Abstract
Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS) is a major complication after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (allo-BMT) and involves the infiltration of donor leukocytes and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. We hypothesized that leukocyte recruitment during IPS is dependent in part upon interactions between chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) and its primary ligand monocyte chemoattractant protein–1 (MCP-1). To test this hypothesis, IPS was induced in a lethally irradiated parent → F1 mouse BMT model. Compared with syngeneic controls, pulmonary expression of MCP-1 and CCR2 mRNA was significantly increased after allo-BMT. Transplantation of CCR2-deficient (CCR2-/-) donor cells resulted in a significant reduction in IPS severity compared with transplantation of wild-type (CCR2+/+) cells and in reduced bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid cellularity and BAL fluid levels of tumor necrosis factor–α (TNF-α) and soluble p55 TNF receptor (sTNFRI). In addition, neutralization of MCP-1 resulted in significantly decreased lung injury compared with control-treated allogeneic recipients. Experimental data correlated with preliminary clinical findings; patients with IPS have elevated levels of MCP-1 in the BAL fluid at the time of diagnosis. Collectively, these data demonstrate that CCR2/MCP-1 interactions significantly contribute to the development of experimental IPS and suggest that interventions blocking these receptor-ligand interactions may represent novel strategies to prevent or treat this lethal complication after allo-BMT.
Introduction
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (allo-BMT) has emerged as an important treatment for several malignant and nonmalignant diseases. Unfortunately, the success of allo-BMT is limited by serious complications. In particular, diffuse lung injury occurs in 25% to 55% of allo-BM transplant recipients and significantly contributes to morbidity and mortality after BMT.1-4 Historically, approximately 50% of all pneumonias seen after BMT have been secondary to infection, but the judicious use of broad-spectrum antimicrobial prophylaxis in recent years has tipped the balance of pulmonary complications from infectious to noninfectious causes.5 Noninfectious lung injury that occurs in the acute setting has been defined as idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS).4 A retrospective study from Seattle showed a lower incidence and earlier onset of IPS than previously reported, but the typical clinical course involving the rapid onset of respiratory failure leading to death remained unchanged.6 A recent review from the University of Michigan Medical Center demonstrated that the frequency of IPS after allogeneic BMT ranged from 5% to 25%, depending upon donor source and the degree of antigenic mismatch between donor and recipient.7 Day-100 mortality was approximately 80%, and the median time from the diagnosis of IPS to death was 13 days despite aggressive treatment with high-dose steroids and broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapy.7
The pathophysiology of IPS is complex, and a significant body of clinical and experimental data has supported roles for both allospecific donor T cells8-10 and the production of inflammatory cytokines.9,11-15 With respect to the latter, both hyporesponsiveness of donor cells to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation12 and the neutralization of tumor necrosis factor–α (TNF-α)11 result in decreased lung injury after BMT, underscoring the importance of TNF-α and donor monocytes and macrophages in the development of IPS.
Inflammatory chemokines are also produced in the lung during murine IPS.16 Interactions between chemokines and their receptors significantly contribute to leukocyte migration and leukocyte function17 and are critical to both adaptive and innate immune responses. Chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) is the receptor for monocyte chemoattractant proteins (MCPs) 1 to 5 and is expressed on a variety of hematopoietic cells, including monocytes, macrophages, effector and memory T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and immature dendritic cells.18-22 MCP-1 (CC-chemokine ligand 2 [CCL-2]; mouse JE) belongs to the CC-chemokine family, binds specifically to CCR2, and is important for monocyte, macrophage, and T-cell recruitment in several inflammatory models.23-26 MCP-1 is produced by hematopoietic, endothelial, epithelial, and smooth muscle cells in response to inflammatory stimuli such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and TNF-α.27-31 Abrogation of CCR2/MCP-1 interactions, either by neutralization or deficiency of the ligand or receptor, results in the impaired recruitment of monocytes, macrophages, and T cells in animal models of inflammatory and pulmonary diseases.23,24,26,32-37
In light of the established role of donor accessory cells and lymphocytes in the development of IPS,8-10,12 we examined the contribution of CCR2/MCP-1 interactions to this process after allo-BMT. We hypothesized that MCP-1 expression in the lung and CCR2 expression on donor leukocytes would have significant impact on recruitment of monocytes, macrophages, and T cells to the lung during IPS. Our results support this hypothesis and demonstrate that the expression of both MCP-1 and CCR2 is significantly increased after allo-BMT. Furthermore, interruption of CCR2/MCP-1 interactions after BMT, either by transplantation of CCR2-/- donor cells or by neutralizing MCP-1, leads to significant reduction in lung injury, underscoring a critical role for this chemokine receptor/ligand pair in the development of IPS.
Patients, materials, and methods
Mice and bone marrow transplantation
Female B6D2F1 (H-2bxd), B6.C-H2 < bm1 > /ByJ (H-2b), B6.C-H2 < bm12 > KhEg (H-2b), C57BL/6 (H-2b), and B6-Ly5.2 (H-2b) were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) or from the Frederick Cancer Research and Development Center (National Cancer Institute; Frederick, MD). CCR2-/- mice38 (B6129F2-Cmkbr2tm1Kuz [H-2b]) were bred at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, MI). In all analyses using CCR2-/- mice, age-matched, CCR2+/+ B6.129PF2/J (H-2b) (Jackson Laboratory) and C57BL/6 mice were included as controls. Animals used for BMT and in vitro experiments were at least 12 weeks old. All experiments were approved by the University of Michigan Committee on the Use and Care of Animals.
Mice received BM transplants according to a previously described protocol.39 When the haploidentical B6 → B6D2F1 system was used, cell mixtures of 5 × 106 BM cells were supplemented with 2 × 106 splenic T cells from syngeneic (B6D2F1) or allogeneic B6.129PF2/J, C57BL/6, B6-Ly5.2, or CCR2-/- donors. T cell-purification was performed by either nylon wool nonadherence or CD4/CD8 magnetic bead separation (autoMACS; Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Approximately 70% of cells obtained after nylon wool passage and more than 85% of cells obtained by autoMACS were positive for CD4 or CD8 (data not shown). Prior to transplantation, host mice received 13 Gy total body irradiation (TBI) (137Cs source) delivered in 2 fractions separated by 3 hours. In the B6 → bm1 BMT system, recipients received 11 Gy TBI, whereas in the B6 → bm12 BMT system, recipients received 9 Gy TBI and 250 000 purified CD4+ T cells. Other transplantation parameters remained unchanged.
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Mice were killed by exsanguination, and BAL was performed as previously described.40 BAL fluid (BALF) supernatants were frozen for subsequent analysis of cytokine and chemokine content, and cells were counted before being analyzed by flow cytometry or used for cytospin analysis.
Cytospin analysis
Aliquots of 50 000 cells were resuspended in 250 μL buffer solution, centrifuged at 162 g for 3 minutes onto Cytoslides (Thermo Shandon, Pittsburgh, PA), and stained by means of the Diff-Quik procedure (Dade Behring, Newark, DE) according the manufacturer's protocol. Cells were differentiated by morphology into lymphocytes, macrophages, monocytes, and neutrophils. Cellular differentials were determined for each sample by counting 300 total cells and were performed in triplicate. Percentages for each sample were then obtained by averaging the 3 results.
Cell surface phenotype analysis
Cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–conjugated monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) to CD45.1, CD45.2, and CD11b; phycoerythrin (PE)–conjugated CD4, CD8, and F4/80; or allophycocyanin (APC)–conjugated CD4 and CD8 as previously described.12 All MoAbs were purchased from BD Pharmingen (San Diego, CA). CCR2 staining was performed with goat antimouse CCR2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) and FITC rabbit antigoat antibodies (Zymed, San Francisco, CA). Three-color flow cytometric analysis was performed by means of a FACSCalibur (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). The FACScan was calibrated with the use of FITC-, PE-, and APC-conjugated, nonspecific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies.
Histopathology and immunohistochemistry
Lung histopathology was determined in BM transplant–recipient animals at 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 weeks after BMT as previously described.40 Immunohistochemical staining was performed with antimouse MCP-1/JE antibody (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) or goat IgG isotype control (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) (both 1:200 dilution) and the Vectastain ABC-AP Kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) plus Fast Red Tablets (Bio-Genex, San Ramon, CA) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Cell function assays
To assess alveolar macrophage TNF-α production in vitro, BALF cells from naive CCR2+/+ and CCR2-/- animals were normalized for alveolar macrophages by cytospin analysis. First, 5 × 104 macrophages were plated per well in 96-well plates (Falcon, BD Labware, Lincoln Park, NJ) with or without stimulation with LPS (5 to 100 ng/mL). After 4 hours, supernatants were analyzed for TNF-α by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). To determine TNF-α production of pulmonary macrophages after BMT, lung cells were harvested from mice at week 6 as previously described,12 normalized for monocytes/macrophages by cytospin analysis, plated at 5 × 104 monocytes/macrophages per well, and finally stimulated and assessed for TNF-α secretion by ELISA. To measure T-cell proliferation in response to alloantigen, 2 × 105 B6 CCR2+/+ or CCR2-/- splenic T cells were cultured for 120 hours in the presence of 1 × 105 irradiated (20 Gy) naive allogeneic (B6D2F1) or syngeneic (B6) peritoneal cells. After 96 hours, supernatant was analyzed for interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and TNF-α. Determination of T-cell proliferation and cytolytic function were completed as previously described.41 For in vivo cytokine production, serum was collected 5 and 21 days after BMT and analyzed for TNF-α and IFN-γ. Donor T-cell expansion was assessed 5 days after BMT. Single-cell splenocyte suspensions were obtained from individual animals, counted, and stained for CD4 and CD8.
RNase protection assay (RPA)
After perfusion of the pulmonary vascular system with ice-cold phospate-buffered saline (PBS), whole-lung tissue was retrieved at various time points after BMT and stored at -80°C. The mRNA was extracted from whole lungs by means of TRIzol following the manufacturer's protocol (GibcoBRL, Grand Island, NY) and quantitated by spectrophotometry. The multiprobe template sets mCK-5b and mCR-5 were purchased from BD Pharmingen. [32P]uridine (5′)-triphosphate (UTP)–radiolabeled antisense riboprobes were synthesized according to the manufacturer's protocol and purified by means of G-25 Sephadex Quick Spin Columns (Roche, Indianapolis, IN). Expression of chemokine genes was quantified by RPA with the use of RiboQuant RPA kits (BD Pharmingen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Protected RNA products were separated on a 5% polyacrylamide gel; the gel was exposed to a storage phosphor screen (Molecular Dynamics, Sunnyvale, CA) for quantification. Signal intensity was measured with ImageQuant(Molecular Dynamics) and standardized to the intensity of the L32 signal for each sample.
Cytokine ELISA
ELISA kits for MCP-1 (BioSource, Camarillo, CA), IFN-γ (BD Pharmingen), TNF-α (R&D Systems for cell culture supernatants; BioSource for BALF), and soluble p55 TNF receptor (sTNFRI) (R&D Systems) were used to measure concentrations of the proteins. Assays were performed according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Anti–MCP-1 treatment
In some experiments, BM transplant recipients were treated with polyclonal antibodies against MCP-1 or with preimmune serum.42 The antiserum containing polyclonal Abs directed against mouse MCP-1/CCL2 was generated in New Zealand White rabbits by means of a well-established protocol.43 The specificity of the anti–MCP-1/CCL2 antiserum was rigorously screened before its use in an experiment, and it lacked cross-reactivity with other chemokines and cytokines.42 Allo-BM transplant recipients were injected intraperitoneally with 250 μL either anti–MCP-1 antibodies (titers of 107/mL) or preimmune serum on days 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, and 28 after transplant. Syngeneic BM transplant recipients received only preimmune serum or were left untreated.
BALF MCP-1 levels in BM transplant recipients and healthy volunteers
BALF samples analyzed for MCP-1 levels were obtained from BM transplant recipients with either acute (IPS) or chronic noninfectious pulmonary dysfunction and from healthy volunteers. BALF was collected in a systematic manner in all BM transplant recipients. A total volume of 2 mL/kg sterile saline (maximum volume, 180 mL) was instilled into the patient's lungs. Collected BALF was pooled, divided into aliquots, and frozen for subsequent analysis. BALF MCP-1 protein levels were measured by means of a human MCP-1 ELISA kit (BD Pharmingen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. All samples were run in duplicate, and the sensitivity of the assay was 15 pg/mL.
Statistical considerations
All values are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The parametric independent sample t test was used for statistical comparisons between groups unless the number of samples was lower than 5, in which case the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used. The Wilcoxon rank test was used for analyzing survival data.
Results
Donor monocytes/macrophages and T cells migrate into the lung and cause lung injury after allogeneic BMT
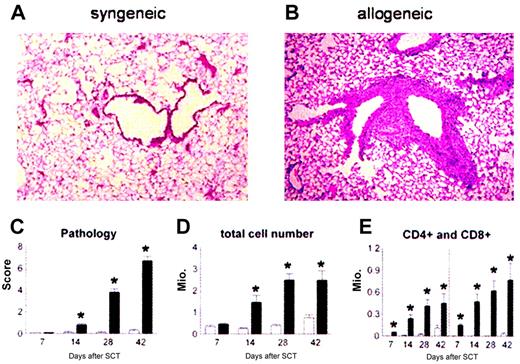
Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received BM transplants with syngeneic (B6D2F1) or allogeneic (B6 Ly5.2) bone marrow and 2 × 106 donor T cells. Animals were analyzed for lung histopathology and BALF cellularity at 1, 2, 4, and 6 weeks after transplantation. Consistent with previous work using other strain combinations,12,40 mice receiving syngeneic BM transplants maintained normal histology at each time point (Figure 1A), whereas recipients of allo-BM transplants developed significant lung injury (Figure 1B). Semiquantitative evaluation of lung sections demonstrated that significant pulmonary damage was first detected 2 weeks after allo-BMT and progressed over time (Figure 1C). Analysis of BALF cellularity demonstrated that the severity of lung histopathology correlated with increasing numbers of inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar space (Figure 1D-E).
Recruitment of donor effector cells to the lungs after BMT. Donor T cells and monocytes/macrophages are recruited to the lung and cause lung injury after allogeneic BMT. B6D2F1 mice received allogeneic (▪) or syngeneic (□) BM transplants, and lungs were examined at weeks 1, 2, 4, and 6 as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Photomicrographs (original magnification, × 200) from hematoxylin-eosin–stained sections obtained 6 weeks after syngeneic (panel A) or allogeneic (panel B) BMT. Recipients of allogeneic BM transplants develop significant lung pathology compared with syngeneic controls as determined with a semiquantitative scoring system (panel C). Total BAL fluid cellularity (panel D) and T-cell counts (panel E) correlate with histologic changes. Data are from 2 experiments representative of 3 and are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 8 to 10 per group per time point; *P < .01.
Recruitment of donor effector cells to the lungs after BMT. Donor T cells and monocytes/macrophages are recruited to the lung and cause lung injury after allogeneic BMT. B6D2F1 mice received allogeneic (▪) or syngeneic (□) BM transplants, and lungs were examined at weeks 1, 2, 4, and 6 as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Photomicrographs (original magnification, × 200) from hematoxylin-eosin–stained sections obtained 6 weeks after syngeneic (panel A) or allogeneic (panel B) BMT. Recipients of allogeneic BM transplants develop significant lung pathology compared with syngeneic controls as determined with a semiquantitative scoring system (panel C). Total BAL fluid cellularity (panel D) and T-cell counts (panel E) correlate with histologic changes. Data are from 2 experiments representative of 3 and are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 8 to 10 per group per time point; *P < .01.
We next investigated the kinetics of donor leukocyte chimerism in the lung by using congenic B6 donors that express the CD45.1 allele for the polymorphic region of the common leukocyte antigen (CD45). B6D2F1 recipients express the CD45.2 allele. BALF cells were collected at 1, 2, and 4 weeks after BMT and analyzed by flow cytometry after staining with CD45.1, CD45.2, and either F4/80 (macrophages) or CD4 and CD8 (T cells). When donor T-cell recruitment to the lung was evaluated, we found that the majority of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the BALF were of donor origin as early as day 7, and that turnover was complete by day 14. By contrast, donor macrophage recruitment occurred more slowly; only 10% of macrophages were of donor origin on day 7, and turnover was not complete until 4 weeks after BMT (data not shown).
MCP-1 levels in the lung are increased after allo-BMT
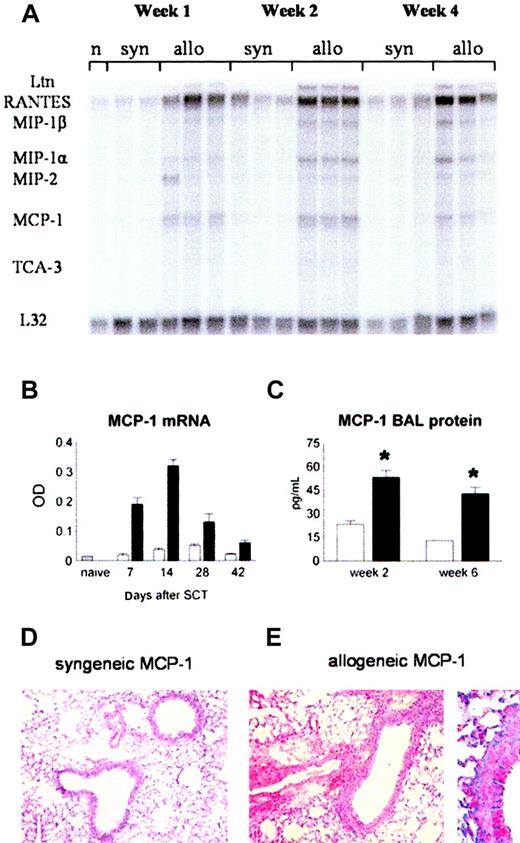
MCP-1 as well as other inflammatory chemokines, like regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α), can be induced by inflammatory mediators like TNF-α and LPS,27 both of which contribute to the development of IPS.11,12,40 We therefore hypothesized that pulmonary expression of inflammatory chemokines, including MCP-1, would be increased after allo-BMT. RNA was isolated from lungs at weeks 1, 2, 4, and 6 after BMT. Using RPA, we found that mRNA expression of RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and MCP-1 was increased in the lungs of allogeneic recipients (Figure 2A). MCP-1 mRNA was increased as early as week 1 (12.7-fold compared with naive), reached its maximal expression by week 2 (21.3-fold), and then declined over time until week 6 after transplantation. At all time points, MCP-1 mRNA expression was higher in allogeneic animals than in syngeneic controls (Figure 2A-B). Pulmonary mRNA expression of MCP-1 after allo-BMT correlated with increases in BALF MCP-1 protein levels at weeks 2 and 6 after BMT and with enhanced MCP-1 expression in the lung tissue as determined by immunohistochemistry (Figure 2C-E).
Increase in MCP-1 levels in the lung after allogeneic BMT. Animals received allogeneic (▪) or syngeneic (□) BM transplants as in Figure 1. (A) MCP-1 mRNA expression was determined after BMT by RNAase protection assay. (B) MCP-1 expression is increased after allogeneic BMT compared with syngeneic controls at all time points. (C) BALF protein levels of MCP-1 (ELISA) are increased at week 2 and week 6 after allogeneic BMT. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3 to 10 animals per group; *P < .01. (D-E) Immunohistochemical alkaline phosphatase staining for MCP-1 in lungs from syngeneic (left) and allogeneic (right) BM transplant recipients 14 days after transplantation. Original magnifications: × 200 (D); × 400 (E).
Increase in MCP-1 levels in the lung after allogeneic BMT. Animals received allogeneic (▪) or syngeneic (□) BM transplants as in Figure 1. (A) MCP-1 mRNA expression was determined after BMT by RNAase protection assay. (B) MCP-1 expression is increased after allogeneic BMT compared with syngeneic controls at all time points. (C) BALF protein levels of MCP-1 (ELISA) are increased at week 2 and week 6 after allogeneic BMT. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3 to 10 animals per group; *P < .01. (D-E) Immunohistochemical alkaline phosphatase staining for MCP-1 in lungs from syngeneic (left) and allogeneic (right) BM transplant recipients 14 days after transplantation. Original magnifications: × 200 (D); × 400 (E).
Pulmonary CCR2 mRNA expression is increased after allo-BMT and correlates with lung pathology
CCR2 is expressed on monocytes, macrophages, and T cells21 and contributes to the recruitment of these cells in various models of disease.23,24,26,32 The expression of CCR2 mRNA was measured at weeks 1, 2, 4, and 6 after BMT. Pulmonary CCR2 mRNA expression was elevated in allogeneic animals compared with syngeneic controls by week 2, continued to rise over time (Figure 3A), and correlated with increasing lung histopathology and BALF cellularity (compare Figure 1). By gating on monocytes/macrophages or costaining with F4/80, fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis of BALF cells demonstrated increases in protein expression of CCR2 and in the percentage of CCR2+ cells after allo-BMT (Figure 3B). In addition, a higher percentage of F4/80+ macrophages also coexpressed CD11b (Figure 3C), consistent with a previously described phenotype of newly recruited alveolar macrophages.44,45
Recruitment of CCR2+ cells to the lung after allogeneic BMT. Animals received BM transplants as in Figure 1. CCR2 mRNA was determined after BMT by RNase protection assay. (A) CCR2 mRNA expression in the lungs of allogeneic recipients (▪) was elevated by week 2 and continued to rise over time through week 6 compared with syngeneic controls (□). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are from 3 to 6 animals per group. (B) CCR2 protein expression is increased on monocytes and macrophages recruited to the alveolar space after allogeneic BMT. (C) F4/80+ macrophages in the BALF show a phenotype previously described for newly recruited monocytes to the alveolar space (F4/80+/CD11b+).44,45 Thin line indicates isotype control; open histogram, syngeneic; and shaded histogram, allogeneic.
Recruitment of CCR2+ cells to the lung after allogeneic BMT. Animals received BM transplants as in Figure 1. CCR2 mRNA was determined after BMT by RNase protection assay. (A) CCR2 mRNA expression in the lungs of allogeneic recipients (▪) was elevated by week 2 and continued to rise over time through week 6 compared with syngeneic controls (□). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are from 3 to 6 animals per group. (B) CCR2 protein expression is increased on monocytes and macrophages recruited to the alveolar space after allogeneic BMT. (C) F4/80+ macrophages in the BALF show a phenotype previously described for newly recruited monocytes to the alveolar space (F4/80+/CD11b+).44,45 Thin line indicates isotype control; open histogram, syngeneic; and shaded histogram, allogeneic.
Lung injury is decreased in recipients of allogeneic CCR2-/- donor cells
To determine the role of CCR2 expression in the development of IPS, B6D2F1 mice received allo-BM transplants from either CCR2+/+ or CCR2-/- donors. BMT parameters otherwise remained unchanged, and syngeneic controls were again included. Allo-BMT with CCR2-/- donor cells resulted in a significant reduction in lung pathology by week 6 compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ controls (Figure 4A-B), whereas graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)–associated target organ injury to liver or gastrointestinal tract and survival were comparable in the 2 groups (Figure 4C; Table 1). Reduced lung injury was associated with decreases in total BALF cellularity (Figure 4D) and in the absolute numbers of BALF monocytes and macrophages as determined by visual differential (Figure 4E) and by flow cytometric analysis for F4/80 and CD11b (data not shown). In addition, the percentage of F4/80+ cells coexpressing CD11b was significantly lower in recipients of CCR2-/- BM transplants compared with CCR2+/+ controls, confirming a reduction in newly recruited macrophages to the alveolar space44,45 (Figure 4F). BALF CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were also decreased after CCR2-/- BMT although the decrease in CD4+ cells did not reach statistical significance (Figure 4E). The reduction of cells recruited to the lung after CCR2-/- BMT was associated with a significant decrease in pulmonary CCR2 mRNA expression (Figure 4G), supporting the hypothesis that increases in CCR2 mRNA levels after allo-BMT reflect the infiltration of CCR2-expressing donor leukocytes. Residual CCR2 mRNA levels observed after CCR2-/- BMT can be explained by the ability of nonhematopoietic cells in the lung to express this receptor.46-48
Development of less severe lung injury in recipients of CCR2-deficient donor cells after allogeneic BMT. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received BM transplants from either allogeneic CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) or syngeneic (□) donors as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” and animals were analyzed 6 weeks after BMT. (A) Photomicrographs of lung tissue 6 weeks after BMT (hematoxylineosin [HE]; original magnification, × 200). (B) (C) Lung injury was significantly reduced after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ controls, whereas target organ injury to liver and gastrointestinal tract (SB = small bowel, LB = large bowel) and survival until time of analysis did not differ. Pathology data are presented from 1 experiment representative of 2; n = 5 to 7 per group; **P < .01. (D) (E) BALF cellularity (panel D) and absolute numbers of monocytes/macrophages and CD8+ T cells (panel E) were significantly decreased after CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ BMT controls. Data presented are from 2 experiments representative of 4; n = 6 to 11 per group; *P < .05. (F) In addition to the total number of F4/80+ cells in the BALF, the percentage of F4/80+/CD11b+ cells was reduced in recipients of CCR2-/- BM transplants. (G) CCR2 mRNA in the lungs was decreased 6 weeks after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT. (H) Reduced lung pathology and BALF cellularity correlated with significantly decreased levels of TNF-α and sTNFRI in the BAL fluid. Data are pooled from 3 experiments; data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 10 to 17 per group; *P < .05. (I) Lung pathology and BALF cellularity are reduced following allogeneic BMT with CCR2-/- cells compared with allogeneic controls in isolated major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II disparate BMT systems. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are from 1 of 2 comparable experiments; n = 3 to 5 per group;*P < .05.
Development of less severe lung injury in recipients of CCR2-deficient donor cells after allogeneic BMT. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received BM transplants from either allogeneic CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) or syngeneic (□) donors as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” and animals were analyzed 6 weeks after BMT. (A) Photomicrographs of lung tissue 6 weeks after BMT (hematoxylineosin [HE]; original magnification, × 200). (B) (C) Lung injury was significantly reduced after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ controls, whereas target organ injury to liver and gastrointestinal tract (SB = small bowel, LB = large bowel) and survival until time of analysis did not differ. Pathology data are presented from 1 experiment representative of 2; n = 5 to 7 per group; **P < .01. (D) (E) BALF cellularity (panel D) and absolute numbers of monocytes/macrophages and CD8+ T cells (panel E) were significantly decreased after CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ BMT controls. Data presented are from 2 experiments representative of 4; n = 6 to 11 per group; *P < .05. (F) In addition to the total number of F4/80+ cells in the BALF, the percentage of F4/80+/CD11b+ cells was reduced in recipients of CCR2-/- BM transplants. (G) CCR2 mRNA in the lungs was decreased 6 weeks after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT. (H) Reduced lung pathology and BALF cellularity correlated with significantly decreased levels of TNF-α and sTNFRI in the BAL fluid. Data are pooled from 3 experiments; data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 10 to 17 per group; *P < .05. (I) Lung pathology and BALF cellularity are reduced following allogeneic BMT with CCR2-/- cells compared with allogeneic controls in isolated major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II disparate BMT systems. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are from 1 of 2 comparable experiments; n = 3 to 5 per group;*P < .05.
Combined survival data from 6 transplant experiments
Recipient type . | Survival, % . |
|---|---|
| Syngeneic | 96.0 ± 4.0 |
| Allogeneic wt | 36.5 ± 6.7 |
| Allogeneic CCR2-/- | 33.9 ± 16.3 |
Recipient type . | Survival, % . |
|---|---|
| Syngeneic | 96.0 ± 4.0 |
| Allogeneic wt | 36.5 ± 6.7 |
| Allogeneic CCR2-/- | 33.9 ± 16.3 |
N equals 5 to 14 animals per group per transplant recipient; data are expressed as means ± SEM.
Monocytes, macrophages, and T cells are significant sources of TNF-α after allo-BMT,12,49,50 and TNF-α is important in the development of IPS.11,13,51,52 Furthermore, sTNFRI has been shown to correlate with GVHD and other transplantation-related complications in humans.53 We therefore measured BALF levels of TNF and sTNFRI and found that both were decreased in recipients of CCR2-/- BM transplants compared with CCR2+/+ controls (Figure 4H). Finally, similar reductions in IPS severity were seen with the use of CCR2-/- donors in the context of a single MHC class I (B6 → bm1) or class II (B6 → bm12) mismatch between donor and host, demonstrating that the reduction in lung injury was not a strain-specific phenomenon (Figure 4I).
CCR2 deficiency of T cells and macrophages does not alter alloreactivity to host antigens or cytokine production
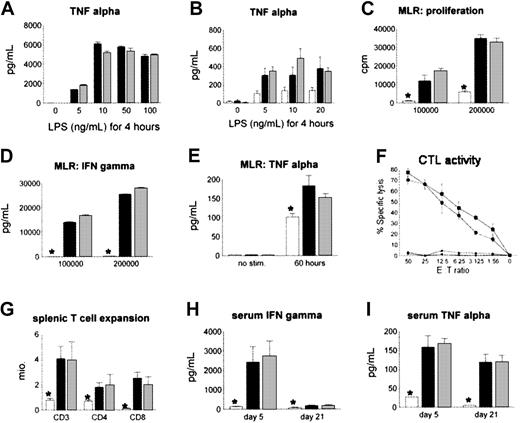
We hypothesized that the reduction in IPS severity after CCR2-/- BMT was secondary to a defect in the recruitment of CCR2-/- donor cells to the lung rather than from intrinsic defects in cytokine production and alloreactivity of CCR2-deficient monocytes/macrophages and T cells, respectively. To examine this possibility, we stimulated alveolar macrophages from naive CCR2-/- and CCR2+/+ animals with LPS in vitro as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” and found no differences in TNF-α production in the 2 groups (Figure 5A). Similar findings were noted ex vivo; pulmonary monocytes and macrophages isolated from recipients of either CCR2-/- or CCR2+/+ allo-BM transplants produced comparable amounts of TNF-α when stimulated with LPS (Figure 5B). Furthermore, when compared with CCR2+/+ cells, naive CCR2-/- T cells showed no differences in proliferation or in IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion (when stimulated in a mixed lymphocyte reaction) or in cytolytic function (Figure 5C-F). Finally, no differences were observed between allogeneic groups when T-cell expansion and systemic IFN-γ and TNF-α levels were measured after BMT (Figure 5G-I).
Effect of CCR2 deficiency in macrophages and T cells on cytokine production or alloreactivity to host antigens. CCR2 deficiency of macrophages and T cells does not impair cytokine production or alloreactivity to host antigens in vitro and in vivo. (A) Naive alveolar macrophages of CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) mice were stimulated in vitro for 4 hours with different concentrations of LPS, and TNF-α levels in the supernatant were determined by ELISA. (B) Pulmonary macrophages were harvested 6 weeks after CCR2+/+ (▪), CCR2-/- (▦), or syngeneic (□) BMT and stimulated with LPS in vitro; *P < .01. (C) (D) (E) Allo-specific proliferation (panel C) and in vitro IFN-γ (panel D) and TNF-α (panel E) production were assessed in a mixed lymphocyte reaction with CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) T cells and allogeneic B6D2F1 stimulators or with CCR2+/+ (□) T cells and syngeneic B6 stimulators. (F) Cytotoxic function of T cells was determined by an alloantigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) assay using P-815 (H2d) and EL-4 (H2b) target cells as described (▪, CCR2+/+ → P-815; •, CCR2-/- → P-815; ▴, CCR2+/+ → EL-4; ♦, CCR2-/- → EL-4). All data presented are from 1 experiment representative of 3. (G) (H) (I) No differences in splenic T-cell expansion, serum IFN-γ, or serum TNF-α levels were observed after allogeneic CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) BMT, and measurements in both allogeneic groups were greater than in syngeneic controls (□). Data are presented as mean ± SEM from 1 of 2 comparable experiments; n = 4 to 5 per group; *P < .01.
Effect of CCR2 deficiency in macrophages and T cells on cytokine production or alloreactivity to host antigens. CCR2 deficiency of macrophages and T cells does not impair cytokine production or alloreactivity to host antigens in vitro and in vivo. (A) Naive alveolar macrophages of CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) mice were stimulated in vitro for 4 hours with different concentrations of LPS, and TNF-α levels in the supernatant were determined by ELISA. (B) Pulmonary macrophages were harvested 6 weeks after CCR2+/+ (▪), CCR2-/- (▦), or syngeneic (□) BMT and stimulated with LPS in vitro; *P < .01. (C) (D) (E) Allo-specific proliferation (panel C) and in vitro IFN-γ (panel D) and TNF-α (panel E) production were assessed in a mixed lymphocyte reaction with CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) T cells and allogeneic B6D2F1 stimulators or with CCR2+/+ (□) T cells and syngeneic B6 stimulators. (F) Cytotoxic function of T cells was determined by an alloantigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) assay using P-815 (H2d) and EL-4 (H2b) target cells as described (▪, CCR2+/+ → P-815; •, CCR2-/- → P-815; ▴, CCR2+/+ → EL-4; ♦, CCR2-/- → EL-4). All data presented are from 1 experiment representative of 3. (G) (H) (I) No differences in splenic T-cell expansion, serum IFN-γ, or serum TNF-α levels were observed after allogeneic CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) BMT, and measurements in both allogeneic groups were greater than in syngeneic controls (□). Data are presented as mean ± SEM from 1 of 2 comparable experiments; n = 4 to 5 per group; *P < .01.
In vivo neutralization of MCP-1 after allo-BMT reduces the severity of IPS
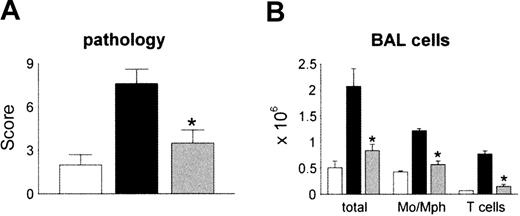
We next determined the effects of in vivo neutralization of MCP-1 on the development of IPS. B6D2F1 recipient mice received either syngeneic or allogeneic BM transplant as described in Figure 1. Allo-BM transplant recipients were injected intraperitoneally with 250 μL of either polyclonal anti–MCP-1 antibodies or control serum starting on day 10 after transplantation as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” We chose this schedule in order to block MCP-1 prior to peak expression of pulmonary mRNA levels and the influx of donor mononuclear cells to the lung. We also opted to avoid neutralizing MCP-1 in the setting of severe systemic inflammation that is seen during the first week after allo-BMT, since a similar strategy proved to be deleterious in an animal model of sepsis.54 Syngeneic controls received preimmune serum at the same volume and schedule. To exclude a potential nonspecific effect of rabbit serum, some syngeneic controls received no treatment. All groups were analyzed by day 30 for lung histopathology and BAL fluid cellularity. MCP-1 neutralization had no effect on mortality (data not shown). Consistent with previous experiments in this system, allo-BM transplant recipients receiving control serum developed significant lung injury, whereas immunoneutralization of MCP-1 resulted in significantly reduced IPS severity and BALF cellularity (Figure 6A-B). Administration of rabbit serum had no effect on lung histopathology in syngeneic controls, nor were symptoms of serum sickness observed (data not shown).
Reduction in the severity of IPS by in vivo neutralization of MCP-1 after allogeneic BMT. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received allogeneic CCR2+/+ BM transplants and either control serum (▪) or anti–MCP-1 (▦) as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Syngeneic animals received control serum (□)or no treatment (data not shown). Neutralization of MCP-1 resulted in significant reductions in both lung injury (panel A) and BALF (panel B) cellularity compared with allogeneic animals treated with control serum. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are pooled from 2 similar experiments; n = 8 to 13 per group; *P < .05.
Reduction in the severity of IPS by in vivo neutralization of MCP-1 after allogeneic BMT. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received allogeneic CCR2+/+ BM transplants and either control serum (▪) or anti–MCP-1 (▦) as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Syngeneic animals received control serum (□)or no treatment (data not shown). Neutralization of MCP-1 resulted in significant reductions in both lung injury (panel A) and BALF (panel B) cellularity compared with allogeneic animals treated with control serum. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are pooled from 2 similar experiments; n = 8 to 13 per group; *P < .05.
MCP-1 levels are increased in the BAL fluid of patients with IPS after allogeneic BMT
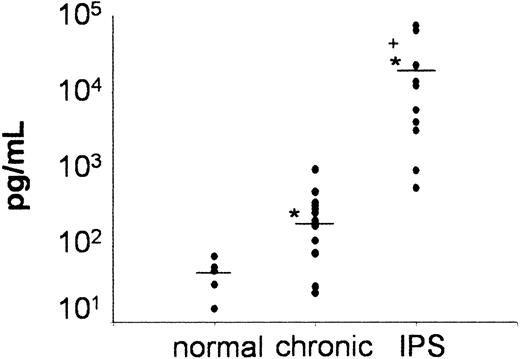
In a final set of experiments, we measured MCP-1 levels in BAL fluid obtained from BM transplant recipients who had either acute (IPS) or chronic noninfectious pulmonary dysfunction and were enrolled on clinical protocols approved by the University of Michigan's Institutional Review Board (IRB) and from healthy volunteers. IPS was diagnosed in adult and pediatric BM transplant recipients (median age, 20 years; range, 1-43 years) if they fulfilled criteria defined by Clark et al.4 IPS was diagnosed within 100 days (median, 12 days; range, 9-56 days) after receipt of full-intensity 5/6 (n = 1) or 6/6 (n = 10) human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–matched allogeneic BM transplants from either a related (n = 2) or unrelated (n = 9) donor. All patients had clinical and radiographic evidence of diffuse lung injury and no evidence of an active systemic (blood/urine) or lower respiratory tract infection as assessed by BAL at time of study entry. Patients who required inotropic blood pressure support or in whom pulmonary dysfunction was believed to be secondary to heart failure or fluid overload were not included. Chronic pulmonary dysfunction was defined as obstructive lung disease (OLD) or restrictive lung disease (RLD) using the following parameters obtained from at least 2 consecutive pulmonary function tests. OLD: forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1.0)/functional vital capacity (FVC) ≤ 80% or FEV1.0/FVC ≥ 15% lower than values measured before BMT, RLD: FVC or total lung capacity (TLC) ≤ 80% or ≥ 15% lower than values measured before BMT. Patients whose baseline (pre-BMT) measurements for FEV1.0/FVC, FVC or TLC were ≤ 80% must have had a ≥ 15% decline in values. Eligible patients were greater than 100 days after BMT and had no evidence for active systemic or lower respiratory tract infection. BALF samples were collected at study entry, processed and assayed for MCP-1 as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” As shown in Figure 7, BALF MCP-1 levels were markedly elevated in patients with IPS compared with patients with chronic pulmonary dysfunction and healthy controls.
Significant increase in BAL fluid levels of MCP-1 in patients with IPS after allogeneic BMT. BAL fluid was obtained from healthy volunteers (n = 5) and from allogeneic BM transplant recipients with IPS (n = 11) or chronic noninfectious lung injury (n = 14) after allogeneic BMT as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Individual data points are expressed. Horizontal bars indicate the average value in each group. *P < .05, IPS and chronic versus healthy controls; +P < .05, IPS versus chronic.
Significant increase in BAL fluid levels of MCP-1 in patients with IPS after allogeneic BMT. BAL fluid was obtained from healthy volunteers (n = 5) and from allogeneic BM transplant recipients with IPS (n = 11) or chronic noninfectious lung injury (n = 14) after allogeneic BMT as described in “Patients, materials, and methods.” Individual data points are expressed. Horizontal bars indicate the average value in each group. *P < .05, IPS and chronic versus healthy controls; +P < .05, IPS versus chronic.
Discussion
IPS remains a frequently fatal complication after allo-BMT. Risk factors for IPS have included conditioning with TBI, acute GVHD, older recipient age, initial diagnosis of malignancy other than leukemia, and the use of methotrexate (MTX) for GVHD prophylaxis.3,6,55-58 The likelihood of developing IPS increases with the number of identified risk factors.2 A recent report from Seattle, WA, found that despite greater patient age and a similar incidence of acute GVHD, recipients of allogeneic BMT using nonmyeloablative conditioning have a reduced risk of IPS compared with patients receiving myeloablative conditioning.59 Once established, pulmonary toxicity was severe in each group and resulted in respiratory failure in the majority of patients. These findings suggest that the intensity of BMT conditioning plays an important role in the development of IPS, and they are consistent with data generated from two mouse BMT models showing that the lung is sensitive to the combined effects of radiation and alloreactive T cells.60,61
Potential etiologies for IPS include direct toxic effects of BMT conditioning regimens, occult pulmonary infections, and the release of inflammatory cytokines that have been implicated in other forms of pulmonary injury.62-64 Immunologic factors may also be important, as suggested by the association of IPS and allogeneic (versus autologous or syngeneic) BMT and severe GVHD (versus mild or no GVHD).2,5,6,55,65 Acute GVHD often precedes IPS, suggesting a possible causal relationship between the two disorders.3,55,66,67 Although the consistent association between lung injury and GVHD after experimental BMT also supports such an etiology,8,9,13,40,52 the role of GVHD and, specifically, alloreactive donor T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of IPS remains a topic of considerable debate. Epithelial apoptosis after BMT is usually attributed to T-cell–mediated injury and is considered pathognomonic for acute GVHD. While observed in the lungs of some patients with IPS,68 epithelial apoptosis has not been consistently identified in allogeneic BM transplant recipients with pulmonary dysfunction.67,69,70 The heterogeneity of pulmonary histopathology after allogeneic BMT is further complicated by the nonspecific changes that occur after mechanical ventilation and by the limited quality and quantity of lung biopsy tissue.
Despite the lack of classic acute GVHD histopathology, several lines of evidence suggest that the lung is susceptible to a 2-pronged immunologic attack involving both inflammatory cytokines and cellular effector pathways. However, the mechanisms by which activated leukocytes traffic to the lung and cause inflammation after allogeneic BMT remain unresolved. Leukocyte trafficking to sites of inflammation involves interactions with endothelial cells that are facilitated by adhesion molecules and by chemokines and their receptors.71 Previous studies have demonstrated that increases in the expression of a variety of inflammatory chemokine ligands and receptors are associated with the development of IPS.16,72 For example, the transfer of alloreactive T-helper 1 (Th1) cells into nonirradiated recipient mice to induce pulmonary inflammation was associated with increased expression of RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, IP-10, and monocyte IFN-γ–inducible protein (Mig).72 In addition, analysis of chemokine expression in the lung of lethally irradiated recipients of fully mismatched BM transplants revealed that protein and mRNA expression of MCP-1, MIP-1α, RANTES, C10, and IP-10 were elevated in the lung 7 days after transplantation.16 Despite these findings, a mechanistic relationship between chemokines and recruitment of cells to the lung during IPS has not been fully elucidated. Although a role for MIP-1α in the recruitment of leukocytes to the lung after BMT was noted in one report,73 subsequent work by the same group suggested that the use of MIP-1-/- mice as allo-BM transplant donors exacerbated rather than reduced early lung injury.74
We demonstrate that both donor T cells and accessory cells infiltrate the lung as histopathology progresses after allo-BMT; turnover of donor T lymphocytes and macrophages in the bronchoalveolar space is complete by weeks 2 and 4, respectively. We hypothesized that the chemokine receptor CCR2 and its principal ligand MCP-1 are critical to the recruitment of these donor cells to the lung after allo-BMT. Our data support this hypothesis and demonstrate that pulmonary MCP-1 mRNA and protein levels are increased early after transplantation and are followed by enhanced CCR2 expression that directly correlates with progressive cellular infiltration into the lung. Furthermore, transplantation of CCR2-/- donor cells reduced the severity of IPS in several strain combinations. Neutralization of MCP-1 after BMT resulted in a significant decrease in lung injury as well, and clinical studies demonstrate that this chemokine is significantly elevated in patients with IPS. Despite the protective effect in the lung, abrogation of CCR2/MCP-1 interactions by either method did not significantly reduce mortality or hepatic and intestinal inflammation after allogeneic BMT. These findings are consistent with data from others showing that successful inhibition of mechanisms responsible for leukocyte trafficking can reduce lung injury without significantly altering other GVHD target organs or survival after allo-BMT.72,75,76 Previously, we showed that the severity of intestinal GVHD within the first week after BMT directly correlates with overall survival77 ; it remains to be determined whether MCP-1 expression is increased in the gastrointestinal tract early after transplantation. Moreover, recent work from our laboratory has shown that CXCR3 expression is critical to T-cell recruitment to the gastrointestinal tract,78 suggesting that the contribution of chemokine receptor-ligand interactions to GVHD induction may be target-organ dependent.
The decrease in lung injury seen after CCR2-/- BMT was associated with significant reductions in BALF levels of TNF-α and sTNFRI. TNF-α has been shown to be a critical effector molecule in the pathogenesis of IPS; neutralization of TNF-α reduces the progression of lung injury after allo-BMT,9,11 and the capacity of donor effector cells to secrete TNF-α in response to LPS stimulation predicts the severity of IPS.12 The p55 TNFR is constitutively expressed on a variety of cell types, and its soluble form is derived via proteolytic cleavage of the membrane-bound protein in response to a variety of inflammatory mediators, including LPS and TNF-α.79,80 The sTNFRI levels are elevated in the BAL fluid of patients with IPS,15 and enhanced serum levels correlate with the development of GVHD and other complications after BMT.53
The reduction in BAL fluid TNF-α levels could have been secondary either to decreased recruitment of TNF-α–producing cells or to an intrinsic defect in cytokine secretion in CCR2-deficient leukocytes. We favor the former for the following reasons: (1) Using fluorescent antibody staining for cell surface antigens and intracytoplasmic TNF-α, we have found that lymphocytes and macrophages are the primary producers of TNF-α in the lung after BMT (data not shown). (2) Allo-BMT with CCR2-/- cells resulted in a significant reduction in the numbers of lymphocytes and macrophages in the bronchoalveolar space. (3) When stimulated in vitro with LPS, CCR2-/- alveolar macrophages harvested from either naive mice (without transplants) or after allo-BMT produced TNF-α in amounts comparable to CCR2+/+ cells. Similar observations were made when CCR2-/- lymphocytes were stimulated in a mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR).
Since previous work has identified a significant role for Th1-effector lymphocytes in the development of IPS,8-10 the reduction in lung injury seen after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT could also have been attributed in part to alterations in T-cell function, recruitment, or both. Our results demonstrate that the absence of CCR2 on donor cells resulted in reduced numbers of lymphocytes in the bronchoalveolar space but had no effect on the functional capacity of these cells; lymphocytes from CCR2-/- mice showed no deficits in proliferation, IFN-γ production, or CTL activity to alloantigens both in vitro and in vivo. It was also possible that diminished lung injury after CCR2-/- BMT was secondary to a Th2 shift in the pulmonary immune response after BMT.81,82 This was unlikely because lymphocytes present in the lung after CCR2-/- BMT express intracellular IFN-γ, and IL-4 was not detected in the cytoplasm of CCR2-/- T cells or in serum or BALF of CCR2-/- BM transplant recipients (data not shown). Collectively, these results suggest that impaired leukocyte recruitment rather than functional defects in CCR2-/- T cells and accessory cells contributed to the reduction of IPS seen after CCR2-/- BMT.
Our studies may also shed light on the mechanism by which donor T cells contribute to the recruitment of monocytes and macrophages during the progression of IPS after allo-BMT. CD8+ T cells are the predominant lymphocyte subset in the lungs of mice with IPS both in the P → F1 and in the B6 → bm1 systems. Other studies have shown that CD8+ T-cell recognition of alveolar epithelial cells triggers chemokine expression by the damaged epithelium that results in progressive inflammation; initial damage can be mediated by TNF-α, and subsequent leukocyte infiltration can be abrogated by in vivo neutralization of MCP-1.35,83-85 In this light, early pulmonary injury induced by infiltrating alloreactive T cells may enhance donor monocyte and macrophage recruitment into the lung via enhancing local MCP-1 secretion by pulmonary epithelial and/or endothelial cells. This possibility is supported by our observations showing that (1) increases in MCP-1 expression correlate with the initial influx of donor lymphocytes into the lung and precede the recruitment of donor macrophages, (2) intense immunohistochemical staining of MCP-1 is found in areas of dense lymphocyte infiltration around bronchial structures and vessels, and (3) MCP-1 neutralization coincident with the initial recruitment of donor T cells reduces subsequent macrophage influx and IPS severity.
In summary, our results demonstrate a critical role for CCR2/MCP-1 interactions in the development of IPS. The reduction in IPS seen after allogeneic BMT with CCR2-/- donor mice and in allogeneic wild-type (wt) recipients treated with a neutralizing antibody to MCP-1 was dependent upon decreased recruitment of donor effector cells into the lung. Elevated MCP-1 levels in patients with IPS suggest that CCR2/MCP-1 interactions may be operative after clinical BMT as well. Since IPS develops and progresses to respiratory failure despite significant systemic immunosuppression, our findings suggest that novel strategies directed toward inhibiting pathways of effector cell recruitment to the lung may serve as effective adjuncts to standard therapy intended to prevent or treat this serious complication.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, November 13, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2003-08-2708.
Supported by National Institutes of Health grants 5K12HD028820-12 and RO1 HL072258-01. G.C.H. is a Deutsche Krebshilfe e.V. Scholar; K.R.C. is an Amy Strelzer-Manasevit Scholar of the National Marrow Program, a Fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Medical Minority Faculty Development Program, and the Recipient of a Translational Research Award from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.


![Figure 4. Development of less severe lung injury in recipients of CCR2-deficient donor cells after allogeneic BMT. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice received BM transplants from either allogeneic CCR2+/+ (▪) or CCR2-/- (▦) or syngeneic (□) donors as described in “Patients, materials, and methods,” and animals were analyzed 6 weeks after BMT. (A) Photomicrographs of lung tissue 6 weeks after BMT (hematoxylineosin [HE]; original magnification, × 200). (B) (C) Lung injury was significantly reduced after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ controls, whereas target organ injury to liver and gastrointestinal tract (SB = small bowel, LB = large bowel) and survival until time of analysis did not differ. Pathology data are presented from 1 experiment representative of 2; n = 5 to 7 per group; **P < .01. (D) (E) BALF cellularity (panel D) and absolute numbers of monocytes/macrophages and CD8+ T cells (panel E) were significantly decreased after CCR2-/- BMT compared with allogeneic CCR2+/+ BMT controls. Data presented are from 2 experiments representative of 4; n = 6 to 11 per group; *P < .05. (F) In addition to the total number of F4/80+ cells in the BALF, the percentage of F4/80+/CD11b+ cells was reduced in recipients of CCR2-/- BM transplants. (G) CCR2 mRNA in the lungs was decreased 6 weeks after allogeneic CCR2-/- BMT. (H) Reduced lung pathology and BALF cellularity correlated with significantly decreased levels of TNF-α and sTNFRI in the BAL fluid. Data are pooled from 3 experiments; data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 10 to 17 per group; *P < .05. (I) Lung pathology and BALF cellularity are reduced following allogeneic BMT with CCR2-/- cells compared with allogeneic controls in isolated major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II disparate BMT systems. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and are from 1 of 2 comparable experiments; n = 3 to 5 per group;*P < .05.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/103/6/10.1182_blood-2003-08-2708/6/m_zh80060458020004.jpeg?Expires=1763568611&Signature=wNG7fxwp3lzEBzHHi2gkVnWEov3B-RTALRz4DjUzfRZbKAYtZTLoyg~bhLYIk7RsY9hR6xiSsZqdpvCgX1orQxVFOFyovt8oFer-B1AyBmMwEiGC0tgMTnJNZIGoAhUgGDw0Y27RS~mYCl8HkETz~udtzzDFzV9p~pqNZXX2zD4iJTKDdzxumsdIwXABS-6k7g1F7GuyEDQneu6zSYJuOsQ-vyzZRBaZVsfBtNjAJQSyU0TkH7Uv8ZLhw28fsn30UW24M1fObJaHUpdc1poHAfew8WF-iN5SloVDOieGymftiOEnifLk7qoMUjp243LZWnGXV0v~U3rYEUItrEqlOw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal