Introduction: Approximately 40% of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) have an activating somatic mutation in CXCR4, including both nonsense and frameshift variants. There are limited data on the impact of CXCR4 mutations on the outcomes to therapy in WM patients. Mounting evidence suggests that CXCR4 mutations adversely affect depth of response and progression-free survival (PFS) to ibrutinib in patients with WM.
Methods: We performed a pooled analysis evaluating the impact of CXCR4 mutations and CXCR4 mutation subtypes on response, PFS and survival after frontline treatment initiation (SAFTI) on 76 WM patients who received proteasome inhibitor-based primary therapy. All patients were participants on three prospective clinical trials evaluating the combinations of bortezomib, dexamethasone and rituximab (BDR; ClinicalTrials.Gov ID NCT00250926), carfilzomib, dexamethasone and rituximab (CaRD; ClinicalTrials.Gov ID NCT01470196), and ixazomib, dexamethasone and rituximab (IDR; ClinicalTrials.Gov ID NCT02400437) in previously untreated patients with WM, and were treated at the Bing Center for WM. All patients met criteria for a clinicopathological diagnosis of WM and for treatment initiation, according to the guidelines established by the 2nd International Workshop for WM (IWWM). CXCR4 mutations were divided in nonsense and frameshift mutations, as previously described. Response to therapy was assessed using response criteria by the 3rdIWWM. We fitted univariate and multivariate logistic regression and proportional-hazard Cox regression models for major response and PFS and SAFTI, respectively. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
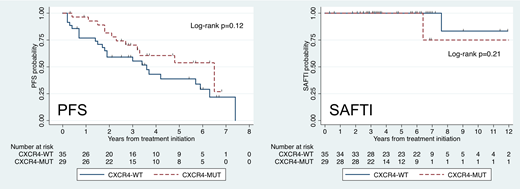
Results: A total of 76 patients were included in this analysis, of which 19 (25%) received BDR, 31 (41%) received CaRD and 26 (34%) received IDR. Thirty-six patients (55%) did not have CXCR4 mutations and 29 (45%) had a CXCR4 mutation, of which 16 had nonsenseand 13 had frameshift CXCR4 mutations. In 11 patients, the CXCR4 mutational status was not determined. The median age at treatment initiation was 63 years (range 46-83 years), median hemoglobin level was 10.3 g/dl (range 6.9-17.1 g/dl), median platelet count was 245 K/uL (range 68-584 K/uL), median serum IgM level was 4,048 mg/dl (range 345-9,550 mg/dl), median serum β2-microglobulin level was 3.5 mg/l (range 1.0-10.8 mg/l), serum albumin was 3.7 g/dl (range 2.4-4.8 g/dl) and median bone marrow involvement was 55% (range 5-95%). There was a higher proportion of serum IgM levels ≥4,000 mg/dl (62% vs. 39%) and lower proportion of serum albumin levels ≤3.5 g/dl (21% vs. 47%) in patients with than in patients without CXCR4 mutations. Our study showed no detectable differences in major response rate at 6 months (OR 0.77, 95% CI 0.27-2.22; p=0.63) and 12 months (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.18-3.23; p=0.71) between patients with and without CXCR4 mutations. The median PFS for patients without CXCR4 mutations was 3.6 years (95% CI 1.7-5.9 years) versus 6.5 years (95% CI 2.7-not reached) for patients with CXCR4 mutations, which was not statistically significantly different (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.29-1.17; p=0.13). Frameshift CXCR4 mutations were associated with better PFS than nonsense CXCR4 mutations in a multivariate Cox regression model (HR 0.22, 95% CI 0.06-0.80; p=0.02). Patients with CXCR4 mutations had a 10-year SAFTI rate of 75% (95% CI 13-96%) versus 83% (95% CI 27-97%) in patients without CXCR4 mutations, which was not statistically significantly different (HR 3.01, 95% CI 0.17-52.6; p=0.45).
Conclusions: We conclude that there is no evidence that CXCR4 mutations adversely impact response, PFS and SAFTI in WM patients receiving proteasome inhibitor-based primary therapy.
Castillo:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Hunter:Janssen: Consultancy. Treon:BMS: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.