymphatic vascular network, with accelerated regression of the preexisting lymphatic vessels (Figure 5B).
Distinct roles of ALK1 and VEGFR3 during lymphatic development. (A top) Analysis of lymphatic development in P4 pups after treatment with ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P2), VEGFR3Fc (1 mg/kg, P1), or combined ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 staining (red), inset shows a greater magnification image of the honeycomb structure that is disrupted by the treatments. Scale bar represents 500 μm. (Middle) Analysis of podoplanin (green) and LYVE1 (red) expression after ALK1Fc, VEGFR3Fc, or combination treatments. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (Bottom) Analysis of LYVE1 (green) and active Caspase3 (red) expression after ALK1Fc, VEGFR3Fc, and combination treatment. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (B) Analysis of lymphatic development in P8 pups after ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5), VEGFR3Fc (10 mg/kg, P6 or P7), or combined ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc treatment. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 staining (red). Scale bar represents 250 μm.
Distinct roles of ALK1 and VEGFR3 during lymphatic development. (A top) Analysis of lymphatic development in P4 pups after treatment with ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P2), VEGFR3Fc (1 mg/kg, P1), or combined ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 staining (red), inset shows a greater magnification image of the honeycomb structure that is disrupted by the treatments. Scale bar represents 500 μm. (Middle) Analysis of podoplanin (green) and LYVE1 (red) expression after ALK1Fc, VEGFR3Fc, or combination treatments. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (Bottom) Analysis of LYVE1 (green) and active Caspase3 (red) expression after ALK1Fc, VEGFR3Fc, and combination treatment. Scale bar represents 250 μm. (B) Analysis of lymphatic development in P8 pups after ALK1Fc (10 mg/kg, P3 and P5), VEGFR3Fc (10 mg/kg, P6 or P7), or combined ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc treatment. Lymphatic development is visualized by LYVE1 staining (red). Scale bar represents 250 μm.
To investigate the fate of the lymphatic vessels after treatment with ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc, endothelial cell apoptosis was assessed by activated Caspase3 staining. The combined treatment with both ALK1Fc and VEGFR3Fc resulted in a marked increase in apoptotic lymphatic endothelial cells, suggesting that blockade of ALK1 signaling sensitizes lymphatic vessels to VEGFC/D depletion (Figure 5A). Interestingly, staining for podoplanin expression revealed that ALK1Fc treatment markedly blocked its expression (Figure 5A). By comparison, podoplanin expression was normal in VEGFR3Fc-treated pups (Figure 5A). A similar block in podoplanin expression by ALK1 inhibition was observed in the ear and intestine lymphatic vessels (data not shown). Podoplanin has been suggested to be a marker of terminally differentiated lymphatic vessels, suggesting ALK1 may regulate differentiation or maturation of lymphatic vessels. It is possible that the failure to induce Podoplanin expression contributes to the remodeling defects caused by ALK1 inhibition. Further experiments, however, are required to test this hypothesis. In addition, ALK1Fc treatment results in dilated lymphatic vessels in the intestinal outer wall (data not shown), which is similar to what is reported to result from podoplanin deficiency.9 These data suggest that ALK1 and VEGFR3 regulate different aspects of lymphatic development.
Interestingly, we found that ALK1Fc only modestly reduced the expression of podoplanin in cultured endothelial cells as opposed to its dramatic in vivo effect. Furthermore, BMP9 stimulation had little effect on podoplanin expression (supplemental Figure 6). By contrast the known ALK1 target genes SMAD6 and ID1 were significantly changed in both conditions. These data suggest that podoplanin is likely not a direct target of the ALK1 pathway and that additional signaling cues are required for the decreased podoplanin expression observed in vivo.
Discussion
ALK1, a member of the TGF-β receptor superfamily, is an important regulator of blood vessel development.19 ALK1-deficient mice die at the onset of lymphatic development, limiting the study of its importance during this process.19 In the current study we provide several lines of evidence suggesting that ALK1 pathway is also intimately involved in the regulation of lymphatic development. We show that the ALK1 pathway is functional in cultured lymphatic endothelial cells. Lymphatic endothelial cells express the key components of the ALK1 pathway. ALK1 target genes, including Smad6, were up-regulated in lymphatic endothelial cells upon stimulation with ALK1 ligands, BMP9 and BMP10. In vivo blockade of ALK1 signaling with the use of soluble decoy receptors or an ALK1-specific antibody resulted in dramatic defects in lymphatic development in multiple organs. In the tail skin of neonatal mice, the lymphatic defects caused by ALK1 inhibition were characterized by the inability of lymphatic endothelial cells to form the stereotypical honeycomb-like pattern of capillary lymphatic vessels. We also show that ALK1 signaling is required for the maturation and remodeling of lymphatic vessels in the tail skin. In ALK1Fc-treated neonatal mice, the extension of lymphatic capillary into the intestinal villi was invariably reduced and in many cases was completely stalled. ALK1 inhibition was associated with the marked loss of podoplanin expression. Podoplanin has been suggested to be a marker of terminally differentiated lymphatic vessels. Podoplanin-deficient mice have defects in lymphatic development. It is possible that loss of podoplanin expression contributes to the abnormal lymphatic development upon ALK1 inhibition.
In our current study, inhibition of ALK1 signaling in neonatal mice by the use of soluble decoy receptors resulted in failed remodeling of the primary retinal plexus into mature vascular pattern, defective arteriogenesis, and vessel dilation (Figure 2A and data not shown), which is consistent with the vascular defects resulting from ALK1 deficiency during embryogenesis. These effects, however, are apparently limited to the neovascular development, the existing blood vessels are largely unaltered. For instance, ALK1Fc has little effect on the skin microvessels or the capillary within the villi of small intestines. Therefore, it is unlikely the observed lymphatic defect is secondary to impaired blood vascular endothelium.
Previous studies and our current work suggest that ALK1 has a dual role, in both vascular and lymphatic development. Such finding of dual action of a signaling pathway is not unprecedented. VEGFR3, in addition to its well-established role in lymphangiogenesis, is also essential for the early blood vessel development in embryos.34 Studies of gene-targeted mice have suggested that the Tie2–angiopoiteins signaling axis not only is important for the remodeling and stability of blood vascular endothelium but also plays a role in lymphangiogenesis.13 Interestingly, the embryonic lethality resulting from targeted deletion of EphrinB2, which is essential for the angiogenic remodeling of blood vessels in early embryo, initially precluded the recognition of its role in the development of lymphatic vessels.14,15 It should be pointed out that the phenotypic outcomes resulting from the disruption of these pathways are oftentimes distinct between the 2 vascular systems.
BMP9 is a circulating factor predominantly expressed in liver, and BMP10 is specifically expressed in the developing and adult heart. Previous in vitro studies have suggested that BMP9 and BMP10 are potential ligands for ALK1. BMP10-knockout mice die during development as the result of cardiac defects before lymphatic development,35 and mice deficient in BMP9 have not been reported. Future studies that use genetic models of mice deficient in BMP9 and BMP10 or ligand specific antibodies will help elucidate the relative contribution of the 2 ligands to ALK1-mediated signaling in regulating angiogenesis and lymphatic angiogenesis.
The findings from experimental models of lymphatic metastasis and clinicopathologic analyses of human cancer have suggested that targeting the VEGFR3–VEGFC/D pathway might be a promising approach of anticancer therapy by reducing the metastatic spread of tumor cells through tumor lymphatic vasculature. Unlike VEGFR3 signaling, which is essential for the proliferation and survival of lymphatic endothelial cells,5 our data demonstrate that ALK1 signaling is apparently involved in controlling the differentiation of lymphatic endothelial cells to influence the lymphatic vascular development and remodeling. Because inhibition of ALK1 signaling sensitizes lymphatic endothelial cells to VEGFC depletion, combined inhibition of both VEGFR3 and ALK1 pathways might be more effective at blocking lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis.
In conclusion, our findings reveal a novel aspect of ALK1 signaling in regulating lymphatic development, in addition to its known role in vascular development, and provide a rationale for targeting ALK1 pathway to modulate lymphangiogenesis in human diseases.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We kindly thank XiaoHuan Liang for reagents and Dr Greg Plowman and Dr Weilan Ye for helpful discussions.
Authorship
Contribution: K.N. designed and performed the experiments and wrote the paper; G.Z. designed and performed the experiments; J.B.R. and H.C. performed the experiments; M.Y. designed the experiments and wrote the paper; and all authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Minhong Yan, Genentech Inc, Tumor Biology and Angiogenesis, 1 DNA Way, MS 93B, South San Francisco, CA 94080; e-mail: minhong@gene.com.
References
Author notes
K.N. and G.Z. contributed equally to this work.





This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal