Abstract
Introduction
Polycythemia vera (PV) is characterized by excessive production of erythroid cells and in most cases a point mutation (V617F) in the Jak2 cytokine signaling kinase. We investigated whether a selective JAK2 inhibitor decreased Jak2 V617F induced erythroid differentiation.
Methods
Wild-type and mutant Jak2 V617F genes were excised from the retroviral Jak2-mus-MSCV-neo vector (Levine et al), cloned into the lentiviral vector pLV CMV IRES2 GFP and their presence verified by DNA sequencing. Lentiviral vectors bearing the wild-type and mutant Jak2 genes or vector alone were used to transduce human peripheral blood CD34+ cells, which were then divided for plating into megacult medium for megakaryocytic colony growth and methylcellulose culture for enumeration of all other progenitor cell types. Normal cord blood HSC (CD34+/CD38−/CD90+) were clone sorted with the FACS Aria and transduced with no vector, backbone vector, wild-type JAK2 or mutant JAK2 vector in methocult media (Stem Cell Technologies Inc, GF+ H4435) +/− 300 nM of a selective JAK2 inhibitor, TG101348. Colonies were scored at day 14. RNA was isolated from the colonies (Qiagen RNeasy kit) and RT-PCR was performed with wild-type and mutant JAK2 allele specific primers.
Results
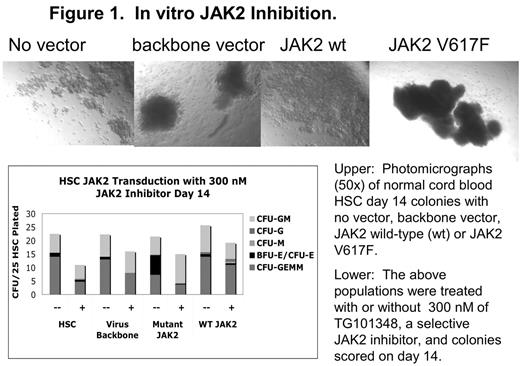
Transduction of cord blood HSC with the mutant Jak2 vector resulted in skewed erythroid colony formation compared to wild-type Jak2, vector alone and untransduced HSC (Figure 1; n=3). RT-PCR with murine Jak2 specific primers resulted in ~900 bp fragments corresponding to murine Jak2 from colonies transduced with the wild-type and mutant Jak2 and confirmed by sequencing, but not those from colonies transduced with the vector alone or the untransduced cells. Like the results in cord blood cells, adult peripheral blood CD34+ cells transduced with the mutant Jak2 developed a skewed developmental pattern, with far greater erythroid colony formation compared to wild-type Jak2 or vector alone. In megacult assays, CD34+ cells transduced with the mutant Jak2 had similar megakaryocytic potential as wild-type Jak2 or vector alone. Addition of TG101348 (300 nM), inhibited mutant kinase-induced erythroid colony formation (Figure 1) in 3 experiments while 100– 300 nM was inhibitory to PV (n=2 patients) HSC and progenitors. Current experiments focus on inhibition of Jak2 in a bioluminescent highly immunocompromised mouse model of Jak2V617F-induced myeloproliferation (Figure 2).
Conclusion
JAK2 V617F skews differentiation of HSC toward the erythroid lineage and may be inhibited with a selective JAK2 inhibitor - TG101348.
In vitro JAK2 Inhibition.
Bioluminescent JAK2 V617F-induced Myeloproliferation Model.
Bioluminescent JAK2 V617F-induced Myeloproliferation Model.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal