Abstract
MyD-1 (CD172) is a member of the family of signal regulatory phosphatase (SIRP) binding proteins, which is expressed on human CD14+ monocytes and dendritic cells. We now show a novel role for MyD-1 in the regulation of the innate immune system by pathogen products such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), purified protein derivative (PPD), and Zymosan. Specifically, we demonstrate that ligation of MyD-1 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) secretion but has no effect on other cytokines induced in response to each of these products. In an attempt to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying this surprisingly selective effect we investigated signal transduction pathways coupled to MyD-1. Ligation of the SIRP was found to recruit the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and promote sequential activation of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase, phospholipase D, and sphingosine kinase. Inhibition of LPS-induced TNFα secretion by MyD-1 appears to be mediated by this pathway, as the PI 3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin restores normal LPS-driven TNFα secretion. MyD-1-coupling to this PI 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway may therefore present a novel target for the development of therapeutic strategies for combating TNFα production and consequent inflammatory disease. (Blood. 2003;102:2532-2540)
Introduction
MyD-1 (CD172), which is expressed on bovine monocytes, macrophages, a subset of afferent lymph veiled cells (ALVCs), and granulocytes,1 has been proposed to be a member of the recently described signal regulatory phosphatase binding protein (SIRP) receptor family.2 MyD-1 has also been shown to be expressed on human, rat (SIRP-1α),3 and mouse (SH2 domain-bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase [SHP] substrate-1 [SHPS-1]) cells,4 with a comparison of the amino acid sequence between bovine MyD-1 and mouse SHPS-1 or the human MyD-1 homolog, SIRP-1alpha, revealing homologies of 67% and 77%, respectively.1 MyD-1 is a type 1 glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily comprising 3 extracellular Ig-like domains with several glycosylation sites, a transmembrane region consisting of a single hydrophobic stretch of 22 amino acids,1 and at least 4 possible tyrosine phosphorylation sites including one or more putative immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs; (V/LI/S)XYXX(L/I)) within the cytoplasmic tail. These tyrosine phosphorylation sites provide potential Src homology 2 (SH2) domain binding sites for SH2 domain-containing signal transducers and indeed, the SH2 domain-containing phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 have been shown to be associated with phosphorylated SIRP receptors in various cell types.3-5 Although the precise mechanisms are obscure, SIRPs, which have been found to be tyrosine-phosphorylated following growth factor stimulation, have recently been proposed to regulate growth factor-mediated signaling and DNA synthesis by recruitment of these tyrosine phosphatases. SHP-2 has been shown to promote mitogenic signaling by enhancing the coupling of growth factor receptors to the phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase and/or extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein (ErkMAP) kinase signaling cascades.6 Thus, it has been suggested that SIRPs can negatively regulate mitogenic signaling by sequestration of this tyrosine phosphatase from growth factor receptors.3,4,7 The finding that SIRPs are substrates for both SHP-1 and SHP-2 indicates that the dephosphorylation of SIRPs, and hence their ability to sequester SHP-2, may be tightly regulated by one or both of the SHP phosphatases.3
The role of MyD-1 in hematopoietic cell biology is less clear; however, a ligand for MyD-1 has recently been identified as the integrin-associated protein (CD47).8,9 CD47 is expressed on a variety of hematopoietic cells including monocytes and T cells10 and as CD47 is known to have immunomodulatory properties,11,12 this novel receptor pair could play roles in regulation of both antigen-presenting cell (APC) and T-cell function. Indeed, we have recently shown that the proliferation of resting memory CD4+ T cells to ovalbumin-pulsed monocytes in vitro was significantly reduced in the presence of blocking and nonblocking monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to MyD-1,1 and that addition of nonblocking anti-MyD-1 strongly inhibited T-cell proliferation in mixed leukocyte reactions (MLRs) and anti-CD3 assays.13 We now show a novel role for MyD-1 in the regulation of activation of the innate immune system by pathogen products generated from bacteria, both Gram-positive and -negative, and yeast suggesting that this inhibitory pathway may play a universal role in regulating the immune response irrespective of the class of pathogen.
Materials and methods
Cells, media, and reagents
Culture medium for human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) consisted of RPMI 1640 (Gibco, Paisley, United Kingdom) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 0.05 mg/mL gentamicin. ILA24, the anti-human MyD-1 mAb recognizes a single band of approximately 120 kDa (p120) by Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates derived from PBMCs or U937 cells and hence selectively recognizes the inhibitory human MyD-1 (human SIRP-1α) rather than the activating human SIRP-β (results not shown). The mAb ILA24 was used to expression clone a cDNA from a bovine monocyte cDNA library which proved by sequencing to be a member of the α subset of the SIRP family. Moreover, this mAb ILA24 was shown to recognize the cloned SIRP alpha molecule expressed in COS-7 cells.1 Furthermore, the mAb stains monocytes in blood from humans and cattle and precipitates a molecule of approximately 120 kDa in both species.
U937 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FCS, 2 mM glutamine, 10 U/mL penicillin, and 10 μg/mL streptomycin at 37°C, 6.8% CO2 in a water-saturated atmosphere. U937:Δp85 cells (a generous gift from Dr L. Stephens, Babraham Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom) were similarly cultured, but in addition were maintained in the presence of 0.6 mg/mL geneticin (G418) and 0.1 mg/mL hygromycin B. Expression of Δp85 was induced with 15 mM isopropyl b-D-thiogalacto-side (IPTG), 5 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, and 100 μM zinc chloride for 10 hours.
Cell separation
PBMCs were isolated from heparinized whole blood of normal healthy donors or buffy coats obtained from the National Blood Services, Collingdale, United Kingdom, by standard density gradient centrifugation with Histopaque (1.077 density) (Sigma, Poole, United Kingdom). PBMCs were harvested from the interface, washed twice in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and stored in freezing medium consisting of 90% FCS plus 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in liquid nitrogen until required.
Cell culture
PBMCs were cultured at a concentration of 1 × 106/mL for between 24 and 72 hours in 24-well plates (Costar) in culture medium alone or containing 10 μg/mL ILA24 (anti-MyD-1) or isotype-matched control (Pharmingen, San Diego, CA). Culture was undertaken in the presence or absence of 100 ng/mL LPS from Escherichia coli (Sigma), 1 μg/mL Zymosan A (Sigma), or 1000 U/mL purified protein derivative (PPD) (Pasteur Merrieux, Maidenhead, Berks, United Kingdom). Some cultures also contained 1 nM wortmannin (Calbiochem-Novabiochem, Nottingham, United Kingdom) or 10 nM to 100 nM Ly294002 (Sigma). At various times of culture, supernatant was either removed for the assessment of cytokine content by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), or cells harvested and analyzed for expression of markers and/or cytokines by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis.
FACS analysis
Binding of mAb to human PBMCs was assessed by direct or indirect immunofluorescence. Briefly, cells were washed 3 times in PBS + 2 mM EDTA, 0.5% BSA, 10% heat inactivated human serum and 0.01% sodium azide (FACS buffer). Cells were incubated for 20 minutes on ice with biotinylated ILA24 mAb, which was prepared as described previously, in the presence or absence of fluorochrome conjugated anti-human CD14 mAb (IgG1) at an optimised dilution or isotype matched control antibodies. Cells were then washed 3 times with FACS buffer and secondary staining was performed using fluorochrome-conjugated streptavidin (Pharmingen).
For the measurement of intracellular interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), cells were washed thoroughly with FACS buffer and then stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies to extracellular cell markers or isotype-matched controls for 20 minutes on ice. Following this, cells were again washed thoroughly and then fixed and permeabilized for 45 minutes at room temperature in the dark using the 1-step reagent Permeafix (Ortho Diagnostic Systems, Raritan, NJ). After washing, cells were stained with either fluorochrome-conjugated anti-human IL-6 or TNFα or an isotype-matched control antibody (all from R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN).
Cells were then washed and suspended in FACS Flow (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany), 10 000 events were acquired using the FACScan (Becton Dickinson), and the expression of fluorescent markers was analyzed using the WinMDI software (Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA).
Cytokine ELISAs
Supernatants were analyzed for cytokine content using the Human Quantakine kits (R&D Systems). Briefly, supernatants were diluted 1 to 5 where appropriate and samples added to the microtiter plate, which had been precoated with anti-human cytokine mAb. The samples were incubated for 2 hours at room temperature before being washed thoroughly and the addition of horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated detecting antibody undertaken. The concentration of cytokine present in supernatants was determined spectrophotometrically at 405 nm on an MR5000 microtiter plate reader (Dynatech, Vienna, VA) after incubation with the chromophore 3,3,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine and H2O2 for up to 15 minutes at room temperature and then addition of 1 M H2SO4 as stop solution. Samples were assayed in triplicate, and the cytokine concentration was determined by extrapolation from a standard curve generated by serial dilution of the appropriate recombinant human cytokine (R&D Systems).
Western blots
Immunoprecipitation and Western blotting were carried out as described previously.14,15 Briefly, PBMCs or U937 cells were stimulated with ILA24 anti-MyD-1 mAb (10 μg/mL). After washing in PBS, the cells were lysed with ice-cold RIPA lysis buffer containing 1 mM PMSF (phenyl methane sulfonyl flouride), 1 μg/mL CLAP (1 μg/mL each of chymostatin, leupeptin, antipain, and pepstatin), 1 mM sodium orthophosphate, and 1 mM sodium fluoride for 30 minutes. Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 13 000 rpm for 15 minutes and the cell lysates were either incubated with the appropriate antibodies for immunoprecipitation or stored at -20°C. Samples were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (0.2-μM pore size). Western blot analysis utilized the following antibodies: anti-phosphotyrosine, 4G10 and anti-p85 (Upstate Biotechnology, Lake Placid, NY), anti-SHP-1 and anti-SHP-2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), and anti-TNFα-converting enzyme (TACE) (AMS Biotechnology, Abingdon, United Kingdom). Blots were developed using the HRP-ECL system (Amersham, Bucks, United Kingdom).
PI 3-kinase activity
PI 3-kinase activity was assayed as described previously.14,16,17 Briefly, U937 cells (2 × 107 cells/mL) were washed and resuspended in phosphate-free RPMI containing 10% dialysed FCS and labeled with 500 μCi/mL (18.5 MBq) [32 P]PO4 for 90 minutes at 37°C. Following stimulations, lipids were extracted by the Bligh-Dyer method and resolved by thin-layer chromatography (tlc) in chloroform/acetone/methanol/acetic acid/water (80:30:26:24:14). PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate) bands were quantified by liquid scintillation counting.
PIP2-phospholipase C (PIP2-PLC) assay
Inositol phosphates were assayed as described previously.17 Briefly, U937 cells were labeled with myo-[3H]-inositol (1 μCi/106 [0.037 MBq]cells) for 16 hours at 37°C. The cells were washed 3 times and resuspended (at 1-3 × 107 cells/mL) in RHB medium (RPMI 1640, 10mM HEPES [N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid], 0.1% bovine serum albumin [BSA]), pH 7.4 at 4°C. Following stimulation, the cells were harvested and lipids extracted by Bligh-Dyer phase separation. Levels of total [3H]-inositol phosphates (reaction mixture containing 10 mM LiCl) were determined by liquid scintillation counting of fractions eluted following Dowex (formate form; Sigma) ion-exchange chromatography of aliquots of the aqueous phase. Results were calculated as the percent of the total radioactivity incorporated in the lipids.
Phospholipase D activity
Phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase D (PtdCho-PLD) activity was measured as previously described using the transphosphatidylation assay.14,16,17 Briefly, U937 cells were labeled (106 cells/mL) with [3H] palmitic acid (5 μCi/mL [0.185 MBq]; Amersham) for 16 hours. Following washing, the cells were incubated at 37°C for 15 minutes in RHB medium containing butan-1-ol (0.3% final). Following stimulation, the lipids were extracted by Bligh-Dyer phase separation. Aliquots from the organic phase were separated by tlc in the solvent ethyl acetate/2,2,4-trimethylpentane/acetic acid/water (11:5:2:10) and the phosphatidylbutanol bands determined by liquid scintillation counting.
Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine-1-phosphate assay
Sphingosine-1-phosphate was measured as described previously.14,16,17 Briefly, cells were preincubated overnight in media containing [32P] or [3H]serine (20 μCi/mL [0.74 MBq]) before being washed and resuspended in RHB medium containing 0.1 mM L-canaline and 4-deoxypyridoxine (0.5 mM) to inhibit sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase. Following stimulation, the lipids were extracted and analyzed by tlc on silica gel G60 using chloroform:methanol:acetic acid:water (90:90:15:6). Bands corresponding to sphingosine-1-phosphate were counted by liquid scintillation.
Quantitative real-time TaqMan reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Quantitation of cytokine mRNA levels was performed using the TaqMan Cytokine Gene Expression Plate 1 (PE Applied Biosystems, Weiterstadt, Germany) according to the kit protocol. Briefly, 50 ng mRNA was reverse transcribed using random hexamers and then PCR amplified in the presence of gene-specific primers and fluorescently labeled probe in a 7700 Sequence Detection System (PE Applied Biosystems).
Antibody-blocking studies
An MyD-1Ig fusion protein was constructed from the extracellular region of bovine MyD-1 together with a human IgG CH1 domain fusion tag (kind gift of Dr P. Linsley, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Wollingford, CT). Freshly prepared bovine PBMCs were resuspended in FACS buffer and incubated with MyD-1Ig (5 μg/mL) that had been preincubated with either an isotype-matched control mAb or the anti-MyD-1 mAb, ILA24, at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. As positive blocking controls, anti-MyD-1 mAb CC149 (Serotec, Oxford, United Kingdom) was preincubated with MyD-1Ig, or anti-CD47 mAb MEM-122 was added to cells prior to addition of MyD1Ig. After washing, the cells were fluorescently labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (cross-adsorbed against mouse IgG) (Pharmingen) and analyzed by FACS.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed statistically using the Student paired t test and are expressed as means ± 1 SD.
Results
Ligation of MyD-1 selectively inhibits TNFα secretion in response to pathogen products
MyD-1 was found to be expressed on essentially all CD14+ monocytes (and monocyte cell lines such as U937) and also on a subset (∼ 30%) of CD83+ dendritic cells (DCs) but not on either B or T cells (data not shown). Expression is also maintained on DCs (characterized as CD1a+, CD11c+, CD80+, CD86+, HLA-DR+, CD40+, CD3-, CD19-, CD83-, and CD14-) generated from these CD14+ monocytes following in vitro culture with IL-4 and GM-CSF18 (data not shown). Encounter of pathogen products such as LPS by monocytes and DCs results in the production of inflammatory cytokines that may then influence the subsequent recruitment and activation of T cells. MyD-1 has been identified as a member of the inhibitory SIRP family that contains ITIM regions within its intracellular domain. Thus, it was possible that MyD-1 might exhibit inhibitory properties relating to the regulation of activation of monocytes and DCs by such pathogen products.
We therefore examined the effect of MyD-1 ligation on the induction of cytokines by LPS. PBMCs were cultured with media or LPS (100 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of MyD-1 ligation for 24 hours after which time supernatants were removed and analyzed for the cytokines IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12 p70, IL-15, interferon gamma (IFNγ), and TNFα by ELISA (Figure 1). MyD-1 ligation alone had no significant effect on any of the cytokines apart from IL-12 p70, which it induced strongly (Figure 1E). In addition, the production of these cytokines in response to LPS was unaffected by ligation of MyD-1 (Figure 1B-I), with the exception of TNFα whose secretion was reduced by more than 50% (Figure 1A). Indeed, pooled data from 13 independent experiments using different individual human donors showed that ligation of MyD-1 suppressed LPS-induced TNFα secretion by 51.5 ± 3.6%, n = 13 (mean ± SEM of 13 independent experiments). Interestingly, IL-6 and IL-1, cytokines that are closely associated with TNFα in the inflammatory response, were not suppressed by MyD-1 ligation (Figure 1B-C). Moreover, although IL-12 p70 induction was modulated by anti-MyD-1 treatment, LPS-mediated induction of this cytokine was not altered by MyD-1. These data indicate not only that the inhibitory properties of MyD-1 on LPS-mediated proinflammatory cytokine secretion are specifically restricted to TNFα but also that secretion of the group of important inflammatory cytokines to which it belongs is differentially regulated.
Ligation of MyD-1 specifically inhibits LPS-stimulated production of TNFα but not other cytokines. Human PBMCs were cultured with LPS (100 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 or the isotype control antibody for 24 hours, after which supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for cytokine production. The results shown are the mean production from triplicate cultures of (A) TNFα, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-1β, (D) IL-10, (E) IL-12 p70, (F) IL-15, (G) IFNγ, (H) IL-2, and (I) IL-8 secretion (means ± 1 SD; *P = .002). Stimulations are as follows: lane 1, medium; lane 2, anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL); lane 3, IgG isotype control (10 μg/mL); lane 4, LPS; lane 5, LPS plus anti-MyD-1; lane 6, LPS plus IgG. These data are representative of up to 14 experiments.
Ligation of MyD-1 specifically inhibits LPS-stimulated production of TNFα but not other cytokines. Human PBMCs were cultured with LPS (100 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 or the isotype control antibody for 24 hours, after which supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for cytokine production. The results shown are the mean production from triplicate cultures of (A) TNFα, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-1β, (D) IL-10, (E) IL-12 p70, (F) IL-15, (G) IFNγ, (H) IL-2, and (I) IL-8 secretion (means ± 1 SD; *P = .002). Stimulations are as follows: lane 1, medium; lane 2, anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL); lane 3, IgG isotype control (10 μg/mL); lane 4, LPS; lane 5, LPS plus anti-MyD-1; lane 6, LPS plus IgG. These data are representative of up to 14 experiments.
It has recently emerged that recognition of pathogens, or pathogen-derived products such as LPS, is mediated by a superfamily of receptors that are referred to as pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs).19-21 These receptors recognize conserved molecular patterns (pathogen-associated molecular patterns, PAMPs) such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which are expressed by many pathogens. A key group of these receptors, the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize many common pathogen products derived from bacteria, yeast, and viruses.19-21 We therefore determined whether MyD-1 only targeted LPS signaling (TLR4) or acted to suppress inflammation initiated by a range of pathogen products. As shown in Figure 2, MyD-1 signaling was also found to inhibit TNFα secretion induced in response to PPD of mycobacteria and Zymosan A, a product of yeast cell walls. Although these pathogen products are much-less-effective inducers of TNFα than LPS, these findings indicate that MyD-1 has a profound regulatory effect on the induction of TNFα secretion and thus the generation of an inflammatory locus regardless of the type of pathogen product detected and the TLR utilized (LPS: TLR4; zymosan: TLR2; mycobacteria: TLR2).
The effect of ligation of MyD-1 on the inhibition of TNFα induced by other pathogen products. Human PBMCs were cultured for 24 hours with either 100 ng/mL LPS, 1 μg/mL Zymosan A, or 1000 U/mL PPD in the presence or absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 or the isotype control antibody, after which supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for TNFα. The results shown are the mean production of TNFα (means ± 1 SD, *P < .01, **P < .005 versus IgG1 control) for (A) LPS, (B) Zymosan A, or (C) PPD cultures. These data are representative of 3 experiments.
The effect of ligation of MyD-1 on the inhibition of TNFα induced by other pathogen products. Human PBMCs were cultured for 24 hours with either 100 ng/mL LPS, 1 μg/mL Zymosan A, or 1000 U/mL PPD in the presence or absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 or the isotype control antibody, after which supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for TNFα. The results shown are the mean production of TNFα (means ± 1 SD, *P < .01, **P < .005 versus IgG1 control) for (A) LPS, (B) Zymosan A, or (C) PPD cultures. These data are representative of 3 experiments.
Ligation of MyD-1 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and association with SHP-2
In order to identify the molecular mechanism by which MyD-1 inhibits the pathogen product-stimulated production of TNFα, we characterized the early signaling events associated with MyD-1 ligation. Essentially identical results were obtained with PBMCs and the human monocyte cell line, U937, as indicated where relevant. Thus, in many of the subsequent downstream signaling studies, U937 cells were used as a model for MyD-1 signaling in PBMCs, due to the difficulties associated with obtaining sufficient cell numbers of PBMCs/purified primary CD14+ monocytes radiolabeled to the high specific activity required for lipid signaling assays.
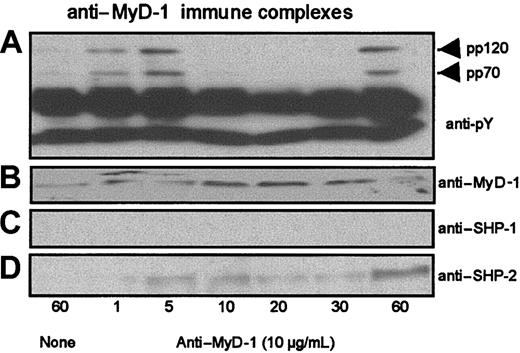
Ligation of MyD-1 on PBMCs or U937 cells induced tyrosine phosphorylation of one or more proteins of molecular weight consistent with that of SHP-1 or SHP-2 (approximately 70 kDa) and an additional protein of p120 (results not shown). It seemed likely that the p120 phosphoprotein might reflect the tyrosine phosphorylation of MyD-1 required for recruitment of SHP-1 and/or SHP-2. Consistent with this proposal, Western blot analysis of anti-MyD-1 immune complexes derived from U937 cells and PBMCs (Figure 3 and results not shown) did indeed reveal transient tyrosine phosphorylation of p120 (Figure 3A) and an associated phosphoprotein of approximately 70 kDa (Figure 3A). Subsequent reprobing with anti-MyD-1 (Figure 3B), anti-SHP-1 (Figure 3C), and anti-SHP-2 (Figure 3D) antibodies revealed these phosphoproteins to be MyD-1 (p120) and SHP-2 (p70). Similarly, analysis of anti-SHP-1 and anti-SHP-2 immune complexes showed that MyD-1 associated with SHP-2 but not SHP-1 (results not shown). Analysis of the kinetics of tyrosine phosphorylation and association of MyD-1 and SHP-2 (Figure 3A) revealed an early peak within 1 to 5 minutes followed by partial dissociation of SHP-2 from anti-MyD-1 immune complexes, presumably as a result of SHP-2-mediated dephosphorylation of MyD-1-ITIM(s). Subsequently, both MyD-1 and SHP-2 were tyrosine phosphorylated and again found in association at 60 minutes (Figure 3A).
Ligation of MyD-1 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment of SHP-2. Cells of the human monocyte cell line U937, which expresses surface MyD-1 (results not shown), were incubated in the presence and absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 antibody (ILA24; 10 μg/mL) for up to 60 minutes at 37°C and immune complexes prepared. The induction of tyrosine phosphorylation after crosslinking MyD-1 was assessed by Western blot analysis of anti-MyD-1 immune complexes using the anti-phosphotyrosine mAb, 4G10 (A). Similarly, anti-MyD-1 immune complexes were assessed for MyD-1 (B), SHP-1 (C), or SHP-2 (D) expression as indicated.
Ligation of MyD-1 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment of SHP-2. Cells of the human monocyte cell line U937, which expresses surface MyD-1 (results not shown), were incubated in the presence and absence of murine anti-human MyD-1 antibody (ILA24; 10 μg/mL) for up to 60 minutes at 37°C and immune complexes prepared. The induction of tyrosine phosphorylation after crosslinking MyD-1 was assessed by Western blot analysis of anti-MyD-1 immune complexes using the anti-phosphotyrosine mAb, 4G10 (A). Similarly, anti-MyD-1 immune complexes were assessed for MyD-1 (B), SHP-1 (C), or SHP-2 (D) expression as indicated.
MyD-1 couples to PI 3-kinase activity
SHP-2 signaling has been reported to promote growth factor-stimulated mitogenic signaling by recruiting PI 3-kinase to membranes via phosphotyrosine SH2 domain-dependent adaptors (p100, Gab, Dos)22-24 and hence we investigated whether MyD-1 mediated its negative regulatory effects via coupling to this pathway. Ligation of MyD-1 on [32P]-labeled human U937 monocytes did indeed stimulate production of [32P]PIP3, the product of PI 3-kinase activity (Figure 4A) with kinetics consistent with PI 3-kinase activation being consequent to the phosphorylation and association of MyD-1 and SHP-2 in these cells (Figure 3). LPS did not stimulate PI 3-kinase activity in U937 cells (results not shown). MyD-1-coupled PIP3 generation was blocked by pretreatment of the cells with the PI 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin (Figure 4A). Moreover, p85, the regulatory subunit of PI 3-kinase, was found in anti-SHP-2 (Figure 4B), but not anti-SHP-1 (results not shown), immune complexes following stimulation of these cells via MyD-1, with maximal levels of p85-SHP-2 association coinciding with peak tyrosine phosphorylation of SHP-2 (1 minute). Association of MyD-1, SHP-2, and p85 PI 3-kinase was similarly enhanced in PBMCs following stimulation with 10 μg/mL anti-MyD-1 (albeit with slower kinetics, maximum 10 minutes; data not shown).
Stimulation of human U937 monocytes with anti-MyD-1 stimulates PI 3-kinase. (A) Uninduced [32P]-labeled U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (▪) and absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Pretreatment (30 minutes) with wortmannin (1 nM) had little effect on basal PIP3 levels (▵) but suppressed anti-MyD-1-stimulated PIP3 production (▴). Similar anti-MyD-1 stimulations were carried out on cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85. IPTG-induced U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (•) and absence (○) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Lipids were extracted and [32P]PIP3 production was identified by TLC and quantified by liquid scintillation counting. Data are presented as means ± SD, n = 3, and are representative of 5 independent experiments demonstrating coupling of MyD-1 to PI 3-kinase. (B) Anti-SHP-2 immune complexes from U937 cells were assessed for p85 expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and SHP-2 expression.
Stimulation of human U937 monocytes with anti-MyD-1 stimulates PI 3-kinase. (A) Uninduced [32P]-labeled U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (▪) and absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Pretreatment (30 minutes) with wortmannin (1 nM) had little effect on basal PIP3 levels (▵) but suppressed anti-MyD-1-stimulated PIP3 production (▴). Similar anti-MyD-1 stimulations were carried out on cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85. IPTG-induced U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (•) and absence (○) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Lipids were extracted and [32P]PIP3 production was identified by TLC and quantified by liquid scintillation counting. Data are presented as means ± SD, n = 3, and are representative of 5 independent experiments demonstrating coupling of MyD-1 to PI 3-kinase. (B) Anti-SHP-2 immune complexes from U937 cells were assessed for p85 expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and SHP-2 expression.
To investigate whether the PI 3-kinase activity detected on MyD-1 ligation was consequent of the association of MyD-1, SHP-2, and p85, a U937 cell line was used that had been stably transfected with an IPTG-inducible dominant-negative form of p85 (U937:Δp85). This dominant-negative protein lacks the binding site for the p110 catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase and so when overexpressed will oblate p85-mediated PI 3-kinase association with p110.17 Indeed, ligation of MyD-1 in U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress Δp85 did not result in PI 3-kinase activity, indicating that MyD-1 was coupled to PI 3-kinase in a p85-dependent manner (Figure 4A).
Maturation-dependent coupling of MyD-1 to phospholipase D and sphingosine kinase downstream of PI 3-kinase
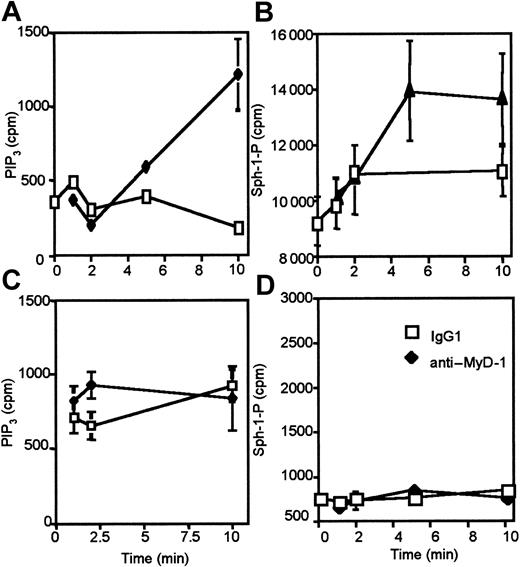
Activation of PI 3-kinase and the generation of PIP3 plays a key role in the recruitment and activation of a wide variety of lipid- and protein kinase-signaling cascades. We could find no evidence of MyD-1 coupling to the Erk, Jnk, or p38 MAP kinase cascades (results not shown) so we investigated the ability of MyD-1 to recruit lipid signaling cascades in a PI 3-kinase-dependent manner. Here we show that ligation of MyD-1 does not induce activation of PIP2-PLC to generate IP3 or diacylglycerol (DAG), second messengers that result in the mobilization of intracellular calcium and the activation of protein kinase C, respectively (Figure 5A). By contrast, ligation of MyD-1 activates PtdCho-PLD resulting in the generation of phosphatidic acid (PtdOH; Figure 5B). That coupling of MyD-1 to PtdCho-PLD is PI 3-kinase-dependent is illustrated by the finding that preincubation with the PI 3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin blocks such PLD activation (Figure 5C). Moreover, ligation of MyD-1 in U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress Δp85, conditions that abrogate PI 3-kinase activity (Figure 4A), did not result in PLD activation, indicating that MyD-1 was coupled to PLD in a p85-dependent manner (Figure 5C). MyD-1 ligation also leads to the activation of sphingosine kinase, resulting in the generation of another lipid second messenger, sphingosine-1-phosphate (Figure 5D). This production of sphingosine-1-phosphate is also dependent on prior p85-dependent PI 3-kinase signaling as generation is blocked either by pretreatment of U937 cells with wortmannin or by induction of Δp85 in U937:Δp85 cells (Figure 5E). Furthermore, sphingosine kinase activation is a consequence of PtdCho-PLD activation as sphingosine-1-phosphate generation is blocked by pretreatment of the cells with the primary alcohol, butan-1-ol (Figure 5F), which acts as an acceptor for the phosphatidyl intermediate of the PLD reaction and blocks formation of PtdOH.14,16,17
MyD-1 is coupled to consequent activation of PI 3-kinase, PtdCho-PLD, and sphingosine kinase. (A) U937 cells labeled with [3H]inositol were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour in the presence of 10 mM LiCl before measuring PIP2-PLC activation by determining total [3H]inositol phosphate generation. (B) U937 cells labeled with [3H]palmitate were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour before measuring PtdCho-PLD activation by determining [3H]PtdBut generation. (C) Uninduced [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated with IgG1 or anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated. (D) [32P]-labeled U937 cells were stimulated in the presence (♦) or absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times before determining levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate. (E) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. (F) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937: Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with 0.1% butan-1-ol as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate determinations from 3 to 6 independent experiments.
MyD-1 is coupled to consequent activation of PI 3-kinase, PtdCho-PLD, and sphingosine kinase. (A) U937 cells labeled with [3H]inositol were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour in the presence of 10 mM LiCl before measuring PIP2-PLC activation by determining total [3H]inositol phosphate generation. (B) U937 cells labeled with [3H]palmitate were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour before measuring PtdCho-PLD activation by determining [3H]PtdBut generation. (C) Uninduced [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated with IgG1 or anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated. (D) [32P]-labeled U937 cells were stimulated in the presence (♦) or absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times before determining levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate. (E) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. (F) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937: Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with 0.1% butan-1-ol as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate determinations from 3 to 6 independent experiments.
Interestingly, when U937 cells are induced to differentiate to a more macrophage-like phenotype by culture in dibutyrl-cAMP,14,16,17 MyD-1 coupling to PI 3-kinase and consequent sphingosine kinase activation is lost (Figure 6). This is in spite of MyD-1 expression being maintained at similar levels in both undifferentiated and differentiated phenotypes of U937 cells (results not shown). These results are consistent with rewiring of MyD-1 signaling following activation and recruitment of monocytes resulting from exposure to pathogens and hence may suggest that MyD-1 acts to prevent aberrant activation of monocytes/DCs in the absence of pathogens.
MyD-1 coupling to PI 3-kinase and sphingosine kinase is maturation dependent. U937 cells (A-B) or U937 cells induced to differentiate toward a macrophage phenotype by culture with dibutyrl cAMP (1 mM) for 48 hours (C-D) were stimulated in the presence (filled symbols) or absence (open symbols) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times and PIP3 (A,C) or sphingosine-1-phosphate (B,D) measured as described in “Materials and methods.”
MyD-1 coupling to PI 3-kinase and sphingosine kinase is maturation dependent. U937 cells (A-B) or U937 cells induced to differentiate toward a macrophage phenotype by culture with dibutyrl cAMP (1 mM) for 48 hours (C-D) were stimulated in the presence (filled symbols) or absence (open symbols) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times and PIP3 (A,C) or sphingosine-1-phosphate (B,D) measured as described in “Materials and methods.”
Inhibition of PI 3-kinase prevents MyD-1-induced suppression of TNFα secretion
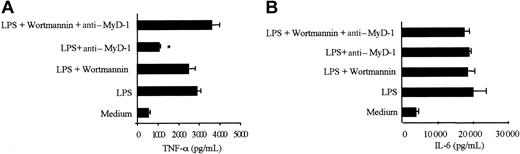
The role of the PI 3-kinase signaling pathway in mediating MyD-1 inhibition of TNFα production in PBMCs was investigated using the PI 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin,25 which strongly suppressed MyD-1-coupled PI 3-kinase activity in U937 cells (Figure 4A). Wortmannin, at a concentration that was specific for PI 3-kinase (1 nM),26 had no effect on basal or LPS-stimulated TNFα production but completely blocked anti-MyD-1-mediated inhibition of this response (Figure 7A). Indeed, while MyD-1 ligation suppressed LPS-induced TNFα secretion (by 51.5 ± 3.6%, n = 13) in untreated cells, culture with wortmannin essentially reversed (83.5 ± 14.8%, means ± SEM, n = 4 independent experiments) the effects of MyD-1 ligation. Similarly, an alternative PI 3-kinase inhibitor, Ly294002, also prevented MyD-1 suppression of TNFα secretion and suppressed PI 3-kinase activity in U937 cells (results not shown). Moreover, wortmannin had no effect on IL-6 production from these cells (Figure 7B), confirming that MyD-1 selectively targets TNFα secretion by this PI 3-kinase pathway.
Inhibition of TNFα by MyD-1 is regulated by a wortmannin-sensitive signaling cascade, but IL-6 secretion is not. Human PBMCs were cultured in the presence or absence of 100 ng/mL LPS, 10 μg/mL ILA24 mouse anti-human MyD-1, and 1 nM wortmannin for 24 hours, after which supernatants were analyzed for TNFα or IL-6 production. The results shown are the mean production of (A) TNFα or (B) IL-6 secretion in the presence of 1 nM wortmannin. The data are generated from triplicate samples and are shown as the mean concentration ± 1 SD. In the absence of 1 nM wortmannin, the levels of TNFα produced by anti-MyD-1 plus LPS compared with LPS are significantly reduced, *P < .001, but in the presence of 1 nM wortmannin there is no significant difference between any groups. These data are representative of 4 experiments.
Inhibition of TNFα by MyD-1 is regulated by a wortmannin-sensitive signaling cascade, but IL-6 secretion is not. Human PBMCs were cultured in the presence or absence of 100 ng/mL LPS, 10 μg/mL ILA24 mouse anti-human MyD-1, and 1 nM wortmannin for 24 hours, after which supernatants were analyzed for TNFα or IL-6 production. The results shown are the mean production of (A) TNFα or (B) IL-6 secretion in the presence of 1 nM wortmannin. The data are generated from triplicate samples and are shown as the mean concentration ± 1 SD. In the absence of 1 nM wortmannin, the levels of TNFα produced by anti-MyD-1 plus LPS compared with LPS are significantly reduced, *P < .001, but in the presence of 1 nM wortmannin there is no significant difference between any groups. These data are representative of 4 experiments.
MyD-1 signaling does not alter TNFα mRNA levels but rather results in intracellular retention of TNFα
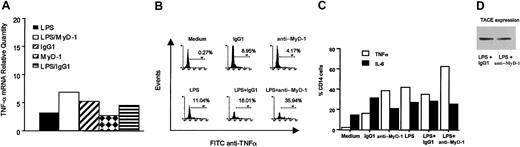
Further analysis by quantitative real-time RT-PCR revealed that MyD-1 ligation did not inhibit LPS-stimulated TNFα mRNA production (Figure 8A) but rather induced increased intracellular retention of the cytokine as measured by intracellular staining (Figure 8B). As indicated by the cytokine secretion results (Figure 1), this mechanism of action is specific to LPS-mediated induction of TNFα as IL-6 retention is not enhanced under the same conditions (Figure 8C). This intracellular retention of TNFα does not reflect down-regulation of TNFα-converting enzyme (TACE) expression, however, suggesting that MyD-1 signaling does not suppress TNFα secretion by modulating processing of membrane-bound TNFα to a mature soluble form (Figure 8D).
The measured decrease in TNFα production is not due to alterations in mRNA production but to retention of TNFα within monocytes. (A) Cytokine mRNA levels were assessed by TaqMan RT-PCR. The results are expressed as the relative change in mRNA compared with a calibrator. (B,C) Intracellular cytokine staining by FACS revealed that TNFα, but not IL-6, was being retained within monocytes after culture in the presence of LPS and anti-MyD-1. The results are expressed as the percentage TNFα-positive CD14+ cells, and these data are representative of 3 experiments. (D) Cell lysates were prepared from human PBMCs stimulated with either LPS (100 ng/mL) plus anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) or LPS plus IgG1 (10 μg/mL) for 24 hours at 37°C. The cell lysates were then subjected to Western blot analysis of TACE expression as described in “Materials and methods.” These lysates were prepared from a single donor and were representative of those from 2 other independent donors.
The measured decrease in TNFα production is not due to alterations in mRNA production but to retention of TNFα within monocytes. (A) Cytokine mRNA levels were assessed by TaqMan RT-PCR. The results are expressed as the relative change in mRNA compared with a calibrator. (B,C) Intracellular cytokine staining by FACS revealed that TNFα, but not IL-6, was being retained within monocytes after culture in the presence of LPS and anti-MyD-1. The results are expressed as the percentage TNFα-positive CD14+ cells, and these data are representative of 3 experiments. (D) Cell lysates were prepared from human PBMCs stimulated with either LPS (100 ng/mL) plus anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) or LPS plus IgG1 (10 μg/mL) for 24 hours at 37°C. The cell lysates were then subjected to Western blot analysis of TACE expression as described in “Materials and methods.” These lysates were prepared from a single donor and were representative of those from 2 other independent donors.
Anti-MyD-1: agonist or antagonist of MyD-1 on PBMCs?
MyD-1 coupling to this PI 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway may present a novel target for the development of therapeutic strategies for combating TNFα production and consequent inflammatory disease. It is therefore important to address whether anti-MyD-1 acts as an agonist or antagonist of MyD-1. To do this, we have determined whether anti-MyD-1 (ILA24) pretreatment blocks binding to lymphocytes of an Fc fusion protein of the cattle MyD-11 (Figure 9). An additional mAb, CC149, which recognizes an epitope distinct from ILA24 on MyD-1Ig,1 and TRT.1 (an isotype control mAb directed against turkey rhinotracheitus virus) were also tested for their blocking ability. Clearly, preincubating with mAb CC149 blocked binding of the MyD-1 fusion protein. Similarly, pretreating the cells with the anti-CD47 mAb (MEM-122) also blocked MyD-1 binding. In contrast, it is clear that mAb ILA24 does not block binding of the MyD-1 fusion protein and hence does not function as an antagonistic antibody. Rather, it would appear that mAb ILA24 acts as an agonistic antibody and mimics ligation of MyD-1 by the natural ligand CD47.
The anti-MyD-1 mAb ILA24 does not block binding of a MyD-1Ig fusion protein to CD47 expressed on lymphocytes. Bovine PBMCs were incubated with MyD-1Ig (5 μg/mL) that had been preincubated with either the anti-MyD-1 mAb ILA24 (open histogram, A), the anti-MyD-1 mAb CC149 (open histogram, B), or the relevant isotype-matched control mAbs (filled histograms). In addition, PBMCs were preincubated with the anti-CD47 mAb MEM-122 (open histogram, C) prior to addition of the MyD-1 fusion protein. All antibodies were used at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. MyD-1 binding was detected by labeling with FITC-conjugated goat anti-human IgG and FACS analysis of lymphocytes gated on the basis of forward and side scatter.
The anti-MyD-1 mAb ILA24 does not block binding of a MyD-1Ig fusion protein to CD47 expressed on lymphocytes. Bovine PBMCs were incubated with MyD-1Ig (5 μg/mL) that had been preincubated with either the anti-MyD-1 mAb ILA24 (open histogram, A), the anti-MyD-1 mAb CC149 (open histogram, B), or the relevant isotype-matched control mAbs (filled histograms). In addition, PBMCs were preincubated with the anti-CD47 mAb MEM-122 (open histogram, C) prior to addition of the MyD-1 fusion protein. All antibodies were used at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. MyD-1 binding was detected by labeling with FITC-conjugated goat anti-human IgG and FACS analysis of lymphocytes gated on the basis of forward and side scatter.
Discussion
The identification of novel immune regulatory molecules with potent therapeutic potential will be an important strategy for the modulation of host immune responses and thus may provide an alternative and possibly safer approach to combat disease. Here we have described the characterization of one such molecule in humans, MyD-1. MyD-1 was initially described in the bovine system where it was found to be expressed on monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and a subset of afferent lymph veiled cells.1,27 Early experiments established that ligation of this molecule with mAbs against MyD-1 could inhibit antigen-specific T-cell responses.1,12 We have now investigated the mechanism of the functional activity of the ILA24 mAb binding to human MyD-1, whose expression is restricted to CD14+ monocytes and subsets of ex vivo CD83+ blood DCs and CD14+ monocyte-derived DCs.
Pathogen products such as LPS are known to activate monocytes and other APCs (such as DCs) to initiate an inflammatory response28 and promote development of T-cell responses.29 The distribution of MyD-1 expression, together with the fact that it is a member of an ITIM-containing inhibitory receptor family, suggested that MyD-1 signaling could act to suppress monocyte/DC activation. This theory was tested by assessing the effect of ligation of MyD-1 on the LPS-stimulated production of inflammatory cytokines. We found that MyD-1 substantially inhibited TNFα secretion (by 51.5 ± 3.6%) from LPS-stimulated (100 ng/mL) PBMCs (Figure 1) in 13 independent experiments using different individual human donors. This inhibitory effect was also exhibited when TNFα was induced by other pathogen products such as PPD and Zymosan A, and is an important point as it raises the possibility that MyD-1 may regulate the activation of the innate immune response to all pathogens. To achieve such reproducible inhibition across an unrelated, random cohort of individuals, given the increasing evidence that TNF promoter polymorphisms dictate the levels of TNFα production and susceptibility to infectious diseases or inflammatory autoimmune disorders,30-33 indicates that the MyD-1-driven inhibition of LPS-induced TNFα production is clearly likely to be biologically significant and have therapeutic potential. In support of this, methotrexate, which is the “gold standard” therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and other acute and chronic inflammatory diseases in which TNFα is a major mediator of the inflammatory response,34-37 is much less effective than anti-Myd-1 at suppressing LPS-stimulated TNFα production in vitro.38-40 Moreover, anti-Myd-1, unlike methotrexate34 or other anti-inflammatory therapies such as IL-10,41 inhibited TNFα without significantly affecting any other cytokines that we measured in response to LPS, including IL-1β and IL-6. This latter finding was perhaps rather surprising given that these 2 cytokines normally share functional characteristics and expression profiles with TNFα and have primarily been defined as part of the acute phase response to infectious pathogens.42 However, as the actions of MyD-1 are specifically targeted to TNFα, such potentially selective therapy could be particularly beneficial as it may allow suppression of the TNF-mediated inflammation associated with the pathogenesis and progression of autoimmune disease without compromising the ability of the host to respond to infection.
Given that the MyD-1 molecule contains ITIM motifs we next investigated which signaling cascades were initiated following ligation of MyD-1 and most importantly, whether these were responsible for the inhibition of TNFα secretion. Initial experiments demonstrated that anti-MyD-1 treatment stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of MyD-1 and target effectors and more detailed kinetic work established that tyrosine phosphorylation of MyD-1 led to association with SHP-2 but not SHP-1 (Figure 3). Although the role of tyrosine phosphorylation in the regulation of SHP-1 or SHP-2 phosphatase activity is controversial,43 such tyrosine phosphorylation is generally indicative of receptor-mediated recruitment. Moreover, the observation of coassociation with SHP-2 has similarly been reported by groups studying other members of the SIRP family.4,44,45 However, we have extended this work further to identify the downstream signaling events following crosslinking of MyD-1 (Figure 10). We have established that an increase in PI 3-kinase activity is detected rapidly following ligation of MyD-1 and that this activation is reflected by coassociation of the regulatory p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase, SHP-2, and MyD-1 (Figure 4). Such coupling to PI 3-kinase appears to be critical for the activation of downstream signals including PtdCho-PLD and sphingosine kinase and is lost following maturation of U937 cells to a macrophage-like phenotype (Figures 5 and 6).
MyD-1 signaling in monocytes. Ligation of MyD-1 results in the tyrosine phosphorylation of MyD-1 and recruitment of SHP-2. Complex formation allows SHP-2 to act as an adaptor for p85 and results in the activation of PI 3-kinase. Generation of PIP3 leads to the activation of PtdCho-PLD, production of PtdOH, and consequent activation of sphingosine kinase.
MyD-1 signaling in monocytes. Ligation of MyD-1 results in the tyrosine phosphorylation of MyD-1 and recruitment of SHP-2. Complex formation allows SHP-2 to act as an adaptor for p85 and results in the activation of PI 3-kinase. Generation of PIP3 leads to the activation of PtdCho-PLD, production of PtdOH, and consequent activation of sphingosine kinase.
The role of these signaling cascades, and in particular PI 3-kinase, in the inhibition of LPS-stimulated TNFα production was further investigated using wortmannin, an inhibitor of PI-3 kinase. Addition of wortmannin can fully overcome the inhibition of TNFα secretion, implying a strong link between activation of this signaling enzyme and the selective regulation of this cytokine by MyD-1. Although we have not shown the precise sites of integration of the MyD-1/PI 3-kinase and LPS/TNF pathways, it is widely established that signaling through TLR4 via MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways is required for effective LPS induction of TNFα production.19-21 Consistent with this, we and others46-49 have shown that Erk, p38 MAPkinase, and NF-κB signaling is necessary for LPS-mediated induction of TNFα production in monocytes/macrophages. Interestingly, Guha and Mackman50 have very recently reported that PI 3-kinase signaling can negatively regulate TNFα production by human monocytes by suppressing LPS-induced activation of Erk1/2, p38, and Jnk MAPkinases. This new report may therefore suggest that the MyD-1/PI 3-kinase signals directly target LPS/TLR-4-derived signals. Importantly, the finding that MyD-1 coupling to PI 3-kinase and downstream signals is lost on maturation to a macrophage-like phenotype suggests that MyD-1 may act to suppress aberrant induction of TNFα and inflammation in the absence or presence of low levels of pathogen products but that this negative signal can be overcome and rewired following activation of the innate immune response by pathogens.
MyD-1-mediated inhibition of TNFα secretion was found not to reflect modulation of TNFα mRNA levels but rather an increased intracellular retention of TNFα (Figure 8). Interestingly, PI 3-kinase signaling has often been postulated to be involved in the regulation of cellular trafficking51 and indeed we have previously shown that a similar, yet distinct (p85-independent) PI 3-kinase/PtdCho-PLD/sphingosine kinase signaling pathway plays a role in regulating vesicular trafficking of immune complexes.14,52 Hence, these results may suggest that MyD-1 employs this novel PI 3-kinase pathway to target TNFα secretion rather than TNFα synthesis. One possibility was that PI 3-kinase signaling was modulating TNFα secretion by regulating “shedding” of membrane-bound TNFα from the cell surface. Indeed, it has been shown in a number of systems53,54 that regulation of TNFα secretion can be achieved by modulating the expression of TACE. However, we have found that MyD-1 signaling does not suppress expression of TACE (Figure 8D), thereby suggesting that ligation of MyD-1 does not disrupt processing of mature secreted TNFα but rather simply regulates secretion. Such MyD-1-mediated retention of mature TNFα therefore presumably provides a mechanism that allows for a rapid, active TNFα response to pathogens when required.
Finally, to address whether anti-MyD-1 mimics stimulation of MyD-1 by its natural ligand CD47, we investigated whether mAb ILA24 could block binding of a MyD-1 fusion protein to CD47-bearing lymphocytes (Figure 9). The data clearly show that anti-MyD-1 mAb ILA24 does not block binding and hence suggests that it acts by mimicking ligation of MyD-1 by the natural ligand CD47. Interestingly, a recent paper by Latour et al55 reports that ligation of SIRP-α on human DCs by a polymeric CD47-Fc fusion protein impairs DC maturation, cytokine secretion, and Th1 development, suggesting that MyD-1/SIRP-α agonists may have therapeutic potential for combating TNFα production and consequent inflammatory disease.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, June 12, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2002-11-3596.
Supported by the Edward Jenner Institute for Vaccine Research. M.H. and W.H. were funded by an Edward Jenner External Collaborative Grant. C.H. is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, and M.H.B. and G.P.B. are funded by the Medical Research Council.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.



![Figure 4. Stimulation of human U937 monocytes with anti-MyD-1 stimulates PI 3-kinase. (A) Uninduced [32P]-labeled U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (▪) and absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Pretreatment (30 minutes) with wortmannin (1 nM) had little effect on basal PIP3 levels (▵) but suppressed anti-MyD-1-stimulated PIP3 production (▴). Similar anti-MyD-1 stimulations were carried out on cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85. IPTG-induced U937:Δp85 cells were stimulated in the presence (•) and absence (○) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times at 37°C. Lipids were extracted and [32P]PIP3 production was identified by TLC and quantified by liquid scintillation counting. Data are presented as means ± SD, n = 3, and are representative of 5 independent experiments demonstrating coupling of MyD-1 to PI 3-kinase. (B) Anti-SHP-2 immune complexes from U937 cells were assessed for p85 expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and SHP-2 expression.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/102/7/10.1182_blood-2002-11-3596/6/m_h81934992004.jpeg?Expires=1767716693&Signature=wJzFH-~eF4S8pfSdsEz-SFA7kIAIKTvj8UkT7L-EJUhFlwiSr-cJAYm7KF5DK3jRyuB~oRkNHyDSGc61I9P8y~8vday5QBaADOlrF6sjrxzsoT~wv9Jpx77NaEbrvHSAVNbeVQCrLnAaUF5PhRgtJhcfFGhbExvIoDk4E-wzI0vrbJvEOlq3ZBHxNpuBp3c1bijoI5dTLg2O62YD6EbSu9KJNTNIDbYPIQioeJcbUdbTgXW90hrC1NLtrCmXcu-B0QKoeOybv9yfj89wY2NViRVSlLGRNUcIIbB8~9Q08rPbBtWtg2FCqu20SljE7JHDaWlm9B0L79Nj0EigfSEB9w__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 5. MyD-1 is coupled to consequent activation of PI 3-kinase, PtdCho-PLD, and sphingosine kinase. (A) U937 cells labeled with [3H]inositol were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour in the presence of 10 mM LiCl before measuring PIP2-PLC activation by determining total [3H]inositol phosphate generation. (B) U937 cells labeled with [3H]palmitate were stimulated with isotype control (IgG1), LPS (100 ng/mL), anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL), or LPS plus anti-MyD-1 for 1 hour before measuring PtdCho-PLD activation by determining [3H]PtdBut generation. (C) Uninduced [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]palmitate-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated with IgG1 or anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated. (D) [32P]-labeled U937 cells were stimulated in the presence (♦) or absence (□) of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for the indicated times before determining levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate. (E) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with wortmannin (5 nM or 50 nM) as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. (F) Uninduced [3H]serine-labeled U937: Δp85 cells or [3H]serine-labeled U937:Δp85 cells induced to overexpress the dominant-negative form of p85 were stimulated in the presence or absence of anti-MyD-1 (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C. Some samples were pretreated (30 minutes) with 0.1% butan-1-ol as indicated and sphingosine-1-phosphate levels determined. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate determinations from 3 to 6 independent experiments.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/102/7/10.1182_blood-2002-11-3596/6/m_h81934992005.jpeg?Expires=1767716693&Signature=BQZN0dSW5PsQ6p9TGRy6uzEM87cUh-jlX1Lu4Ju9wRAXQVWpoz~kqlqNtJvud0xU4UdQFB4WD1JPifzEzbdPiTril9lKUZdc8ozlSTBqjFnqIuOVt4L9TDpABDgWrmcPxbs3JPU4v0jnANNjlSRYg-IvTzmC2FFbdY2De9pdva3LI2Wcf8TqC3ziXE8z8aGX2EJepAVX5pmxjuewwLzQDFXGrB9EmH~vxNiPNDEIDsxDhmOYcqfmZ~QA9q~5TcudVn5ytNCz-QQvBdiJhFoMp7GFOQNyDi6HOYTNrNb5yUB0enhKdGZKt2yhRlg8fwlzTJinbwU3j6MhkjJGyfNKNg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal