Abstract
The suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS1) protein is a tumor suppressor. Hypermethylation of SOCS1, resulting in transcriptional silencing, is suggested to play an important role in the development of cancers. We sought to characterize SOCS1 methylation in primary myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and to clarify its clinical implications. We analyzed the methylation status of SOCS1 by methylation specific polymerase chain reaction in 114 patients with primary MDS and performed serial studies in 29 of them. SOCS1 methylation occurred in 54 patients (47.4%), more frequently in patients with high-risk subtypes of MDS than in those with low-risk ones (52.6% vs. 25.8%, p = 0.011). SOCS1 methylation was closely associated with N-RAS gene mutation (p = 0.010) and inversely associated with good-risk karyotype (p = 0.021). With a median follow-up of 17 months (range, 1 to 231 months), two patients, who did not have SOCS1 methylation at diagnosis, acquired it during disease progression. SOCS1 methylation disappeared after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in two patients who had it initially. The patients with SOCS1 methylation had a higher cumulative risk of leukemic transformation than the others (55.8% vs. 27.7% at 3 years, p = 0.004). This difference remained significant within the subgroup of patients with high-risk subtypes of MDS (67.3% vs 45.1% at 3 years, p = 0.045). This is the first report to demonstrate the clinical relevance of SOCS1 methylation in MDS. It may play an important role in the pathogenesis of MDS, especially among patients with high-risk subtypes.
Correlation of SOCS1 methylation with clinical characteristics, cytogenetics and RAS mutations
| . | Total(n=114) . | SOCS1 methylated(n=54) . | SOCS1 unmethylated(n=60) . | p value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 64(7~68) | 64(7~84) | 65(19~86) | 0.231 |
| Sex(M/F) | 81/33 | 36/18 | 45/15 | 0.327 |
| WBC(1000/ml) | 4675(220~227200) | 4710(440~227200) | 4640(1570~87420) | 0.913 |
| Hemoglobin(g/dl) | 8.5(3.9~14.4) | 8.9(4.4~12.9) | 7.8(3.9~14.4) | 0.348 |
| Platelet(1000/ml) | 88.5(2~607) | 102(2~400) | 74(3~607) | 0.453 |
| BM blast(%) | 5.8(0~54.8) | 7.2(0~54.8) | 4.4(0~25.4) | 0.033 |
| Cytogenetics | 0.021 | |||
| Poor | 19 | 13(68.4%) | 6(31.6%) | |
| -7/7q- | 11 | 8(72.7%) | 3(27.3%) | |
| complex | 10 | 6(60%) | 4(40%) | |
| Intermediate | 15 | 10(66.7%) | 5(33.3%) | |
| Good | 70 | 27(38.6%) | 43(61.4%) | |
| FAB subtypes | 0.011 | |||
| Low-risk | 31 | 8(25.2%) | 23(74.2%) | |
| RA | 21 | 4(19.0%) | 17(81.0) | |
| RARS | 10 | 4(40%) | 6(60%) | |
| High-Risk | 78 | 41(52.6%) | 37(47.4%) | |
| RAEB | 33 | 20(60.6%) | 13(39.4%) | |
| RAEB-T | 20 | 11(55.0%) | 9(45.0%) | |
| CMML | 25 | 10(40.0%) | 15(60.0%) | |
| AML | 5 | 5(100%) | 0 | |
| IPSS | 0.008 | |||
| Low-risk | 57 | 21(36.8%) | 36(63.2%) | |
| Low | 21 | 4(19.0%) | 17(81.0%) | |
| Int-1 | 10 | 4(40.0%) | 6(60.0%) | |
| High-risk | 46 | 29(63.0%) | 17(37.0%) | |
| Int-2 | 33 | 29(63.0%) | 17(37.0%) | |
| High | 20 | 11(55.0%) | 9(45.0%) | |
| N-RAS | 0.010 | |||
| Mutated | 11 | 9(81.8%) | 2(18.2%) | |
| Wild | 96 | 38(39.6%) | 58(60.4%) | |
| K-RAS | 1.000 | |||
| Mutated | 4 | 2(50%) | 2(50%) | |
| Wild | 101 | 44(43.6%) | 57(56.4%) |
| . | Total(n=114) . | SOCS1 methylated(n=54) . | SOCS1 unmethylated(n=60) . | p value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 64(7~68) | 64(7~84) | 65(19~86) | 0.231 |
| Sex(M/F) | 81/33 | 36/18 | 45/15 | 0.327 |
| WBC(1000/ml) | 4675(220~227200) | 4710(440~227200) | 4640(1570~87420) | 0.913 |
| Hemoglobin(g/dl) | 8.5(3.9~14.4) | 8.9(4.4~12.9) | 7.8(3.9~14.4) | 0.348 |
| Platelet(1000/ml) | 88.5(2~607) | 102(2~400) | 74(3~607) | 0.453 |
| BM blast(%) | 5.8(0~54.8) | 7.2(0~54.8) | 4.4(0~25.4) | 0.033 |
| Cytogenetics | 0.021 | |||
| Poor | 19 | 13(68.4%) | 6(31.6%) | |
| -7/7q- | 11 | 8(72.7%) | 3(27.3%) | |
| complex | 10 | 6(60%) | 4(40%) | |
| Intermediate | 15 | 10(66.7%) | 5(33.3%) | |
| Good | 70 | 27(38.6%) | 43(61.4%) | |
| FAB subtypes | 0.011 | |||
| Low-risk | 31 | 8(25.2%) | 23(74.2%) | |
| RA | 21 | 4(19.0%) | 17(81.0) | |
| RARS | 10 | 4(40%) | 6(60%) | |
| High-Risk | 78 | 41(52.6%) | 37(47.4%) | |
| RAEB | 33 | 20(60.6%) | 13(39.4%) | |
| RAEB-T | 20 | 11(55.0%) | 9(45.0%) | |
| CMML | 25 | 10(40.0%) | 15(60.0%) | |
| AML | 5 | 5(100%) | 0 | |
| IPSS | 0.008 | |||
| Low-risk | 57 | 21(36.8%) | 36(63.2%) | |
| Low | 21 | 4(19.0%) | 17(81.0%) | |
| Int-1 | 10 | 4(40.0%) | 6(60.0%) | |
| High-risk | 46 | 29(63.0%) | 17(37.0%) | |
| Int-2 | 33 | 29(63.0%) | 17(37.0%) | |
| High | 20 | 11(55.0%) | 9(45.0%) | |
| N-RAS | 0.010 | |||
| Mutated | 11 | 9(81.8%) | 2(18.2%) | |
| Wild | 96 | 38(39.6%) | 58(60.4%) | |
| K-RAS | 1.000 | |||
| Mutated | 4 | 2(50%) | 2(50%) | |
| Wild | 101 | 44(43.6%) | 57(56.4%) |
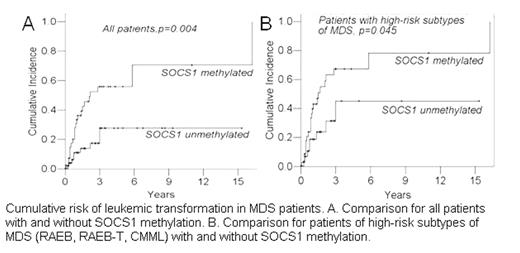
Cumulative risk of leukemic transformation in MDS patients. A. Comparison for all patients with and without SOCS1 methylation. B. Comparison for patients of high-risk subtypes of MDS (RAEB, RAEB-T, CMML) with and without SOCS1 methylation
Cumulative risk of leukemic transformation in MDS patients. A. Comparison for all patients with and without SOCS1 methylation. B. Comparison for patients of high-risk subtypes of MDS (RAEB, RAEB-T, CMML) with and without SOCS1 methylation
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal