Abstract
Background: Many prognostic models have been proposed for staging patients with MM, most recently the ISS system utilizing B2M and albumin.
Patients and Methods: In the context of Total Therapy 2 (TT2) for newly diagnosed MM, we identified 220 patients in whom 4 standard prognostic factors (SPF: B2M, albumin, LDH, hemoglobin), imaging data (MRI-defined focal lesions [MRI-FL]), metaphase-derived cytogenetic abnormalities (CA), FISH-derived amp1q21 and del13q14, and gene expression profiling (GEP)-derived data are available. The baseline characteristics and clinical outcome of the 220 patients are similar to those of the entire population of 668 patients receiving TT2. The median follow-up of the 220 patients is 42mo compared to 52mo for all 668 patients. Five multivariate analysis-based prognostic models were derived, utilizing SPF only (model I), with progressive addition of CA (model II), MRI (model III), FISH (model IV) and GEP (model V).
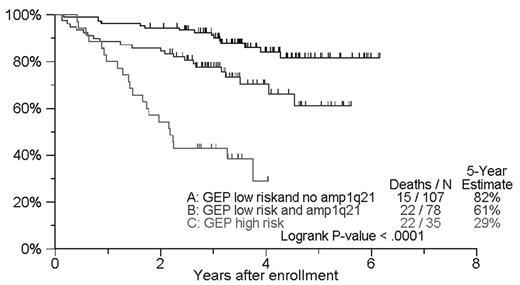
Results: In model I, B2M, LDH and hemoglobin, but not albumin were independently significantly associated with overall survival (OS) (R2=22.5%); upon introduction of CA (model II) (p=.008), only LDH remained significant (p=.033) (R2=28.3%); addition of MRI (model III) was not significant (R2=31.1%); addition of FISH (model IV) was significant for amp1q21 (p=.003) but not for del13q13, with CA remaining significant (p=.023) (R2=38.1%); when GEP was added (model V), the 70 gene-derived model (p<.001) and FISH-based amp1q21 (p=.025) were the only significant variables associated with OS (R2=43.4%). Indeed when GEP was entered into the model first, its R2 value was 24.6%, with the addition of amp1q21 raising R2 to 31.8%, beyond which only minor contributions were made by the remaining 7 variables. With the combined use of GEP and amp1q21, 3 risk groups could be distinguished with 5-yr OS rates of 82% with GEP-low risk/no amp1q21 (n=107), 61% with GEP-low risk/amp1q21 (n=78) and 29% with GEP-high risk regardless of amp1q21 status (n=35).
Conclusion: Among an ever increasing prognostication armamentarium in MM, few studies have investigated the concurrent use of all reputedly important variables. Here, we clearly show, in a comparison of 5 prognostic models that, once molecular genetic variables were introduced, standard prognostic parameters provided little if any further contribution. Therefore, such genetic tests should be more widely performed in order to adequately evaluate the results of clinical therapeutic trials and identify robust high-risk subgroups for novel therapies with purportedly unique mechanisms of action.
Disclosures: PO1 Grant - CA55819.; Millennium, Celgene.; Millennium, Celgene.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal