At present, there is no method available to predict response to farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs). We analyzed gene expression profiles from the bone marrow of patients from a phase 2 study of the FTI tipifarnib in older adults with previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The RASGRP1/APTX gene expression ratio was found to predict response to tipifarnib with the greatest accuracy using a “leave one out” cross validation (LOOCV; 96%). RASGRP1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates RAS, while APTX (aprataxin) is involved in DNA excision repair. The utility of this classifier for predicting response to tipifarnib was validated in an independent set of 58 samples from relapsed or refractory AML, with a negative predictive value (NPV) and positive predictive value (PPV) of 92% and 28%, respectively (odds ratio of 4.4). The classifier also predicted for improved overall survival (154 vs 56 days; P < .001), which was independent of other covariates, including a previously described prognostic gene expression classifier. Therefore, these data indicate that a 2-gene expression assay may have utility in categorizing a population of patients with AML who are more likely to respond to tipifarnib.
Introduction
Tipifarnib (R115777; ZARNESTRA, Janssen Ortho, Gurabo, Puerto Rico) was one of the first farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) to be tested in the clinic.1 It has demonstrated significant activity in hematologic disorders, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), multiple myeloma (MM), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), with complete response rates in AML and MDS of up to approximately 15%.2,,,–6 FTIs function by competitively inhibiting the addition of a farnesyl moiety to a number of important signaling molecules, including RAS.1,7
Historically, the mutation status of the RAS gene was considered to be a candidate biomarker for patient response to FTIs. This rationale was based on the finding that specific point mutations within RAS genes cause constitutive activation of the RAS pathway in many cancers,8 and on preclinical evidence that FTIs could block RAS-transformed cells.9,10 Since it is generally accepted that tumors are heavily reliant on the activation of 1 or 2 pathways (“oncogene addiction” hypothesis), it follows that patients whose tumors are promoted by aberrant expression of one or more components of those pathways should respond to drugs that inhibit those components.11 However, pathways can be activated by multiple events, and it has been found that RAS can be up-regulated in the absence of activating RAS mutations.12 Furthermore, no correlation between RAS mutations and response to FTIs has been demonstrated in clinical studies.2,13 Indeed, while several early clinical studies focused on cancers that exhibited high frequencies of RAS mutations, the response rates to FTIs were disappointingly low in those trials.3,14,15
Microarray technology has been used to identify gene expression profiles that are predictive of response or resistance to a number of different therapeutic modalities in a variety of cancers, including chemotherapies or endocrine therapies in breast cancer,16,,–19 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma,20,–22 and leukemia.23,24 We have previously used gene expression profiling to identify molecular predictors of response to tipifarnib in relapsed or refractory AML.13 Here, we have extended this work to newly diagnosed AML, which has led to the identification of a 2-gene expression ratio (RASGRP1/APTX) that is predictive of clinical outcome. We further show that this classifier also has predictive utility in relapsed or refractory AML, and that stratification is specific to tipifarnib response.
Methods
Clinical samples and processing
Approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Boards of all participating institutions for these studies. Informed consent was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The current study used 67 pretreatment bone marrow (BM) samples collected from patients entered in an open-label, multicenter, single-arm phase 2 study investigating the efficacy and safety of FTI tipifarnib in 158 adults aged 65 years or older with previously untreated AML. A total of 34 of these samples was successfully assayed for global gene expression, and microarray data from 26 patients were used to identify classifiers that predict response to tipifarnib. The findings were validated using 58 pretreatment BM samples from a phase 2 study in relapsed and refractory AML.13 The clinical results for these studies have been published elsewhere.4,6,13
BM samples were collected from consenting patients before treatment with tipifarnib, and mononuclear cells were processed on site as previously described.13 Total RNA was extracted from cell samples using the Trizol Kit (Qiagen, Santa Clarita, CA). RNA quality was determined by assessing the presence of ribosomal bands on an Agilent Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA). Good-quality samples were further processed for microarray analysis. DNA was isolated from the same sample of Trizol-processed BM as per the manufacturer's instructions (Qiagen). Samples were assayed for global gene expression, NRAS mutations, and/or quantitative polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) of specific genes (Table S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
NRAS mutational status
Analysis of activating mutations in NRAS was determined in 32 patient samples by PCR and restriction fragment–length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis as previously described.9 Exons 1 and 2 of the NRAS gene were simultaneously amplified in a single multiplex reaction, and an aliquot was used for a second round of PCR. Resistance to cleavage at natural- or primer-induced restriction enzyme sites in second-round amplicons indicated the presence of a mutation that had abolished the site at the loci being analyzed. Restriction enzymes for the analysis of specific loci were BslI (NRAS codons 12 and 13), MscI (NRAS codon 61, positions 1 and 2), and BfaI (NRAS codon 61, position 3). Reactions were digested overnight, and PCR products were analyzed on an Agilent Bioanalyzer.
Microarray analysis
The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)25 and are accessible through GEO Series accession no. GSE8970.
Synthesis of cDNA and cRNA were performed according to Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) protocols. Since the total RNA yield of many samples was low, 2 rounds of linear amplification were performed, and cRNA was labeled and hybridized to the U133A GeneChip as previously described.13 The total fluorescence intensity for each array was scaled to the uniform value of 600. Chip performance was quantified by calculating a signal-to-noise ratio (raw average signal–noise). Chips were removed from further analysis if their signal-to-noise ratio was less than 20 or if the present calls on the chip was less than 30%. Genes were only included in further analysis if they were called “present” in at least 10% of the chips. Approximately 12 000 Affymetrix probe sets remained following this cutoff. The quality of the gene expression data was further controlled by identifying outliers based on principal components analysis and by analyzing the normal distributions of the gene intensities (Partek Pro V5.1; Partek, St Louis, MO). A total of 34 patient samples (39 arrays) passed quality control (QC) criteria and were used for further analyses. The signal intensities from replicate microarrays were averaged. The microarray data have been deposited in the NCBI GEO and are accessible through GEO series accession no. GSE8970. The gene expression profile of 58 patients with relapsed or refractory AML has previously been described (GEO series accession no. GSE5122).6,13
Clinical response definitions
Response to tipifarnib is reported in the clinical study report and was defined as patients who had a complete remission (CR), a partial remission (PR), or hematologic improvement (HI).4 PR and HI patients were included as responders, since it was previously shown that they had a similar survival benefit to those achieving a CR.4 Briefly, CR was defined as BM showing less than 5% myeloblasts with normal maturation of all cell lines, absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of at least 109/L (1000/μL), and a platelet count of 100×109/L (100 000/μL). PR was defined as the presence of recovery of ANC and platelets to the above stated levels, but with 5% to 19% BM blasts, and a greater than 50% decrease in BM blast percentage from baseline. HI was defined as the same as PR, except with recovery of ANC to 0.5 to 1×109/L (500 to 1000/μL) and platelet count to 20 to 100×109/L (20 000 to 100 000/μL). Progressive disease (PD) was defined as any of the following: more than 50% increase in BM blast percentage from baseline (more than 5% blasts if baseline is less than 5%, more than 10% blasts if baseline is 5% to 10%, and more than 20% blasts if baseline 10% to 20%); greater than 50% increase in circulating blasts; new appearance of circulating blasts on at least 2 consecutive occasions; or development of extramedullary leukemia. Stable disease (SD) was defined as any response not meeting CR, PR, HI, or PD criteria.
Real-time QPCR
For each sample, 1 μg total RNA (as assessed by OD260) was reversed-transcribed using the High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Samples were then incubated at 25°C for 10 minutes and then 37°C for 30 minutes for optimum RNA conversion. QPCR was performed using the ABI Prism 7900HT sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems) with all samples run in triplicate. Each reaction contained 5 μL Taqman Universal PCR Master Mix containing uracil-N-glycosylase (Applied Biosystems), 4.5 μL cDNA template, and 0.5 μL of 20 × Assay on Demand Gene Expression Assay Mix (Applied Biosystems) or 9 pmol both forward and reverse primer and 2.5 pmol probe in a total reaction volume of 10 μL. All primer and fluorescein amidite (FAM) fluorogenic probe sets were chosen to generate amplicons less than 100 nucleotides, allowing for amplification of transcripts from degraded RNA samples. Primers and probes used were APTX (Applied Biosystems), RASGRP1 (Applied Biosystems), and HMBS (Forward, 5′-CCT-GCC-CAC-TGT-GCT-TCC-T-3′; Reverse, 5′-GGT-TTT-CCC-GCT-TGC-AGA-T-3′; Probe, 5′-6FAM-CTG GCT TCA CCA TCG-MGBNFQ-3′). If the control gene HMBS Ct was greater than 30, the QPCR was designated a failure and the assay was repeated. All primer sets span exon boundaries and thus specifically amplify mRNA transcripts and not genomic DNA. The RASGRP1/APTX expression ratio was calculated as previously described.16 First, the raw Ct values were normalized by subtracting the mean Ct from the sample set, dividing by the standard deviation, and then calculating the difference of the normalized Ct values of each gene (APTX − RASGRP1).
Cell-culture assays
All cell lines were acquired from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and propagated according to the supplier's instructions. Cells were plated at a concentration of 105 cells/mL in triplicate cultures and maintained by refreshing media every 3 days. Cells were grown in the presence of tipifarnib (serial dilutions from 800 nM to 0.2 nM) for 4 days and then counted using a Z2 Coulter Counter (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA). The IC50 was determined using the GraphPad Prism 4 software (San Diego, CA). Total RNA was isolated from 106 cells using the Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Bullinger prognostic signature analysis
The 149 IMAGE clones (133 unique genes) identified by Bullinger et al were mapped to 167 unique probe sets on the Affymetrix U133A GeneChip.26 Of these, 93 probe sets (75 unique genes) were called present in at least 10% of the GeneChips in our dataset13 ; therefore, these filtered probe sets were used for further analysis (Table S2). Hierarchical clustering was performed on log2-transformed data using complete linkage and a Euclidean distance metric. The compound covariate prediction (CCP) algorithm was used to define the Bullinger prognostic classifier using our 93 filtered probe sets as previously described.27 Overall survival was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. A RASGRP1/APTX (Affymetrix probe sets 205590_at:218527_at) gene expression cutoff of −1.10216 was used for patient stratification, as defined from the training set. Hazard ratios associated with survival were calculated using Cox univariate and multivariate analyses.
Statistical analysis
A total of 2 approaches were used to identify genes predictive of response to tipifarnib. The first was a t test–based algorithm. The following gene-filtering criteria were used to identify genes differentially expressed between clinical responders (CR, PR, or HI) and patients with progressive disease: specificity for identifying “responder” with 100% sensitivity greater than or equal to 40%, t test P value (log2-transformed data with unequal variance) less than .05, and mean fold change greater than 2. The genes that passed these criteria were ranked by the area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC). ROC analysis was used to test the overall predictive value of individual genes and/or multigene classifiers. To build a classifier, the response score was used to calculate each patient's chance of response to tipifarnib therapy. The score was defined as the linear combination of weighted expression signals with the t statistic as the weight. The threshold was determined from the ROC curve of the training set to ensure 100% sensitivity and the highest specificity. To determine how many genes needed to be included in the predictor, “leave one out” cross validation (LOOCV) was carried out. The response scores for the “left-out” samples based on different numbers of genes were recorded. The performances of the predictors with different numbers of genes were assessed based on misclassification error rate, sensitivity, specificity, and P values measuring the separation of Kaplan-Meier curves of the 2 predicted groups. Thus, the best predictor was selected accordingly.
The second approach used the top scoring pair (TSP) algorithm, which was first introduced by Geman et al.28 In essence, the algorithm ranks all the gene pairs (genes i and j) based on the absolute difference (Dij) in the frequency of events where gene i has higher expression value than gene j in samples among class C1 to C2. In the case of multiple TSPs (all sharing the same Dij), we selected the top pair by a secondary rank score that measures the magnitude to which inversions of gene-expression levels occur from one class to the other within a pair of genes. The top pair with highest frequency of absolute Dij greater than 2-fold in all samples was selected as a candidate pair. The candidate pair was then assessed in an independent testing dataset. LOOCV was carried out in training set to evaluate the maximum misclassification error rate of the model.
A Cox proportional hazards model was used for investigating the relationship between well-known clinical parameters (ie, age, sex, AML class, karyotype, baseline white blood cell [WBC] count, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score, and baseline BM blast count), Bullinger CCP, the 2-gene ratio and overall survival. A univariate approach was first tested for each of the variable. A multivariate test was carried out to evaluate the independence of variables that showed significance in univariate analysis. All the statistical analyses were done using R (R Development Core Team, 2006; http://www.r-project.org/).
Results
In an attempt to identify predictive markers of tipifarnib response in patients with AML, we examined gene-expression profiles of leukemic BM samples from patients enrolled in a phase 2 clinical trial of single-agent tipifarnib in poor-risk elderly patients with previously untreated AML.4 As previously reported, this trial had an overall response rate of 23% (14% CR, 9% PR or HI), with an additional 32% of patients exhibiting SD (Table 1). For the present pharmacogenomic study, BM from 67 patients was collected before treatment with tipifarnib, and leukemic myeloid cells were enriched by Ficoll-density centrifugation (Tables 1,S1). Useable material was not available from the remaining 91 patients. Good-quality total RNA from 13 responders (9 CR, 4 HI), 8 patients with SD, and 13 patients with PD was amplified, labeled, and hybridized to the Affymetrix U133A GeneChip. No patients who exhibited a PR were present in our dataset. Based on RNA and DNA availability, a total of 30 samples were evaluated by QPCR for validation of specific genes, and 32 samples were evaluated for NRAS mutational status. There was no significant difference in patient demographics between the pharmacogenomically assayed subset of patients compared with the entire patient population (Table 1). There were some differences in the response profile between the 2 groups such as a higher prevalence of responders in the pharmacogenomic subset. However, the median overall survival was not significantly different between the pharmacogenomic subgroup and the entire population.
Clinical characteristics of the newly diagnosed AML cohort
| Characteristic . | All treated patients, n = 158 . | All profiled patients, n = 67 . | P to all patients . | Microarray-profiled patients, n = 34 . | P to all patients . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age, y (range) | 74 (34-85) | 73 (63-85) | NS | 73 (63-85) | NS |
| Sex, no. male (%) | 95 (60) | 41 (61) | NS | 22 (65) | NS |
| Prior MDS, yes (%) | 119 (75) | 48 (72) | NS | 24 (71) | NS |
| CR, no. (%) | 22 (14) | 14 (21) | .05 | 9 (26) | .04 |
| PR, no. (%) | 3 (2) | 1 (2) | NS | 0 (0) | NS |
| HI, no. (%) | 12 (8) | 7 (10) | NS | 4 (12) | NS |
| SD, no. (%) | 50 (32) | 15 (22) | .01 | 8 (24) | NS |
| PD, no. (%) | 58 (37) | 30 (44) | .03 | 13 (38) | NS |
| NE, no. (%) | 13 (8) | 0 (0) | NS | 0 (0) | NS |
| Characteristic . | All treated patients, n = 158 . | All profiled patients, n = 67 . | P to all patients . | Microarray-profiled patients, n = 34 . | P to all patients . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age, y (range) | 74 (34-85) | 73 (63-85) | NS | 73 (63-85) | NS |
| Sex, no. male (%) | 95 (60) | 41 (61) | NS | 22 (65) | NS |
| Prior MDS, yes (%) | 119 (75) | 48 (72) | NS | 24 (71) | NS |
| CR, no. (%) | 22 (14) | 14 (21) | .05 | 9 (26) | .04 |
| PR, no. (%) | 3 (2) | 1 (2) | NS | 0 (0) | NS |
| HI, no. (%) | 12 (8) | 7 (10) | NS | 4 (12) | NS |
| SD, no. (%) | 50 (32) | 15 (22) | .01 | 8 (24) | NS |
| PD, no. (%) | 58 (37) | 30 (44) | .03 | 13 (38) | NS |
| NE, no. (%) | 13 (8) | 0 (0) | NS | 0 (0) | NS |
P to remaining patients was NS in all cases.
NE indicates not evaluable; and NS, not significant.
Identification of predictive genes from the newly diagnosed AML cohort
As expected, no correlation was found between RAS mutational status and response to tipifarnib (Document S1). To identify novel genes that are predictive of response to tipifarnib in the newly diagnosed AML population, we generated good-quality transcriptional profiles of pretreatment marrow samples from 13 responders (9 CR and 4 HI) and 13 patients with PD (our “discovery set”) within the 67-patient sample set. Patients who had an HI were included in the responder group since these patients have a similar overall survival benefit to those who achieved a CR.4 Patients with SD were not used in this analysis because these patients are not considered optimal responders. We first used the same approach previously used to identify markers of tipifarnib response in patients with relapsed and refractory AML (Document S1).13 A total of 45 probe sets (corresponding to 38 unique genes) predictive of response were identified (Table S2). The top gene was the RAS guanyl-releasing protein 1 (RASGRP1; probe set ID, 205590_at), which showed an AUC of 0.95 in a LOOCV and a mean increase in RNA expression of approximately 4-fold in responders. Using a cutoff that biases for high sensitivity, a LOOCV demonstrated that the expression of the RASGRP1 gene provided an overall predictive accuracy of 77% (Figure S1). However, serial addition of genes to this single gene classifier did not improve its predictive value.
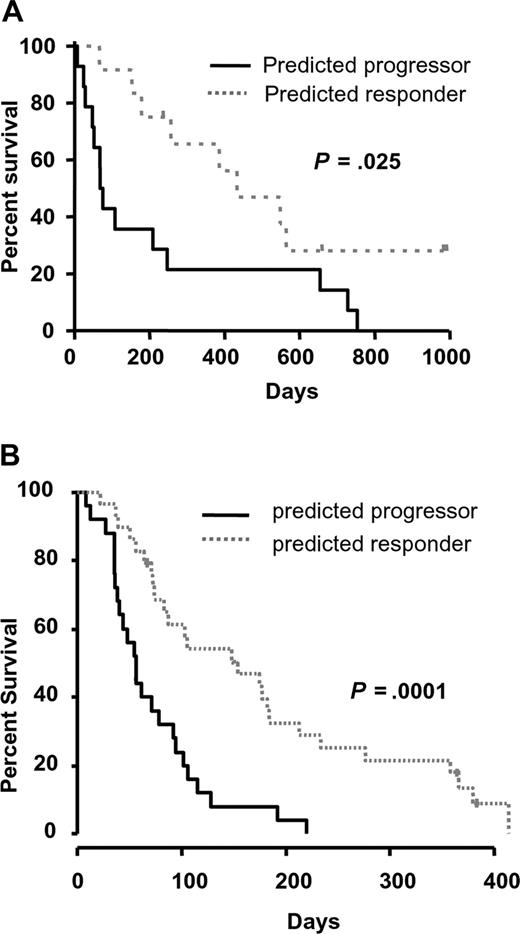
We therefore used an alternative gene-selection algorithm to identify genes that would improve the predictive value of RASGRP1 alone. To this end, we used the TSP algorithm to identify the best pair of genes that would provide the greatest predictive accuracy.28 This approach was used to exploit the greatest difference in expression between 2 genes and may be useful when aiming to develop a QPCR-based diagnostic assay. The TSP identified from the training set was RASGRP1 and aprataxin (APTX; probe set ID, 218527_at). The APTX protein is a member of the histine triad (HIT) family of nucleotide hydrolases and is involved in the repair of DNA strand breaks.29,30 RASGRP1 and APTX were highly and lowly expressed in responders, respectively. A robust LOOCV showed that this 2-gene ratio provided 93% NPV and 100% PPV in the training set of samples, with an overall mean error rate of only 4% (Table 2). These data demonstrated that the model-building algorithm had a low associated prediction error rate, and therefore no attempt was made to increase the performance of the classifier. As expected, the predicted responders demonstrated a significantly higher median overall survival of 433 days compared with only 73 days for those predicted to have progressive disease (Figure 1A).
Accuracy rates of the RASGRP1/APTX gene pair as a predictor of response to tipifarnib in AML
| . | Clinical response . | Total . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD . | R . | ||
| Newly diagnosed AML* | |||
| Predicted R | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Predicted PD | 13 | 1 | 14 |
| Total newly diagnosed | 13 | 13 | 26 |
| Relapsed or refractory AML† | |||
| Predicted R | 21 | 8 | 29 |
| Predicted PD | 23 | 2 | 25 |
| Total relapsed or refractory | 44 | 10 | 54 |
| . | Clinical response . | Total . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD . | R . | ||
| Newly diagnosed AML* | |||
| Predicted R | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Predicted PD | 13 | 1 | 14 |
| Total newly diagnosed | 13 | 13 | 26 |
| Relapsed or refractory AML† | |||
| Predicted R | 21 | 8 | 29 |
| Predicted PD | 23 | 2 | 25 |
| Total relapsed or refractory | 44 | 10 | 54 |
R and PD represent responders and patients with progressive disease, respectively.
For newly diagnosed AML, sensitivity was 92.3%; specificity, 100%; NPV, 92.9%; PPV, 100%; and prevalence, 50%.
For relapsed or refractory AML, sensitivity was 80%; specificity, 52.3%; NPV, 92%; PPV, 27.6%; prevalence, 18.5%; and odds ratio, 4.4.
Performance of the RASGRP1/APTX gene pair as a predictor of response to tipifarnib in AML. (A) The overall survival of newly diagnosed patients with AML stratified by RASGRP1/APTX was plotted using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The median overall survival of those predicted to be responders or nonresponders was 433 and 73 days, respectively. (B) The overall survival of patients with relapsed/refractory AML stratified with the 2-gene classifier is shown. The median overall survival of those predicted to be responders or nonresponders was 154 and 56 days, respectively.
Performance of the RASGRP1/APTX gene pair as a predictor of response to tipifarnib in AML. (A) The overall survival of newly diagnosed patients with AML stratified by RASGRP1/APTX was plotted using Kaplan-Meier analysis. The median overall survival of those predicted to be responders or nonresponders was 433 and 73 days, respectively. (B) The overall survival of patients with relapsed/refractory AML stratified with the 2-gene classifier is shown. The median overall survival of those predicted to be responders or nonresponders was 154 and 56 days, respectively.
In addition, we performed analytical validation of the 2-gene ratio using Taqman QPCR (Document S1). In 30 samples profiled, we found a similar stratification of responders and nonresponders with an associated odds ratio of 4.3. The correlation between platforms was 0.74 (P = .02).
Validation of the RASGRP1/APTX classifier in an independent set of relapsed or refractory AML
We next performed external validation of the 2-gene classifier in an independent microarray dataset comprising of 54 samples from patients with relapsed or refractory AML who were also treated with single-agent tipifarnib.6,13 Importantly, a diagnostic assay that aims to predict response to a cancer therapy should have a high sensitivity (and a high NPV), since it is important to capture as many potential responders as possible. Therefore, to define an appropriate cutoff for testing the TSP classifier, we considered the need to obtain a high sensitivity of predicting responders while maintaining an acceptable level of specificity. In the training set, the level of specificity that could be achieved ranged from approximately 30% to 100% when the sensitivity for identifying responders was set at 100% to 80%, respectively. To ensure the classifier would predict as many responders as possible, we tested a conservative cutoff that provided a specificity of approximately 60% in the training set. When this cutoff was applied to the independent testing set of relapsed/refractory AML, the RASGRP1/APTX gene classifier stratified responders with 92% NPV and 28% PPV (compared with 18.5% prevalence of responders; Table 2). The associated odds ratio for being a responder was 4.4. While this was similar to the predictive accuracy of RASGRP1 alone, the application of the TSP classifier demonstrated a better NPV and an improved difference in median overall survival between predicted responders and progressors (Figures 1B,S1D). Similarly, the 2-gene classifier significantly stratified patients based on disease-free survival (P = .001).
As expected, baseline BM counts and ECOG performance scores were also significantly associated with overall survival in both univariate and multivariate analyses (Table 3). However, in the multivariate analysis the 2-gene classifier contributed most significantly to the model of overall survival when taking into account the traditional prognostic factors.
Cox univariate and multivariate analysis for overall survival in relapsed or refractory AML patients treated with tipifarnib
| Characteristic . | No. patients . | % . | Univariate analysis . | Multivariate analysis . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR . | 95% CI . | P . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | |||
| Age* | 1.2 | 0.68-2.14 | .53 | — | — | — | ||
| Older than 63 y | 25 | 53 | ||||||
| 63 y or younger | 27 | 47 | ||||||
| Sex | 0.768 | 0.45-1.33 | .34 | — | — | — | ||
| Male | 28 | 48 | ||||||
| Female | 30 | 52 | ||||||
| AML class | 0.645 | 0.38-1.11 | .11 | — | — | — | ||
| Relapsed | 31 | 53 | ||||||
| Refractory | 27 | 47 | ||||||
| Favorable karyotype | 0.97 | 0.54-1.72 | .93 | — | — | — | ||
| No | 40 | 69 | ||||||
| Yes | 18 | 31 | ||||||
| Baseline WBC | 1.71 | 0.88-3.34 | .11 | — | — | — | ||
| 30 × 109/L or more | 11 | 19 | ||||||
| Less than 30 × 109/L | 47 | 81 | ||||||
| ECOG prognostic score | 2.41 | 1.2-4.84 | .013 | 2.751 | 1.30-5.81 | .008 | ||
| Over 1 | 11 | 19 | ||||||
| 0 to 1 | 47 | 81 | ||||||
| Baseline BM blasts | 2.16 | 1.23-3.85 | .007 | 2.17 | 1.18-4.0 | .013 | ||
| Less than 40% | 23 | 40 | ||||||
| 40% or more | 35 | 60 | ||||||
| Bullinger CCP | 2.11 | 1.19-3.73 | .01 | 1.54 | 0.81-2.93 | .19 | ||
| Less than 208 | 26 | 45 | ||||||
| 208 or more | 32 | 55 | ||||||
| RASGRP1/APTX | 2.94 | 1.69-5.3 | < .001 | 3.34 | 1.79-6.25 | < .001 | ||
| Less than −1.102 | 28 | 48 | ||||||
| −1.102 or more | 30 | 52 | ||||||
| Characteristic . | No. patients . | % . | Univariate analysis . | Multivariate analysis . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR . | 95% CI . | P . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | |||
| Age* | 1.2 | 0.68-2.14 | .53 | — | — | — | ||
| Older than 63 y | 25 | 53 | ||||||
| 63 y or younger | 27 | 47 | ||||||
| Sex | 0.768 | 0.45-1.33 | .34 | — | — | — | ||
| Male | 28 | 48 | ||||||
| Female | 30 | 52 | ||||||
| AML class | 0.645 | 0.38-1.11 | .11 | — | — | — | ||
| Relapsed | 31 | 53 | ||||||
| Refractory | 27 | 47 | ||||||
| Favorable karyotype | 0.97 | 0.54-1.72 | .93 | — | — | — | ||
| No | 40 | 69 | ||||||
| Yes | 18 | 31 | ||||||
| Baseline WBC | 1.71 | 0.88-3.34 | .11 | — | — | — | ||
| 30 × 109/L or more | 11 | 19 | ||||||
| Less than 30 × 109/L | 47 | 81 | ||||||
| ECOG prognostic score | 2.41 | 1.2-4.84 | .013 | 2.751 | 1.30-5.81 | .008 | ||
| Over 1 | 11 | 19 | ||||||
| 0 to 1 | 47 | 81 | ||||||
| Baseline BM blasts | 2.16 | 1.23-3.85 | .007 | 2.17 | 1.18-4.0 | .013 | ||
| Less than 40% | 23 | 40 | ||||||
| 40% or more | 35 | 60 | ||||||
| Bullinger CCP | 2.11 | 1.19-3.73 | .01 | 1.54 | 0.81-2.93 | .19 | ||
| Less than 208 | 26 | 45 | ||||||
| 208 or more | 32 | 55 | ||||||
| RASGRP1/APTX | 2.94 | 1.69-5.3 | < .001 | 3.34 | 1.79-6.25 | < .001 | ||
| Less than −1.102 | 28 | 48 | ||||||
| −1.102 or more | 30 | 52 | ||||||
— indicates not applicable.
63 years was the median age for the whole population.
The RASGRP1/APTX classifier specifically predicts response to tipifarnib
We next investigated whether the RASGRP1/APTX classifier was predicting improved survival irrespective of tipifarnib treatment. Bullinger et al have previously identified a prognostic signature by performing cDNA microarray analysis of 116 patients with AML treated with chemotherapeutic regimes which included induction therapy of idarubicin, cytarabine, and etoposide (ICE), one consolidation cycle of high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone (HAM), and a risk-adapted late consolidation cycle based on cytogenetic findings.26 We first tested the utility of this gene signature in our Affymetrix gene expression dataset of patients with relapsed or refractory AML that were treated with tipifarnib (Document S1). Cluster analysis recapitulated the stratification of 2 distinct subgroups (Figure 2A). The groups were not significantly correlated with clinical response to tipifarnib; however, there was a significant difference in overall survival (Figure 2B; P < .001), indicating the Bullinger signature has utility in predicting prognosis in this group of patients.
RASGRP1/APTX is independent of the Bullinger prognostic classifier. (A) AML samples from 58 relapsed or refractory patients (including 4 patients with stable disease) were ordered according to hierarchic clustering using 93 probe sets that correspond to 75 of the 133 prognostic genes identified by Bullinger et al. Patients in cluster II are predicted to have a good prognosis. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival estimates of the hierarchic cluster–defined groups of patients. The median overall survival is 213 and 64 days for the good and poor prognostic subgroups, respectively. (C) The overall survival of the relapsed or refractory AML patient population stratified by the Bullinger CCP diagnostic classifier. The median overall survival is 128 and 73 days for the predicted good- and poor-prognosis patients, respectively. (D) The overall survival of patients stratified by both the Bullinger CCP prognostic classifier and the RASGRP1/APTX gene-expression ratio. “Double positive” patients are those who were predicted to both have a good prognosis and respond to tipifarnib. “Double negative” patients are those who are predicted to have a poor prognosis and be resistant to tipifarnib. “Positive/negative” patients are those who are predicted to either have a good prognosis and be resistant to tipifarnib or have a poor prognosis and respond to tipifarnib. The median overall survival was 182 days for “double positive” patients, 83 days for “positive/negative” patients, and 56 days for “double negative” patients, respectively (double positive vs positive/negative groups, P = .003; double negative vs positive/negative groups, P = .06).
RASGRP1/APTX is independent of the Bullinger prognostic classifier. (A) AML samples from 58 relapsed or refractory patients (including 4 patients with stable disease) were ordered according to hierarchic clustering using 93 probe sets that correspond to 75 of the 133 prognostic genes identified by Bullinger et al. Patients in cluster II are predicted to have a good prognosis. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival estimates of the hierarchic cluster–defined groups of patients. The median overall survival is 213 and 64 days for the good and poor prognostic subgroups, respectively. (C) The overall survival of the relapsed or refractory AML patient population stratified by the Bullinger CCP diagnostic classifier. The median overall survival is 128 and 73 days for the predicted good- and poor-prognosis patients, respectively. (D) The overall survival of patients stratified by both the Bullinger CCP prognostic classifier and the RASGRP1/APTX gene-expression ratio. “Double positive” patients are those who were predicted to both have a good prognosis and respond to tipifarnib. “Double negative” patients are those who are predicted to have a poor prognosis and be resistant to tipifarnib. “Positive/negative” patients are those who are predicted to either have a good prognosis and be resistant to tipifarnib or have a poor prognosis and respond to tipifarnib. The median overall survival was 182 days for “double positive” patients, 83 days for “positive/negative” patients, and 56 days for “double negative” patients, respectively (double positive vs positive/negative groups, P = .003; double negative vs positive/negative groups, P = .06).
Radmacher et al recently used a compound covariate prediction (CCP) algorithm to develop a classifier based on the Bullinger signature and validated it on an independent cohort of uniformly treated patients with normal cytogenetics.27 We also used the CCP algorithm using the gene weightings defined by Radmacher in our dataset and significantly stratified patients based on overall survival (Figure 2C; P = .009). There was no significant correlation between the stratified prognostic groups and any other clinical covariate, including response to tipifarnib, karyotype, baseline blasts, or WBC counts, or resistance or relapse to previous therapy (Table S5). This confirmed the prognostic utility of the Bullinger signature in tipifarnib-treated relapsed or refractory AML. Importantly, when the RASGRP1/APTX classifier was applied to the Bullinger-CCP classified groups, additional stratification was achieved (Figure 2D; P < .001). The 2-gene classifier was confirmed to be independent of other prognostic factors, including the Bullinger-CCP classifier, since it maintained a significant hazard ratio following Cox multivariate analysis (Table 3). Furthermore, when the RASGRP1/APTX classifier was applied to the Bullinger dataset, using a range of cutoffs, no significant separation in overall survival was seen (Table S6; Figure S3). These data indicated that the RASGRP1/APTX classifier specifically stratifies patients who have been treated with tipifarnib and has less prognostic relevance to non-FTI therapies.
In vitro validation of RASGRP1/APTX
A total of 6 leukemic cell lines (3 AML, 3 T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [T-ALL]) were profiled for sensitivity to tipifarnib and expression of RASGRP1 and APTX (Figure S4). The correlation between tipifarnib-mediated growth inhibition (IC50) and the RASGRP1/APTX expression ratio was 0.94 (Pearson correlation, P = .005), providing additional evidence that the classifier has utility in predicting response to tipifarnib in leukemia.
Discussion
Stratification of patient populations to predict therapeutic response is becoming increasingly valuable in the clinical management of patients with neoplastic disorders. For example, companion diagnostics are useful for the stratification of patients being treated with targeted therapies such as trastuzumab (Genentech, South San Francisco, CA) in metastatic breast cancer,31 and cetuximab (Merck, Whitehouse Station, NJ) in colorectal cancer.32 Predictive biomarkers are also being used for imatinib (Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) in gastrointestinal stromal tumors,33 and for erlotinib (OSI Pharmaceuticals, Farmingdale, NY) and gefitinib (Astra-Zeneca, Wilmington, DE) in lung cancer.34,35 Currently, a reliable biomarker to predict response to the FTI, tipifarnib, in any indication is unavailable. To identify genes that are associated with greater sensitivity to the FTI tipifarnib, we performed gene expression profiling of leukemic BM samples from a phase 2 study of poor-risk elderly patients with previously untreated AML.4 Importantly, an assay that aims to predict response to an antineoplastic therapy should have a high NPV, since it is necessary to capture as many potential responders as possible. Therefore, using criteria to identify markers that predict response with high sensitivity, we identified 38 genes in the newly diagnosed AML BM samples that were differentially expressed between responders and patients with progressive disease.
We found no significant correlation of NRAS mutations, cytogenetics, or baseline phosphorylation status of ERK or AKT and response to tipifarnib.2,4 Nonetheless, we did identify genes predictive of response to tipifarnib that are involved in RAS activation, including PTPN6 (a protein tyrosine phosphatase that is farnesylated, down-regulated in responders), CD3D, TRAT1, LTB, TNFRSF17, TNFSF13, and RASGRP1.36,–38 It is well known that activation of the RAS pathway can be caused by events other than constitutive activation of the RAS protein itself.39,40 Indeed, NRAS and KRAS have been identified in their activated state in AML in the absence of activating mutations.12 It is therefore plausible that RAS signaling deregulation is an important target of tipifarnib in AML regardless of RAS mutational status.41 In support of this, Feldkamp et al demonstrated that isotype-specific RAS.GTP levels in brain tumors correlates with response to the FTI SCH66336 irrespective of RAS-activating mutations.42 In addition, Bild et al recently showed that a gene-expression signature based on RAS overexpression could predict response to another FTI in vitro.43 However, we have been unable to find an association with their classifier and response to tipifarnib using our clinically relevant gene-expression datasets.
RASGRP1 was the most robust single predictive gene-expression marker with an overall predictive accuracy of 96% in the cross-validated training set. RASGRP1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that specifically activates RAS.38 Expression of RASGRP1 has been found in the brain, T cells, cells of monocytic lineage, and primitive hematopoietic precursors.44,–46 Interestingly, another RASGRP (RASGRP4) was previously identified as a potential oncogene in AML.47 The present data, however, are the first to examine and demonstrate expression of RASGRP1 in AML cells in addition to implicating its importance in response to FTIs.
How might increased RASGRP1 expression lead to sensitivity to FTIs? RASGRP1 has been shown to activate HRAS and NRAS, but not KRAS, exclusively on the Golgi apparatus.48,49 Further, KRAS and NRAS can be alternatively geranylgeranylated following farnesyltransferase inhibition.50 HRAS, on the other hand, is only farnesylated, and this may explain the observation that tumors transformed with HRAS are more sensitive to FTIs than those transformed with NRAS or KRAS.9,51 Thus, it is possible that elevated expression of RASGRP1 in AML leads to activation of the NRAS and HRAS pathways, but it is the blockage of HRAS that is causing the antitumorigenic effect. Therefore, while HRAS-activating mutations have not been identified in AML, the specific activation of HRAS pathways by other means (such as RAS-specific GEFs) may still be a target of FTIs in certain tumors. Further experiments will be required to test this hypothesis.
We previously identified AKAP13 expression as being predictive of resistance to tipifarnib in relapsed or refractory AML.6,13 Interestingly, AKAP13 is also a GEF, but activates the RHO pathway.52 However, while showing utility in relapsed or refractory AML, expression of AKAP13 did not demonstrate predictive utility in newly diagnosed AML. This may be because the leukemic cell becomes more “addicted” to AKAP13 expression only in late-stage disease. The other question that arises is why overexpression of the RASGRP1 GEF increases sensitivity while overexpression of the AKAP13 GEF increases resistance to tipifarnib. RHO GEFs have been found to drive cellular transformation in a RAS-independent fashion.53,54 Thus, one hypothesis is that AKAP13 activates a downstream compensatory pathway in RHOA while RAGRP1 activates RAS, a clear target of FTIs. We recognize that additional biochemical analyses will need to be done to investigate this model. Nevertheless, the identification of 2 GEFs playing opposing roles in responsiveness to an FTI does highlight the importance of this class of small GTPase activators in FTI-mediated therapy. It also highlights the need for multiple markers in predicting response to targeted therapies across a wide range of diseases and disease subtypes. As GEFs are increasingly becoming attractive drug targets, it may also be of interest to investigate combination therapies of FTIs and inhibitors of specific GEFs.
We found that the combination of RASGRP1 and APTX provided the most robust predictive accuracy (approximately 96%) for a multigene classifier. APTX is involved in DNA excision repair and was found to be down-regulated in responders.29 Defective DNA repair may lead to a cellular environment that is more conducive to apoptosis that, in turn, may allow for better outcome in these patients.30 Additional work will need to be performed to investigate the importance of APTX in AML. The 2-gene classifier showed predictive utility in the discovery set of newly diagnosed AML when a cross-validation of the microarray data and an independent QPCR assay were performed. In the absence of a larger independent set of newly diagnosed AML samples, we also used 54 relapsed or refractory AML samples from our previous investigation as an independent testing set.6,13 Surprisingly, even though the samples were from a biologically distinct population of AML patients, the 2-gene classifier showed significant stratification of responders and nonresponders (odds ratio = 4.4), resulting in an increase in overall response of approximately 50%. Furthermore, the stratified predicted responders had a median overall survival that was approximately 3-fold longer than patients predicted to be resistant to tipifarnib. Importantly, we found no significant association with the 2-gene classifier and patient prognosis in an independent set of patients with AML who were treated with conventional cytotoxic chemotherapeutics. This indicated that the current classifier specifically predicts response to tipifarnib treatment. Further work needs to be done to clarify whether the RASGRP1/APTX expression ratio has utility for other classes of FTIs, and whether a QPCR assay can be applied in clinical practice.
Tipifarnib has recently been demonstrated to have potential utility in T-ALL in an in vitro screening model.55 To validate the utility of the 2-gene classifier, we showed that RASGRP1/APTX expression correlated with response to tipifarnib in AML and T-ALL cell lines. Since RASGRP1 is generally highly expressed in T-ALL, it will be of interest to investigate the association between RASGP1 expression levels and response to FTIs in patients with this disease.
In summary, we have identified and validated a 2-gene expression ratio that can be assayed using simple QPCR. The classifier has predictive utility in both newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory AML. In addition, stratification with this classifier significantly predicts for improved overall survival, which is independent of other prognostic factors including a previously described genomic signature. Our data compares favorably to the use of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved companion diagnostics for targeted cancer therapies such as trastuzumab. For instance, it has been demonstrated that stratification of patients with metastatic breast cancer with overexpression of ERBB2 predicts an improved overall response to trastuzumab and paclitaxel combination therapy, with odds ratios of 2.6 and 3.9 when using the HercepTest (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) or PathVysion tests (Abbott, Des Plaines, IL), respectively.31 Our data therefore indicate that a simple 2-gene expression assay may have similar utility in diagnosing a population of patients with AML who are more likely to respond to tipifarnib.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jackie Greer for coordinating sample collection; Mary Ellen Rybak and Wayne Rackoff from Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development, and David Atkins from Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, who supported this pharmacogenomic investigation; Tao Shi and Yi Zhang for statistical input; and Dr Scott Kaufmann for critical review of the manuscript. Finally, we thank the patients, and their families, who participated in this study.
Authorship
Contribution: M.R. designed the correlative study and wrote the paper; H.F. performed the statistical analyses; L.D. and G.L. performed laboratory assays; I.G., E.J.F., J.G., L.M., J.-L.H., J.E.L., B.L., R.S., P.L.G., J.J.W., and J.E.K. performed the clinical research and contributed vital new reagents; and Y.W. participated in the design of the analyses.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.R., H.F., L.D., G.L., P.D.P., and Y.W. are employees of a company (Johnson and Johnson) whose product (Tipifarnib) was studied in the present work. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Mitch Raponi, Veridex LLC, A Johnson and Johnson Co, 3210 Merryfield Row, San Diego, CA, 92121; e-mail: mraponi1@ocdus.jnj.com.