On page 105 in the 5 July 2012 issue, Figure 3 panels B, C, and D contained errors in the graphics, which were generated separately using FloJo software after analysis of the primary data using CellQuest software. These were errors in the display of the data, but the primary data and its analyses were unaffected and there is no impact on the results and conclusions of the manuscript.
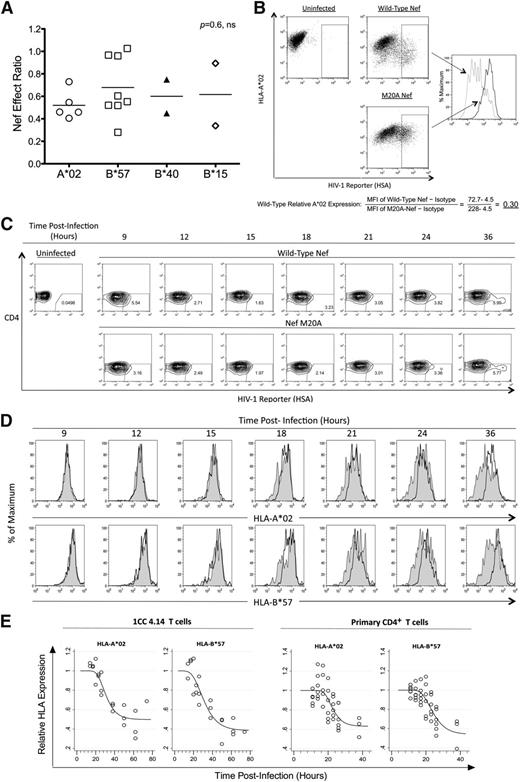
The effect of Nef on HIV-1–specific CTL antiviral activity is unrelated to HLA-I restriction of the epitope. The impact of Nef was compared across presenting HLA-I types. (A) Nef-effect ratios plotted for the indicated HLA-I types. Each dot represents one epitope; the horizontal bar represents the mean. There was no significant difference between groups (Kruskal-Wallis test). (B) A flow cytometric approach was used to measure Nef-mediated down-regulation of HLA-I A*02 and HLA-I B*57 on acutely HIV-1–infected cells. A representative experiment shows the analysis of HLA-A*02 down-regulation after gating on infected cells (positive for the HSA reporter) and determination of MFI of A*02 staining. The relative expression of A*02 on cells infected with wild-type Nef virus (gray dotted histogram) was then calculated as a fraction of MFI compared with Nef-M20A virus (black solid histogram) after subtraction of background MFI (from an isotype control). (C) Expression of cell-surface CD4 and the HSA reporter over time is demonstrated after acute infection of primary CD4+ T lymphocytes from an HIV-1–infected donor with both A*02 and B*57 (subject number 00036, a slow progressor not on treatment). (D) The infected (HSAhigh+ and CD4dim/−, percentages shown) primary CD4+ T lymphocytes were gated and analyzed for A*02 (top panel) and B*57 (bottom panel) expression. HLA-I expression is plotted for HIV-1 with wild-type Nef (gray shaded histograms) versus Nef-M20A (black histograms). (E) Gompertz plots of Nef-mediated down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are shown for the laboratory T-cell line 1CC4.14 (top panel) or primary CD4+ T lymphocytes* (bottom panel). In the top panel, the estimates for time to 10% A*02 versus B*57 down-regulation by Nef are 22.1 and 19.6 hours after infection, respectively. The slopes of the fitted curves at 10% down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are −0.016 and −0.015, respectively. The maximum levels of down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are estimated to be 50% and 40%, respectively. These parameters are not significantly different for A*02 versus B*57. In the bottom panel, the estimates for time to 10% A*02 versus B*57 down-regulation by Nef are 18.1 and 18.0 hours after infection, respectively. The slopes of the fitted curves at 10% down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are −0.023 and −0.021, respectively. The maximum levels of down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are estimated to be 60% and 50%, respectively. These parameters are not significantly different for A*02 versus B*57. The efficiency of infection was higher (approximately 40%-50% vs the 10% shown in Figure 3C) and Nef-mediated HLA-I down-regulation occurred earlier (approximately 12 hours after infection) in virus-infected primary CD4+ T lymphocytes of HIV-1–uninfected donors (data not shown).
The effect of Nef on HIV-1–specific CTL antiviral activity is unrelated to HLA-I restriction of the epitope. The impact of Nef was compared across presenting HLA-I types. (A) Nef-effect ratios plotted for the indicated HLA-I types. Each dot represents one epitope; the horizontal bar represents the mean. There was no significant difference between groups (Kruskal-Wallis test). (B) A flow cytometric approach was used to measure Nef-mediated down-regulation of HLA-I A*02 and HLA-I B*57 on acutely HIV-1–infected cells. A representative experiment shows the analysis of HLA-A*02 down-regulation after gating on infected cells (positive for the HSA reporter) and determination of MFI of A*02 staining. The relative expression of A*02 on cells infected with wild-type Nef virus (gray dotted histogram) was then calculated as a fraction of MFI compared with Nef-M20A virus (black solid histogram) after subtraction of background MFI (from an isotype control). (C) Expression of cell-surface CD4 and the HSA reporter over time is demonstrated after acute infection of primary CD4+ T lymphocytes from an HIV-1–infected donor with both A*02 and B*57 (subject number 00036, a slow progressor not on treatment). (D) The infected (HSAhigh+ and CD4dim/−, percentages shown) primary CD4+ T lymphocytes were gated and analyzed for A*02 (top panel) and B*57 (bottom panel) expression. HLA-I expression is plotted for HIV-1 with wild-type Nef (gray shaded histograms) versus Nef-M20A (black histograms). (E) Gompertz plots of Nef-mediated down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are shown for the laboratory T-cell line 1CC4.14 (top panel) or primary CD4+ T lymphocytes* (bottom panel). In the top panel, the estimates for time to 10% A*02 versus B*57 down-regulation by Nef are 22.1 and 19.6 hours after infection, respectively. The slopes of the fitted curves at 10% down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are −0.016 and −0.015, respectively. The maximum levels of down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are estimated to be 50% and 40%, respectively. These parameters are not significantly different for A*02 versus B*57. In the bottom panel, the estimates for time to 10% A*02 versus B*57 down-regulation by Nef are 18.1 and 18.0 hours after infection, respectively. The slopes of the fitted curves at 10% down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are −0.023 and −0.021, respectively. The maximum levels of down-regulation of A*02 versus B*57 are estimated to be 60% and 50%, respectively. These parameters are not significantly different for A*02 versus B*57. The efficiency of infection was higher (approximately 40%-50% vs the 10% shown in Figure 3C) and Nef-mediated HLA-I down-regulation occurred earlier (approximately 12 hours after infection) in virus-infected primary CD4+ T lymphocytes of HIV-1–uninfected donors (data not shown).
In generating Figure 3B, the illustrative sample plots for A*02 downregulation were mistakenly substituted with those for B*57 downregulation, and thus the MFI values in the sample calculation of HLA downregulation did not match the plot. Furthermore, the gating in this example was different from that used in the primary data analysis plotted in Figure 3E, generating slightly different values. The corrected Figure 3B now shows an example matching the primary data analysis.
In generating Figure 3D, the histograms for the 18- and 24-h time points were duplicated for the M20A arm. Furthermore, the gating in this example was slightly different from that used in the primary data analysis plotted in Figure 3E, generating different values. The corrected Figure 3D (and associated Figure 3C) now shows an example matching the primary data analysis. Panels A and E are unchanged from the original.