Abstract
In this article, we report on 904 patients undergoing transplantation for follicular lymphoma. A total of 176 (19%) received allogeneic, 131 (14%) received purged autologous, and 597 (67%) received unpurged autologous transplants. Five-year treatment-related mortality (TRM) rates were 30%, 14%, and 8% and 5-year recurrence rates were 21%, 43%, and 58% after allotransplantation, purged autotransplantation, and unpurged autotransplantation, respectively. In multivariate analyses, allotransplantation had higher TRM and lower disease recurrence. Purged autotransplantation had a 26% lower recurrence risk than unpurged autotransplantation. Five-year probabilities of survival were 51%, 62%, and 55% after allogeneic, purged autotransplantation, and unpurged autotransplantation, respectively. Advanced age, prolonged interval from diagnosis to transplantation, high lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), refractory disease, bone marrow involvement, low performance scores, and transplantation between 1990 and 1993 were associated with adverse outcomes. Total body irradiation was associated with higher TRM but lower recurrence. There was no association between acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease and recurrence after allotransplantation. We conclude that both allogeneic and autologous transplantation can induce durable remissions. There may be a benefit to graft purging in autologous transplantation. The decreased recurrence after allotransplantation is offset by increased TRM. We did not detect a correlation between graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and recurrence. Finally, outcomes of transplantation for follicular lymphoma show improvement over the past decade. (Blood. 2003;102:3521-3529)
Introduction
Follicular lymphoma is considered an indolent disorder but can have an unpredictable and often relentless course.1-5 Treatments such as chemotherapy, biologic response modifiers, and monoclonal antibodies are not considered curative and, with the possible exception of interferon, do not prolong survival.6,7 In contrast, autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is shown in several phase 2 studies to induce remissions in patients with recurrent or newly diagnosed disease.8-21 Although recurrence rates are high in some of these studies, some patients have very durable remissions and may be cured.22 Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is also a potentially curative approach. Recurrence rates after allogeneic transplantation are low, but treatment-related mortality (TRM) is high, related, in part, to a tendency to use this therapy in patients with very advanced disease.23-32 To evaluate the roles of allogeneic versus autologous transplantation, as well as to gather additional insights into mechanisms of disease control, we studied 904 patients undergoing allogeneic or autologous transplantation for follicular lymphoma between 1990 and 1999 who were reported to the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry (IBMTR) or the Autologous Blood and Marrow Transplant Registry (ABMTR).
Patients and methods
Data sources
The IBMTR is a voluntary working group of more than 350 transplantation centers worldwide that contribute detailed data on consecutive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantations to a statistical center at the Health Policy Institute of the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee. The ABMTR is a voluntary organization of more than 250 transplantation centers primarily in North and South America that report data on consecutive autotransplantations to the same statistical center. On the basis of data collected in the Centers for Disease Control Hospital Surveys and the U.S. Government Accounting Office and worldwide surveys of transplantation activity, approximately 35% of allogeneic transplantations worldwide and more than 50% of autotransplantations in North and South America are registered with the IBMTR/ABMTR. Participating centers are required to register all transplants consecutively; compliance is monitored by on-site audits. Patients are followed longitudinally, with yearly follow-up. Computerized checks for errors, physician reviews of submitted data, and on-site audits of participating centers ensure data quality.
The IBMTR/ABMTR collects data at 2 levels: registration and research. Registration data include disease type, age, sex, pretransplantation performance status, disease stage and chemotherapy responsiveness, date of diagnosis, donor and graft type (bone marrow- and/or blood-derived stem cells), high-dose conditioning regimen, posttransplantation engraftment, graft-versus-host disease, disease recurrence and survival, development of a new malignancy, and cause of death. Requests for data on disease or death for registered patients are at 6-month intervals. All IBMTR/ABMTR teams contribute registration data on all patients. Research data are collected on subsets of registered patients selected by using a weighted randomization scheme, including comprehensive pretransplantation and posttransplantation clinical information.
Patients
We reviewed all HLA-identical sibling transplantations and autologous transplantations for follicular lymphoma performed between 1990 and 1999 and reported to the IBMTR/ABMTR. A total of 2459 registered cases were identified. Of these cases, 904 patients with follicular lymphoma both at diagnosis and at the time of transplantation had full research data and were included in the analysis. This analysis included patients with follicular small cleaved-cell lymphoma (Working Formulation group B), follicular mixed-cell lymphoma (Working Formulation group C), and follicular large cell lymphoma (Working Formulation group D). Patients initially diagnosed with follicular lymphoma, but whose disease transformed to intermediate-grade or high-grade lymphoma before transplantation, were excluded. Patients receiving nonmyeloablative conditioning regimens for allogeneic transplantation were excluded. To ensure that the research patients were representative of all registered patients, demographics, relapse rates, and survival rates between research and registered patients were compared; no differences were noted. Patients were considered to have “early” disease if they received their transplant in first or second complete remission or at the time of first relapse. All other patients were considered to have advanced disease.
Endpoints
Primary outcomes were survival, disease-free survival (DFS; survival without lymphoma after transplantation), recurrence, and TRM (treatment-related or nonrelapse mortality). Any death occurring within 28 days after transplantation was considered a TRM. Additionally, any death occurring 28 days or more after transplantation in a patient in continuous remission was considered treatment related. Patients with recurrent lymphoma were censored at the time of relapse, and those patients alive in remission were censored at the last follow-up evaluation. For DFS, patients were considered treatment failures at the time of relapse or death from any cause; patients alive in continuous complete remission were censored at the last follow-up evaluation. Patients who never achieved complete remission were analyzed as having recurrent lymphoma on day 28. Other outcomes examined were acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and chronic GVHD. Acute GVHD was defined as moderate to severe (grades II to IV) disease using established criteria; patients surviving more than 21 days with evidence of engraftment were considered at risk. Chronic GVHD was determined by clinical criteria in patients surviving more than 90 days with evidence of engraftment.
Statistical analysis
Univariate comparisons were done by using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous data and the chi-square test for categorical variables. Probabilities of survival and DFS were calculated by using the Kaplan-Meier product-limit estimate. Probabilities of relapse and TRM were calculated by using cumulative incidences to allow for competing risks. The 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were computed by using the arc sine-square root transformation. TRM, relapse, DFS, and survival after autologous (purged/unpurged) versus HLA-identical sibling transplantation were evaluated in multivariate analyses by using Cox proportional hazards regression to adjust for other potentially confounding differences between the cohorts. Variables considered in multivariate analysis are as follows: type of transplant, age, sex, Karnofsky performance score at transplantation, disease stage at transplantation, chemosensitivity, bone marrow involvement at diagnosis and transplantation, histology type, presence of B symptoms at diagnosis, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) at transplantation, initial chemotherapy given, interval from diagnosis to transplantation, use of total body irradiation (TBI) or other field radiation, use of growth factors, graft source, and year of transplantation. Each model contained the main effect (type of transplant: unpurged autologous transplant versus purged autologous transplant versus HLA-identical sibling transplant). We tested the proportional hazards assumption for each factor in the Cox model by using time-dependent covariates. When this statistic indicated differential effects over time (nonproportional hazards), models were constructed to break the posttransplantation time course into 2 periods, using the maximized partial likelihood method to find the most appropriate breakpoint. Interactions between the type of transplant and all covariates were tested prior to stepwise modeling. After modeling time-varying effects and interactions, the final multivariate model was built by using a forward stepwise model selection approach. Factors significantly associated with the outcome variable at a 5% α level were kept in the final model. First-order interactions were again examined between the type of transplant and all significant prognostic factors. Examination for center effects used a random effects or frailty model. No statistically significant center effect was noted. All P values are 2-sided.
Results
Patient and transplant characteristics
Patient-, disease-, and transplant-related characteristics are listed in Table 1 and compared across the 3 treatment groups. A total of 176 patients underwent allogeneic transplantation and 728 underwent autologous transplantation; 131 of the autologous grafts were treated in vitro to remove residual lymphoma cells (purged). There was a slight majority of men in each of the groups, reflective of the slightly higher incidence of follicular lymphoma in men.
Patient-, disease-, and transplantation-related characteristics
. | Type of transplant . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables . | HLA-identical sibling . | Autologous purged . | Autologous unpurged . | ||
| N | 176 | 131 | 597 | ||
| Median age, y (range) | 42 (22-64) | 49 (29-64) | 49 (18-71) | ||
| Men (%) | 95 (54) | 83 (63) | 320 (54) | ||
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| No more than 80% | 60 (34) | 17 (13) | 183 (31) | ||
| 90%-100% | 116 (66) | 114 (87) | 414 (69) | ||
| CMV status at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| Negative | 85 (48) | 16 (12) | 153 (26) | ||
| Positive | 88 (50) | 32 (25) | 205 (34) | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | 83 (63) | 239 (40) | ||
| Disease status at transplantation (%)*† | |||||
| Early | 85 (48) | 69 (53) | 350 (59) | ||
| Advanced | 91 (52) | 62 (47) | 247 (41) | ||
| Bone marrow involvement at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| Absent | 102 (58) | 71 (54) | 355 (59) | ||
| Present | 74 (42) | 60 (46) | 242 (41) | ||
| Bone marrow involvement at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| Absent | 119 (68) | 103 (79) | 486 (81) | ||
| Present | 57 (32) | 28 (21) | 111 (19) | ||
| Histology (%)* | |||||
| Follicular, small cleaved | 91 (52) | 67 (51) | 218 (36) | ||
| Follicular, mixed small and large | 72 (41) | 52 (40) | 242 (41) | ||
| Follicular, large cell | 13 (7) | 12 (9) | 137 (23) | ||
| Disease stage at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| I-II | 22 (13) | 23 (17) | 113 (19) | ||
| III-IV | 152 (86) | 107 (82) | 476 (80) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 8 (1) | ||
| B symptoms at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| Absent | 116 (66) | 94 (72) | 367 (62) | ||
| Present | 48 (27) | 33 (25) | 182 (30) | ||
| Unknown | 12 (7) | 4 (3) | 48 (8) | ||
| Chemosensitivity (%)* | |||||
| Sensitive | 118 (67) | 111 (85) | 488 (82) | ||
| Resistant | 31 (18) | 14 (11) | 66 (11) | ||
| Untreated/unknown | 27 (15) | 6 (4) | 43 (7) | ||
| Serum LDH at diagnosis (%)* | |||||
| Normal | 117 (67) | 55 (42) | 389 (65) | ||
| Abnormal | 44 (25) | 27 (21) | 174 (29) | ||
| Unknown | 15 (8) | 49 (37) | 34 (6) | ||
| Initial chemotherapy (%)* | |||||
| CHOP ± other | 44 (25) | 57 (44) | 206 (34) | ||
| Fludarabine ± other | 29 (16) | 7 (5) | 63 (11) | ||
| Other | 44 (25) | 32 (24) | 221 (37) | ||
| Unknown | 59 (34) | 35 (27) | 107 (18) | ||
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation (%) | |||||
| Less than 1 y | 26 (15) | 27 (21) | 115 (19) | ||
| 1-2 y | 56 (32) | 32 (24) | 156 (26) | ||
| More than 2 y | 94 (53) | 72 (55) | 326 (55) | ||
| Graft type (%)* | |||||
| Bone marrow | 135 (77) | 100 (76) | 89 (15) | ||
| Peripheral blood/both | 41 (23) | 31 (24) | 508 (85) | ||
| Year of transplantation (%)* | |||||
| 1990-1993 | 50 (28) | 70 (54) | 181 (30) | ||
| 1994-1996 | 64 (37) | 41 (31) | 269 (45) | ||
| 1997-1999 | 62 (35) | 20 (15) | 147 (25) | ||
| Conditioning regimen (%)* | |||||
| TBI | 120 (68) | 44 (34) | 184 (31) | ||
| Non-TBI | 56 (32) | 87 (66) | 413 (69) | ||
| Use of involved field radiation (%) | |||||
| No | 169 (96) | 128 (98) | 576 (96) | ||
| Yes | 7 (4) | 3 (2) | 21 (4) | ||
| GVHD prophylaxis (%) | |||||
| T-cell depletion | 28 (16) | — | — | ||
| MTX ± other | 113 (64) | — | — | ||
| CSA ± other/other or none | 35 (20) | — | — | ||
| AGVHD (%) | |||||
| None-mild | 108 (61) | — | — | ||
| Moderate-severe | 65 (37) | — | — | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | — | — | ||
| Chronic GVHD (%) | |||||
| None | 131 (74) | — | — | ||
| Mild-severe | 42 (24) | — | — | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | — | — | ||
| Number of centers | 56 | 21 | 98 | ||
. | Type of transplant . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables . | HLA-identical sibling . | Autologous purged . | Autologous unpurged . | ||
| N | 176 | 131 | 597 | ||
| Median age, y (range) | 42 (22-64) | 49 (29-64) | 49 (18-71) | ||
| Men (%) | 95 (54) | 83 (63) | 320 (54) | ||
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| No more than 80% | 60 (34) | 17 (13) | 183 (31) | ||
| 90%-100% | 116 (66) | 114 (87) | 414 (69) | ||
| CMV status at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| Negative | 85 (48) | 16 (12) | 153 (26) | ||
| Positive | 88 (50) | 32 (25) | 205 (34) | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | 83 (63) | 239 (40) | ||
| Disease status at transplantation (%)*† | |||||
| Early | 85 (48) | 69 (53) | 350 (59) | ||
| Advanced | 91 (52) | 62 (47) | 247 (41) | ||
| Bone marrow involvement at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| Absent | 102 (58) | 71 (54) | 355 (59) | ||
| Present | 74 (42) | 60 (46) | 242 (41) | ||
| Bone marrow involvement at transplantation (%)* | |||||
| Absent | 119 (68) | 103 (79) | 486 (81) | ||
| Present | 57 (32) | 28 (21) | 111 (19) | ||
| Histology (%)* | |||||
| Follicular, small cleaved | 91 (52) | 67 (51) | 218 (36) | ||
| Follicular, mixed small and large | 72 (41) | 52 (40) | 242 (41) | ||
| Follicular, large cell | 13 (7) | 12 (9) | 137 (23) | ||
| Disease stage at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| I-II | 22 (13) | 23 (17) | 113 (19) | ||
| III-IV | 152 (86) | 107 (82) | 476 (80) | ||
| Unknown | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 8 (1) | ||
| B symptoms at diagnosis (%) | |||||
| Absent | 116 (66) | 94 (72) | 367 (62) | ||
| Present | 48 (27) | 33 (25) | 182 (30) | ||
| Unknown | 12 (7) | 4 (3) | 48 (8) | ||
| Chemosensitivity (%)* | |||||
| Sensitive | 118 (67) | 111 (85) | 488 (82) | ||
| Resistant | 31 (18) | 14 (11) | 66 (11) | ||
| Untreated/unknown | 27 (15) | 6 (4) | 43 (7) | ||
| Serum LDH at diagnosis (%)* | |||||
| Normal | 117 (67) | 55 (42) | 389 (65) | ||
| Abnormal | 44 (25) | 27 (21) | 174 (29) | ||
| Unknown | 15 (8) | 49 (37) | 34 (6) | ||
| Initial chemotherapy (%)* | |||||
| CHOP ± other | 44 (25) | 57 (44) | 206 (34) | ||
| Fludarabine ± other | 29 (16) | 7 (5) | 63 (11) | ||
| Other | 44 (25) | 32 (24) | 221 (37) | ||
| Unknown | 59 (34) | 35 (27) | 107 (18) | ||
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation (%) | |||||
| Less than 1 y | 26 (15) | 27 (21) | 115 (19) | ||
| 1-2 y | 56 (32) | 32 (24) | 156 (26) | ||
| More than 2 y | 94 (53) | 72 (55) | 326 (55) | ||
| Graft type (%)* | |||||
| Bone marrow | 135 (77) | 100 (76) | 89 (15) | ||
| Peripheral blood/both | 41 (23) | 31 (24) | 508 (85) | ||
| Year of transplantation (%)* | |||||
| 1990-1993 | 50 (28) | 70 (54) | 181 (30) | ||
| 1994-1996 | 64 (37) | 41 (31) | 269 (45) | ||
| 1997-1999 | 62 (35) | 20 (15) | 147 (25) | ||
| Conditioning regimen (%)* | |||||
| TBI | 120 (68) | 44 (34) | 184 (31) | ||
| Non-TBI | 56 (32) | 87 (66) | 413 (69) | ||
| Use of involved field radiation (%) | |||||
| No | 169 (96) | 128 (98) | 576 (96) | ||
| Yes | 7 (4) | 3 (2) | 21 (4) | ||
| GVHD prophylaxis (%) | |||||
| T-cell depletion | 28 (16) | — | — | ||
| MTX ± other | 113 (64) | — | — | ||
| CSA ± other/other or none | 35 (20) | — | — | ||
| AGVHD (%) | |||||
| None-mild | 108 (61) | — | — | ||
| Moderate-severe | 65 (37) | — | — | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | — | — | ||
| Chronic GVHD (%) | |||||
| None | 131 (74) | — | — | ||
| Mild-severe | 42 (24) | — | — | ||
| Unknown | 3 (2) | — | — | ||
| Number of centers | 56 | 21 | 98 | ||
CMV indicates cytomegalovirus; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunomycin, Oncovin, prednisone; MTX, methotrexate; CSA, cyclosporin A; —, not applicable; and AGVHD, acute graft-versus-host disease.
P <.01 for difference between transplant groups.
Early disease indicates patients whose disease status at transplantation is in first or second complete remission, or in first relapse; advanced disease, patients whose disease status at transplantation is in second or greater relapse, in third complete remission, or with primary induction failure.
The median age of those patients receiving allogeneic transplants was 42 versus 49 years for those patients receiving autologous transplants. This difference was not statistically significant. There were statistically significant imbalances among the 3 treatment groups in several other characteristics. Allograft recipients were more likely to have poor performance status, advanced disease, increased LDH, and bone marrow involvement at transplantation and to have chemotherapy-resistant disease. Autograft recipients were more likely to have follicular large cell lymphoma.
Transplantation regimens also varied significantly. Bone marrow grafts and TBI conditioning were most commonly used for allogeneic transplantation. Chemotherapy conditioning was more commonly used for autologous transplantation. Bone marrow was more commonly used for purged autologous grafts, whereas peripheral blood was the preferred stem cell source for unpurged autologous transplantations. Purged autologous transplantation was performed more commonly at the beginning of the decade, whereas allogeneic transplantation was increasingly used toward the late 1990s.
The median follow-up of survivors was 36 months for allograft recipients, 49 months for purged autograft recipients, and 41 months for unpurged autograft recipients.
The types of purging used are summarized in Table 2. A variety of methodologies were reported, but purging by in vitro exposure to 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide was the most common, accounting for 50% of purged grafts.
Purging methods used for autologous transplantation (N = 131)
. | n(%) . |
|---|---|
| Monoclonal antibody | 14 (11) |
| 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide | 65 (50) |
| Positive stem cell selection | 28 (21) |
| Drugs | 24 (18) |
| 4-hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide | 65 |
| Etoposide + methylprednisolone | 18 |
| Vincristine + methylprednisolone | 6 |
. | n(%) . |
|---|---|
| Monoclonal antibody | 14 (11) |
| 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide | 65 (50) |
| Positive stem cell selection | 28 (21) |
| Drugs | 24 (18) |
| 4-hydroperoxy cyclophosphamide | 65 |
| Etoposide + methylprednisolone | 18 |
| Vincristine + methylprednisolone | 6 |
Outcomes
Outcomes are summarized in Table 3. TRM after allogeneic transplantation was 24% at 1 year and 30% at 5 years. TRM after autologous transplantation was 4% to 8% at 1 year and 8% to 14% at 5 years. The recurrence rate after allogeneic transplantation was 19% at 1 year with very few relapses thereafter. The recurrence rate after unpurged autologous transplantation was 36% at 1 year and 58% at 5 years. The recurrence rate after purged autologous transplantation was 25% at 1 year and 43% at 5 years.
Univariate outcome probabilities
. | Type of transplant, probability, % (95% CI) . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes . | HLA-identical sibling . | Autologous purged . | Autologous unpurged . | ||
| Treatment-related mortality* | |||||
| 1 y | 24 (18-32) | 8 (5-15) | 4 (3-6) | ||
| 3 y | 28 (21-36) | 10 (6-17) | 6 (4-8) | ||
| 5 y | 30 (23-40) | 14 (8-22) | 8 (6-11) | ||
| Relapse* | |||||
| 1 y | 19 (14-26) | 25 (18-34) | 36 (32-40) | ||
| 3 y | 21 (15-28) | 40 (32-50) | 52 (48-57) | ||
| 5 y | 21 (15-28) | 43 (35-54) | 58 (53-63) | ||
| Disease-free survival† | |||||
| 1 y | 55 (48-62) | 66 (58-74) | 59 (55-63) | ||
| 3 y | 48 (40-55) | 48 (39-57) | 41 (37-45) | ||
| 5 y | 45 (36-53) | 39 (30-48) | 31 (27-36) | ||
| Overall survival† | |||||
| 1 y | 61 (54-68) | 82 (76-89) | 81 (78-84) | ||
| 3 y | 54 (47-62) | 71 (63-79) | 65 (61-69) | ||
| 5 y | 51 (43-60) | 62 (53-72) | 55 (50-60) | ||
. | Type of transplant, probability, % (95% CI) . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes . | HLA-identical sibling . | Autologous purged . | Autologous unpurged . | ||
| Treatment-related mortality* | |||||
| 1 y | 24 (18-32) | 8 (5-15) | 4 (3-6) | ||
| 3 y | 28 (21-36) | 10 (6-17) | 6 (4-8) | ||
| 5 y | 30 (23-40) | 14 (8-22) | 8 (6-11) | ||
| Relapse* | |||||
| 1 y | 19 (14-26) | 25 (18-34) | 36 (32-40) | ||
| 3 y | 21 (15-28) | 40 (32-50) | 52 (48-57) | ||
| 5 y | 21 (15-28) | 43 (35-54) | 58 (53-63) | ||
| Disease-free survival† | |||||
| 1 y | 55 (48-62) | 66 (58-74) | 59 (55-63) | ||
| 3 y | 48 (40-55) | 48 (39-57) | 41 (37-45) | ||
| 5 y | 45 (36-53) | 39 (30-48) | 31 (27-36) | ||
| Overall survival† | |||||
| 1 y | 61 (54-68) | 82 (76-89) | 81 (78-84) | ||
| 3 y | 54 (47-62) | 71 (63-79) | 65 (61-69) | ||
| 5 y | 51 (43-60) | 62 (53-72) | 55 (50-60) | ||
Cumulative incidence.
Kaplan-Meier estimate.
These marked differences in recurrence rates and TRM resulted in a higher treatment failure (relapse or death) among patients who received allogeneic transplants in the first year after transplantation. But the results were almost identical for disease-free and overall survival after autologous or allogeneic transplantation by 5 years after transplantation.
Multivariate analysis
Multivariate analyses allowed comparisons among the 3 main groups, taking into account the potentially confounding effects of other important patient, disease, and treatment-related variables. Results are summarized in Tables 4, 5, 6, 7.
Multivariate analysis of treatment-related mortality
Variables . | Relative risk of treatment-related mortality (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001† | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.98 (0.52-1.87) | .96 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175 | 4.44 (2.81-7.02) | < .001 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001† | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 2.71 (1.69-4.36) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.78 (0.99-3.19) | .06 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001† | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 2.03 (1.32-3.14) | .001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 2.69 (1.43-5.04) | .002 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 198 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 703 | 1.98 (1.21-3.26) | .007 |
| Conditioning regimen | ||
| Non-TBI, n = 553 | 1.00 | — |
| TBI, n = 348 | 1.80 (1.16-2.77) | .008 |
| Year of transplantation | .03† | |
| 1990-1993, n = 300 | 1.00 | — |
| 1994-1996, n = 373 | 0.67 (0.42-1.06) | .09 |
| 1997-1998, n = 228 | 0.49 (0.28-0.87) | .01 |
Variables . | Relative risk of treatment-related mortality (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001† | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.98 (0.52-1.87) | .96 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175 | 4.44 (2.81-7.02) | < .001 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001† | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 2.71 (1.69-4.36) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.78 (0.99-3.19) | .06 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001† | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 2.03 (1.32-3.14) | .001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 2.69 (1.43-5.04) | .002 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 198 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 703 | 1.98 (1.21-3.26) | .007 |
| Conditioning regimen | ||
| Non-TBI, n = 553 | 1.00 | — |
| TBI, n = 348 | 1.80 (1.16-2.77) | .008 |
| Year of transplantation | .03† | |
| 1990-1993, n = 300 | 1.00 | — |
| 1994-1996, n = 373 | 0.67 (0.42-1.06) | .09 |
| 1997-1998, n = 228 | 0.49 (0.28-0.87) | .01 |
— indicates reference group; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; and TBI, total body irradiation.
Allogeneic versus autologous-purged (relative risk [RR], 4.52; 95% CI, 2.29-8.92; P < .001).
Determined by 2-degree of freedom test.
Multivariate analysis of relapse
Variables . | Relative risk of relapse (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001‡ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.74 (0.55-0.99) | .04 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175 | 0.46 (0.33-0.66) | < .001 |
| Disease stage at transplantation† | — | |
| Early, n = 501 | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced, n = 400 | 1.29 (1.06-1.58) | .01 |
| Chemosensitivity | .001‡ | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 1.69 (1.27-2.23) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 0.98 (0.68-1.42) | .93 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001‡ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 1.51 (1.21-1.87) | < .001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 1.00 (0.69-1.43) | .98 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 641 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.31 (1.07-1.61) | .01 |
| Conditioning regimen | — | |
| Non-TBI, n = 553 | 1.00 | — |
| TBI, n = 348 | 0.77 (0.62-0.95) | .02 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .05‡ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.37 (1.01-1.87) | .05 |
| More than 2 y, n = 489 | 1.40 (1.06-1.84) | .01 |
| Bone marrow involvement at transplantation | — | |
| No, n = 705 | 1.00 | — |
| Yes, n = 196 | 1.31 (1.04-1.65) | .02 |
Variables . | Relative risk of relapse (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001‡ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.74 (0.55-0.99) | .04 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175 | 0.46 (0.33-0.66) | < .001 |
| Disease stage at transplantation† | — | |
| Early, n = 501 | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced, n = 400 | 1.29 (1.06-1.58) | .01 |
| Chemosensitivity | .001‡ | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 1.69 (1.27-2.23) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 0.98 (0.68-1.42) | .93 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001‡ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 1.51 (1.21-1.87) | < .001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 1.00 (0.69-1.43) | .98 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 641 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.31 (1.07-1.61) | .01 |
| Conditioning regimen | — | |
| Non-TBI, n = 553 | 1.00 | — |
| TBI, n = 348 | 0.77 (0.62-0.95) | .02 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .05‡ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.37 (1.01-1.87) | .05 |
| More than 2 y, n = 489 | 1.40 (1.06-1.84) | .01 |
| Bone marrow involvement at transplantation | — | |
| No, n = 705 | 1.00 | — |
| Yes, n = 196 | 1.31 (1.04-1.65) | .02 |
— indicates reference group; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; and TBI, total body irradiation.
Allogeneic versus autologous purged transplantation (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.41-0.97; P < .03).
Early disease indicates complete remission (1st or 2nd) or relapse (1st); advanced disease, complete remission (3rd) or relapse (> 2nd) or primary induction failure.
Determined by 2-degree of freedom test.
Multivariate analysis of disease-free-survival
Variables . | Relative risk of treatment failure (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001§ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.82 (0.63-1.07) | .14 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175† | — | |
| First 6 mo after transplantation | 1.77 (1.34-2.34) | < .001 |
| 6 mo after transplantation | 0.35 (0.22-0.57) | < .001 |
| Disease stage at transplantation‡ | — | |
| Early (n = 501) | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced (n = 400) | 1.27 (1.07-1.52) | .007 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001∥ | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 1.92 (1.52-2.44) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.12 (0.83-1.53) | .45 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001∥ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 1.58 (1.30-1.93) | < .0001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 0.95 (0.70-1.30) | .76 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 641 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.31 (1.09-1.57) | .004 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .05∥ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.37 (1.04-1.80) | .03 |
| More than 2 y, n = 489 | 1.35 (1.06-1.72) | .02 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 198 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 703 | 1.31 (1.04-1.64) | .02 |
Variables . | Relative risk of treatment failure (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001§ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 596 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 130 | 0.82 (0.63-1.07) | .14 |
| Allogeneic, n = 175† | — | |
| First 6 mo after transplantation | 1.77 (1.34-2.34) | < .001 |
| 6 mo after transplantation | 0.35 (0.22-0.57) | < .001 |
| Disease stage at transplantation‡ | — | |
| Early (n = 501) | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced (n = 400) | 1.27 (1.07-1.52) | .007 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001∥ | |
| Sensitive, n = 714 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 1.92 (1.52-2.44) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.12 (0.83-1.53) | .45 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001∥ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 243 | 1.58 (1.30-1.93) | < .0001 |
| Unknown, n = 97 | 0.95 (0.70-1.30) | .76 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 641 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.31 (1.09-1.57) | .004 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .05∥ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.37 (1.04-1.80) | .03 |
| More than 2 y, n = 489 | 1.35 (1.06-1.72) | .02 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 198 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 703 | 1.31 (1.04-1.64) | .02 |
— indicates reference group; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
Time-dependent covariate; such that risk of death before and after 6 months after transplantation varies.
Allogeneic (≤ 6 months) versus autologous-purged transplantation (RR, 2.15; 95% CI, 1.50-3.08; P < .001); allogeneic (> 6 months) versus autologous-purged transplantation (RR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.26-0.73; P < .001).
Early disease indicates complete remission (1st or 2nd) or relapse (1st); advanced disease, complete remission (3rd) or relapse (> 2nd) or primary induction failure.
Determined by 3-degree of freedom test.
Determined by 2-degree of freedom test.
Multivariate analysis of overall survival
Variables . | Relative risk of death (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001§ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 597 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 131 | 0.67 (0.48-0.95) | .03 |
| Allogeneic, n = 176† | — | |
| First 6 mo after transplantation | 3.59 (2.52-5.10) | < .001 |
| 6 mo after transplantation | 0.71 (0.44-1.13) | .14 |
| Disease stage at transplantation‡ | — | |
| Early, n = 504 | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced, n = 400 | 1.26 (1.01-1.57) | .04 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001∥ | |
| Sensitive, n = 717 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 2.63 (2.01-3.44) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.42 (1.00-2.02) | .06 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001∥ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 245 | 2.26 (1.79-2.84) | < .001 |
| Unknown, n = 98 | 2.11 (1.48-3.01) | < .001 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 644 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.51 (1.21-1.88) | < .001 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .001∥ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.71 (1.20-2.42) | .003 |
| More than 2 y, n = 492 | 1.38 (1.01-1.90) | .05 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 199 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 705 | 1.42 (1.07-1.88) | .01 |
| Year of transplantation | .007∥ | |
| 1990-1993, n = 301 | 1.00 | — |
| 1994-1996, n = 374 | 0.71 (0.55-0.90) | .006 |
| 1997-1998, n = 229 | 0.67 (0.49-0.2) | .01 |
Variables . | Relative risk of death (95% CI) . | P . |
|---|---|---|
| Type of transplant* | < .001§ | |
| Autologous unpurged, n = 597 | 1.00 | — |
| Autologous purged, n = 131 | 0.67 (0.48-0.95) | .03 |
| Allogeneic, n = 176† | — | |
| First 6 mo after transplantation | 3.59 (2.52-5.10) | < .001 |
| 6 mo after transplantation | 0.71 (0.44-1.13) | .14 |
| Disease stage at transplantation‡ | — | |
| Early, n = 504 | 1.00 | — |
| Advanced, n = 400 | 1.26 (1.01-1.57) | .04 |
| Chemosensitivity | < .001∥ | |
| Sensitive, n = 717 | 1.00 | — |
| Resistant, n = 111 | 2.63 (2.01-3.44) | < .001 |
| Untreated/unknown, n = 76 | 1.42 (1.00-2.02) | .06 |
| Serum LDH at transplantation | < .001∥ | |
| Normal, n = 561 | 1.00 | — |
| Abnormal, n = 245 | 2.26 (1.79-2.84) | < .001 |
| Unknown, n = 98 | 2.11 (1.48-3.01) | < .001 |
| Karnofsky performance score at transplantation | — | |
| 90%-100%, n = 644 | 1.00 | — |
| No more than 80%, n = 260 | 1.51 (1.21-1.88) | < .001 |
| Interval from diagnosis to transplantation | .001∥ | |
| Less than 1 y, n = 168 | 1.00 | — |
| 1-2 y, n = 244 | 1.71 (1.20-2.42) | .003 |
| More than 2 y, n = 492 | 1.38 (1.01-1.90) | .05 |
| Age at transplantation | — | |
| No older than 40 y, n = 199 | 1.00 | — |
| Older than 40 y, n = 705 | 1.42 (1.07-1.88) | .01 |
| Year of transplantation | .007∥ | |
| 1990-1993, n = 301 | 1.00 | — |
| 1994-1996, n = 374 | 0.71 (0.55-0.90) | .006 |
| 1997-1998, n = 229 | 0.67 (0.49-0.2) | .01 |
— indicates reference group; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
Time-dependent covariate; such that risk of death before and after 6 months after transplantation varies.
Allogeneic (≤ 6 months) versus autologous-purged transplantation (RR, 5.33; 95% CI, 3.34-8.50; P < .001); allogeneic (> 6 months) versus autologous-purged transplantation (RR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.60-1.83; P < .87).
Early disease indicates complete remission (1st or 2nd) or relapse (1st); advanced disease, complete remission (3rd) or relapse (> 2nd) or primary induction failure.
Determined by 3-degree of freedom test.
Determined by 2-degree of freedom test.
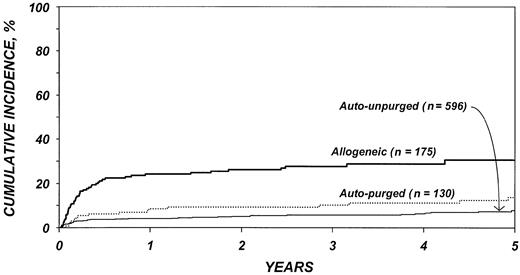
After adjustment for other covariates, the risk of TRM (Table 4) was 4.4 times higher after allogeneic than after autologous transplantation (P < .001). There was no statistically significant difference in TRM after purged versus unpurged autotransplantation. Other factors significantly associated with higher TRM were age older than 40 years, chemotherapy-resistant disease, high serum LDH at transplantation, TBI for conditioning, and transplantation between 1990 and 1993. Figure 1 shows the cumulative incidence of TRM by type of transplant.
Cumulative incidences of treatment-related mortality by type of transplant.
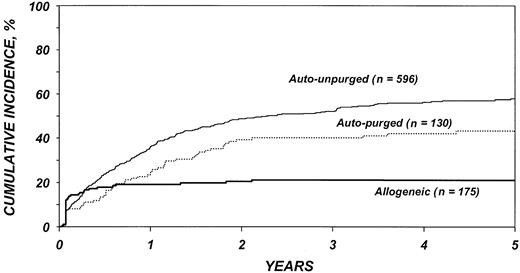
The risk for disease recurrence (Table 5) was 54% lower in recipients of allogeneic transplants (P < .001) and 26% lower in recipients of purged autotransplants (P = .04) than in recipients of unpurged autotransplants. Other factors associated with higher risk of relapse were advanced disease, high serum LDH at transplantation, chemotherapy-resistant disease, poor Karnofsky performance score, bone marrow involvement, and an interval greater than 1 year between diagnosis and transplantation. The use of TBI was associated with a lower risk of disease recurrence. Figure 2 shows the cumulative incidence of relapse by type of transplant.
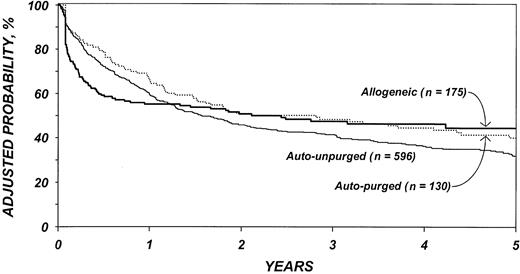
The risk of treatment failure (relapse or death) (Table 6) was higher after purged autologous than unpurged autologous transplantation, although this difference was not statistically different (P = .14). In the first 6 months after transplantation, the risk of treatment failure was higher among patients who received allotransplants than autotransplants (P < .001). Among patients surviving 6 months in remission, the subsequent risk of treatment failure was significantly lower among patients who received allotransplants than autotransplants (P < .001). Again, advanced disease stage, chemotherapy-resistant disease, high LDH at transplantation, age older than 40 years, poor performance status, and prolonged delay between diagnosis and transplantation were associated with lower DFS. We failed to detect statistical difference in DFS by year of transplantation; however, this could be due to lack of statistical power. Figure 3 shows the probability of DFS by type of transplant adjusted for other significant covariates.
Probabilities of disease-free survival by type of transplant, adjusted for other significant covariates listed inTable 6.
Probabilities of disease-free survival by type of transplant, adjusted for other significant covariates listed inTable 6.
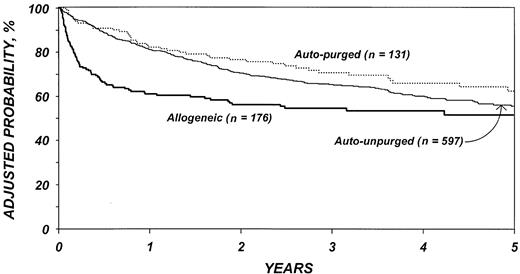
The risk of mortality (Table 7) was lower after purged versus unpurged autotransplantation (P = .03). In the first 6 months after transplantation, the risk of death was higher among patients who received allogeneic transplants than autologous transplants (P < .001). Among patients who survived the first 6 months, there was a slightly lower risk of death in the allotransplant group (P = .14). Advanced disease stage, chemotherapy-resistant disease, high serum LDH at transplantation, age older than 40 years, poor performance status, and prolonged delay between diagnosis and transplantation were associated with worse survival as was transplantation in the first 3 years of the decade. Figure 4 shows the probability of survival by type of transplant adjusted for other significant covariates. The 5-year adjusted probabilities of survival after allotransplantations, purged autologous transplantations, and unpurged autologous transplantations were 51% (95% confidence interval [CI], 43%-60%), 62% (95% CI, 53%-72%), and 55% (95% CI, 50%-60%), respectively.
Probabilities of survival by type of transplant adjusted for other significant covariates listed inTable 7.
Probabilities of survival by type of transplant adjusted for other significant covariates listed inTable 7.
In a separate multivariate analysis restricted to recipients of allogeneic transplants, we evaluated the effect of acute and chronic GVHD on the probability of disease recurrence by using a time-dependent covariate. The risk of relapse for patients with acute GVHD was not significantly different from that of patients without acute GVHD. The risk of relapse for patients with chronic GVHD after transplantation was not significantly different from that of patients without chronic GVHD.
Discussion
Follicular lymphoma, although unpredictable and often associated with a prolonged course, is in most cases a fatal illness.1 Although numerous treatment modalities are effective, very few are shown to prolong survival, and none are curative, with the possible exception of autologous or allogeneic transplantation.22 A recently reported randomized study of 89 patients with a median follow-up of 6 years indicates a considerable benefit in disease-free survival (P = .0037) and survival (P = .079) of autologous transplantation compared with conventional chemotherapy for patients with recurrent follicular lymphoma.33
The identification of patient- or disease-related prognostic variables in a large group of patients undergoing these procedures constituted a major purpose of the current analysis. We hoped to identify patient populations that might specifically benefit from allogeneic versus autologous transplantation and studied the effect of conditioning (TBI versus non-TBI), stem cell source (peripheral blood versus bone marrow), and stem cell manipulation (purged versus unpurged) on outcome. In a separate analysis restricted to recipients of allogeneic transplants, we evaluated the relationship between acute and chronic GVHD and disease recurrence. We excluded patients receiving nonmyeloablative regimens because few of such reported patients have yet achieved sufficient follow-up for meaningful analysis.22
We confirmed that both autologous and allogeneic transplantation induce long-term disease control in a proportion of patients. Disease-free survival at 5 years is approximately 50% with both procedures, a result consistent with previous studies. As in most previous studies a continuous pattern of treatment failure was observed after autologous transplantation, suggesting that cure may be achieved in only a small minority of patients. Most late failures were due to disease recurrence, but some were also related to the occurrence of secondary hematologic malignancy, a well-known complication following autologous transplantation.34-36 (Table 8). The pattern of treatment failure after allogeneic transplantation was markedly different from that after autologous transplantation. The recurrence rate was only 20%, with almost all recurrences occurring within the first year after transplantation. This recurrence rate was virtually identical to that observed in our previous report that included many fewer patients with follicular lymphoma and covered, in part, an earlier time period.27 Long-term outcome after allogeneic transplantation was, however, adversely affected by a high early TRM rate.
Causes of nonrelapse mortality
. | Type of transplant, % . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cause of death . | HLA-identical sibling, n = 50 . | Autologous purged, n = 18 . | Autologous unpurged, n = 45 . | ||
| New malignancy | — | 5 | 9 | ||
| GVHD | 10 | — | — | ||
| Interstitial pneumonitis | 28 | 20 | 28 | ||
| Infection | 18 | 24 | 22 | ||
| Organ failure | 24 | 22 | 18 | ||
| Other causes | 16 | 17 | 13 | ||
| Unknown | 4 | 12 | 10 | ||
. | Type of transplant, % . | . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cause of death . | HLA-identical sibling, n = 50 . | Autologous purged, n = 18 . | Autologous unpurged, n = 45 . | ||
| New malignancy | — | 5 | 9 | ||
| GVHD | 10 | — | — | ||
| Interstitial pneumonitis | 28 | 20 | 28 | ||
| Infection | 18 | 24 | 22 | ||
| Organ failure | 24 | 22 | 18 | ||
| Other causes | 16 | 17 | 13 | ||
| Unknown | 4 | 12 | 10 | ||
—indicates no events.
Patient- and disease-related covariates that adversely affected overall outcome included advanced age, poor performance status, an interval between diagnosis and transplantation of more than 1 year, chemotherapy-refractory disease, and increased serum LDH at transplantation. Patients with any of these features had lower overall survival regardless of the type of transplant they received. Age,12 serum LDH,16 chemotherapy refractory disease,12,13,16,17 and bone marrow involvement10 have all been previously correlated with adverse outcome of autologous transplantation. In our prior report on allogeneic transplantation, patient age older than 40 years and chemotherapy refractory disease were associated with a worse outcome.27 Of note, neither disease histology (or lymphoma “grade,” by World Health Organization [WHO] classification37 ), stem cell source (bone marrow versus peripheral blood stem cells), nor use of posttransplantation myeloid growth factors correlated with outcome in multivariate analysis.
The Dana-Farber group initially reported a correlation between outcome of transplantation and optimal purging of the stem cell product.38 In an update of their experience, patients receiving transplants of stem cell products devoid of lymphoma cells had up to 80% DFS at 8 years after transplantation.10 Those patients receiving cells that were contaminated with lymphoma had a very high recurrence rate. These results are confirmed in some,14,39 but not all studies,8,12,13,33,40,41 and the clinical benefits of stem cell purging remain a matter of ongoing study. Our analysis is the first controlled comparison between the outcomes of purged versus unpurged transplantation in a large patient group. In multivariate analyses, an effect of stem cell purging on recurrence rates and overall survival was found. As indicated by the relapse curve, there is a decrease in early as well as late recurrences associated with purging. These data suggest that graft purging, even with current technical limitations, might be of clinical benefit in patients with follicular lymphoma undergoing autologous transplantation. This observation is consistent with our observation of a markedly reduced recurrence rate after syngeneic versus autologous transplantation in follicular lymphoma, because syngeneic transplantation may be considered the equivalent of an optimally purged autologous transplantation.42
Allogeneic transplantation was associated with a low early recurrence rate and near absence of documented recurrences beyond 1 year after transplantation. The lack of late recurrences confirms the curative potential of allogeneic transplantation. Whether cure results from graft-versus-lymphoma (GVL) effects28,43-48 or from the complete eradication of tumor by high-dose chemotherapy followed by infusion of uncontaminated stem cells (a “purging” effect)10,42 or from a combination of both is unclear. In the current study, we were unable to detect a GVL effect of either acute or chronic GVHD. Because of sample size limitations, it is possible we lacked the power to detect such an effect.
The use of TBI was associated with increased TRM, but with decreased recurrence rates. In our previous analysis of allogeneic transplantation for follicular lymphoma, the use of TBI was associated with an improved outcome.27 By contrast, a European analysis of patients undergoing autologous transplantation indicated a worse overall survival for patients with low-grade lymphoma receiving TBI.41 Although these data must be interpreted with caution, they may indicate that TBI is a highly effective although toxic treatment for follicular lymphoma. They may also suggest that less toxic methods of administration of radiation, perhaps in the form of radiolabeled antibodies, may improve transplantation outcomes.49
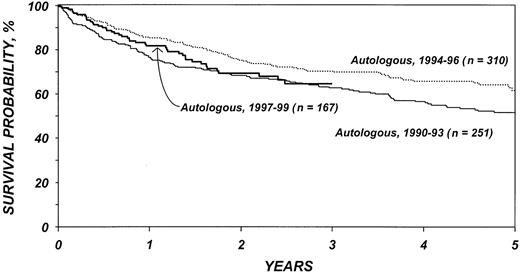
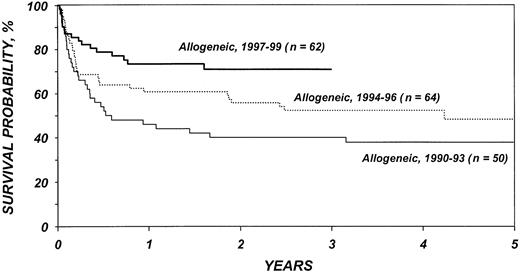
Figures 5 and 6 show survival rates after autologous and allogeneic transplantation during successive 3-year periods. It is reassuring that, independent of other covariates, TRM after transplantation, particularly after allogeneic transplantation, declined over the past decade. This decline is probably related to selection of patients with more favorable characteristics, improvements in supportive care, and improvements in early diagnosis and treatment of opportunistic infections.
Probabilities of survival after autologous transplantation by year of transplantation.
Probabilities of survival after autologous transplantation by year of transplantation.
Probabilities of survival after HLA-identical sibling transplantation by year of transplantation.
Probabilities of survival after HLA-identical sibling transplantation by year of transplantation.
This analysis confirms that transplantation has its major benefit when performed early in the course of disease. Transplantation for refractory disease is associated with a dismal course and should probably be avoided. When comparing the patient characteristics of patients in this study with those of our previous report on allogeneic transplantation for low-grade lymphoma, it is apparent that this is the approach increasingly favored by most physicians. Patients in the current study had, on average, far less advanced disease than those in our previous report that included patients receiving transplants between 1985 and 1995.
Whether to recommend autologous or allogeneic transplantation for patients who have an HLA-matched sibling donor remains, at present, a matter of physician and patient preference. We had hoped to identify variables that would have a differential effect on allogeneic versus autologous transplantation but were unable to do so. Adverse prognostic features had similar effects on long-term outcome of both allogeneic and autologous transplantation.
If autologous transplantation is performed, consideration should be given to the use of in vitro or in vivo stem cell purging. Novel in vitro purging methods continue to be explored and are of considerable interest.50,51 Data indicating that administration of rituximab results in highly efficient purging of peripheral blood stem cell products require testing in larger cohorts of patients.52 Whenever one recommends autologous transplantation, the considerable risk for secondary myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) should be taken into account.34-36 Allogeneic transplantation has an increased risk of early TRM, but, as shown in Figure 5, survival has improved in recent years. In the most recent patient cohorts, 1-year survival after transplantation is approximately 80%. The rapid development of new transplantation technologies may further reduce recurrence rates as well as TRM and, thus, affect the risk-benefit ratios of these procedures. Reduced intensity conditioning, which relies on graft-versus-lymphoma effects, is one of the strategies currently under study. Our analysis failed to identify a beneficial effect of GVHD on the incidence of relapse, thus raising some concerns about the ultimate effect of reduced intensity conditioning. However, with highly effective high-dose conditioning, an otherwise effective GVL reaction may have been difficult to detect. A plethora of novel agents and approaches are now available or are under study for management of follicular lymphoma. These agents include rituximab, its radiolabeled equivalent ibritumomab, and other monoclonal antibodies, as well as vaccine approaches. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous and allogeneic transplantation constitute a different, but possibly complementary, approach. Future studies integrating various approaches might render curative therapy for all patients with follicular lymphoma a realistic goal.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, July 31, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1205.
Supported by Public Health Service grant U24-CA76518 from the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and grants from Allianz Life/Life Trac; American Cancer Society; American Red Cross; American Society of Clinical Oncology; Amgen, Inc; Anonymous; Aventis Pharmaceuticals; Baxter Healthcare Corp; Baxter Oncology; Berlex Oncology; Biotransplant Inc; Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association; The Lynde and Harry Bradley Foundation; Bristol Myers Squibb Oncology; Cedarlane Laboratories Ltd; Cell Pathways; CelMed Biosciences; Centocor, Inc; Cubist Pharmaceuticals; Darwin Medical Communications, Ltd; Dynal Biotech ASA; Edwards Lifesciences RMI; Endo Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Excess, Inc; Fujisawa Healthcare, Inc; Gambro BCT, Inc; GlaxoSmithKline, Inc; Human Genome Sciences; ICN Pharmaceuticals, Inc; ILEX Oncology; The Kettering Family Foundation; Kirin Brewery Co; Ligand Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Eli Lilly and Co; Nada and Herbert P. Mahler Charities; Merck & Co; Millennium Pharmaceuticals; Miller Pharmacal Group; Milliman USA, Inc; Miltenyi Biotec; Irving I. Moskowitz Foundation; National Marrow Donor Program; NeoRx; Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals; Orphan Medical, Inc; Ortho Biotech, Inc; Osiris Therapeutics, Inc; PacifiCare Health Systems; Pall Medical; Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals; Pharmacia Corp; Pharmametrics; Pharmion Corp; Protein Design Labs; Roche Laboratories; SangStat Medical; Schering AG; StemCyte, Inc; StemCell Technologies, Inc; Stemco Biomedical; StemSoft Software, Inc; SuperGen, Inc; Sysmex; THERAKOS, a Johnson & Johnson Co; Unicare Life & Health Insurance; University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank; ViaCell, Inc; ViaCor Biotechnologies; WB Saunders Mosby Churchill; and Zymogenetics, Inc.
The contents of this article are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal