Abstract
Chaetocin, a thiodioxopiperazine natural product previously unreported to have anticancer effects, was found to have potent antimyeloma activity in IL-6–dependent and –independent myeloma cell lines in freshly collected sorted and unsorted patient CD138+ myeloma cells and in vivo. Chaetocin largely spares matched normal CD138− patient bone marrow leukocytes, normal B cells, and neoplastic B-CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) cells, indicating a high degree of selectivity even in closely lineage-related B cells. Furthermore, chaetocin displays superior ex vivo antimyeloma activity and selectivity than doxorubicin and dexamethasone, and dexamethasone- or doxorubicin-resistant myeloma cell lines are largely non–cross-resistant to chaetocin. Mechanistically, chaetocin is dramatically accumulated in cancer cells via a process inhibited by glutathione and requiring intact/unreduced disulfides for uptake. Once inside the cell, its anticancer activity appears mediated primarily through the imposition of oxidative stress and consequent apoptosis induction. Moreover, the selective antimyeloma effects of chaetocin appear not to reflect differential intracellular accumulation of chaetocin but, instead, heightened sensitivity of myeloma cells to the cytotoxic effects of imposed oxidative stress. Considered collectively, chaetocin appears to represent a promising agent for further study as a potential antimyeloma therapeutic.
Introduction
Chaetocin, a small-molecule natural product produced by Chaetomium species fungi,1,2 is representative of a class of fungal secondary metabolites known as thiodioxopiperazines sharing in common a characteristic disulfide-bridged piperazine ring. Although the biologic effects of several thiodioxopiperazines (most prominently gliotoxin) have been previously studied, those of chaetocin have remained almost entirely unexplored. Other thiodioxopiperazines, however, have been previously reported to have a wide range of biologic activities, including antimicrobial,3 antiparacitic,4 antiviral,5 immunosuppressive,6 and/or anti-inflammatory effects.7 Although some thiodioxopiperazines also have antineoplastic activity,8–11 none has yet been evaluated for antimyeloma activity. Presumably, thiodioxopiperazines may be produced by fungi to gain a competitive advantage over adjacent fungal and other saprophytic organisms through toxic and antiproliferative effects on adjacent organisms.12
Based upon promising preclinical activity, there is currently much interest in the development of inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDACs) as potential therapeutics for multiple myeloma,13–16 with HDAC inhibitors now undergoing early evaluation in the clinic as potential antimyeloma therapeutics.17 We hypothesized that chaetocin might represent a potential antimyeloma therapeutic based upon its chemical structural similarities to the acetylated lysine residue of histones that is mimicked by histone deacetylase inhibitors (Figure 1A). 18 However, although preliminary studies demonstrated chaetocin to have potent antimyeloma activity in vitro and to inhibit HDACs in 1 cancer cell line (A549) at high concentrations, chaetocin was not found to inhibit HDACs at cytotoxic concentrations in myeloma cells, prompting more detailed testing and mechanistic studies. We now report for the first time the assessment of the antimyeloma effects and mechanisms of action of chaetocin.
Chaetocin bears chemical structural similarity to the acetylated histone lysine moiety mimicked by many histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) and has antimyeloma activity in vitro yet does not appreciably alter levels of acetylated histone H3 in myeloma cells. (A) The chemical structure of chaetocin, indicating similarities to the acetylated histone lysine moiety. (B-C) Effects of chaetocin (24-hour drug exposures) on survival (assessed by trypan blue exclusion) of KAS-6 IL-6–dependent myeloma cells (B) or OCI-MY5 IL-6–independent myeloma cells (C) in vitro. Displayed results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (D) Effects of chaetocin on the cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 in A549 human non–small-cell lung cancer cells. (E) Effects of chaetocin or the known HDACIs aphidicolin, LAQ 824, or trichostatin A on the cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 in U266 human myeloma cells. (D-E) Levels of acetylated histone H3 and actin were assessed using immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates (50 μg total cellular proteins loaded per lane, 24-hour drug exposures).
Chaetocin bears chemical structural similarity to the acetylated histone lysine moiety mimicked by many histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) and has antimyeloma activity in vitro yet does not appreciably alter levels of acetylated histone H3 in myeloma cells. (A) The chemical structure of chaetocin, indicating similarities to the acetylated histone lysine moiety. (B-C) Effects of chaetocin (24-hour drug exposures) on survival (assessed by trypan blue exclusion) of KAS-6 IL-6–dependent myeloma cells (B) or OCI-MY5 IL-6–independent myeloma cells (C) in vitro. Displayed results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (D) Effects of chaetocin on the cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 in A549 human non–small-cell lung cancer cells. (E) Effects of chaetocin or the known HDACIs aphidicolin, LAQ 824, or trichostatin A on the cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 in U266 human myeloma cells. (D-E) Levels of acetylated histone H3 and actin were assessed using immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates (50 μg total cellular proteins loaded per lane, 24-hour drug exposures).
Patients, materials, and methods
Reagents
Chaetocin, doxorubicin, dexamethasone, apicidin, trichostatin A, reduced glutathione, N-acetyl cysteine, H2O2, aphidicolin, DRB (5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole), DL-buthionine-(S, R)-sulfoximine (BSO), and cycloheximide were purchased from Sigma (St Louis, MO). Tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRM), 5,6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (CMH2DCFDA), and hydroethiduum (HE) were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). LAQ 824 (a small-molecule HDAC inhibitor currently in clinical trials)15 was kindly provided by Drs Chunrong Yu and Alex Adjei (Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN).
Cell culture
Cells were cultured in the following media: A549 (obtained from American Type Culture Collection, Chicago, IL) in RPMI 1640 containing 5% FBS; myeloma cell lines KAS6/1, OCI-MY5, MM1S/R, and RPMI 8226S/R in RPMI 1640 containing 10% FBS; patient bone marrow cells in MEM containing 20% FBS; KAS6/1 cells were supplemented with 1 ng/mL IL-6. All media contained 100 U/mL penicillin G, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 2 mM l-glutamine. Cells lines were passaged twice weekly and maintained at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 95% air–5% CO2 (vol/vol).
Patient samples
All described ex vivo experiments used excess/waste bone marrow cells obtained from patients in conjunction with their standard clinical care and in accord with institutional review board (IRB)–approved protocols, with consent provided in accord with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Colony-forming assays
Briefly, 650 suspended A549 cells obtained from trypsinization of stock flasks of subconfluent cell cultures were deposited into each of triplicate sets of 35-mm tissue-culture plates and allowed to adhere for 16 hours. Cells were then treated for 24 hours with diluent and/or drugs as indicated. After drug removal and washing, cells were allowed to proliferate in drug-free medium for 7 to 10 days, washed twice with serum-free phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), stained with Coomassie blue, and then manually counted.
Assessment of drug effects on patient cells
Patient bone marrow cells were collected via posterior superior iliac crest bone marrow aspiration under local anesthesia in accord with approved Mayo Clinic IRB protocols. Patient bone marrow leukocytes were divided into myeloma (CD138+) and nonmyeloma/normal leukocyte (CD138−) fractions employing sorting using magnetic bead technology in kit form (magnetic-activated cell separation [MACS] CD138 microbeads; Miltenyi Biotech, Auburn, CA). Sorted cells were plated in 96-well tissue-culture plates at a concentration of 5 × 105 cells and dosed with indicated drug concentrations for 24 hours. Survival was assessed using a trypan blue exclusion assay.
Fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analyses assessing the effects of chaetocin on marrow cell populations were accomplished using anti–annexin V (Caltag Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and 7 amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD; Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) staining to identify viable, apoptotic, and dead cells. Briefly, 100 μL of treated unsorted cells washed and resuspended in annexin-binding buffer (ABB; 0.15 M NaCl, 0.0033 M CaCl2 HEPES buffer, pH 7.4; 1 × 106 cells/100 μL) was added to each of 2 tubes along with 5 μL each anti–annexin V fitc, anti-CD38 pe (phycoerythrin), and anti-CD45 apc in 1 tube and anti-CD56 fitc, anti-CD38 pe, and anti-CD45 apc in the second. Cells were incubated (4°C, 15 min), washed with ABB, and resuspended in 500 μL of ABB, and 2.5 μL of 7-AAD (2 mg/mL stock) was then added to each tube. Cells were subsequently incubated 15 minutes, washed, resuspended in 500 μL of ABB, and immediately run on a FACScaliber (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) with data analyzed using Cellquest Pro Software (BD Biosciences). Multivariate analysis using the typical CD45−, bright CD38 gating and forward scatter (FSC) versus side scatter (SSC) (size vs granularity) identified the viable, apoptotic, and dead fractions of examined cell populations.
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells were obtained from patients with persistent lymphocytosis of greater than 5 × 109 lymphocytes/L; a CD5+, dim surface Ig expression; and monoclonal κ or λ expression. Peripheral-blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from heparinized blood by Ficoll (Gallard-Schlesinger Industries, Plainview, NY) density gradient centrifugation were washed twice with normal saline, counted using a Vi Cell XR cell viability analyzer (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, CA), and resuspended to 100 million/mL in PBS with 2% FBS, and the B-cell population was isolated using the Human B-Cell Enrichment Kit (without CD43 depletion; StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) in conjunction with a RoboSep Fully Automated Cell Separator (StemCell Technologies). After separation, cells were washed twice in sterile saline and counted. Cell purity assessed with CD19 fitc and CD5 pe (both from BD Biosciences) was routinely above 98%. Resulting red blood/polynuclear pellets from the Ficoll step were lysed by addition of 5 mL ACK Lysis Solution (BioSource International/Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA; 10 min, 37°C), washed twice with sterile saline, and used for subsequent neutrophil experiments. Isolation of normal human B cells used a similar procedure, saving that Human CD 19 Positive Selection Kit (StemCell Technologies) was used for separation on the RoboSep described above.
Assessment of apoptosis
Apoptosis was assessed using transmission electron microscopy (JOEL 1200; JOEL, Pleasanton, CA; 792 Gatan Camera; Digital Micrograph v. 3.4 acquisition software) and Hoechst 33258 staining using fluorescence microscopy by examining cells for apoptotic morphologic changes, expressing number of apoptotic cells as a percentage of 200 total counted cells, as previously described.19
Evaluation of loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm)
Chaetocin-treated OCI-MY5 cells were sedimented, washed with PBS, resuspended in medium, stained with TMRM (50 nM, 45 min, 37°C), placed on ice for 5 minutes, and immediately subjected to flow microfluorometry using a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, CA; 488-nm laser). Fluorescence emission was observed through a 585/42-nm filter, and 20 000 events were analyzed using CellQuest software (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME).
Immunoblotting
Cells grown in suspension culture at densities of 3 × 105 to 6 × 105 cells/mL and treated as indicated were washed 3 times with PBS, lysed in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 400 mM NaCl; 0.5% NP-40; 10% glycerol; 1 mM EDTA supplemented immediately before use with 10 ng/μL pepstatin A, 500 μM PMSF, 10 ng/μL leupeptin, 10 ng/μL aprotinin, and 200 μM sodium orthovanidate), and processed for SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subsequent immunoblotting for acetylated histone H3 (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA), poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP; BD PharMingen, San Diego, CA), and actin (Sigma).
Evaluation of DNA ladder formation
Chaetocin- and diluent-treated OCI-MY5 cells treated as indicated were washed twice with PBS and processed for DNA electrophoresis, with gel bands visualized and documented using a Syngene Image documentation system (Frederick, MD).
Measurement of intracellular and extracellular chaetocin levels
Tumor cells treated with indicated chaetocin concentrations were washed twice with ice-cold PBS, immediately solubilized in 0.5 M perchloric acid, and evaluated “real-time” via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using Beckman System Gold Nouveau Software with a dual-pump 125 gradient pump system, 507e autosampler, 168 diode array detector, and Beckman Ultrasphere ODS column (4.6 mm ×15 mm × 7 μm) using the following elution profile: 100% water to 100% methanol linear gradient over 40 minutes followed by a 10-minute period of elution with 100% methanol. Quantitation was accomplished using a standard curve of peak areas derived from analogous HPLC data using varying concentrations of chaetocin.
Chemical modifications of chaetocin
Reduced chaetocin was prepared by treating chaetocin with 100 mM dithiothreitol for 30 minutes at room temperature. To synthesize S-methyl chaetocin, sodium borohydride (1.7 mg, 0.046 mmol) was added to chaetocin (2 mg, 0.0029 mmol) in 75% dichloromethane and 25% methanol at 0°C under dry nitrogen and stirred for 1 hour before addition of excess methyl iodide (3.2 mmol).20 The solution was stirred for an additional 16 hours and washed with 10% HCl (1 × 0.5 mL), and the organic layer was then extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 1 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried over magnesium sulfate, and evaporated to dryness. When compared with the 1H NMR spectra of chaetocin, 2 new peaks were observed (2.2 ppm, s, 6H; 1.8 ppm, s, 6H), confirming reduction and methylation of the disulfide bonds. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was also performed to confirm the identity of the compound, calculated as follows: [M+H+] = 757.8, Found: [M+H+] = 757.2, [M + NH
Assessment of cellular oxidative stress
Cellular oxidative stress was assessed using 5,6-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (CMH2DCFDA) or hydroethiduum (HE), as cell-permeable fluorescent probes, and FACS analyses. Briefly, cells were treated with the indicated drug for 24 hours and incubated in warm PBS containing 6 μM (CMH2DCFDA) or 2 μM (HE) probe at 37°C for 1 hour, after which time the PBS + probe was removed and cells were allowed to recover in warm media for 15 minutes. Cells were then sedimented and resuspended in cold PBS before flow microfluorimetry (FACScan flow cytometer; Becton Dickinson) with a 488-nm laser. Fluorescence emission was observed through a 530/30-nm filter, and 20 000 events were analyzed using CellQuest software (Verity Software House).
Assessment of intracellular glutathione
Reduced glutathione was quantitated using a kit (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) that employs glutathione reductase and colorimetric detection of the breakdown product of DTNB. Briefly, treated cells were washed, lysed by sonication in MES buffer, and deproteinated by metaphosphoric acid. The assay quantitated total glutathione and oxidized glutathione using 2-vinylpyridine to derivatize GSH (detection at 405 nm; Beckman AD340 plate reader; Beckman Coulter). Reduced glutathione values were obtained by subtracting oxidized from total glutathione.
In vivo experiments
The in vivo effects of chaetocin were preliminarily explored at Southern Research Institute with assistance from Dr William Waud (Birmingham, AL) in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice using established subcutaneously flank-implanted RPMI 8226 myeloma xenografts employing a twice-weekly intraperitoneal administration schedule, with chaetocin formulated in 25% DMSO and 75% PEG400. Tumor weights were calculated from volumes derived from direct tumor measurements. The control group consisted of 10 animals, whereas treatment groups consisted of 6 animals each.
Statistics
Differences between cell lines were assessed using 2-sided t tests and pooled estimates of variance.
Results
Chaetocin potently kills IL-6–dependent and –independent myeloma cell lines
To preliminarily assess the antimyeloma effects of chaetocin, we used IL-6–dependent KAS-6 and IL-6–independent OCI-MY5 cells. Chaetocin (Figure 1A) readily killed both lines without cellular recovery at chaetocin concentrations above about 25 nM (Figure 1B and C, respectively). Other tested myeloma cell lines including RPMI 8226 and MM1 were also similarly killed by chaetocin (Figure S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Figures link at the top of the online article).
Chaetocin has structural similarities to HDACIs yet does not appreciably alter cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 at cytotoxic concentrations in myeloma cells
As chaetocin bears a high degree of structural similarity to the acetylated histone lysine moiety mimicked by many histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs; Figure 1A),18 we evaluated whether HDAC inhibition might accompany chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity. Although treatment of A549 human non–small-cell lung cancer cells with high-nanomolar chaetocin concentrations led to increased acetylated histone H3 levels (Figure 1D), treatment of U266, KAS 6/1, or OCI-MY5 human myeloma cells with chaetocin had no appreciable effects on cellular levels of acetylated histone H3 (Figure 1E; data not shown). Because chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity was unexpectedly not correlated with observed induced alterations in levels of acetylated histone H3 in myeloma cells, we next pursued additional mechanistic studies in search of an alternative explanation for chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity.
Chaetocin kills myeloma cells in vitro via induction of morphologic apoptosis accompanied by DNA ladder formation and PARP cleavage
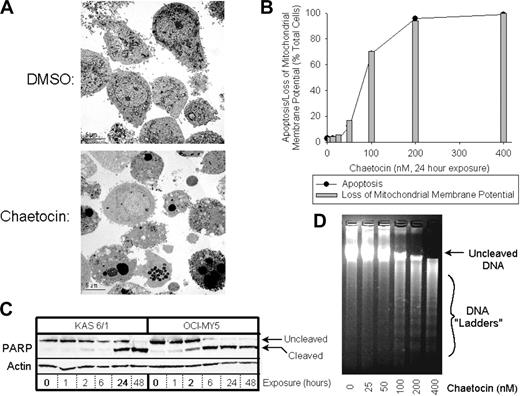
In vitro antimyeloma activity of chaetocin was associated with induction of apoptotic morphologic changes as assessed by electron microscopy (Figure 2A), Hoechst 33258 staining (Figure 2B), loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (Figure 2B), PARP cleavage (Figure 2C), and DNA ladder formation (Figure 2D).
Chaetocin kills myeloma cells in vitro via induction of morphologic apoptosis accompanied by loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, PARP cleavage, and DNA ladder formation. (A) Transmission electron photomicrographs (4000×) of OCI-MY5 myeloma cells treated with DMSO or 100 nM chaetocin for 24 hours. (B) Effects of 24-hour exposure of OCI-MY5 myeloma cells to varying chaetocin concentrations on mitochondrial membrane depolarization (⊡) and apoptosis (•). Mitochondrial membrane potential was assessed via FACS, whereas apoptosis was assessed via fluorescence microscopy using Hoechst 33256 staining as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Results shown are representative of 4 independent experiments. (C) Induction of PARP cleavage in KAS 6/1 and OCI-MY5 myeloma cells by 100 nM chaetocin (time course). Upper bands represent the results of PARP immunoblotting, whereas the lower band indicates actin control immunoblotting. Results shown are representative of 4 independent experiments. (D) Electrophoresis of DNA extracted from diluent- or chaetocin-treated OCI-MY5 myeloma cells for 24 hours. Bands corresponding to uncleaved DNA and cleaved DNA ladders are indicated at the right. Results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Chaetocin kills myeloma cells in vitro via induction of morphologic apoptosis accompanied by loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, PARP cleavage, and DNA ladder formation. (A) Transmission electron photomicrographs (4000×) of OCI-MY5 myeloma cells treated with DMSO or 100 nM chaetocin for 24 hours. (B) Effects of 24-hour exposure of OCI-MY5 myeloma cells to varying chaetocin concentrations on mitochondrial membrane depolarization (⊡) and apoptosis (•). Mitochondrial membrane potential was assessed via FACS, whereas apoptosis was assessed via fluorescence microscopy using Hoechst 33256 staining as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Results shown are representative of 4 independent experiments. (C) Induction of PARP cleavage in KAS 6/1 and OCI-MY5 myeloma cells by 100 nM chaetocin (time course). Upper bands represent the results of PARP immunoblotting, whereas the lower band indicates actin control immunoblotting. Results shown are representative of 4 independent experiments. (D) Electrophoresis of DNA extracted from diluent- or chaetocin-treated OCI-MY5 myeloma cells for 24 hours. Bands corresponding to uncleaved DNA and cleaved DNA ladders are indicated at the right. Results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Chaetocin selectively kills freshly collected sorted patient CD138+ myeloma cells with superior efficacy to the commonly used antimyeloma agents dexamethasone and doxorubicin
We next undertook more rigorous studies employing freshly collected sorted CD138+ myeloma cells from 20 patients in accord with an approved IRB protocol, using matched negatively sorted patient CD138− bone marrow leukocytes as controls. In all evaluated patient samples, chaetocin demonstrated dramatic antimyeloma activity while largely sparing matched (CD138−) normal bone marrow leukocytes (Figure 3A-C; representative results from 3 patients shown). Impressively, the antimyeloma effects of chaetocin were uniformly superior to those produced by therapeutically relevant doses of the first-line antimyeloma agents doxorubicin and dexamethasone (Figure S2). Furthermore, the potent and selective antimyeloma effects of chaetocin were observed in samples obtained from patients afflicted with a broad range of different myeloma subtypes, including smoldering myeloma and heavily treated myeloma after peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation, as well as in myeloma cells demonstrating a wide array of cytogenetic abnormalities (see Figure 3A-C for examples; patient details provided in figure legend).
Chaetocin kills freshly collected sorted patient CD138+ myeloma cells while sparing matched normal CD138− bone marrow leukocytes, normal B cells, and neoplastic B-CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) cells. Results from 3 representative myeloma patients (of 20 similarly assessed; A-C), 3 healthy patients (D-F), and 3 B-CLL patients (G-H) are displayed. (A-C) Chaetocin kills patient myeloma cells while sparing matched normal patient leukocytes. Patient A (M-1) had therapy-refractory myeloma, failing prior treatment with thalidomide, dexamethasone, and bortezomib (labeling index = 0.6%); patient B (M-2) had previously untreated smoldering myeloma (labeling index = 1%); patient C (M-3) had stable disease, currently undergoing treatment with dexamethasone (labeling index = 0.2%). (D-F) Chaetocin treatment of normal B cells or matched leukocytes from 3 healthy patients indicates that, unlike myeloma cells, normal B cells are not selectively killed by chaetocin. (G-H) Treatment of B-CLL cells or matched patient leukocytes from 2 B-CLL patients with chaetocin also indicates that, unlike myeloma cells, B-CLL cells are not selectively killed by chaetocin. All patient samples were treated with chaetocin for 24 hours, with survival assessed at that time using trypan blue exclusion and quantitation with a hemocytometer.
Chaetocin kills freshly collected sorted patient CD138+ myeloma cells while sparing matched normal CD138− bone marrow leukocytes, normal B cells, and neoplastic B-CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) cells. Results from 3 representative myeloma patients (of 20 similarly assessed; A-C), 3 healthy patients (D-F), and 3 B-CLL patients (G-H) are displayed. (A-C) Chaetocin kills patient myeloma cells while sparing matched normal patient leukocytes. Patient A (M-1) had therapy-refractory myeloma, failing prior treatment with thalidomide, dexamethasone, and bortezomib (labeling index = 0.6%); patient B (M-2) had previously untreated smoldering myeloma (labeling index = 1%); patient C (M-3) had stable disease, currently undergoing treatment with dexamethasone (labeling index = 0.2%). (D-F) Chaetocin treatment of normal B cells or matched leukocytes from 3 healthy patients indicates that, unlike myeloma cells, normal B cells are not selectively killed by chaetocin. (G-H) Treatment of B-CLL cells or matched patient leukocytes from 2 B-CLL patients with chaetocin also indicates that, unlike myeloma cells, B-CLL cells are not selectively killed by chaetocin. All patient samples were treated with chaetocin for 24 hours, with survival assessed at that time using trypan blue exclusion and quantitation with a hemocytometer.
In order to further explore the antimyeloma activity of chaetocin in comparison to dexamethasone or doxorubicin, we next evaluated the effects of chaetocin in paired myeloma cell lines resistant to each of these 2 drugs. In particular, dexamethasone-resistant MM1RL cells21 were found to be equally sensitive to chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity as were dexamethasone-sensitive MM1S cells, despite maintaining a high level of resistance to dexamethasone (Figure S1A-B), confirming no cross-resistance to chaetocin. We additionally found that P-glycoprotein–overexpressing 8226R cells22 exhibited only modest cross-resistance to chaetocin in comparison to doxorubicin (Figure S1C-D). Hence, studies employing drug-resistant myeloma cell lines recapitulated ex vivo results to confirm that dexamethasone- or doxorubicin-resistant myeloma cells appear largely non–cross-resistant to chaetocin.
Whereas chaetocin potently and selectively kills sorted patient myeloma cells, it largely spares closely lineage-related normal B lymphocytes and neoplastic B-CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) cells
To further examine the selectivity of chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity in patient hematologic cells more closely lineage-related to myeloma/plasma cells, we studied the effects of chaetocin in sorted normal patient B lymphocytes and in neoplastic B-CLL cells (myeloma/plasma cells are of B-cell lineage). Impressively, chaetocin did not differentially kill sorted patient normal B lymphocytes (Figure 3D-F) or sorted patient neoplastic B-CLL cells (Figure 3G-H), indicating a high degree of selectivity of the cytotoxic effects of chaetocin even in very closely lineage-related normal and neoplastic B cells.
Chaetocin potently kills patient myeloma cells when treated in mixed bone marrow cultures
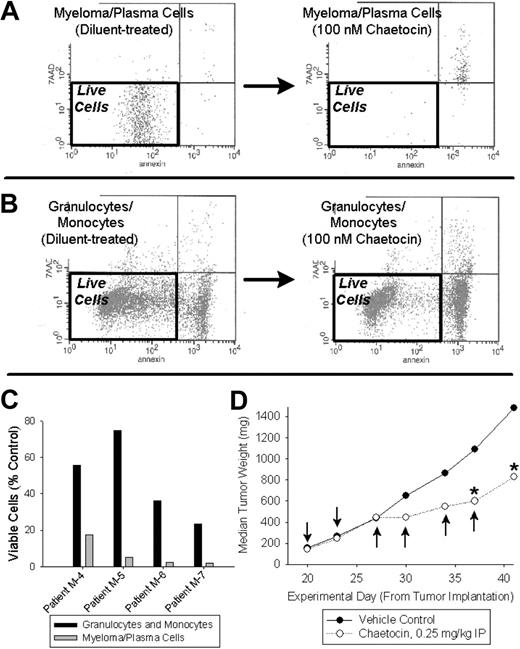
Over concern that the observed cytotoxic effects of chaetocin might reflect an artifact seen only in sorted myeloma cells, we evaluated chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity in myeloma cells and paired granulocytes/monocytes treated in mixed bone marrow cultures. Unsorted bone marrow cells obtained from relapsed myeloma patients were treated with chaetocin (100 nM) or diluent in mixed culture (24 hours), with the cytotoxic effects of chaetocin evaluated using multi-channel FACS analyses. Consistent with the selectivity observed in sorted cells, chaetocin also killed myeloma cells with selectivity in comparison to control patient granulocytes/monocytes in mixed culture (Figure 4A-C).
Patient myeloma cells treated in whole bone marrow cell–mixed culture are selectively killed by chaetocin in comparison to other bone marrow leukocytes, and chaetocin has in vivo antimyeloma activity. (A-C) Unsorted bone marrow leukocytes obtained from 4 patients with multiple myeloma were treated with 100 nM chaetocin or diluent for 24 hours and subjected to FACS analyses examining cell death in various leukocyte subpopulations. Myeloma cells were readily killed by chaetocin (A; representative data shown), and combined granulocytes and monocytes (B; representative data shown) were relatively spared. Results from 4 unsorted patient marrow leukocyte samples are indicated in panel C, with surviving cells defined as those with low annexin and 7-AAD staining. (D) Chaetocin has in vivo antimyeloma activity in established RRMI 8226 SCID flank xenograft mouse tumors. Arrows indicate times of intraperitoneal chaetocin administration, whereas * indicates statistically significant differences from corresponding vehicle control values (P < .05). The control group consisted of 10 animals, and treatment groups consisted of 6 animals each.
Patient myeloma cells treated in whole bone marrow cell–mixed culture are selectively killed by chaetocin in comparison to other bone marrow leukocytes, and chaetocin has in vivo antimyeloma activity. (A-C) Unsorted bone marrow leukocytes obtained from 4 patients with multiple myeloma were treated with 100 nM chaetocin or diluent for 24 hours and subjected to FACS analyses examining cell death in various leukocyte subpopulations. Myeloma cells were readily killed by chaetocin (A; representative data shown), and combined granulocytes and monocytes (B; representative data shown) were relatively spared. Results from 4 unsorted patient marrow leukocyte samples are indicated in panel C, with surviving cells defined as those with low annexin and 7-AAD staining. (D) Chaetocin has in vivo antimyeloma activity in established RRMI 8226 SCID flank xenograft mouse tumors. Arrows indicate times of intraperitoneal chaetocin administration, whereas * indicates statistically significant differences from corresponding vehicle control values (P < .05). The control group consisted of 10 animals, and treatment groups consisted of 6 animals each.
Chaetocin has in vivo antimyeloma activity
Preliminary in vivo experiments demonstrated antiproliferative activity of chaetocin (0.25 mg/kg intraperitoneally twice weekly) in an RPMI 8226 myeloma SCID mouse model of established flank xenografts (P < .05), with T/C (treatment/control) values in the 50% to 60% range (Figure 4D).
Chaetocin is rapidly and dramatically accumulated in cancer cells by means that require intact/unreduced chaetocin disulfide bonds
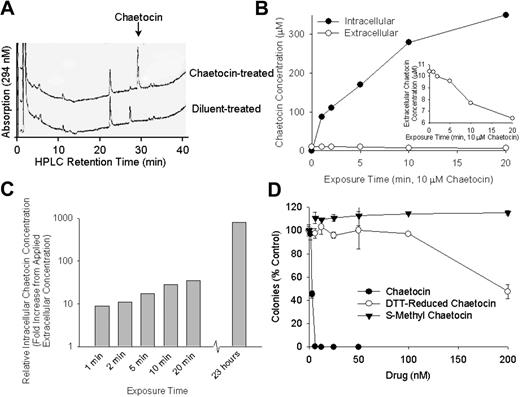
Having encountered promising in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo antimyeloma activity of chaetocin, we undertook detailed studies of its cellular handling and mechanisms of action. As the related compound gliotoxin is concentrated in mammalian cells,23 we evaluated whether chaetocin might be subject to intracellular accumulation in myeloma cell lines, freshly collected patient myeloma cells, and A549 cells. Results were similar for all examined cell types. In particular, real-time assessment of intracellular chaetocin levels in A549 cells using HPLC (Figure 5A) demonstrated rapid and dramatic dose-dependent intracellular accumulation of chaetocin in unmodified form (Figure 5B), with simultaneous decrement of chaetocin concentrations in media (Figure 5B inset). Impressively, intracellular accumulation of chaetocin reached 10-fold higher than applied extracellular concentration within 1 to 2 minutes and up to 800- to 1000-fold higher than applied levels at 24 hours (Figure 5B-C).
Chaetocin is rapidly and dramatically accumulated in cancer cells by means that require intact/unreduced chaetocin disulfide bonds. (A) HPLC tracing indicating results of assessment of levels of intracellular chaetocin in chaetocin-treated A549 cells as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Note that only a single new HPLC peak, corresponding to that of unaltered/unreduced chaetocin, resulted from treatment with chaetocin. (B) Assessment of intracellular (A549 cells) and extracellular (media) chaetocin concentrations as functions of time in response to addition of 10 μM chaetocin to culture media at time 0. (Inset) Expansion to better show changes in media chaetocin concentration over time. (C) Time course of intracellular accumulation of chaetocin in A549 cells. Results shown are presented to indicate the fold changes relative to concentrations of chaetocin applied to media at time = 0. (B-C) Chaetocin concentrations were determined as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” using HPLC. (D) Effects of dithiothreitol-reduced chaetocin or S-methyl chaetocin on colony formation in A549 cells, indicating loss of cytotoxicity upon modification of the chaetocin disulfide bond. Cells were exposed to all agents for 24 hours; error bars indicate 1 standard deviation.
Chaetocin is rapidly and dramatically accumulated in cancer cells by means that require intact/unreduced chaetocin disulfide bonds. (A) HPLC tracing indicating results of assessment of levels of intracellular chaetocin in chaetocin-treated A549 cells as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Note that only a single new HPLC peak, corresponding to that of unaltered/unreduced chaetocin, resulted from treatment with chaetocin. (B) Assessment of intracellular (A549 cells) and extracellular (media) chaetocin concentrations as functions of time in response to addition of 10 μM chaetocin to culture media at time 0. (Inset) Expansion to better show changes in media chaetocin concentration over time. (C) Time course of intracellular accumulation of chaetocin in A549 cells. Results shown are presented to indicate the fold changes relative to concentrations of chaetocin applied to media at time = 0. (B-C) Chaetocin concentrations were determined as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” using HPLC. (D) Effects of dithiothreitol-reduced chaetocin or S-methyl chaetocin on colony formation in A549 cells, indicating loss of cytotoxicity upon modification of the chaetocin disulfide bond. Cells were exposed to all agents for 24 hours; error bars indicate 1 standard deviation.
Because of reports indicating that intracellular accumulation of the structurally related thiodioxopiperazine gliotoxin might be attenuated by reduction of its disulfide,23 we examined the effects of reduction of chaetocin disulfides on cytotoxicity and on the intracellular accumulation of derivatized chaetocin. Reduction of chaetocin disulfides with dithiothreitol (DTT) dramatically attenuated chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 5D ○), prompting more definitive evaluations examining the effects of S-methylation of the chaetocin disulfides (S-methylation prevents spontaneous reformation of the chaetocin disulfide bonds). Consistent with a critical role of the intact chaetocin disulfides on intracellular accumulation, S-methylation resulted in complete abrogation of its cytotoxicity (Figure 5D ▾). Subsequent cellular uptake studies demonstrating that S-methyl chaetocin was not accumulated in cancer cells (data not shown) provided an explanation for its diminished cytotoxicity and indicated the requirement of intact chaetocin disulfide bonds for the observed high levels of intracellular accumulation of chaetocin.
Glutathione pretreatment attenuates chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity and impairs cellular accumulation of chaetocin
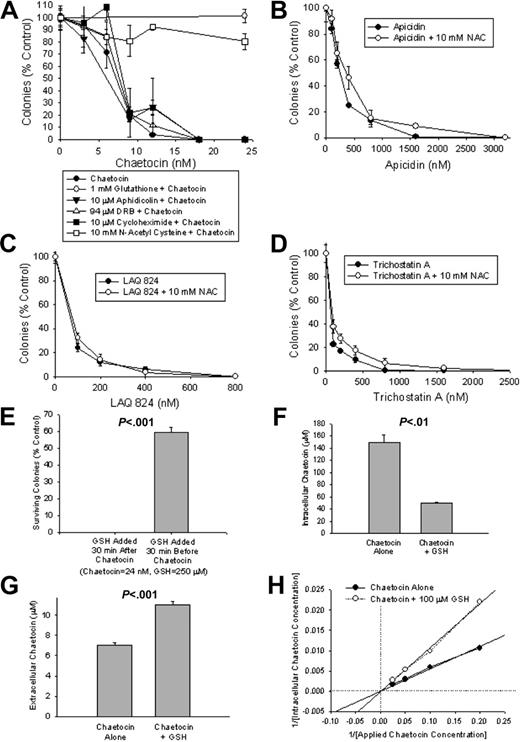
We next turned our attention to seeking a mechanistic basis for chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity, evaluating the effects of glutathione (the primary intracellular reductant), N-acetyl cysteine (NAC; a cell-permeable glutathione precursor), aphidicolin (an inhibitor of DNA synthesis), DRB (an inhibitor of RNA synthesis), or cycloheximide (an inhibitor of protein synthesis) on the ability of chaetocin to inhibit colony formation in A549 cells. Only NAC and glutathione attenuated chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 6A; results recapitulated in myeloma cell lines; data not shown), whereas, importantly, neither agent reduced chaetocin disulfide bonds in culture media (assessed using HPLC; data not shown). Collectively, these results raise the possibility that the induction of oxidative stress by chaetocin may play a role in its cytotoxicity. Consistent with this possibility, buthionine sulfoximine (BSO; an agent that depletes levels of cellular reduced glutathione) was found to enhance chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity, as might be anticipated for an agent that kills cells via induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS; data not shown).
Unlike HDAC inhibitors, chaetocin-induced reductions in A549 cell-colony formation are attenuated by cotreatment with glutathione or NAC. (A) Glutathione or NAC, but not inhibitors of DNA (aphidicolin), RNA (DRB), or protein (cycloheximide) synthesis, attenuate chaetocin-induced reductions in colony formation in A549 cells. (B-D) In contrast, apicidin-, LAQ 824–, and trichostatin A–induced reductions in A549 cell-colony formation are not altered by cotreatment with NAC (B, C, and D, respectively). (E) The ability of glutathione to attenuate chaetocin-induced inhibition of colony formation is highly time dependent and is maximal when glutathione is added before initiation of chaetocin exposure. (F-G) The effects of glutathione pretreatment on intracellular (F) and extracellular (media; G) chaetocin concentration in response to treatment with 10 μM chaetocin for 5 minutes, without or with 100 μM glutathione added 5 minutes before chaetocin addition. (H) Double reciprocal plot indicating the effects of 5-minute pretreatment with 100 μM glutathione or diluent on intracellular chaetocin concentrations resulting from treatment with varying concentrations of chaetocin for 5 minutes. (F-H) Intracellular and extracellular chaetocin concentrations were assessed in A549 cells using HPLC as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” under “Measurement of intracellular and extracellular chaetocin levels.” Results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. Error bars indicate 1 standard deviation.
Unlike HDAC inhibitors, chaetocin-induced reductions in A549 cell-colony formation are attenuated by cotreatment with glutathione or NAC. (A) Glutathione or NAC, but not inhibitors of DNA (aphidicolin), RNA (DRB), or protein (cycloheximide) synthesis, attenuate chaetocin-induced reductions in colony formation in A549 cells. (B-D) In contrast, apicidin-, LAQ 824–, and trichostatin A–induced reductions in A549 cell-colony formation are not altered by cotreatment with NAC (B, C, and D, respectively). (E) The ability of glutathione to attenuate chaetocin-induced inhibition of colony formation is highly time dependent and is maximal when glutathione is added before initiation of chaetocin exposure. (F-G) The effects of glutathione pretreatment on intracellular (F) and extracellular (media; G) chaetocin concentration in response to treatment with 10 μM chaetocin for 5 minutes, without or with 100 μM glutathione added 5 minutes before chaetocin addition. (H) Double reciprocal plot indicating the effects of 5-minute pretreatment with 100 μM glutathione or diluent on intracellular chaetocin concentrations resulting from treatment with varying concentrations of chaetocin for 5 minutes. (F-H) Intracellular and extracellular chaetocin concentrations were assessed in A549 cells using HPLC as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” under “Measurement of intracellular and extracellular chaetocin levels.” Results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. Error bars indicate 1 standard deviation.
To determine whether known HDAC inhibitors (HDACIs) might similarly appear to induce cytotoxicity via imposition of cellular oxidative stress, we in parallel also examined the impact of NAC pretreatment on the effects of the HDACIs apicidin, LAQ 824, or tricostatin A in A549 colony-formation assays. In contrast to results obtained from similar studies of chaetocin (Figure 6A), reductions in colony formation for each tested HDACI were not attenuated by NAC (Figure 6B-D). Collectively, these results support the hypothesis that chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity may be mediated via imposition of increased levels of cellular oxidative stress and, further, that chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity seems mediated via effects on molecular targets distinct from those affected by HDACIs.
However, because the cytoprotective effects of glutathione required application preceding and not subsequent to chaetocin exposure (Figure 6E), we wondered whether glutathione might among other things inhibit chaetocin cellular uptake (as it did not reduce chaetocin disulfides). Indeed, glutathione pretreatment somewhat attenuated the cellular accumulation of chaetocin (Figure 6F-G), with preliminary kinetic evaluation suggesting that glutathione and chaetocin may interact with the same cellular transport system (Figure 6H). However, the extent to which glutathione diminished intracellular chaetocin accumulation (Figure 6F) was seemingly modest in comparison to the magnitude of its effects on chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 6A), leading to the hypothesis that additional effects of glutathione might also be contributory to its cytoprotective effects. Because both glutathione and NAC are known to attenuate levels of cellular oxidative stress, we therefore next examined whether these agents might also exert cytoprotective effects via opposing cytotoxic cellular oxidative stress putatively imposed by chaetocin.
Chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity is associated with the induction of oxidative stress without depletion of intracellular levels of reduced glutathione
FACS analyses employing the oxidative stress–sensitive probe 5,6-carboxy-2′,7′-difluoro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate demonstrated that, indeed, chaetocin induced increased levels of cellular oxidative stress in a dose-dependent fashion in A549 cells, albeit at a cytotoxic dose (Figure 7A-D). Further, NAC pretreatment attenuated chaetocin-induced oxidative species (Figure 7C-D), concordant with the ability of NAC to attenuate chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 6A). Nevertheless, chaetocin did not substantially deplete intracellular reduced glutathione (Figure 7E), indicating that depletion of glutathione is not involved in the imposition of cytotoxic cellular oxidative stress by chaetocin.
Chaetocin induces oxidative stress in A549 cells without substantial depletion of intracellular reduced glutathione levels, whereas the selective cytotoxicity of chaetocin in freshly collected myeloma cells appears to be attributable to their increased sensitivity to oxidative stressors. Treatment of A549 cells with 200 μM hydrogen peroxide (A; positive control) or 400 nM chaetocin (B) for 24 hours resulted in increased intracellular oxidative species as assessed by FACS analyses. Increased chaetocin-induced oxidative species are attenuated by cotreatment with 10 mM NAC (C). (D) Summary of results from FACS indicating changes of oxidative species induced in response to various treatments. Results shown are representative of 3 independent FACS experiments as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” (*P < .05, **P < .01). (E) Chaetocin alone does not appreciably alter intracellular concentrations of reduced glutathione. A549 cells were exposed to the indicated concentration of chaetocin for 24 hours, with addition of glutathione or diluent 30 minutes prior to chaetocin treatment. Glutathione levels were assessed by spectrophotometric assay as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (F) Effects of chaetocin or hydrogen peroxide (in comparison to diluent) on ROS (superoxide) levels in U266 myeloma cells as assessed using FACS analyses as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (G) Relative intracellular chaetocin levels in patient CD138+ myeloma cells relative to that attained in matched normal patient CD138− bone marrow cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM chaetocin for 20 minutes prior to assay; calculated intracellular chaetocin levels were measured by HPLC, with adjustments for differences in average cell volume (calculated from measured cell radii ascertained via light microscopy). Data points are plotted as •, whereas the shaded area represents a 1–standard deviation confidence interval, with the central bar reflecting the mean relative intracellular chaetocin level. (H) CD138+ patient myeloma cells are more sensitive to the cytotoxic effects of hydrogen peroxide than matched patient CD138− bone marrow leukocytes. Cells from 4 myeloma patients were exposed to 200 μM hydrogen peroxide for 24 hours prior to assay, with trypan blue exclusion used to assess surviving cells. (D, F, H) Error bars indicate 1 sample standard deviation and results are replicated in triplicate.
Chaetocin induces oxidative stress in A549 cells without substantial depletion of intracellular reduced glutathione levels, whereas the selective cytotoxicity of chaetocin in freshly collected myeloma cells appears to be attributable to their increased sensitivity to oxidative stressors. Treatment of A549 cells with 200 μM hydrogen peroxide (A; positive control) or 400 nM chaetocin (B) for 24 hours resulted in increased intracellular oxidative species as assessed by FACS analyses. Increased chaetocin-induced oxidative species are attenuated by cotreatment with 10 mM NAC (C). (D) Summary of results from FACS indicating changes of oxidative species induced in response to various treatments. Results shown are representative of 3 independent FACS experiments as described in “Patients, materials, and methods” (*P < .05, **P < .01). (E) Chaetocin alone does not appreciably alter intracellular concentrations of reduced glutathione. A549 cells were exposed to the indicated concentration of chaetocin for 24 hours, with addition of glutathione or diluent 30 minutes prior to chaetocin treatment. Glutathione levels were assessed by spectrophotometric assay as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (F) Effects of chaetocin or hydrogen peroxide (in comparison to diluent) on ROS (superoxide) levels in U266 myeloma cells as assessed using FACS analyses as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” (G) Relative intracellular chaetocin levels in patient CD138+ myeloma cells relative to that attained in matched normal patient CD138− bone marrow cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM chaetocin for 20 minutes prior to assay; calculated intracellular chaetocin levels were measured by HPLC, with adjustments for differences in average cell volume (calculated from measured cell radii ascertained via light microscopy). Data points are plotted as •, whereas the shaded area represents a 1–standard deviation confidence interval, with the central bar reflecting the mean relative intracellular chaetocin level. (H) CD138+ patient myeloma cells are more sensitive to the cytotoxic effects of hydrogen peroxide than matched patient CD138− bone marrow leukocytes. Cells from 4 myeloma patients were exposed to 200 μM hydrogen peroxide for 24 hours prior to assay, with trypan blue exclusion used to assess surviving cells. (D, F, H) Error bars indicate 1 sample standard deviation and results are replicated in triplicate.
As 5,6-carboxy-2′,7′-difluoro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate is not suitable for use in the detection of ROS in myeloma cell lines,24 we instead used the alternative FACS probe hydroethidium to assess ROS (superoxide in particular) in U266 myeloma cells. Two hundred nanomolar chaetocin induced a FACS peak shift of 43.26 ± 3.67 relative to stained, untreated U266 cells (Figure 7F; P < .001), confirming that ROS is also induced by chaetocin in myeloma cells. Of particular note also is that chaetocin was about 1000 times more potent than hydrogen peroxide in inducing cellular oxidative stress in U266 myeloma cells (Figure 7F).
Differential cytotoxicity observed between patient myeloma cells and paired normal patient leukocytes is not related to differential cellular accumulation of chaetocin
Having established that the dramatic accumulation of chaetocin in cancer cells and that the induction of oxidative stress by chaetocin are important factors in chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity, we next examined how these factors might relate to the differential cytotoxicity observed between myeloma cells and normal bone marrow leukocytes (Figure 3). In initial experiments, evaluation of the levels of intracellular chaetocin resulting from treating freshly collected matched patient CD138+ (myeloma) and CD138− (nonmyeloma) cells with chaetocin (10 μM, 20 minutes) was undertaken using HPLC in samples from 4 myeloma patients. Differential chaetocin sensitivity of examined cells was evaluated by parallel assessment of the cytotoxic effects of treating each cell population with 100 nM chaetocin for 24 hours (data not shown, similar to Figure 3A-C). After correction for average cell volumes, we found no indication of decreased intracellular accumulation of chaetocin in the less-sensitive normal CD138− leukocytes (Figure 7G), indicating that the observed heightened sensitivity of CD138+ myeloma cells to the cytotoxic effects of chaetocin is not attributable to differential cellular accumulation of drug.
Differential chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity observed between patient myeloma cells and paired normal patient leukocytes may be attributable to a relative hypersensitivity of myeloma cells to imposed oxidative stress
Having found no indication that the heightened cytotoxicity of chaetocin in myeloma cells in comparison to matched normal leukocytes might be attributable to increased intracellular accumulation of chaetocin in the more-sensitive myeloma cells (Figure 7G), we hypothesized that myeloma cells might instead be inherently more susceptible to the cytotoxic effects of oxidative stressors. To preliminarily examine this possibility, we evaluated the cytotoxic effects of another oxidative stressor, H2O2, or chaetocin in paired CD138+ myeloma cells and negatively sorted CD138− normal marrow leukocytes. Indeed, not only were patient myeloma cells more sensitive to chaetocin than their normal marrow leukocyte counterparts (data not shown, results similar to Figure 3A-C) but they were also more sensitive to peroxide-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 7H). Considered together, the observed selective cytotoxicity of chaetocin in myeloma cells therefore appears, at least in part, to be attributable to a generally heightened susceptibility of myeloma cells to oxidative stressors.
Discussion
Multiple myeloma is an incurable cancer characterized by the clonal proliferation of B-cell lineage plasma cells resulting in the production of monoclonal proteins in serum and/or urine, destructive bony lesions, and the deaths of about 12 000 individuals in the United States alone annually.25 Although increasing numbers of therapeutics are becoming available to treat this disease with the potential for significant symptom palliation, induction of disease responses, and prolongation of disease-free survival, available therapeutic approaches including peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation and newer agents have had only a modest impact on patient overall survival in several randomized trials.26–28 As a consequence, there is still much need for improved antimyeloma therapies.
The present report indicating for the first time that chaetocin has promising potent and selective antimyeloma activity is of potential importance in several respects. First, this manuscript provides evidence that chaetocin represents a promising agent for further development as a candidate antimyeloma therapeutic. Chaetocin has not only potent in vitro antimyeloma activity (Figures 1B-C, 2; Figure S1) but also striking ex vivo antimyeloma potency and selectivity (Figures 3–4; Figure S2) as well as in vivo antimyeloma efficacy (Figure 4D). Furthermore, the selective ex vivo antimyeloma effects of chaetocin are impressive even when compared with standard first-line antimyeloma agents such as dexamethasone and doxorubicin (Figure S2); and dexamethasone- or doxorubicin-resistant myeloma cells appear largely non–cross-resistant to chaetocin (Figures S1–2). Moreover, chaetocin exhibits striking selectivity in killing myeloma cells even in comparison to closely lineage-related normal and neoplastic B lymphocytes (Figure 3D-H).
Of particular note is that the antimyeloma activity of chaetocin was observed in samples obtained from patients afflicted with all types of myeloma, including smoldering myeloma and even heavily pretreated myeloma patients who had previously undergone peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation. Myeloma cells from patients who had previously received newer therapeutics such as thalidomide or bortezomib and those obtained from patients with a diverse array of cytogenetic abnormalities were also readily killed by chaetocin.
Second, it is also noteworthy from the mechanistic standpoint that chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity requires its dramatic intracellular accumulation (Figure 5), whereas induction of oxidative stress also seems to play a critical role in its cytotoxic effects (Figures 6–7).
Third, the ability of chaetocin to selectively kill myeloma cells appears to be mediated based not upon differential cellular accumulation of drug (Figure 7G) but instead upon an increased susceptibility of myeloma cells to oxidative stressors (Figure 7H). These observations have potentially important implications not only for the further development of chaetocin itself but also for the future evaluation of other agents that similarly induce cellular oxidative stress as additional candidate antimyeloma therapeutics.
Fourth, the present studies of chaetocin also indicate that intact chaetocin disulfide bonds are required for cellular entry and therefore for cytotoxicity (Figure 5D).
Fifth, it is remarkable that although results indicating that glutathione or NAC cotreatment abrogates chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 6A) might ordinarily be interpreted as clear evidence that oxidative stress is involved, the reality of the situation is significantly more complicated. In addition to alleviating oxidative stress, glutathione cotreatment also attenuated intracellular accumulation of chaetocin, apparently via interaction with the transport system responsible for chaetocin accumulation (Figure 6). While it is interesting to speculate that chaetocin may interact with a glutathione transporter, little is currently known about glutathione transport. Furthermore, glutathione is generally believed to be poorly cell permeable. Alternatively, it may instead be that glutathione itself is not the primary subject of the involved transport system but a regulator of the system that also happens to facilitate intracellular accumulation of chaetocin.
Sixth, notwithstanding the ability of glutathione to attenuate the intracellular uptake of chaetocin, it was our observation that the extent of attenuation of intracellular chaetocin accumulation by glutathione cotreatment (eg, Figure 6F-G) appeared insufficient to account for the observed attenuation of chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity (Figure 6A). Indeed, chaetocin was also found to induce cellular oxidative stress 1000 times more potently than H2O2 (Figure 7A-D, F). Hence, glutathione pretreatment appears to attenuate chaetocin-induced cytotoxicity via 2 means: (1) attenuation of intracellular accumulation of chaetocin (Figure 6), and (2) attenuation of chaetocin-induced oxidative stress (Figure 7).
Of note, however, is that chaetocin-induced increases in cellular oxidative stress are observed only at chaetocin levels that induce substantial cytotoxicity and not at lower concentrations (eg, 100 nM; Figure 7D). This could either be attributable to the insensitivity of available FACS probes for the assessment of ROS or instead to the possibility that the induction of increased levels of ROS by chaetocin might be a relatively late event in chaetocin-mediated cell killing. Regardless, ROS is both induced by chaetocin (Figure 7A-E) and causally linked to the induction of cytotoxicity in chaetocin-treated cells (Figures 6–8; NAC and glutathione cytoprotection data).
Based upon presented evidence that chaetocin-induced oxidative stress may be responsible for its antineoplastic effects, it is intriguing to speculate that induction of oxidative stress may represent a generally useful therapeutic strategy in treating multiple myeloma. Indeed, while we saw no evidence that chaetocin was selectively accumulated in myeloma cells relative to less-sensitive normal leukocytes (Figure 7G), we instead found that myeloma cells were more sensitive not only to chaetocin but also to the oxidative stressor H2O2 (Figure 7H). Hence, the observed selective cytotoxic effects of chaetocin in myeloma cells may be attributable to a generally heightened sensitivity of myeloma cells to oxidative stress.
Interestingly, there are data indicating that cancer cells are overall more susceptible to the cytotoxic effects of oxidative stressors, leading to the hypothesis that agents that induce cellular oxidative stress may be generally effective as cancer therapeutics.29 In the case of myeloma, the antimyeloma effects of several other therapeutics including imexon,24 epigallocatechin-3-gallate,30 motexafin gadolinium,31 arsenic trioxide,32 radiotherapy,33 and the combination of bortezomib with HDAC inhibitors34 have all been attributed in part to the imposition of oxidative stress. Furthermore, superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD-2) has been reported to be epigenetically silenced in many cancers, including some myeloma cell lines (eg, Kas-6), and this silencing appears to contribute to the proliferation of myeloma cells under at least some conditions.35 Although enhancing proliferation, the silencing of SOD-2 unavoidably attenuates the ability of myeloma cells to withstand oxidative stress, thereby potentially sensitizing myeloma cells to oxidative stress–induced cytotoxicity in comparison to normal cells. Indeed, down-regulated activity of several enzymes responsible for the cellular dissipation of oxidative stress has been reported to arise from therapy in myeloma patients,36 perhaps accounting for why even therapy-resistant myeloma cells appear to be sensitive to agents that induce oxidative stress (eg, Figure 3). Considered collectively, available data including those presented here preliminarily support the hypothesis that myeloma cells may have generally enhanced sensitivity to oxidative stressors and that the induction of oxidative stress may be an effective and selective therapeutic strategy in multiple myeloma. If correct, this hypothesis has important implications for the development of novel antimyeloma therapeutics that specifically target the induction of oxidative stress as a means of selectively inducing cytotoxicity.
In summary, we report here for the first time that the thiodioxopiperazine natural product chaetocin has potent and selective in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo antimyeloma activity that appears to require both intact chaetocin disulfides to facilitate intracellular accumulation and infliction of oxidative stress upon cell entry. The elicitation of multiple cellular effects apparently working together to optimize the cytotoxicity induced by a single molecule is noteworthy. Also noteworthy is that myeloma cells are not only more sensitive than normal leukocytes to oxidative stress induced by chaetocin but that they are also seemingly more sensitive to other oxidative stressors as well. This suggests that other agents that similarly induce cellular oxidative stress may also hold promise for further development as potential antimyeloma therapeutics.
Authorship
Contribution: K.C.B. and J.D.T. designed research/experiments; C.R.I., J.D.T., W.J., R.X., M.M.T., and K.C.B. performed experiments; K.C.B. wrote the manuscript; and C.R.I., J.D.T., and K.C.B. edited/revised the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: None of the authors have any financial or other conflicts of interest to report in conjunction with the present manuscript.
C.R.I. and J.D.T. contributed equally to this manuscript.
Correspondence: Keith C. Bible, Division of Medical Oncology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St, SW, Rochester, MN 55905; e-mail: bible.keith@mayo.edu.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI; R01 CA97129 and R01 CA98118; K.C.B.), with myeloma cell processing supported by NIH/NCI (CA62242), and by a Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship (J.D.T.).
The authors are grateful to Dr Diane Jelinek for technical guidance and provision of myeloma cell lines including Kas 6/1 and OCI-My5 cells and for provision of normal and neoplastic B-CLL cells; to Drs John Lust, Wei Meng, Thomas Witzig, Viji Shridhar, and Matthew Ames for helpful discussion; to Dr Scott Kaufmann for helpful discussions, technical guidance, and provision of access to HPLC instrumentation; and to Drs Philip Greipp and Angela Dispenzieri of the Mayo Clinic Myeloma and Disproteinemia Group for helpful discussions, and especially for kindly proving patient bone marrow cells (with technical assistance from Kim Henderson, Kristy Finke, and Roberta DeGoey). We also thank Drs Alex Adjei and Chunrong Yu for kindly providing LAQ 824; Dr William Dalton (H. Lee Moffit Cancer Center, Tampa, FL) for providing RPMI 8226 doxorubicin-resistant myeloma cells; Dr S. T. Rosen (Northwestern University, Chicago, IL) for providing MM1 dexamethasone-resistant myeloma cells; and Dr Madeleine Joullie for valuable correspondence. We are also appreciative of technical assistance provided by Renee Tschumper in the processing of B-CLL and normal B cells, to the staffs of the Mayo Clinic FACS and electron microscopy facilities for critical technical assistance, and of the assistance provided by Dr William Waud of Southern Research Institute (Birmingham, AL) related to in vivo experiments.




This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal