Key Points
NOX5 and p22phox are both involved in Mo-DC differentiation.
In Mo-DC, NOX5 and p22phox create a complex on the outer membrane of the mitochondria.
Abstract
Dendritic cells (DCs) are a heterogeneous population of professional antigen-presenting cells and are key cells of the immune system, acquiring different phenotypes in accordance with their localization during the immune response. A subset of inflammatory DCs is derived from circulating monocytes (Mo) and has a key role in inflammation and infection. The pathways controlling Mo-DC differentiation are not fully understood. Our objective was to investigate the possible role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced form oxidases (NOXs) in Mo-DC differentiation. In this study, we revealed that Mo-DC differentiation was inhibited by NOX inhibitors and reactive oxygen species scavengers. We show that the Mo-DC differentiation was dependent on p22phox, and not on gp91phox/NOX2, as shown by the reduced Mo-DC differentiation observed in chronic granulomatous disease patients lacking p22phox. Moreover, we revealed that NOX5 expression was strongly increased during Mo-DC differentiation, but not during Mo-macrophage differentiation. NOX5 was expressed in circulating myeloid DC, and at a lower level in plasmacytoid DC. Interestingly, NOX5 was localized at the outer membrane of the mitochondria and interacted with p22phox in Mo-DC. Selective inhibitors and small interfering RNAs for NOX5 indicated that NOX5 controlled Mo-DC differentiation by regulating the JAK/STAT/MAPK and NFκB pathways. These data demonstrate that the NOX5-p22phox complex drives Mo-DC differentiation, and thus could be critical for immunity and inflammation.
Introduction
Dendritic cells (DCs) are professional antigen-presenting cells and are key cells of the immune system.1-3 Subsets of DC can be classified according to their tissue location and their functions.4 Monocyte-derived dendritic cells (Mo-DC) have a key role in inflammation5 and infection6 and have been termed “inflammatory DCs.”4,7 During infection/inflammation, monocytes (Mos) emigrate from the bone marrow to the systemic circulation where they differentiate into immature DCs that regulate antigen uptake and processing.7,8 DCs then undergo antigen/cytokine-driven maturation, acquiring an enhanced T-cell stimulatory capacity while in the lymph nodes.9 DCs can be generated from Mos under different conditions5,10 ; however, the mechanisms involved in this process remain poorly understood.
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced form (NADPH) oxidases (NOXs) are multi-subunit complexes that are associated with membranes and are responsible for the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).11 To date, 7 NOX isoforms have been identified: NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1), and DUOX2. The best characterized isoform is the phagocyte NADPH oxidase (NOX2), which is highly expressed in neutrophils,12 Mos,13,14 macrophages13,15 and DCs.14,16 This multicomponent enzyme system is composed of membrane proteins (p22phox and gp91phox/NOX2) and cytosolic proteins (p47phox, p67phox, p40phox, and rac1/2), which assemble at membrane sites upon cell activation.12 The p22phox subunit has been shown to have an important structural role by stabilizing NOX217 and the other family members, NOX1, NOX3, and NOX411 ; however, studies have shown that p22phox is not required for NOX5 expression and activation.18 The critical role of NOX2 in innate immunity and host defense has been demonstrated by the severe, life-threatening infections and inflammatory complications observed in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patients who lack one of the NOX2 subunits19,20 and therefore are unable to produce ROS for pathogen killing.
In the last years, there has been an increased interest in NOX2 function in DCs, with the demonstration of NOX2 roles in the killing of Escherichia coli and in controlling the acidification of phagosomes, promoting antigen cross-presentation by DCs.16,21 As ROS have been involved in several cell functions such as signaling, this study aimed to investigate the expression and the possible involvement of NOXs in the differentiation and/or maturation of Mo-DC, which remain poorly understood. We demonstrate here that NOX5 and p22phox are 2 novel regulators of Mo-DC differentiation. In addition, our study revealed the previously unknown localization of NOX5 and p22phox in the mitochondria, and their unexpected interaction in Mo-DC. Therefore, targeting the NOX5-p22phox complex to limit Mo-DC differentiation could be a beneficial strategy to treat human inflammatory diseases.
Methods
Ethics statement
Cells were isolated from the venous blood of healthy volunteers and CGD patients with their written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All experiments were approved by the INSERM Institutional Review Board and ethics committee. Data collection and analyses were performed anonymously.
Isolation of Mos, neutrophils, and DCs
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated by Ficoll gradient centrifugation.22,23 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were washed and suspended in phosphate-buffered saline with 0.5% bovine serum albumin to a final concentration of 5 × 107 cells/mL. Mos, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC), and myeloid DC (mDC) were purified by magnetic negative isolation with the EasySep kits (Stemcell) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Mo-derived DC differentiation and maturation
Freshly isolated Mos were plated in RMPI 1640 media with 10% fetal bovine serum and stimulated with 50 ng/mL granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and 1000 U/mL interleukin-4 (IL-4) for 6 days in order to obtain immature Mo-DC as described previously.24 To induce maturation, cells were further stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 µg/mL) for 2 more days as described previously.25
Flow cytometry
Differentiation and maturation of Mo-DC were analyzed by flow cytometry. Analyses were performed with a Canto II cytometer fluorescence-activated cell sorter (BD) as described in the supplemental Methods, available on the Blood Web site.
RNA extraction and polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was extracted from Mos and Mo-DC using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. One microgram of RNA was converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) with the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Endpoint polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time PCR were conducted using standard techniques.
Western blot
Protein expression and phosphorylation were evaluated by western blot, using standard sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) techniques26 as described in the supplemental Methods.
Measurement of ROS production by luminol-amplified chemiluminescence
ROS production was measured by the luminol-amplified chemiluminescence method.22 Briefly, cells (2.5 × 105) were suspended in 0.5 mL Hanks balanced salt solution containing 10 μM luminol preheated to 37°C in the luminometer. Cells were stimulated with 10−6 M N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLF) or 1 µM ionomycin, and chemiluminescence was recorded. In some experiments, cells were treated with 20 µM of the gp91-tat peptide inhibitor or scrambled peptide (AnaSpec, Fremont, CA) for 30 minutes before stimulation.
p22phox and NOX5 silencing by siRNA
Mitochondria isolation
Mitochondria from Mo-DC were isolated by using a differential centrifugation kit (Millipore), and by magnetic separation with a mitochondria isolation kit (Miltenyi-Biotec), following the manufacturers’ instructions (supplemental Methods).
Confocal microscopy
Localization of NOX5 was analyzed by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. Images were acquired with an inverted confocal laser scanning microscope (Leica SP8; Leica Microsystem) with a ×40 objective and were analyzed with Leica Microsystem LAS AF software.
Coimmunoprecipitation and 2-dimensional blue native/SDS gel electrophoresis
The coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) and blue native (BN)-PAGE29 experiments were performed as described in the supplemental Methods.
Duolink proximity ligation assay
The Duolink proximity ligation assay (Duolink-PLA; Sigma) was performed in isolated neutrophils and Mo-DC following the manufacturer’s instructions (supplemental Methods).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed with the GraphPad Prism 5 software. Differences between groups were analyzed by the 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test with Tukey multiple comparison posttest unless otherwise stated in the figures. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001 values were considered as significant.
Results
NOX inhibition and ROS scavenging prevent Mo-DC differentiation and maturation independently of gp91phox/NOX2
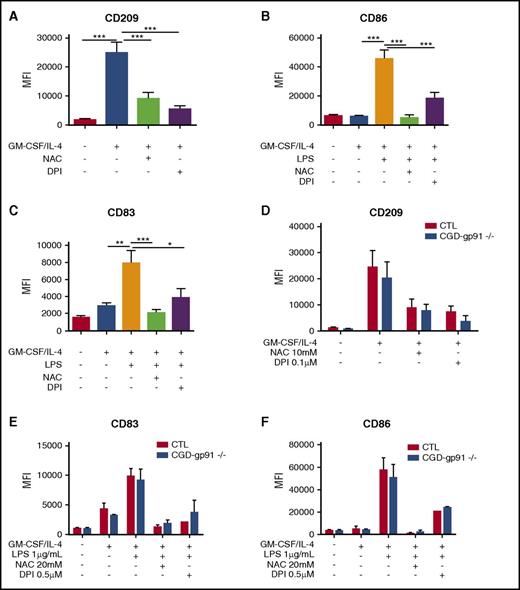
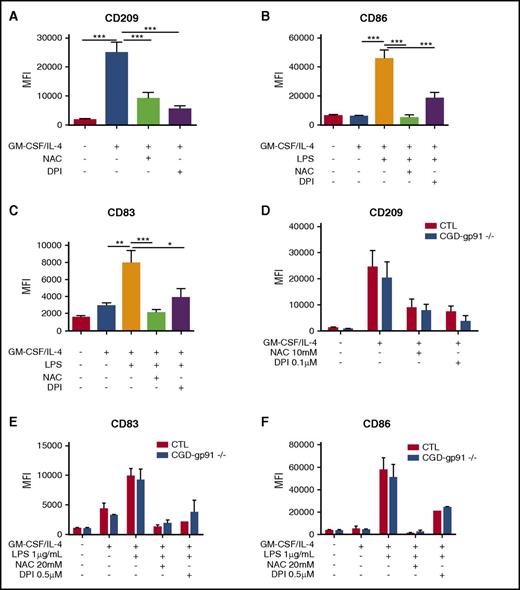
In order to evaluate the possible role of NOXs and ROS in the development of Mo-DC, freshly isolated Mos were treated for 15 minutes with the ROS scavenger, N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC), or the NOX inhibitor, diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) prior to adding the differentiation inducers (GM-CSF and IL-4),24 or the maturation inducer (LPS).25 Markers for Mo-DC differentiation (CD209)30 and maturation (CD86 and CD83)25 were analyzed by flow cytometry. Pretreatment with NAC or DPI strongly and significantly reduced the DC differentiation (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1A) and maturation markers (Figure 1B-C; supplemental Figure 1B-C), suggesting a role for ROS and NOXs in GM-CSF/IL-4–induced Mo-DC differentiation and LPS-induced DC maturation. Allopurinol, a xanthine-oxidase inhibitor, and NG-methyl-l-arginine acetate, a NOS inhibitor, had no effect on both differentiation and maturation of Mo-DC (supplemental Figure 2).
ROS and NOXs regulate Mo-DC differentiation and maturation independently of NOX2. Freshly isolated Mos from healthy donors (A-C) (n = 10) or gp91phox/NOX2−/− CGD patients (D-F) (n = 4) were treated with or without NAC or DPI at indicated concentrations for 15 minutes prior to adding GM-CSF/IL-4 differentiation stimuli or LPS maturation stimuli. Differentiation was carried out for 6 days and LPS maturation for 2 more days. On day 7 (immature Mo-DC) or day 9 (mature Mo-DC), cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD209 (A and D), CD86 (B and F), and CD83 (C and E) and are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001.
ROS and NOXs regulate Mo-DC differentiation and maturation independently of NOX2. Freshly isolated Mos from healthy donors (A-C) (n = 10) or gp91phox/NOX2−/− CGD patients (D-F) (n = 4) were treated with or without NAC or DPI at indicated concentrations for 15 minutes prior to adding GM-CSF/IL-4 differentiation stimuli or LPS maturation stimuli. Differentiation was carried out for 6 days and LPS maturation for 2 more days. On day 7 (immature Mo-DC) or day 9 (mature Mo-DC), cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD209 (A and D), CD86 (B and F), and CD83 (C and E) and are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001.
As the phagocyte NOX2 is the major NOX enzyme expressed in Mos and DCs, we further investigated its role in Mo-DC differentiation and maturation. We first used a chimeric peptide that inhibits p47phox association with gp91phox (gp91phox-tat), and therefore NOX2 activity.31 The use of the gp91phox-tat inhibitor did not affect the expression of CD209 in Mo-DC, suggesting that NOX2 is not involved in the Mo-DC differentiation (supplemental Figure 1D). To confirm these data, cells from CGD patients lacking the membrane subunit gp91phox/NOX220,32 were stimulated to induce Mo-DC differentiation and maturation. Flow cytometry analysis revealed normal expression of CD209 (Figure 1D) and CD86/CD83 (Figure 1E-F) in Mo-DC derived from gp91phox-deficient cells when compared with controls, suggesting that gp91phox/NOX2 is not required for Mo-DC differentiation and maturation. Interestingly, cells from gp91phox−/− CGD patients were still sensitive to NAC and DPI treatment, which inhibited Mo-DC differentiation and maturation as was observed with cells from control donors, suggesting that other NOX members might be involved in this process.
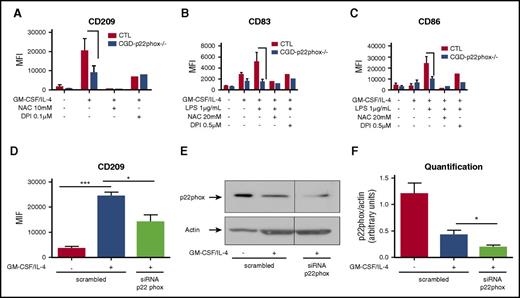
p22phox is involved in Mo-DC differentiation and maturation
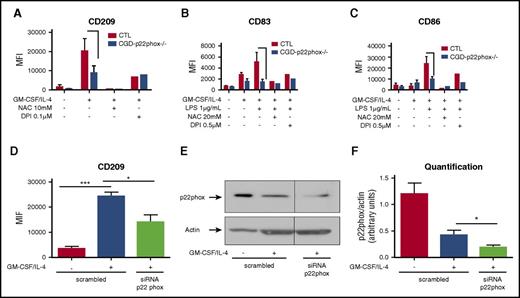
Having shown a lack of direct involvement of NOX2 in Mo-DC development, we evaluated the possible contribution of p22phox, a membrane subunit of the NOXs complex. Interestingly, Mos from CGD patients lacking p22phox subunit exhibited an impaired differentiation (lower level of CD209; Figure 2A), and a subsequent impaired maturation (lower levels of CD83 and CD86; Figure 2B-C). To confirm the involvement of p22phox in Mo-DC differentiation, a pool of 3 siRNAs specific for p22phox was used. Expression of p22phox was indeed reduced at the protein level (Figure 2E-F), and expression of CD209 was substantially decreased after cytokine stimuli when compared with incubation with a scrambled siRNA (Figure 2D), indicating that p22phox plays a role in the differentiation and maturation of Mo-DCs.
p22phox is involved in Mo-DC differentiation and maturation. (A-C) Freshly isolated Mos from 2 p22phox CGD patients (experiments repeated twice) were treated with or without NAC or DPI at indicated concentrations 15 minutes prior to GM-CSF/IL-4 differentiation stimuli or LPS maturation stimuli. Differentiation was carried out for 6 days and LPS maturation for 2 more days. On day 7 (immature Mo-DC) or day 9 (mature Mo-DC), cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as MFI. (D) Mos were transfected with 200 nM scrambled or p22phox siRNA. Five days later, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as MFI of CD209 and are expressed as mean ± SEM of n = 4. (E) Representative western blot analysis of Mo-DC siRNA transfection and (F) relative quantification (n = 4, arbitrary units). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
p22phox is involved in Mo-DC differentiation and maturation. (A-C) Freshly isolated Mos from 2 p22phox CGD patients (experiments repeated twice) were treated with or without NAC or DPI at indicated concentrations 15 minutes prior to GM-CSF/IL-4 differentiation stimuli or LPS maturation stimuli. Differentiation was carried out for 6 days and LPS maturation for 2 more days. On day 7 (immature Mo-DC) or day 9 (mature Mo-DC), cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as MFI. (D) Mos were transfected with 200 nM scrambled or p22phox siRNA. Five days later, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. Data are presented as MFI of CD209 and are expressed as mean ± SEM of n = 4. (E) Representative western blot analysis of Mo-DC siRNA transfection and (F) relative quantification (n = 4, arbitrary units). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
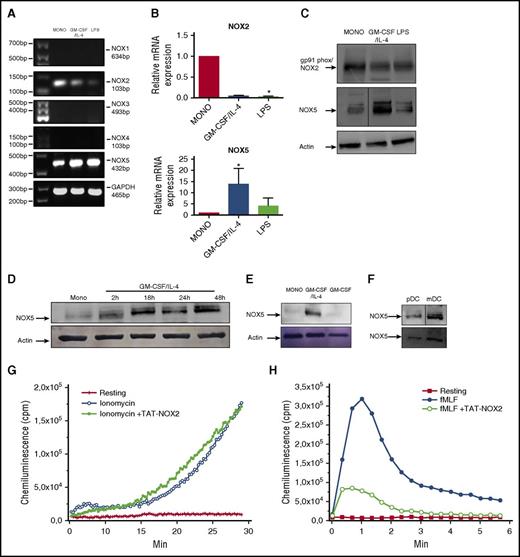
NOX5 expression is strongly increased during Mo-DC differentiation
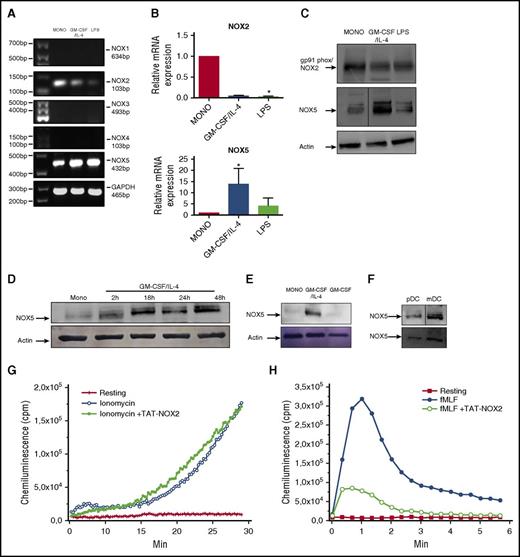
As shown here and by others, NOX2 subunits are expressed in Mos and Mo-DCs.13,14 In contrast, to the best of our knowledge, the presence of other NOXs in human Mo-DC is still unknown. Therefore, we evaluated the expression of all NOXs in Mo-DCs at the messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels. Endpoint PCR confirmed a strong presence of NOX2 mRNA in Mos, which was reduced in Mo-DCs (Figure 3A). Moreover, NOX5 mRNA was detected in Mos and was highly increased by Mo-DC differentiation. NOX1, NOX3, and NOX4 were not expressed at the mRNA level (Figure 3A) and protein level (data not shown) in human Mos and DCs. DUOX1 and DUOX2 expressions were not always detectable and very variable among different donors (data not shown). These data were confirmed by real-time PCR, where a 10-fold increase in NOX5 expression and a decrease in NOX2 expression were observed in differentiated Mo-DCs when compared with controls (freshly isolated Mos) (Figure 3B). Interestingly, NOX5 levels were strongly reduced in LPS-treated Mo-DC cells. A similar modulation was observed and confirmed at the protein level (Figure 3C). Quantification and statistics of these experiments are shown in supplemental Figure 3A-B. NOX5-increased expression was an early event during differentiation, as it was observed as soon as 2 hours after stimulation with the differentiation inducers (Figure 3D; supplemental Figure 3C); however, its expression was maximum after 18 hours of treatment and remained stable for 7 days (data not shown). Considering the strong increase of NOX5 during Mo-DC differentiation and its decrease during Mo-DC maturation, we focused our attention on the role of NOX5 in Mo-DC differentiation, a key event in immunity; for the rest of the study, we will therefore refer to Mo-DC to indicate Mo differentiation to DCs (immature DC).
Mo-DC express high levels of active NOX5. Total RNA was extracted from freshly isolated Mos (MONO), immature Mo-DCs (GM-CSF/IL-4), and mature Mo-DCs (LPS) by standard techniques. mRNA levels for (A) NOX1-5 were determined by endpoint PCR using specific primers. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as loading control. The size of the products is represented in base pairs (bp). (B) Real-time PCR of NOX2 and NOX5. Relative expression to control (MONO) levels for each gene was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method, with normalization to the average hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT) and GAPDH housekeeping genes. One-way ANOVA with Dunn post-test, *P < .05. (C) Representative western blot analysis for NOX2 (gp91phox), NOX5, and actin (n = 3) in Mos and DC. (D) Time course of expression of NOX5 in Mos treated with GM-CSF/IL-4. (E) Representative western blot (n = 3) for NOX5 and actin in MONO, Mo-DC (GM-CSF/IL-4) cells, and macrophage (GM-CSF). (F) Representative western blots for NOX5 expression in freshly isolated pDC and mDC (n = 2). Quantification of these data can be found in supplemental Figure 3. (G-H) Mos were treated with GM-CSF/IL-4 for 48 hours, incubated in the absence or presence of 20 µM TAT-NOX2 peptide, stimulated with 1 µM ionomycin (G) or 1 µM fMLF (H), and ROS production was measured using luminol-amplified chemiluminescence (n = 3).
Mo-DC express high levels of active NOX5. Total RNA was extracted from freshly isolated Mos (MONO), immature Mo-DCs (GM-CSF/IL-4), and mature Mo-DCs (LPS) by standard techniques. mRNA levels for (A) NOX1-5 were determined by endpoint PCR using specific primers. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as loading control. The size of the products is represented in base pairs (bp). (B) Real-time PCR of NOX2 and NOX5. Relative expression to control (MONO) levels for each gene was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method, with normalization to the average hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT) and GAPDH housekeeping genes. One-way ANOVA with Dunn post-test, *P < .05. (C) Representative western blot analysis for NOX2 (gp91phox), NOX5, and actin (n = 3) in Mos and DC. (D) Time course of expression of NOX5 in Mos treated with GM-CSF/IL-4. (E) Representative western blot (n = 3) for NOX5 and actin in MONO, Mo-DC (GM-CSF/IL-4) cells, and macrophage (GM-CSF). (F) Representative western blots for NOX5 expression in freshly isolated pDC and mDC (n = 2). Quantification of these data can be found in supplemental Figure 3. (G-H) Mos were treated with GM-CSF/IL-4 for 48 hours, incubated in the absence or presence of 20 µM TAT-NOX2 peptide, stimulated with 1 µM ionomycin (G) or 1 µM fMLF (H), and ROS production was measured using luminol-amplified chemiluminescence (n = 3).
Mos have been shown to be able to differentiate into DC and macrophages.10,33 To determine whether the increase in NOX5 expression was unique to Mo-DC differentiation, we differentiated Mos into macrophages with GM-CSF and compared with Mo-derived DCs induced as before. Figure 3E clearly shows that the NOX5 protein was only increased by GM-CSF/IL-4 in Mo-DC, whereas macrophages exhibited low levels of NOX5 expression, similar to those observed in Mos (Figure 3E, supplemental Figure 3D). IL-4 stimulation alone did not alter NOX5 expression (data not shown). In order to check if circulating DCs also expressed NOX5, we isolated pDC and mDC from the blood of healthy donors by magnetic separation. NOX5 expression was found in both DC subsets, although its level seemed to be higher in mDC (Figure 3F, supplemental Figure 3E). These results show that NOX5 is expressed in human Mo-derived DCs generated in vitro as well as in circulating DCs.
ROS production by NOX5 activation is known to be calcium dependent and thus can be induced by ionomycin, a calcium ionophore.34 Interestingly, after 48 hours of Mo-DC differentiation, ionomycin-induced ROS production and the gp91phox-tat peptide inhibitor did not inhibit this response, while inhibiting fMLF-induced ROS production (Figure 3G-H). These data suggest that ROS production in response to ionomycin is due to NOX5 in human Mo-DC cells.
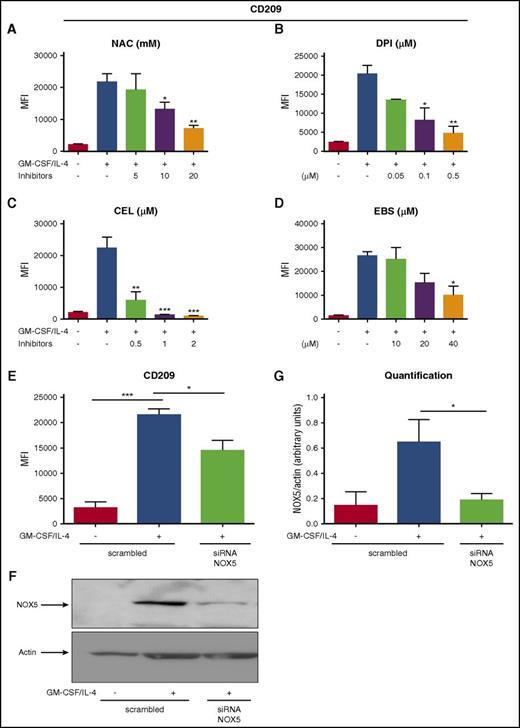
NOX5 is required for Mo-DC differentiation
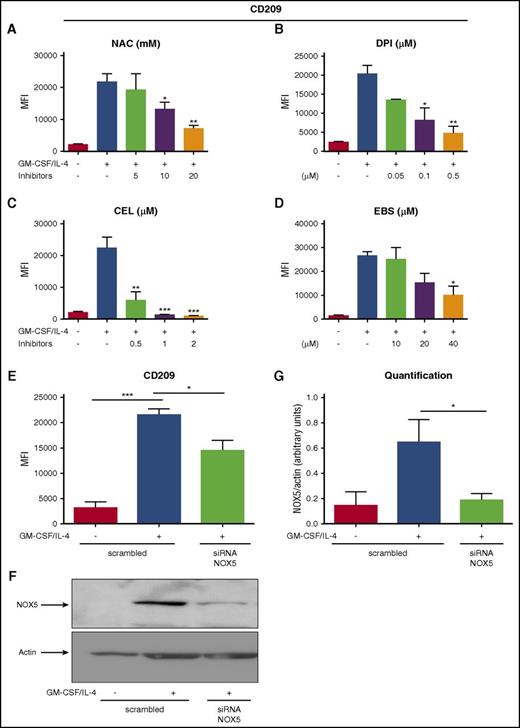
In order to evaluate a possible role of NOX5 in Mo-DC differentiation, we first inhibited its activity. Indeed, rodents do not express NOX5,35 making the knockout approaches impossible to study its role in vivo. Currently, there are no available specific inhibitors for NOX5, but some inhibitors have been shown to block NOX5 more selectively. For example, Celastrol (CEL) and Ebselen (EBS) inhibit NOX5-dependent ROS production.36,37 We therefore tested these 2 inhibitors, together with NAC and DPI as controls. As expected, NAC and DPI inhibited the expression of CD209 in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 4A-B). In addition, CEL and EBS also inhibited CD209 expression in a concentration-dependent fashion, and Mo-DC differentiation (Figure 4C-D). Interestingly, apocynin, another commonly used NOX inhibitor that has been shown to have very mild effect on NOX5 activity,38 had minimal effect on Mo-DC differentiation (supplemental Figure 4A), strengthening our observations. These results strongly suggest that the decreased Mo-DC differentiation observed in the presence of CEL and EBS is due to inhibition of NOX5 activity. To further confirm the role of NOX5 in Mo-DC differentiation, we specifically inhibited its expression by using a pool of 3 target-specific siRNAs for NOX5. Transfection of Mos with the scrambled siRNA maintained their differentiation ability toward DC, showing a significant increase of CD209 in transfected cells stimulated with GM-CSF/IL-4 (Figure 4E), whereas transfection with NOX5 siRNA resulted in a significant decrease of NOX5 protein levels (Figure 4F-G) and Mo-DC differentiation when compared with the scrambled siRNA (Figure 4E). These results show that NOX5 is critical for Mo-DCs differentiation.
NOX5 regulates Mo-DC differentiation. Flow cytometry analysis of Mos treated with increasing concentration of (A) NAC (5-20 mM), (B) DPI (0.05-0.5 µM), (C) CEL (0.5-2 µM), and (D) EBS (10-40 µM) 15 minutes prior to addition of the cytokine differentiation stimuli (GM-CSF/IL-4) for 6 days. On day 7, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. (E) Mos treated for 18 hours with GM-CSF/IL-4 to induce NOX5 expression and then transfected with 200 nM scrambled or NOX5 siRNA. Five days later, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis as above. Data are presented as MFI of CD209 and are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). (F) Representative western blot analysis of Mo-DC transfection and (G) relative quantification (n = 4, arbitrary units). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
NOX5 regulates Mo-DC differentiation. Flow cytometry analysis of Mos treated with increasing concentration of (A) NAC (5-20 mM), (B) DPI (0.05-0.5 µM), (C) CEL (0.5-2 µM), and (D) EBS (10-40 µM) 15 minutes prior to addition of the cytokine differentiation stimuli (GM-CSF/IL-4) for 6 days. On day 7, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis after incubation with CD86 PE/CD209 PerCP-Cy5.5/CD83 APC cocktail antibodies for 20 minutes in the dark. (E) Mos treated for 18 hours with GM-CSF/IL-4 to induce NOX5 expression and then transfected with 200 nM scrambled or NOX5 siRNA. Five days later, cells were harvested and prepared for flow cytometry analysis as above. Data are presented as MFI of CD209 and are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). (F) Representative western blot analysis of Mo-DC transfection and (G) relative quantification (n = 4, arbitrary units). One-way ANOVA with Tukey test. *P < .05, ***P < .001.
NOX5 and p22phox interact in Mo-DC cells
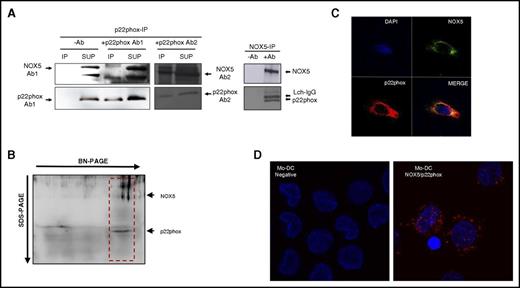
It has been shown in the literature that NOX5, contrary to other NOXs, does not require p22phox for its expression and activation.34,39 However, the results presented here suggest that both NOX5 and p22phox are involved in Mo-DC differentiation. To investigate if these 2 subunits could interact in Mo-DC, we first performed co-IP studies in Mo-DCs, immobilizing p22phox or NOX5 antibodies onto A-agarose beads and analyzing the presence of NOX5/p22phox by western blot of the immunoprecipitated fractions. Interestingly, NOX5-IP revealed the presence of p22phox in the coimmunoprecipitates (Figure 5A right). Similarly, NOX5 was detected in the p22phox-IP as shown with different p22phox and NOX5 antibodies (Figure 5A left). To confirm that NOX5 and p22phox interact, we also performed 2-dimensional BN-PAGE, which allows the separation of proteins complexes.29 Results confirmed that NOX5 and p22phox were present in the same complex (Figure 5B red box). We further confirmed these results by confocal studies, showing that NOX5 and p22phox colocalized in Mo-DC (Figure 5C). In addition, we used the Duolink-PLA assay analysis, which further demonstrated the interaction between NOX5 and p22phox in Mo-DC (Figure 5D red dots). As a positive control, the Duolink-PLA assay was performed in freshly isolated human neutrophils, which showed the well-known interaction between gp91phox and p22phox (supplemental Figure 4B).
NOX5 and p22phox interact in Mo-DC. (A) Representative western blot of co-IP. p22phox (left) and NOX5 (right) were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to p22phox and NOX5, respectively, and 2 different NOX5 antibodies were used for detection. IP (immunoprecipitate) fractions with or without antibodies (−Ab and +Ab); SUP (supernatant) after immunoprecipitation. (B) Total lysates were separated by 2-dimensional BN/SDS-PAGE (4%-16% and 12%) and immunoblotted with NOX5 and p22phox antibodies. The NOX5-p22phox complex is shown in the red box. (C) Confocal microscopy of Mo-DC, labeled with anti-NOX5 and Alexa 488, anti-p22phox and Alexa 555, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; nuclei); 40× objective, zoom 6×. (D) Representative image using the Duolink proximity ligation assay in Mo-DC. Interaction between NOX5 and p22phox is represented by red dot signals (right panel). In the negative control (left, without primary antibodies), only the DAPI signal can be observed; 63× objective, zoom 2×.
NOX5 and p22phox interact in Mo-DC. (A) Representative western blot of co-IP. p22phox (left) and NOX5 (right) were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to p22phox and NOX5, respectively, and 2 different NOX5 antibodies were used for detection. IP (immunoprecipitate) fractions with or without antibodies (−Ab and +Ab); SUP (supernatant) after immunoprecipitation. (B) Total lysates were separated by 2-dimensional BN/SDS-PAGE (4%-16% and 12%) and immunoblotted with NOX5 and p22phox antibodies. The NOX5-p22phox complex is shown in the red box. (C) Confocal microscopy of Mo-DC, labeled with anti-NOX5 and Alexa 488, anti-p22phox and Alexa 555, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; nuclei); 40× objective, zoom 6×. (D) Representative image using the Duolink proximity ligation assay in Mo-DC. Interaction between NOX5 and p22phox is represented by red dot signals (right panel). In the negative control (left, without primary antibodies), only the DAPI signal can be observed; 63× objective, zoom 2×.
NOX5 is intracellular and mainly localizes on the external membrane of mitochondria where it interacts with p22phox
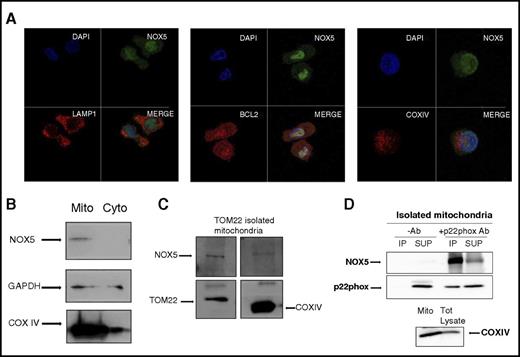
NOX enzymes are transmembrane proteins that are localized either in intracellular granules and vesicles or on the surface of cell membranes.21,40,41 Here, we evaluated the subcellular localization of NOX5 in Mo-DCs. NOX5 was diffusely localized in the cytoplasm of Mos (supplemental Figure 5A-B). In Mo-DCs, however, the expression was more intense, with a very defined dotted distribution (Figure 6A green; supplemental Figure 5A), which prompted us to further analyze its localization using lysosome (LAMP142 ) and mitochondria markers (BCL2 for the outer membrane43 and COXIV for the inner membrane44 ). The first panel in Figure 6A shows a lack of colocalization of NOX5 and LAMP-1 in Mo-DC, suggesting that NOX5 is not localized in lysosomes. In the second panel, a clear colocalization (yellow) between BCL2 (red) and NOX5 (green) was found in Mo-DC, suggesting a possible mitochondrial localization of NOX5. This localization was confirmed by using another marker of the outer mitochondria membrane, TOM22,45 which also colocalized with NOX5 in Mo-DC, although to a lesser extent (supplemental Figure 5C). However, the inner membrane marker, COXIV, did not colocalize with NOX5, suggesting that NOX5 might be localized at the outer and not at the inner membrane of mitochondria. To confirm these results, we isolated mitochondria from Mo-DC by differential centrifugation. As expected, NOX5 was detected in the mitochondrial fraction (Mito), and not in the cytosolic fraction (Cyto) (Figure 6B). In addition, we also used an isolation protocol based on magnetic separation with TOM22, which is an established method to obtain highly pure and healthy mitochondria.46 The mitochondrial preparations were free of Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum fractions (supplemental Figure 6A). The purified mitochondria had high levels of TOM22 and COXIV and contained NOX5 (Figure 6C), strengthening our observation that NOX5 has a mitochondrial localization. We then investigated the localization of p22phox in Mo-DC, showing a strong presence of p22phox in the TOM22 purified mitochondria (supplemental Figure 6B). In addition, we confirmed the interaction of NOX5 and p22phox at the mitochondrial level by performing co-IP studies on isolated mitochondria. The results clearly show the presence of the NOX5 protein in the p22phox immunoprecipitates (Figure 6D).
NOX5 is expressed on the outer membrane of the mitochondria and interacts with p22phox. (A) Confocal microscopy of Mo-DC, labeled with anti-NOX5 and Alexa 488, anti-LAMP-1 (lysosome marker), anti-BCL2 (outer membrane mitochondrial marker), or anti-COXIV (inner membrane mitochondrial marker) and Alexa 555, and DAPI (nuclear staining). 40× objective, zoom 6×. (B) Representative western blots of Cyto and Mito fractions isolated by differential centrifugation. Blots were incubated with anti-NOX5, anti-GAPDH (for cytosol), and anti-COXIV (for mitochondria) antibodies. (C) Mitochondria isolation in Mo-DC by magnetic anti-TOM22 separation. A representative western blot from 2 independent isolations is shown. Blots were incubated with anti-NOX5, anti-TOM22, and anti-COXIV antibodies. (D) Representative western blot of co-IP in isolated mitochondria. Immunoprecipitation was achieved with p22phox Ab, and NOX5 Ab was used for detection. Immunoprecipitate fractions with or without antibodies (−Ab and +Ab). Supernatant (SUP) after pull-down. For control, COXIV was detected in the mitochondrial fraction and total (Tot) lysate (bottom panel). Each experiment was repeated 3 times.
NOX5 is expressed on the outer membrane of the mitochondria and interacts with p22phox. (A) Confocal microscopy of Mo-DC, labeled with anti-NOX5 and Alexa 488, anti-LAMP-1 (lysosome marker), anti-BCL2 (outer membrane mitochondrial marker), or anti-COXIV (inner membrane mitochondrial marker) and Alexa 555, and DAPI (nuclear staining). 40× objective, zoom 6×. (B) Representative western blots of Cyto and Mito fractions isolated by differential centrifugation. Blots were incubated with anti-NOX5, anti-GAPDH (for cytosol), and anti-COXIV (for mitochondria) antibodies. (C) Mitochondria isolation in Mo-DC by magnetic anti-TOM22 separation. A representative western blot from 2 independent isolations is shown. Blots were incubated with anti-NOX5, anti-TOM22, and anti-COXIV antibodies. (D) Representative western blot of co-IP in isolated mitochondria. Immunoprecipitation was achieved with p22phox Ab, and NOX5 Ab was used for detection. Immunoprecipitate fractions with or without antibodies (−Ab and +Ab). Supernatant (SUP) after pull-down. For control, COXIV was detected in the mitochondrial fraction and total (Tot) lysate (bottom panel). Each experiment was repeated 3 times.
NOX5-derived ROS regulate the signaling pathways involved in Mo-DC differentiation
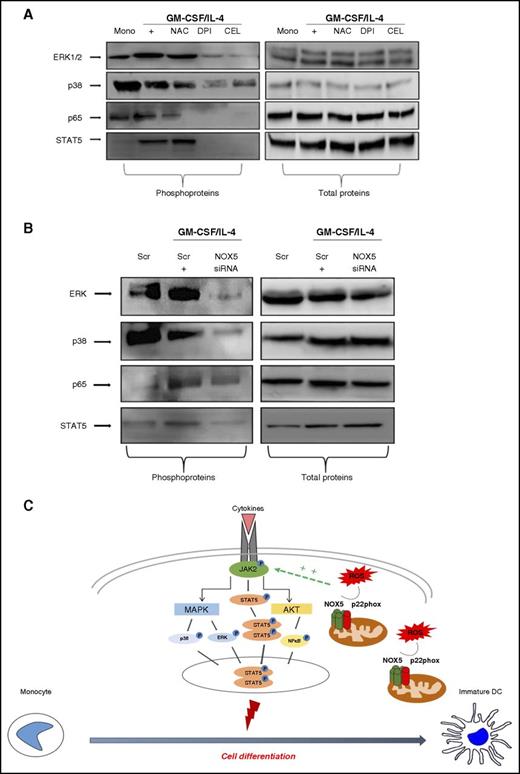
Different pathways, such as NFκB and MAPKinases, are redox-sensitive and have been shown to have a role in Mo-DC development.47-52 We thus evaluated the effect of NOX pharmacological inhibitors on the phosphorylation of the NFκB subunit p65, p38MAPKinase, ERK1/2, and STAT5, in response to the differentiation stimuli. Results showed (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 7A) that in freshly isolated Mos, GM-CSF and IL-4 increased the basal level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Interestingly, the ROS scavenger NAC, the NOX inhibitor DPI, and the more selective NOX5 inhibitor CEL inhibited this phosphorylation. Phospho-p38MAPK was slightly reduced during differentiation and further reduced by the NOX inhibitors, in particular with DPI and CEL. Moreover, the increased phosphorylation of the NFκB p65 subunit observed during differentiation was also inhibited by NAC, DPI, and CEL. These results suggest that NOX5-derived ROS are involved in the regulation of these signaling pathways. The analysis of the JAK/STAT pathway, which is upstream of the MAPKinase and NFκB pathways, revealed that DPI and CEL strongly inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT5, which is the direct target of JAK2.52 To confirm that these pathways were regulated by NOX5, their activation status was evaluated in NOX5-siRNA–transfected cells, demonstrating that NOX5-siRNA clearly inhibited ERK1/2, p38MAPK, NFκB p65, and STAT5 phosphorylation, but did not affect their total protein levels (Figure 7B; supplemental Figure 7B). Thus, these data demonstrate that NOX5 drives Mo-DC differentiation by altering the JAK/STAT/MAPK and NFκB signaling pathways as depicted in Figure 7C.
NOX5 inhibition impairs MAPK and NFκB pathways during Mo-DC differentiation. Representative western blot analysis (n = 3) of (A) Mos treated with NAC (10 mM), DPI (0.1 µM), CEL (2 µM), or EBS (40 µM) for 15 minutes prior to addition of cytokine differentiation stimuli (GM-CSF/IL-4) for 6 days. On day 7, cells were harvested and lysed. (B) Mos were treated for 18 hours with GM-CSF/IL-4 to induce NOX5 expression and then transfected with 200 nM scrambled or NOX5 siRNA. Blots were incubated with (left) anti-phospho ERK, anti-phospho p38, anti-phospho p65, anti-phospho STAT5, or (right) with antibodies against the total proteins. Blot quantification can be found in supplemental Figure 7A-B. (C) Our model of regulation of Mo-DC differentiation shows that the complex located on the outer membrane of the mitochondria releases ROS that positively regulate, directly or indirectly, the cytokine-induced JAK2 phosphorylation, leading to subsequent activation of STAT5 phosphorylation, which then dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, promoting cell differentiation. In parallel, JAK2 activation will also induce MAPKinase and AKT/NFκB activation. These signaling events promote differentiation into DCs. Scr, scrambled.
NOX5 inhibition impairs MAPK and NFκB pathways during Mo-DC differentiation. Representative western blot analysis (n = 3) of (A) Mos treated with NAC (10 mM), DPI (0.1 µM), CEL (2 µM), or EBS (40 µM) for 15 minutes prior to addition of cytokine differentiation stimuli (GM-CSF/IL-4) for 6 days. On day 7, cells were harvested and lysed. (B) Mos were treated for 18 hours with GM-CSF/IL-4 to induce NOX5 expression and then transfected with 200 nM scrambled or NOX5 siRNA. Blots were incubated with (left) anti-phospho ERK, anti-phospho p38, anti-phospho p65, anti-phospho STAT5, or (right) with antibodies against the total proteins. Blot quantification can be found in supplemental Figure 7A-B. (C) Our model of regulation of Mo-DC differentiation shows that the complex located on the outer membrane of the mitochondria releases ROS that positively regulate, directly or indirectly, the cytokine-induced JAK2 phosphorylation, leading to subsequent activation of STAT5 phosphorylation, which then dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, promoting cell differentiation. In parallel, JAK2 activation will also induce MAPKinase and AKT/NFκB activation. These signaling events promote differentiation into DCs. Scr, scrambled.
Discussion
In this study, we identified NOX5 and p22phox as novel regulators of the differentiation of Mos into DCs. Furthermore, we documented a novel role for p22phox in Mo-DC development, which was independent of gp91phox/NOX2. Our data also suggest that NOX5 and p22phox are in a complex in the membrane of the mitochondria, as demonstrated by co-IP and confocal microscopy studies.
The inhibition of DC differentiation and maturation by the NOX inhibitor, DPI, and the ROS scavenger, NAC, suggested a role for NOXs in this process. However, our data show that Mo-DC differentiation and maturation were not altered in CGD patients lacking gp91phox/NOX2, as shown by Vulcano et al.14 It also suggested that other members of the NOX family might be involved. A recent study had demonstrated the presence of NOX5 in Mos.15 This observation was confirmed in our study at both the mRNA and the protein levels. Another report had also shown the presence of NOX4 in Mos,13 but it was undetectable in our cells. Interestingly, we observed a very strong and consistent upregulation of NOX5 expression during Mo-DC differentiation induced by GM-CSF and IL-4. In contrast, GM-CSF alone, which induced the differentiation of Mos into macrophages, was not able to induce NOX5 expression, indicating that NOX5 expression is restricted to Mo-DC. In addition, we also found high levels of NOX5 in circulating mDCs and at lower levels in plasmacytoid DCs.
We used 2 selective NOX5 inhibitors that have been shown to efficiently block NOX5 activity CEL, which blocks NOX5-dependent hydrogen peroxide production in HEK stably expressing NOX5,35 and EBS, which inhibits NOX5 activity in a whole cell system.36 Both inhibitors, with different efficiency, reduced Mo-DC differentiation in a dose-dependent manner, whereas apocynin, which lacks activity on NOX5,37 did not alter Mo-DC differentiation. The siRNA approach allowed us to confirm these observations as silencing NOX5 at its peak of expression resulted in impaired Mo-DC differentiation. Previous reports have suggested a role of NOX5 in cellular functions; NOX5 was reported to be involved in proliferation and survival of carcinoma cells,53 in PDGF-driven human aortic smooth cells proliferation,54 as well as in the upregulation of CX3CL1 induced by cigarette smoking and in mononuclear cell arrest.55 Moreover, NOX5, together with NOX3, has recently been shown to induce oligodendrocyte differentiation.56 Therefore, our data showing that NOX5 is a new regulator of the important immune process of DC generation from Mos extend our knowledge on the functions of NOX5 in immunity.
Contrary to other NOX enzymes, it is believed that NOX5 does not require cytosolic subunits for its activation and does not require the presence of p22phox as a stabilizing protein.57 Its unique N-terminal region contains 4 EF hands (two alpha helices called E and F linked by a short loop region) that bind calcium and regulate its activity.34 Nevertheless, it has been shown that p22phox can interact with NOX5 in endothelial cells, although this interaction was not essential for NOX5-mediated ROS production in these cells.58 Co-IP, BN gels, confocal studies, and Duolink technology all showed that p22phox interacts with NOX5 in Mo-DC. Considering that both subunits are involved in Mo-DC differentiation, it could be speculated that this interaction is functional. In addition, we observed a reduced expression of NOX5 in CGD patients lacking p22phox and in p22phox-siRNA–transfected cells (supplemental Figure 8), suggesting that p22phox might regulate NOX5 expression. Further studies will be needed to investigate the significance of this novel interaction in more details.
Previous studies regarding the localization of NOX5 indicated a cytoplasmic and perinuclear localization, with a modest plasma membrane localization.37,59,60 Here, we show, for the first time, a mitochondrial localization of NOX5 in DCs, specifically on the outer membrane, as shown by colocalization with BCL2 and TOM22, but not with COXIV.43,44 This localization was confirmed by the presence of NOX5 and p22phox in highly purified mitochondria, obtained with magnetic separation with TOM22, which is considered one of the most efficient purification techniques.46 It is not the first time that a NOX isoform is found in mitochondria; NOX4, in fact, has been shown to be located in the mitochondria of glomerular mesangial cells and aortic endothelial cells.61 These data are in agreement with the work of Del Prete et al,62 showing that inhibitors of mitochondrial activity led to a significantly reduced Mo-DC differentiation, suggesting the involvement of mitochondrial ROS. Although further studies will be needed to confirm that the NOX5/p22phox complex in the mitochondria is the source of intracellular ROS, our data with NAC and DPI strongly indicate that ROS are involved in Mo-DC differentiation.
We demonstrated that NOX5-derived ROS are involved in several redox-sensitive signaling pathways such as the MAPKinase and NFκB as shown by using pharmacological inhibitors and NOX5-siRNA. Thus, we can propose a model of Mo-DC differentiation where NOX5 is in a complex with p22phox at the outer membrane of mitochondria, which releases ROS that positively regulate, directly or indirectly, the cytokine-induced JAK2 phosphorylation, leading to subsequent activation of the JAK/STAT pathway through STAT5 phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus, promoting cell differentiation of Mos into DCs (Figure 7C). In parallel, JAK2 activation will also induce MAPKinases and AKT/NFκB activation. The ROS-dependent crosstalk activation pathway generated by cytokines has been previously described in human cells, revealing a role for ROS as a second messenger in the amplification of IL-4–mediated signal transduction via the activation of NOX5 and NOX1.63
In conclusion, this study revealed that the interaction of NOX5 with p22phox is important in Mo-DC development. Moreover, we showed that NOX5 and p22phox have a previously unknown localization on the outer membrane of mitochondria and regulate several signaling cascades involved in Mo-DC differentiation. As DCs are a major regulator of immune response and inflammation, NOX5 and p22phox could be novel pharmacological targets in immune and inflammatory disorders.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank William Nauseef (University of Iowa) and Corinne Dupuy (IGR, Université Paris Sud) for the NOX5 and DUOX antibodies, respectively, Martine Torres for her critical reading of the manuscript, and Samira Benadda for her help with confocal microscopy experiments.
This research was supported by LabEx Inflamex, INSERM, CNRS (French National Center for Scientific Research), and University Denis-Diderot Paris 7.
Authorship
Contribution: V.M. designed and performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; M.H.-N. and C.P. performed experiments and analyzed data; A.T. analyzed DuoLink experiments; J.-C.M. contributed to the experiments and analyzed data; R.C.M. and M.-A.G.-P. recruited the patients and contributed to the discussion; P.M.-C.D. and J.E.-B. supervised the project and co-wrote the manuscript. All the authors have read the manuscript and agree with the data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jamel El-Benna, INSERM U1149, Faculté de Médecine Xavier Bichat, 16 Rue Henri Huchard, Paris F-75018, France; e-mail: jamel.elbenna@inserm.fr.