Abstract
Intermittent parathyroid hormone (iPTH) treatment expands hemopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), but the involved mechanisms and the affected HSPC populations are mostly unknown. Here we show that T cells are required for iPTH to expand short-term HSPCs (ST-HSPCs) and improve blood cell engraftment and host survival after BM transplantation. Silencing of PTH/PTH-related protein receptor (PPR) in T cells abrogates the effects of iPTH, thus demonstrating a requirement for direct PPR signaling in T cells. Mechanistically, iPTH expands ST-HSPCs by activating Wnt signaling in HSPCs and stromal cells (SCs) through T-cell production of the Wnt ligand Wnt10b. Attesting to the relevance of Wnt10b, iPTH fails to expand ST-HSPCs in mice with Wnt10b−/− T cells. Moreover, iPTH fails to promote engraftment and survival after BM transplantation in Wnt10b null mice. In summary, direct PPR signaling in T cells and the resulting production of Wnt10b play a pivotal role in the mechanism by which iPTH expands ST-HSPCs. The data suggest that T cells may provide pharmacologic targets for HSPC expansion.
Introduction
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a major regulator of calcium metabolism that defends against hypocalcemia, in part by stimulating bone resorption and thereby the release of calcium from the skeleton. However, when injected daily, a regimen known as intermittent PTH (iPTH) treatment, the hormone markedly stimulates bone formation, leading to improved bone microarchitecture and increased strength.1 As a result, intermittent treatment with the 1-34 fragment of PTH is an FDA-approved treatment modality for postmenopausal osteoporosis. In addition, PTH has important effects on the hemopoietic system. PTH expands the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) pool and regulates the activity of the HSPC niche,2 the specialized microenvironment that maintains HSPCs. Accordingly, patients with primary hyperparathyroidism have an increased number of circulating BM-derived HSPCs in the peripheral blood.3 Moreover, some PTH regimens increase the population that can later be mobilized by G-CSF,4 whereas others induce mobilization of progenitor cells from the BM into the peripheral circulation,5 thus mimicking the effects of G-CSF. Because of these properties, PTH has been investigated as a potential therapeutic agent to enhance HSPC mobilization.6 However, the mechanism by which PTH increases the number of HSPCs has only been partially elucidated. Limited data4 have addressed whether PTH regulates the most primitive long-term reconstituting subset of HSPCs (LT-HSPCs), or the short-term reconstituting subset of HSPCs (ST-HSPCs), a population that arises from LT-HSPCs and possess limited self-renewal activity.7
A pivotal effect of PTH is that of increasing the HSPC pool through regulatory actions on the HSPC niche. The HSPC niche is composed of a variety of cells, including stromal cells (SCs) and osteoblasts (OBs).8 Early studies had linked this activity of PTH to its capacity to increase the osteoblastic expression of the Notch ligand, Jagged1, leading to the activation of Notch signaling in HSPCs in vivo.2 PTH directly up-regulates the expression of Jagged1 mRNA in OBs.9 In addition, Jagged1 is up-regulated in SCs when canonical Wnt signaling is activated resulting in stabilization of β-catenin,10 a key effect of PTH in osteoblastic cells.11 These and other reports have confirmed that Notch signaling plays a relevant role in regulating HSPC self-renewal, but the exact role of Notch signaling remains controversial because some studies suggest that Notch signaling may not be required for HSPC homeostasis.12
Another intracellular system that regulates HSPC expansion is canonical Wnt signaling.13-15 PTH activates Wnt signaling in SCs and OBs through multiple mechanisms, which include Wnt ligand-independent activation of the Wnt coreceptor LRP6,16 increased production of Wnt ligands by bone and BM cells,17 and suppression of sclerostin production.18
Whereas SCs, OBs, and osteocytes represent the major targets of PTH in bone,19-21 reports from our laboratory have disclosed that T lymphocytes play an unexpected role in the mechanism of action of PTH in bone.22-25 Importantly, treatment with daily PTH increases the T-cell production of Wnt10b,23,25 a Wnt ligand that stimulates osteoblastogenesis by activating Wnt signaling in SCs and OBs,23 through direct targeting of the T-cell PTH/PTH-related protein receptor (PPR).25 As a result, the bone anabolic activity of daily PTH treatment is markedly reduced in T cell–deficient mice and in mice with a specific disruption of Wnt10b production by T cells.23
Although T cells contribute to the actions of PTH in bone, the effects of this hormone in other organs are completely T cell– independent. For example, the finding that T cell–deficient mice possess normal serum levels of calcium and phosphate and a significant increase in serum calcium, but not in bone resorption in response to PTH treatment,22 indicate that T cells are not required for PTH to exerts its effects in the kidney.
The lack of information on whether T cells contribute to the effects of PTH on HSPCs prompted us to investigate the role of T cells in the mechanism by which PTH acts on HSPCs. We show that direct activation of PPR signaling in T cells is required for PTH to expand ST-HSPCs. The involved mechanism hinges on the capacity of PTH to induce T-cell production of Wnt10b, a Wnt ligand critical for the activation Wnt signaling in both SCs and HSPCs.
Methods
Animals
All the animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Emory University. Female C57BL6/J (CD45.2), B6.SJL (CD45.1+), and C57BL6/J TCRβ−/− mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. C57BL6/J Wnt10b−/− mice26 were provided by Dr Timothy Lane (University of California, Los Angeles, CA). All mice were maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions and fed sterilized food and autoclaved water ad libitum.
In vivo PTH treatment
Mice at 6 weeks of age were injected with 80 μg/kg per day of human PTH(1-34; Bachem California) or vehicle daily subcutaneously for 4 weeks as described.23
T-cell transfer
WT spleen T cells purified by negative immunoselection using MACS Pan T cell isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec) were injected (5 × 106 cells per mouse) intravenously into TCRβ−/− recipient mice 3 weeks before treatment. Successful T-cell engraftment was confirmed by flow cytometry of the spleens of the recipient mice harvested at death.
SC purification
Flow cytometry and cell sorting
Methods and reagents are described in supplemental Methods.
Real-time RT-PCR and primers
Assays were carried out as previously described.27 Primers are provided in supplemental Methods.
Transplantation experiments
BM cells (2.5 × 105) were suspended in PBS and transplanted by tail vein injection into lethally irradiated recipients. Before transplantation, recipients received 1300 cGy total body irradiation (137Cs source) as a split dose with 3 hours between doses. Mice were housed in sterilized microisolator cages and received sterilized chow and autoclaved water (pH 3.0). Recipient mice were killed at 8 weeks after transplantation, and the reconstitution in spleen, blood, and BM was analyzed by flow cytometry using the lineage markers B220, CD11b, Gr-1, and CD3.
For competitive transplantation assays, mice expressing the marker CD45.2 were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. BM cells (2.5 × 105) from treated C57Bl/6, TCRβ−/−, T cell reconstituted TCRβ−/−, and Wnt10b−/− mice were mixed with BMCs (5 × 105) from B6.SJL mice expressing the marker CD45.1 to obtain 1:2 competition and intravenously injected in CD45.1-expressing recipient mice. Recipient mice (8-10 weeks old) were lethally irradiated as described in this section. Repopulation was evaluated at the times indicated after transplantation in peripheral blood by flow cytometry using the hemopoietic makers CD45.1, CD45.2, CD11b, B220, Gr-1, and CD3. The primary recipients were killed 36 weeks after transplantation, and the BMCs were analyzed for the population of LSK cells and used for secondary transplantation.
For secondary transplantation, BM cells from primary recipients were mixed with BM cells from a competitor animal expressing the marker CD45.1 at a ratio of 1:2. A total of 7.5 × 105 cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1-expressing secondary recipients. Peripheral blood from the secondary recipients was analyzed at the times indicated after transplantation by flow cytometry using the hemopoietic makers as previously described. The secondary recipients were killed after 12 weeks transplantation and the reconstitution in spleen and BM was analyzed.
Statistical analysis
All values are expressed as mean ± SEM. The Mantel-Cox log-rank test was used for survival data. For all other comparisons, a 2-way ANOVA or an ANOVA for repeated measures was applied as appropriate. Additional information is provided in supplemental Methods.
Results
In vivo iPTH treatment expands ST-HSPC/MPPs through T cells
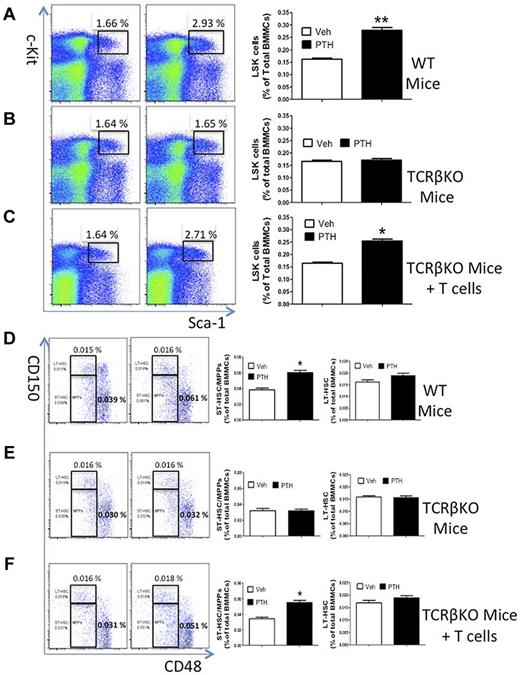
In vivo PTH treatment is known to increase the Lin−Sca-1+c-kit+ (LSK) population of hemopoietic progenitors.2 To determine whether T lymphocytes are required for intermittent PTH to exert its effects on HSPCs, 6-week-old wild-type (WT) and congenic TCRβ−/− mice, a strain completely devoid of αβ T cells, were injected daily with vehicle or 80 μg/kg of hPTH 1-34 for 4 weeks, a treatment modality referred to hereafter as iPTH. To control for strain-dependent confounders, the study included TCRβ−/− mice subjected to adoptive transfer of WT T cells 3 weeks before initiation of iPTH treatment, a procedure that is followed by the engraftment and homeostatic expansion of the donor T cells.23,24
Flow cytometric analysis of splenocytes harvested at death from mice subjected to adoptive transfer of T cells confirmed the engraftment and the expansion of adoptively transferred T cells (supplemental Figure 1). Analysis of BM samples revealed that vehicle-treated WT mice, TCRβ−/− mice, and TCRβ−/− mice reconstituted with T cells had a similar number of BM mononucleated cells and LSK cells (supplemental Figure 2) and a similar relative frequency of LSK cells (Figure 1A-C). Treatment by iPTH caused an ∼ 2-fold increase in the relative number LSK cells of WT and reconstituted TCRβ−/− mice (Figure 1A,C), whereas there was no effect in BM samples from T cell–deficient TCRβ−/− mice (Figure 1B). These findings demonstrate that T cells are required for iPTH to expand the LSK population. Confirming earlier reports,2,28 iPTH had no effects on more differentiated lineages of the peripheral blood (supplemental Figure 3). The LSK compartment of the BM contains at least 3 populations of cells with multilineage potential but progressively limited self-renewal. These populations include LT-HSPCs, ST-HSPCs, and multipotent progenitors (MPPs). LT-HSPCs are CD150+CD48−, while ST-HSPCs/MPPs are CD150−CD48−.29,30 We found that in vivo iPTH treatment increased the frequency of ST-HSPC/MPPs in BM samples from WT mice and TCRβ−/− mice subjected to adoptive transfer of WT T cells (Figure 1D,F), whereas it had no effects in BM samples from TCRβ−/− mice (Figure 1E). By contrast, iPTH did not increase the frequency of LT-HSPCs in T cell–replete and T cell–deficient mice. Together, these data indicate that iPTH expands HSPCs with limited self-renewal through T cells.
Effect of iPTH treatment on HSPC expansion in T cell-replete and T cell–deficient mice. (A-C) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of LSK cells in WT mice, TCRβKO mice, and TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of T cells. Lin− cells were gated and analyzed for Sca-1 and c-Kit expression using isotype control settings. Left panels: Representative flow cytometric dot plots from 1 mouse per group. Black box represents c-Kit+ Sca-1+ cells. Parent population is Lin−. Data are expressed as percentage of total Lin− cells. Right panels: Mean ± SEM for each group. Data are expressed as percentage of total BM mononucleated cells (BMMCs). (D-F) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of CD150−CD48− LSK cells (ST-HSPCs/MPPs) and CD150+CD48− LSK cells (LT-HSPCs) in WT, TCRKO, and TCRβKO mice previously reconstituted with T cells. Left panels: Representative flow cytometric dot plots from 1 mouse per group using the SLAM receptors CD150 and CD48. Parent population is Lin−Sca1+c-Kit+. Upper boxes represent LT-HSPCs; and lower boxes, ST-HSPCs + MPPS. Right panels: Mean ± SEM for each group. Data are expressed as percentage of BMMCs. n = 10 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group. **P < .01 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Effect of iPTH treatment on HSPC expansion in T cell-replete and T cell–deficient mice. (A-C) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of LSK cells in WT mice, TCRβKO mice, and TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of T cells. Lin− cells were gated and analyzed for Sca-1 and c-Kit expression using isotype control settings. Left panels: Representative flow cytometric dot plots from 1 mouse per group. Black box represents c-Kit+ Sca-1+ cells. Parent population is Lin−. Data are expressed as percentage of total Lin− cells. Right panels: Mean ± SEM for each group. Data are expressed as percentage of total BM mononucleated cells (BMMCs). (D-F) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of CD150−CD48− LSK cells (ST-HSPCs/MPPs) and CD150+CD48− LSK cells (LT-HSPCs) in WT, TCRKO, and TCRβKO mice previously reconstituted with T cells. Left panels: Representative flow cytometric dot plots from 1 mouse per group using the SLAM receptors CD150 and CD48. Parent population is Lin−Sca1+c-Kit+. Upper boxes represent LT-HSPCs; and lower boxes, ST-HSPCs + MPPS. Right panels: Mean ± SEM for each group. Data are expressed as percentage of BMMCs. n = 10 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group. **P < .01 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
iPTH increases short-term, but not long-term, hemopoietic engraftment only in the presence of T cells
To further investigate whether T cells are required for iPTH to expand HSPCs with limited self-renewal, we performed a series of competitive repopulation assays.31 To this end, CD45.2+ WT mice, TCRβ−/− mice, and TCRβ−/− previously reconstituted with WT CD45.2+ T cells were treated with iPTH or vehicle for 4 weeks. BM was then harvested, mixed with BM from untreated CD45.1+ WT mice at a ratio of 1:2 (donor/competitor), and injected into lethally irradiated untreated CD45.1+ recipient mice. To evaluate engraftment, the peripheral blood of recipient mice was analyzed by flow cytometry every 2-4 weeks up to 36 weeks. The peripheral blood of recipient mice that were transplanted with BM from iPTH-treated WT and reconstituted mice demonstrated greater reconstitution in the myeloid (CD11b+), granulocytic (Gr-1+), and B cell (B220+) compartment at 4 weeks after transplantation, compared with recipients transplanted with BM from corresponding vehicle-treated donors (Figure 2A-B). However, the engraftment advantage conferred by iPTH treatment was no longer evident at week 8 after transplantation for the myeloid and granulocytic lineages (Figure 2C), and at 12 weeks after transplantation for the B-cell lineage (Figure 2D). By contrast, recipient mice that were transplanted with BM from iPTH-treated TCRβ−/− mice did not demonstrate greater reconstitution in any lineage at all time points (Figure 2A,F). These findings demonstrate that T cells are required for iPTH to expand ST-HSPCs.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment on peripheral blood cell expansion. (A-F) After primary competitive repopulation. (H) After secondary competitive repopulation. (A-F) Percentage of CD45.2+ myeloid cells (CD11b+), granulocytic cells (GR-1+), and B lineage cells (B220+) in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice that received CD45.2+ BM donor cells mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells. CD45.2+ BM cells were obtained from WT, TCRβKO, and reconstituted TCRβKO mice treated with iPTH or vehicle for 4 weeks. CD45.1+ BM cells were obtained from untreated WT mice. (G) Relative frequency of donor-derived CD45.2+LSK cells in the BM of primary recipients at death. (H) Percentage of donor-derived CD45.2+ cells in the peripheral blood of secondary recipients 10 weeks after transplantation. In these experiments, CD45.1/CD45.2 BM cells were obtained from primary recipients at death, mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice, and transplanted into CD45.1+ untreated WT recipients. n = 10 donor and 10 recipient mice per group *P < .05 compared with the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment on peripheral blood cell expansion. (A-F) After primary competitive repopulation. (H) After secondary competitive repopulation. (A-F) Percentage of CD45.2+ myeloid cells (CD11b+), granulocytic cells (GR-1+), and B lineage cells (B220+) in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice that received CD45.2+ BM donor cells mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells. CD45.2+ BM cells were obtained from WT, TCRβKO, and reconstituted TCRβKO mice treated with iPTH or vehicle for 4 weeks. CD45.1+ BM cells were obtained from untreated WT mice. (G) Relative frequency of donor-derived CD45.2+LSK cells in the BM of primary recipients at death. (H) Percentage of donor-derived CD45.2+ cells in the peripheral blood of secondary recipients 10 weeks after transplantation. In these experiments, CD45.1/CD45.2 BM cells were obtained from primary recipients at death, mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice, and transplanted into CD45.1+ untreated WT recipients. n = 10 donor and 10 recipient mice per group *P < .05 compared with the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Stimuli that lead to the expansion of the ST-HSPC pool may cause depletion of the LT-HSPC pool.32 To investigate whether iPTH depletes LT-HSPCs, secondary transplantations were performed 36 weeks after the primary transplantation. At this time point after transplantation, the relative frequency of donor-derived LSK cells (CD45.2+ LSKs) in the BM of primary recipients was the same in mice that received BM from vehicle or iPTH-treated donors (Figure 2G).
Engraftment in the secondary recipients was measured at 10 weeks, a time point when iPTH no longer induced engraftment superiority in the primary recipients. We found that the peripheral blood of secondary recipients that were transplanted with BM derived from iPTH-treated mice demonstrated equal reconstitution all compartment, compared with recipients transplanted with BM from vehicle-treated donors (Figure 2H). These findings indicate that the accelerated short-term engraftment induced by iPTH did not hamper long-term repopulation.
iPTH improves survival after BM transplantation in the presence but not in the absence of T cells
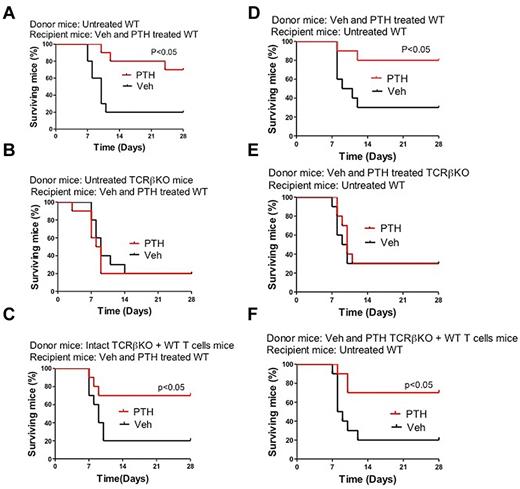
To determine whether the effects of iPTH on HSPCs might be relevant in a clinical setting, we assessed the effect of iPTH on the survival of mice undergoing myeloablative BM transplantation using a limiting number of donor cells derived from T cell–replete and T cell–null mice. Thus, 8-week-old WT mice were lethally irradiated and transplanted with BM cells harvested from WT mice, TCRβ−/− mice, and TCRβ−/− mice subjected to adoptive transfer of WT T cells 3 weeks earlier. In a first experiment, donor mice were left untreated whereas recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks starting the day of the BM transplantation (Figure 3A-C). In a second experiment, donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for the 4 weeks before the BM harvest, whereas recipient mice were left untreated (Figure 3D-F). In both experiments, survival at 4 weeks of mice treated with vehicle was ∼ 20% regardless of whether the donors were T cell–replete or T cell–deficient. Treatment with iPTH of either donor mice or recipient mice increased by ∼ 3-fold the survival at 4 weeks of recipients transplanted with T cell–replete BM. By contrast, PTH had no effect on the survival of mice transplanted with BM from T cell–null mice. Thus, in a setting of therapeutic need, iPTH affects HSPC expansion only in the presence of T cells.
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from WT mice, TCRβKO mice, and TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of T cells. (A-C) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (D-F) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10 in each group.
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from WT mice, TCRβKO mice, and TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of T cells. (A-C) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (D-F) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10 in each group.
Analysis of BM at 28 days revealed that the increase in survival induced by iPTH was mirrored by an increase in the relative frequency of LSKs in the BM of recipient mice (supplemental Figure 4).
PPR signaling in T cells is required for iPTH to expand HSPCs and increase survival after BM transplantation
To determine whether this stimulatory effect of PTH on HSPCs is the result of direct PPR signaling in T cells, we made use of PPRT cells−/− mice, a strain with a silent PPR in all T cells.24,25 These mice were generated by crossing C57BL/6 mice harboring a PPR allele with floxed exon E1 (PPRfl/fl) developed by Kobayashi et al33 with C57BL/6 Lck-Cre transgenic mice, a strain that expresses the Cre recombinase in the early stages (DN2-DN3) of thymocyte development.34 Thus, in the PPRT cells−/− mouse, the PPR gene is silenced in T-cell precursors and mature αβ and γδ T cells. PPRT cells−/− mice have a normal number of T cells that exhibit a degree of activation and proliferation similar to control T cells.24 PPRT cells−/− and control mice also have a similar number of B cells and myeloid cells.25
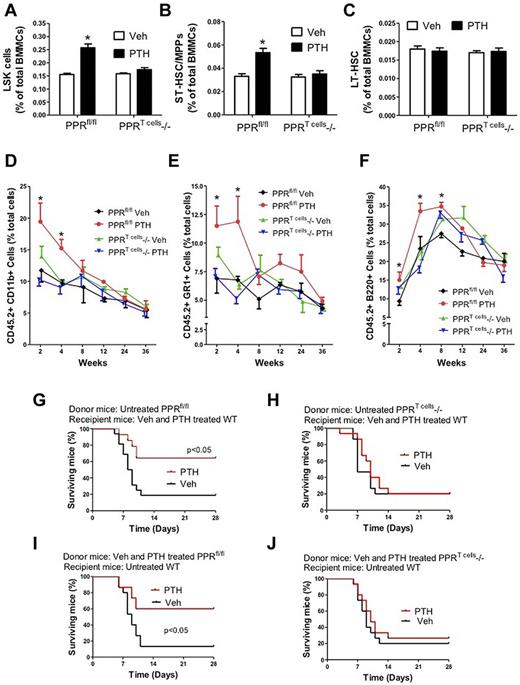
In a first experiment, 6-week-old female PPRT cells−/− and control PPRfl/fl mice were treated with iPTH for 4 weeks. BM analysis revealed that iPTH increased by ∼ 2-fold the frequency of LSK cells in the BM of control mice, whereas it had no effect in samples from PPRT cells−/− mice (Figure 4A). Similarly, analysis of the SLAM markers CD150 and CD48 revealed that iPTH expands ST-HSPCs/MPPs in control mice but not in PPRT cells−/− mice (Figure 4B). Moreover, iPTH did not increase the frequency of LT-HSPCs in control and PPRT cells−/− mice (Figure 4C). Together, these findings demonstrate that direct activation of the PPR receptor in T cells is required for iPTH to expand HSPCs that have limited self-renewal capacity.
Analysis of the effects (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment in PPRT cells−/− and control mice of 6 weeks of age. (A) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of BM LSK cells. (B-C) Effect of iPTH on the relative frequency of ST-HSPCs/MPP and LT-HSPCs. (D-F) Effect of iPTH on peripheral blood cell expansion after primary competitive repopulation. The percentages of CD11b+, GR-1+, and B220+ cells in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice are shown. Recipient mice received CD45.2+ BM donor cells from control or PPRT cells−/− mice (treated with vehicle or iPTH) mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice. (G-J) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from PPRT cells−/− and control (PPRfl/fl) mice. (G-H) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (I-J) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10-15 in each group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Analysis of the effects (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment in PPRT cells−/− and control mice of 6 weeks of age. (A) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of BM LSK cells. (B-C) Effect of iPTH on the relative frequency of ST-HSPCs/MPP and LT-HSPCs. (D-F) Effect of iPTH on peripheral blood cell expansion after primary competitive repopulation. The percentages of CD11b+, GR-1+, and B220+ cells in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice are shown. Recipient mice received CD45.2+ BM donor cells from control or PPRT cells−/− mice (treated with vehicle or iPTH) mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice. (G-J) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from PPRT cells−/− and control (PPRfl/fl) mice. (G-H) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (I-J) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10-15 in each group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
To confirm that PPR signaling in T cells is required for iPTH to improve short-term repopulation, we conducted a second set of competitive repopulation experiments. CD45.2 PPRT cells−/− and control PPRfl/fl mice were treated with iPTH or vehicle for 4 weeks. BM was then mixed with BM from untreated CD45.1+ WT mice at a ratio of 1:2 (donor/competitor) and injected into lethally irradiated CD45.1+ recipient mice. To evaluate engraftment, the peripheral blood of recipient mice was analyzed by flow cytometry every 2-4 weeks up to 36 weeks. The peripheral blood of recipient mice that were transplanted with BM from iPTH-treated PPRfl/fl mice demonstrated greater reconstitution in the myeloid (CD11b+) and granulocytic (Gr-1+) compartments at 2 and 4 weeks after transplantation, compared with recipients transplanted with BM from vehicle-treated donors (Figure 4D-E). However, the engraftment advantage conferred by iPTH treatment was no longer evident at week 8 after transplantation. Transplantation of BM from iPTH-treated PPRfl/fl mice increased the engraftment of B220+ cells for 8 weeks (Figure 4F). However, the engraftment superiority conferred by iPTH was no longer statistically significant starting at 12 weeks after transplantation. By contrast, iPTH did not confer engraftment superiority at any time point in mice transplanted with BM from PPRT cells−/− mice, thus demonstrating a requirement for PPR signaling in T cells.
Next, we assessed the effect of iPTH on the survival of mice undergoing myeloablative BM transplantation using donor cells derived from control and PPRT cells−/− mice. In these experiments, 8-week-old WT mice were lethally irradiated and transplanted with BM cells harvested from PPRfl/fl and PPRT cells−/− mice. In one set of experiments, donor mice were left untreated whereas recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks starting the day of the BM transplantation (Figure 4G-H). In a second set of experiments, donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for the 4 weeks before the BM harvest, whereas recipient mice were left untreated (Figure 4I-J). These studies revealed that treatment with iPTH of either donor or recipient mice increased by ∼ 3-fold the survival at 4 weeks of recipients transplanted with control BM. By contrast, PTH had no effect on the survival of mice transplanted with BM from PPRT cells−/− mice. These data demonstrate that direct activation of the PPR receptor in T cells is required for iPTH to affect the function of HSPCs during myeloablative recovery.
T cells regulate HSPCs through Wnt10b
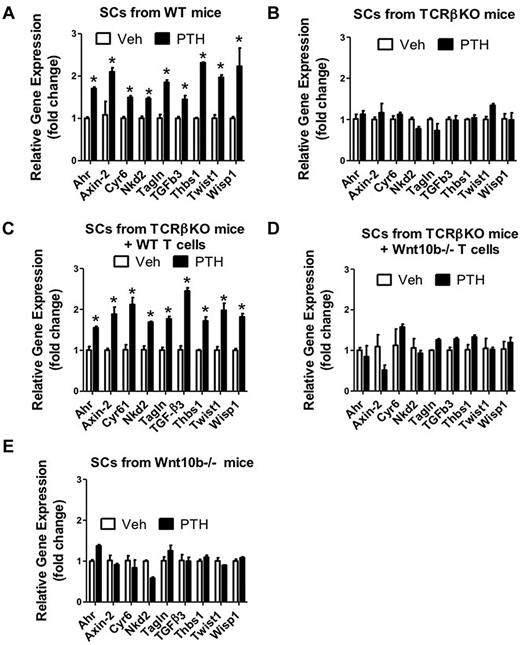
Treatment with iPTH increases the T-cell production of Wnt10b,23,25 whereas activation of Wnt signaling in both SCs and HSPCs promotes HSPC expansion and self-renewal.13-15 Therefore, we sought to investigate whether iPTH activates Wnt signaling in SCs and HSPCs through T cell–produced Wnt10b. In a first set of experiments, we harvested SCs from mice treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks and then analyzed the mRNA expression of genes specifically up-regulated by Wnt signaling. The analyzed genes were chosen, as they are sensitive markers of Wnt activation.35 The analyzed genes were: aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr), Axin, cysteine rich protein 61 (Cyr61), naked cuticle 2 homolog (Nkd2), transgelin (TagIn), transforming growth factor β3 (TGFβ3), thrombospondin 1 (Thbs1), Twist gene homolog 1 (Twist1), and Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (Wisp1). Analysis of purified SCs revealed that the levels of mRNA for the 9 tested genes were all increased by iPTH in SCs from T cell–replete mice and T cell–deficient mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT T cells (Figure 5A,C). By contrast, iPTH did not increase the expression of Wnt-dependent genes in SCs from T cell–deficient (Figure 5B) and Wnt10b null mice (Figure 5E). Attesting to the specific role of T cell–produced Wnt10b, iPTH also failed to up-regulate the expression of Wnt-dependent genes in T cell–deficient mice previously reconstituted with T cells from Wnt10b−/− mice (Figure 5D). Thus, T cells and their production of Wnt10b are required for iPTH to activate Wnt signaling in SCs.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH on the SC expression of mRNA of genes known to be up-regulated by Wnt signaling and Jagged1. BM harvested at death was cultured for 1 week. SCs were purified, and mRNA levels determined by real-time RT-PCR. SCs were obtained from WT mice, TCRβKO mice, TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT or Wnt10b−/− T cells, and Wnt10b−/− mice. (A-E) The Wnt-dependent analyzed genes were aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr), Axin, cystein rich protein 61 (Cyr61), naked cuticle 2 homolog (Nkd2), transgelin (TagIn), transforming growth factor β 3 (TGFβ3), thrombospondin 1 (Thbs1), Twist gene homolog 1 (Twst1), and Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (Wisp1) and Jagged1. n = 5 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH on the SC expression of mRNA of genes known to be up-regulated by Wnt signaling and Jagged1. BM harvested at death was cultured for 1 week. SCs were purified, and mRNA levels determined by real-time RT-PCR. SCs were obtained from WT mice, TCRβKO mice, TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT or Wnt10b−/− T cells, and Wnt10b−/− mice. (A-E) The Wnt-dependent analyzed genes were aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr), Axin, cystein rich protein 61 (Cyr61), naked cuticle 2 homolog (Nkd2), transgelin (TagIn), transforming growth factor β 3 (TGFβ3), thrombospondin 1 (Thbs1), Twist gene homolog 1 (Twst1), and Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (Wisp1) and Jagged1. n = 5 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
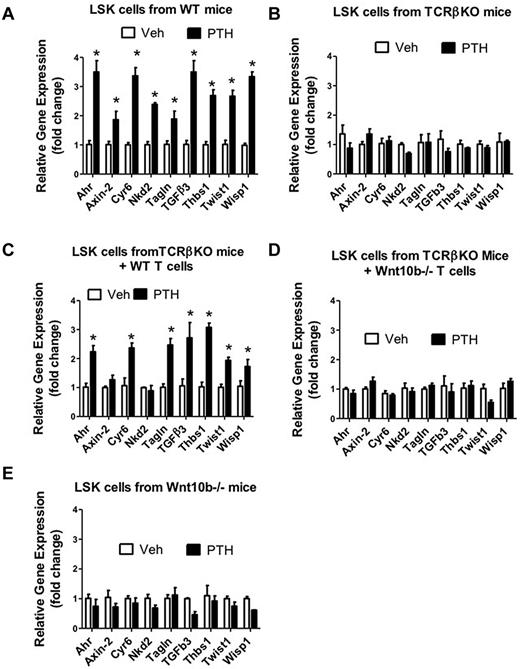
Next, HSPCs were purified by FACS sorting from the BM of mice treated with vehicle and iPTH for 4 weeks and assessed the expression of Wnt-dependent genes. We again found that the levels of mRNA for the 9 tested genes were all increased 2- to 3-fold by iPTH in HSPCs from WT mice (Figure 6A), and T cell–deficient mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT T cells (Figure 6C). By contrast, iPTH did not increase the expression of Wnt-dependent genes in HSPCs from T cell–deficient (Figure 6B), T cell–deficient mice previously reconstituted with T cells from Wnt10b−/− mice (Figure 6D), and Wnt10b null mice (Figure 6E). These data indicate that iPTH up-regulates Wnt signaling in HSPCs through T cell–produced Wnt10b.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH on the LSK cell expression of mRNA of genes known to be up-regulated by Wnt signaling. LSK cells were purified by FACS sorting from the BM of vehicle and iPTH-treated WT mice, TCRβKO mice, TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT or Wnt10b−/− T cells, and Wnt10b−/− mice. The Wnt-dependent analyzed genes were the same as shown in Figure 5. n = 6 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Effect (mean ± SEM) of iPTH on the LSK cell expression of mRNA of genes known to be up-regulated by Wnt signaling. LSK cells were purified by FACS sorting from the BM of vehicle and iPTH-treated WT mice, TCRβKO mice, TCRβKO mice previously subjected to adoptive transfer of WT or Wnt10b−/− T cells, and Wnt10b−/− mice. The Wnt-dependent analyzed genes were the same as shown in Figure 5. n = 6 mice per group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
To further investigate the hypothesis that T cells regulate HSPC expansion through Wnt10b, we assessed the effects of iPTH on the number of LSK cells in WT mice, Wnt10b−/− mice, and TCRβKO mice previously reconstituted with Wnt10b−/− T cells. Analysis by flow cytometry revealed that iPTH increased by ∼ 2-fold the frequency of LSK cells in the BM of WT mice, whereas it had no effect in BM from Wnt10b−/− mice and TCRβKO mice reconstituted with Wnt10b−/− T cells (Figure 7A). Analysis of SLAM markers expression revealed that iPTH expands ST-HSPCs/MPPs in WT mice but not in Wnt10b−/− mice and TCRβKO mice reconstituted with Wnt10b−/− T cells (Figure 7B), thus demonstrating that iPTH expands STHSPCs/MPPs through T cell–produced Wnt10b. As expected, IPTH did not cause the expansion of LT-HSPCs in all mice (Figure 7C). The effects of iPTH on the number of LSK cells, HSPCs/MPPs, and LT-HSPCs in TCRβKO mice reconstituted with WT T cells is shown in Figure 1C and F.
Analysis of the effects (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment in WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. (A) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of BM LSK cells. (B-C) Effect of iPTH on the relative frequency of ST-HSPCs/MPP and LT-HSPCs. (D-F) Effect of iPTH on peripheral blood cell expansion after primary competitive repopulation. The percentages of CD11b+, GR-1+, and B220+ cells in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice are shown. Recipient mice received CD45.2+ BM donor cells from vehicle- and iPTH-treated WT and Wnt10−/− mice mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice. (G-J) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. (G-H) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (I-J) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10 in each group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
Analysis of the effects (mean ± SEM) of iPTH treatment in WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. (A) Effects of iPTH on the relative frequency of BM LSK cells. (B-C) Effect of iPTH on the relative frequency of ST-HSPCs/MPP and LT-HSPCs. (D-F) Effect of iPTH on peripheral blood cell expansion after primary competitive repopulation. The percentages of CD11b+, GR-1+, and B220+ cells in the peripheral blood of untreated WT recipient mice are shown. Recipient mice received CD45.2+ BM donor cells from vehicle- and iPTH-treated WT and Wnt10−/− mice mixed in a 1:2 ratio with CD45.1+ competitor BM cells from untreated WT mice. (G-J) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of WT mice transplanted with limiting number of BM cells derived from WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. (G-H) Donor mice were untreated. Recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. (I-J) Donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks. Recipient mice were untreated. n = 10 in each group. *P < .05 versus the corresponding vehicle-treated group.
To obtain additional confirmation of the specific role of Wnt10b, a constitutively active (ca) form of Wnt10b was expressed in WT BM cells using a retroviral expression vector.36 BM cells expressing caWnt10b were transplanted into lethally irradiated WT recipients. Mock-transduced BM cells were used as controls. Eight weeks after transplantation, Wnt10b mRNA levels were higher in BM cells from mice transplanted with caWnt10b BM compared with those transplanted with control BM (supplemental Figure 5A). Analysis by flow cytometry revealed that mice transplanted with caWnt10b BM cells had ∼ 2-fold higher relative number of LSK cells than mice transplanted with control BM cells (supplemental Figure 5B-C).
Additional competitive repopulation assays were then conducted using WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. CD45.2+ WT mice and Wnt10b−/− mice were treated with iPTH or vehicle for 4 weeks. Their BM was then mixed with BM from untreated CD45.1+ WT mice at a ratio of 1:2 and injected into lethally irradiated CD45.1+ host mice. Analysis of host peripheral blood at 2-24 weeks revealed an increase in the engraftment of cells from iPTH-treated WT mice at weeks 2 and 4, compared with cells from vehicle-treated WT mice (Figure 7D-F). By contrast, iPTH did not increase the engraftment of cells from Wnt10b−/− mice at any time point, thus demonstrating that Wnt10b is required for iPTH to expand ST-HSPCs.
To assess the relevance Wnt10b dependent expansion of HSPCs, we assessed the effect of PTH on the survival of lethally irradiated mice after transplantation of BM derived from WT and Wnt10b−/− mice. In a first experiment, donor mice were left untreated whereas recipient mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for 4 weeks starting the day of the BM transplantation (Figure 7G-H). In a second set of experiments, donor mice were treated with vehicle or iPTH for the 4 weeks before the BM harvest, whereas recipient mice were left untreated (Figure 7I-J). These studies revealed that treatment with iPTH of either donor or recipient mice increased by ∼ 3-fold the survival at 4 weeks of recipients transplanted with WT BM. By contrast, PTH had no effect on the survival of mice transplanted with BM from Wnt10b−/− mice. Thus, T cells and Wnt10b are required for iPTH to activate Wnt signaling in HSPCs and increase survival after BM transplantation.
T cell-independent mechanisms have been proposed by others to explain the effects of iPTH on HSPCs. Increased expression of Jagged1 by SCs was the first such mechanism to be identified.2 To determine whether T cells participate in this regulatory mechanism, we examined the expression of Jagged1 mRNA in SCs from various strains of mice treated with vehicle or iPTH. These experiments revealed that iPTH increases by ∼ 4-fold the expression of Jagged1 mRNA in SCs from WT mice and TCRβ−/− previously reconstituted with WT T cells. By contrast, iPTH did not increase Jagged1 expression in SCs from TCRβ−/− mice, TCRβ−/− mice previously reconstituted with Wnt10b−/− T cells, and Wnt10b−/− mice (supplemental Figure 6). These data suggest that T-cell production of Wnt10b is required for iPTH to up-regulate Jagged1 in SCs.
Discussion
We report that iPTH expands ST-HSPCs and improves blood cell engraftment and survival after BM transplantation. The regulatory activity of iPTH on ST-HSPCs requires the presence of T cells and direct PPR signaling in T cells. HSPC expansion resulted from increased production of Wnt10b by T cells, an event leading to activation of Wnt signaling in SCs and HSPCs (supplemental Figure 7). Therefore, T cells are direct targets of PTH that play a pivotal role in the hemopoietic activity of iPTH.
LT-HSPCs are required and sufficient to ensure lifelong hemopoietic reconstitution after complete myeloablation. However, rapid and efficient hemopoietic recovery, which is critical to overcome acute insults, is most efficiently provided by ST-HSPCs because LT-HSPCs are quiescent and have delayed production of mature progeny.37 Using SLAM markers and competitive transplantation assays, we established that iPTH treatment for 4 weeks regulates ST-HSPCs. Whereas the duration of superior engraftment induced by iPTH varied somewhat among lineages, consistent with previous reports,2,4 superior long-term reconstitution was not found in any experiments. These results update the initial report on the action of PTH on the HSPC niche2 and delineate the HSPC subset expanded by PTH action. Moreover, our data demonstrate that T cells are a targetable component of the HSPC niche, a concept supported by a recent report demonstrating that regulatory T cells reside in the proximity of HSPCs and are required for allo-HSPC persistence.38
Confirming an earlier report,4 we also found that iPTH has no negative effects on long-term hemopoietic expansion. Thus, iPTH does not expand ST-HSPCs at the expense of LT-HSPC self-renewal. This finding may reflect a complex effect of iPTH on the niche, leading the niche to restrain the HSPC pool, even when it is stimulated to expand. The data highlight the potential benefit of therapeutic strategies designed to stimulate HSPC expansion indirectly through targeting of the niche. Further studies are needed to resolve whether the stimulatory effect of PTH on the ST-HSPC pool are the results of niche actions on LT-HSPCs, which are stimulated to undergo asymmetric cell division, or whether ST-HSPCs are the direct targets of Wnt action.
A previously unreported finding of our study is that direct, ligand-dependent activation of PPR signaling in T cells and the resulting production of Wnt10b are required for iPTH to expand HSPCs. This conclusion is supported by the observation that deletion of T cells or silencing of PPR signaling in T cells blocks the expansion of HSPCs induced by iPTH. Attesting to the translational relevance of these observations, we found that the lack of T cells, or of PPR signaling in T cells, prevents iPTH treatment from increasing the survival of lethally irradiated mice subjected to BM transplantation.
Although direct, Wnt10b-independent effects of T cells on HSPCs cannot be excluded, our data point to a pivotal mechanistic role of T cell–produced Wnt10b as mediator of the effects of iPTH in HSPCs. The relevance of Wnt10b was demonstrated by the novel findings that iPTH fails to activate Wnt signaling in SCs and HSCs and expand ST-HSPC in mice specifically lacking T-cell production of Wnt10b. Another relevant finding of this study is that iPTH does not improve survival after BM transplantation in Wnt10b−/− mice. Previous reports from our laboratory had disclosed that treatment with iPTH induces a blunted bone anabolic response in mice with a global25 and a T cell–specific deletion of Wnt10b production.23 Therefore, the findings of the current study together with earlier reports from our laboratory23,25 demonstrate that Wnt10b is a central common mediator of the effects of iPTH on HSPCs and bone. However, it should be underscored that not all of the effects of PTH are mediated by T cells and Wnt10b. Indeed, T cell–deficient mice not only display a significant residual bone response to iPTH but also possess a normal renal response to PTH.22
Our results are in keeping with those of earlier studies on the role of Wnt signaling in HSPC biology. Studies in models of hemopoietic regeneration have revealed not only that the production of Wnt10b by hemopoietic cells and SCs is strongly up-regulated in conditions of hematopoietic recovery,39 but also that Wnt10b directly induces HSPC expansion.39 Moreover, It is well established that canonical Wnt signaling regulates HSPC expansion.13-15 However, until recently, there has been significant controversy as gain- and loss-of-function studies led to the conclusion that activation of Wnt signaling enhances or depletes the HSPC pool according to the experimental strategy.13,15,40-43 A recent report has however disclosed that canonical Wnt signaling regulates hematopoiesis in a dose-dependent fashion.44 Accordingly, a mild increase in Wnt signaling activation in HSPCs results in HSPC expansion, wheresa a marked increase in Wnt signaling impairs HSPC self-renewal.44 In accordance with these observations, we found that the increased production of Wnt10b by T cells resulted in a moderate (∼ 2- to 3-fold) stimulation of Wnt signaling in HSPCs. However, our study did not formally demonstrate a causal relationship between Wnt activation and ST-HSPC expansion.
T cell–independent mechanisms have been previously identified which explain the effects of iPTH on HSPCs. Among them is a stimulatory effect of PTH on Notch signaling. It is well established that activation of Notch signaling in HSPCs results in increased generation of HSPCs in vitro and in vivo45 and stimulated HSPC self-renewal. In addition, stimulation of HSPCs by the notch ligand Jagged1 increases HSPC engraftment in vivo.46 Jagged1 is expressed by SCs and OBs,46 and PTH increases its surface levels.2,12 Up-regulation of Jagged1 expression in bone cells was indeed the first reported mechanism by which PTH regulates HSPCs.2 Notch signaling has been observed to intersect Wnt signaling in HSPCs and SCs. Notch signaling must indeed be intact in HSPCs for Wnt proteins to enhance HSPC self-renewal.47 Moreover, Wnt ligand-induced activation of Wnt signaling in SCs is followed by up-regulation of Notch ligand expression by SCs and activation of Notch signaling in HSPCs in contact with the Wnt-activated SCs.10 A finding of the current study is that T-cell production of Wnt10b is required for iPTH to up-regulate the expression of Jagged1 in SCs. Therefore, iPTH up-regulates Jagged 1 expression in SCs via a stimulatory effect on the production of Wnt10b by T cells. However, direct stimulation of osteoblastic Jagged1 by PTH or constitutive activation of PPR signaling in OBs has been reported.2,9 These findings are not in contrast with the results of the current study because activation of PPR signaling in OBs is likely to stimulate osteoblastic production of Wnt10b via a cAMP-dependent mechanism.48 Therefore, it is likely that activation of PPR signaling in both osteoblastic cells and T cells contributes to the local increase in Jagged1 in response to iPTH.
Another mechanism by which some PTH treatment modalities may regulate HSPCs is via increased production of IL-6, a hemopoietic cytokine that, in concert with fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand, limits HSPC apoptosis.28 It is possible that this regulatory mechanism might be also linked to T cells because PTH increases T-cell production of soluble IL-6 receptor.49 Because whether HSPC express membrane bound IL-6 receptor or secrete soluble IL-6 receptor remains to be determined, the production of soluble IL-6 receptor by BM T cells may be required for IL-6 to affect HSPCs.
In conclusion, our findings provide a new insight into the signaling integration between cells of the immune system, bone cells, and HSPCs, and the impact of such cellular interaction on hematopoiesis. Understanding the PPR signaling in T cells may therefore yield novel therapeutic strategies for hematologic disorders and BM transplantation.
There is an Inside Blood commentary in this article in this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Edmund K. Walker (Emory University and the Winship Cancer Institute) for his comments and suggestions.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants DK091780, AR54625, and AR49659). M.N.W. was supported by the Biomedical Laboratory Research & Development Service of the Veterans Administration Office of Research and Development (5I01BX000105), National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (AR059364; AR056090 and AR053607), National Institute on Aging (AG040013), and the Georgia Research Alliance.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: J.-Y.L. designed and performed research and analyzed data; J.A. performed research; L.M.C. wrote the paper and designed research; T.F.L. provided mice and wrote the paper; R.D.P. performed research and wrote the paper; and M.N.W. and R.P. designed research and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Roberto Pacifici, Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Lipids, Emory University School of Medicine, 101 Woodruff Cir, Rm 1309, Atlanta, GA 30322; e-mail: roberto.pacifici@emory.edu.