Abstract
A somatic mutation (V617F) in the pseudokinase domain of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase JAK2 is found in virtually all patients with the myeloproliferative disease (MPD) polycythemia vera (PV), and about half of those with essential thrombocythemia and chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis. When expressed in mice by retroviral bone marrow transduction and transplantation, JAK2 V617F but not JAK2 wild-type induces leukocytosis with neutrophilia and recapitulates the entire erythroid phenotype of PV, with polycythemia, reticulocytosis, low plasma Epo, and endogenous erythroid colonies (
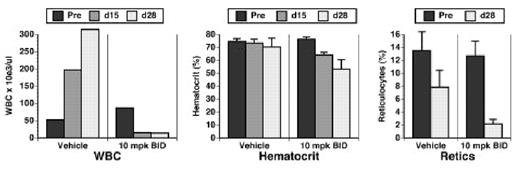
An orally available JAK2 inhibitor decreases the leukocyte count, hematocrit, and reticulocyte count in mice with JAK2 V617F-induced MPD. Leukocyte count (left), hematocrit (center) and reticulocyte counts (right) of cohorts of mice with JAK2 V617F-induced MPD treated with vehicle or drug at 10 mg/kg BID. Blood counts were assessed at 15 and 28 days of treatment. Decreases in d28 hematocrit and retic count in the drug-treated cohorts were significant (p=0.008 and p<0.0001, respectively, t-tests).
Author notes
Disclosure:Employment: R.C., M.Z., and D.H. are employees of AstraZeneca. Research Funding: R.A.V. receives research funding from AstraZeneca. Membership Information: R.A.V. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of AstraZeneca.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal