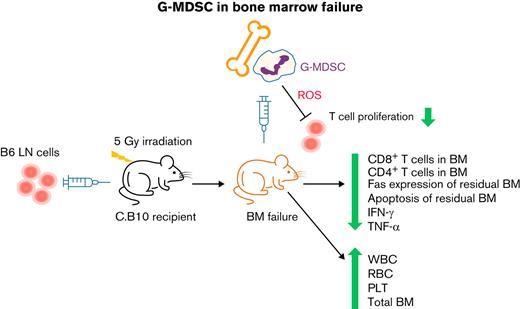
Key Points
Granulocytic MDSCs attenuate immune marrow failure in a minor histocompatibility antigen mismatched murine model.
T-cell inhibition and hematopoietic cell preservation are key mechanisms of granulocytic MDSC therapy.
Abstract
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are immature myeloid cells that originate in the bone marrow (BM) and have immunoregulatory functions. MDSCs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases but have not been investigated in immune aplastic anemia (AA). We examined the roles of granulocytic-MDSCs (G-MDSCs) in murine models of human AA and BM failure (BMF). As both prophylaxis and therapy, BM-derived G-MDSCs improved pancytopenia and BM cellularity and suppressed BM T-cell infiltration in major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-matched C.B10 BMF mice. These effects were not obtained in the MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 AA model, likely because of MHC disparity between G-MDSCs and donor T cells. Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrated that G-MDSCs downregulated cell cycle–related genes in BM-infiltrated T cells, consistent with suppression of T-cell proliferation by G-MDSCs through reactive oxygen species pathways. Clearance of G-MDSCs in the MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 model using anti-Ly6G antibody facilitated T cell–mediated BM destruction, suggesting an intrinsic immunosuppressive property of G-MDSCs. However, the same anti-Ly6G antibody in the MHC-matched C.B10 AA model mildly mitigated BMF, associated with expansion of an intermediate Ly6G population. Our results demonstrate that G-MDSC eradication and therapeutic efficacy are immune context-dependent.
Introduction
Aplastic anemia (AA) is the stereotypical bone marrow failure (BMF) syndrome, featuring characteristic marrow hypocellularity and peripheral blood pancytopenia.1 A significant role of immune dysfunction in AA pathology is inferred from many clinic observations of hematologic recovery following immunosuppressive therapy (IST),2-5 as well as from animal models of AA in which infusion of allogeneic lymphocytes incites massive T-cell expansion and leads to marrow destruction.6-9
Although it is generally believed that myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are immature cells derived from myeloid progenitors, recent studies provide evidence that mature neutrophils may also transform to MDSCs when stimulated by specific cytokines.10,11 MDSCs are categorized based on their monocytic (M-MDSC) and granulocytic (G-MDSC) origins.12-14 In mice, these 2 MDSC subsets differ in cell surface markers, with CD11b+Ly6ChighLy6G− for M-MDSCs and CD11b+Ly6ClowLy6G+ for G-MDSCs, as well as in functional activities and interactions with other cellular components.14 The pathophysiologic role of MDSCs is illustrated in the tumor microenvironment, where MDSCs accumulate and suppress host immune function, allowing cancer cell growth and metastasis.15-18 In addition, MDSCs play important roles in autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes,19,20 arthritis,21,22 experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE),23-27 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),28-31 and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).11,32-36 Because of the autoimmune pathophysiology of AA and the immunosuppressive property of MDSCs, we reasoned that MDSCs might be involved in the pathophysiology of AA and potentially be a cell therapy, as they have in other autoimmune diseases such as EAE, IBD, and GVHD. We focused on G-MDSCs in our murine models, which are more consistently described as having immunosuppressive functions, whereas M-MDSCs have been reported to have conflicting roles in autoimmunity.23,24,37
Materials and methods
Animals and induction of AA and BMF
Inbred C57BL/6 (B6) and BALB/cBy (BALB), congenic C.B10-H2b/LilMcd (C.B10), and hybrid (BALB/cBy × C57BL/6)F1 (CByB6F1) mice were from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Mice were bred and maintained in National Institutes of Health animal facilities under conditions of standard care and nutrition and were used at 2 to 5 months of age. All animal studies were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Bone marrow failure was induced using previously described methods.8,38 Briefly, inguinal, axillary, and lateral axillary lymph nodes (LNs) were collected from B6 donor mice, homogenized using a mini-tissue grinder (Daigger & Company, Vernon Hills, IL) in RPMI 1640 media, filtered through 90-μM nylon mesh (Small Parts, Miami Lake, FL), and counted by a Vicell counter (Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL). To induce AA, we injected B6 LN cells into sex-matched but minor-histocompatibility (minor-H)–mismatched C.B10 (B6⇒C.B10 LN-cell infusion model, minor H–mismatched AA model) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-mismatched CByB6F1 (B6⇒CByB6F1 LN-cell infusion model, MHC-mismatched AA model) recipients, respectively, at 3 to 5 × 106 cells per recipient through lateral tail vein. All recipients received 5 Gy total body irradiation (TBI) from a Gammacell 40 (K2K 1 × 8; MDS Nordion, Ontario, Canada) 4 to 6 hours before LN cell infusion. Recipient mice were bled and killed at days 7 to 14 after LN infusion to collect tissues for various measurements.
G-MDSC enrichment and administration
BM cells were extracted from tibiae and femurs of B6, C.B10, CByB6F1, and BALB donor mice, incubated with Ly6G microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, Auburn, CA), and passed through a magnetic column to collect Ly6G+ cells, which were confirmed by flow cytometry to contain 94% to 97% cells with the CD11b+Ly6G+Ly6Clow phenotype characteristic for G-MDSCs, and these cells suppressed T-cell proliferation in a dose-dependent fashion in vitro (supplemental Figure 1).
In the minor H–mismatched AA model, G-MDSCs enriched from BM of C.B10 donors were infused into C.B10 recipients at 10 × 106 cells/recipient, at the same time of B6 LN cell infusion (prophylaxis) or at day 3 after B6 LN cell infusion (therapy). In a specific study, we enriched G-MDSCs from male C.B10 donors and infused them into female C.B10 recipients at the same time of LN cell injection from female B6 donors. Recipients were assessed at day 14 after LN cell infusion. In a separate experiment, we induced BM suppression in C.B10 mice with 5Gy TBI without LN infusion, IV injected 10 × 106 G-MDSCs to each mouse and evaluated the mice at 14 days after irradiation.
In the MHC-mismatched AA model, we obtained G-MDSCs from B6, BALB, and CByB6F1 donors and infused 10 × 106 G-MDSCs to each CByB6F1 recipient at the time of B6 LN cell infusion. Recipient mice were assessed at day 14 after LN cell infusion.
Anti-Ly6G antibody treatment
Ultra-LEAF purified rat anti-mouse Ly6G antibody (clone 1A8) were obtained from Biolegend (San Diego, CA) and were diluted in normal saline (Nurse Assist) to 1 mg/mL. In both minor H–mismatched and MHC-mismatched AA models, anti-Ly6G antibody was injected intraperitoneally into C.B10 or CByB6F1 recipients at 500 μg/mouse 1 hour after LN cell infusion. Recipient mice were assessed at days 13 to 14.
Cell counts and flow cytometry
At the end of each experiment, blood was taken from the retro-orbital sinus of each recipient mouse into Eppendorf tubes with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as an anticoagulant. Complete blood counts were performed using an Element HT5 hematology analyzer (Heska Corporation, Loveland, CO) to measure white blood cells (WBCs), neutrophils (NEU), red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin (HGB), and platelets (PLTs). Mice were killed by CO2. BM cells were extracted from tibiae and femurs, filtered through 90-μM nylon mesh, and counted by a Vi-Cell counter (Beckman Coulter, Miami, FL) to estimate the total BM cells per mouse, assuming that 2 tibiae and 2 femurs contain 25% of total BM cells.
Blood and BM cells were stained with specific antibody mixtures for flow cytometry. Monoclonal antibodies for murine CD3 (clone 145-2C11), CD4 (clone GK 1.5), CD8 (clone 53-6.72), CD11b (clone M1/70), CD95 (clone SA367H8), CD178 (clone MFL3), Ly6C (clone HK1.4), Ly6G (clone 1A8), Sca-1 (clone D-7), CD117 (c-Kit, clone 2B8), interferon γ (IFN-γ; clone XMG1.2), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α; clone MP6-XT22), and Ki67 (clone 16A8) were all from Biolegend (San Diego, CA). Antibodies were conjugated to Alexa Fluor 700 (AF-700), fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), phycoerythrin (PE), Percp-Cy5.5, PE-cyanin 5 (PE-Cy5), PE-cyanin 7 (PE-Cy7), allophycocyanin, allophycocyanin-Cy7 (APC-Cy7), pacific blue, brilliant violet 421 (BV421), or brilliant violet 711 (BV711). PE-labeled Annexin V and 7AAD dye were purchased from BD Biosciences (San Diego, CA). Stained cells were acquired using BD FACSCanto II and BD LSRFortessa flow cytometers operated by FACSDiva software (Becton Dickson, San Diego, CA), and flow data were analyzed using FlowJo software.
Histology
Sterna were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, sectioned at 5 μm thickness, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (VitroVivo Biotech LLC, Rockville, MD). Slides were examined under a Zeiss Axioskop2 plus microscope with images captured at ×20 magnification using a Zeiss AxioCam HRC camera (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Jena, Germany).
Cell culture in vitro
T-cell proliferation was measured by carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dye dilution as reported previously.39 In brief, LN cells from B6 mice were first labeled with CSFE dye and stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin at concentrations of 50 ng/mL and 500 μM, respectively, and then were cultured with G-MDSCs or MDSC subsets at different ratios for 5 days at 37°C with 5% CO2 in complete RPMI 1640 medium (Life Technologies) supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 U/mL streptomycin, 292 μg/mL l-glutamine, and 10% fetal bovine serum (Life Technologies). In some experiments, N-acetylcysteine (1 mM; Sigma, St. Louis, MO) or anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (10 μg/mL; BioLegend) was added to LN cell culture. Cells were harvested and stained with CD4 and CD8 antibodies and analyzed for CFSE dye dilution using a BD LSRFortessa flow cytometer.
Total-Seq
BM cells from minor H–mismatched C.B10 AA mice treated with or without G-MDSCs were obtained at 14 days and then barcoded using “TotalSeq C hash-tag” oligonucleotides (Biolegend). Hashtagged samples were pooled and stained with Total-seq antibodies (various cell surface markers conjugated with oligonucleotides, Biolegend) per the manufacturer’s protocol (https://www.biolegend.com/en-us/protocols/totalseq-b-or-c-with-10x-feature-barcoding-technology). Stained cells were encapsulated for single-cell reverse transcription using the Chromium Single-Cell V(D)J Reagent Kit v1.1 (10X Genomics, Pleasanton, CA) as per the manufacturer’s protocol (https://assets.ctfassets.net/an68im79xiti/6se7DVQQ0xSCVYp4eQd4Ld/9b822ceb045ec7b20df633cddfe3021f/CG000208_ChromiumNextGEMSingleCellV_D_J_ReagentKit_v1.1_FeatureBarcodingtechnology_RevD.pdf). Single cell RNA-seq libraries (including 5′ gene expression libraries, V(D)J enriched libraries, and cell surface protein libraries) were pooled and sequenced on an Illumina Novaseq System (Illumina, San Diego, CA) with a customized paired end, single indexing (26/8/0/98-bp) format according to 10X Genomics recommendations. Raw sequencing data were processed with the Cell Ranger Software (Version 6.0.0), using the cellranger multi workflow and mm10 references for gene expression and totalSeq antibody barcode sequences, to generate gene-cell and protein-cell matrices for each sample for further analysis. In total, after removing the cell barcode with <500 genes, 1041 to 3435 and 2845 to 5268 cells were captured from BMF control mice and G-MDSC–treated mice, respectively, with 6609 and 6592 mean reads per cell and 1215 medium genes detected per cell. Genes with at least 1 unique molecular identifier count detected in at least 1 cell were used (filtering data). The top 1000 most variable genes were identified based on their mean and dispersion (variance/mean). Thirty-nine graph-based clusters of cells were visualized by 2-dimensional t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) in Seurat4 (resolution 2). In each cluster, the mean expression of each gene was calculated across all cells to identify genes that were enriched in a specific cluster. Each gene from the cluster was compared with the median expression of the same gene from cells in all other clusters. We downloaded raw data of GSE122467 and processed data (https://nicheview.shiny.embl.de) for signature gene identification.40 Cell types were assigned to each cluster based on significance in overlap between signature genes and cluster-specific genes, as well as well-established surface markers. FindMarkers function in Seurat were used to identify differentially expressed genes between BMF+G-MDSC mice and BMF control mice. Gene set enrichment analysis was performed to identify enriched gene sets of all genes with differential expression (based on average log fold change). Single cell gene expression data were submitted to National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO accession number GSE193421).
Statistics
Data were analyzed using JMP (SAS Institute) or with GraphPad Prism statistical software with standard variance analyses followed by multiple comparisons. Results are shown as means with standard errors. Statistical significance was declared at P < .05, P < .01, P < .001, and P < .0001 levels.
Results
G-MDSCs suppress T-cell proliferation in vitro
To characterize MDSC subtypes, we collected BM cells from healthy C.B10 mice and identified BM MDSCs by flow cytometry. There were 3 subsets: Ly6G+Ly6Clow, Ly6G+Ly6C−, and Ly6G-Ly6C+ cells. Most Ly6G+Ly6Clow cells were G-MDSCs and about half of Ly6G-Ly6C+ cells were M-MDSCs based on surface marker expression, whereas Ly6G+Ly6C− cells were not MDSCs (Figure 1A). When these cell populations were sorted by flow cytometry and added to stimulated CFSE-labeled T cells from B6 mice, Ly6G+Ly6Clow cells (G-MDSCs) suppressed proliferation of both CD4 and CD8 T cells, but Ly6G+Ly6C− cells had no effect and Ly6G−Ly6C+ cells (M-MDSCs) further stimulated T-cell proliferation compared with T cells alone (Figure 1A). This result confirmed suppression of T-cell proliferation to be specific to G-MDSCs in the Ly6G+Ly6Clow cell subset.
As prophylaxis, G-MDSCs attenuate BMF in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 model. (A) Suppression of T-cell proliferation in vitro by G-MDSCs. BM Ly6G+Ly6Clow (G-MDSCs), Ly6G+Ly6C−, and Ly6G−Ly6C+ cells from C.B10 mice were sorted by flow cytometry and added to CFSE-labeled LN cells from C57BL/6 (B6) mice at 1:1 ratio for 5 days after stimulation by PMA (50 ng/mL) with ionomycin (500 μM). A representative result of duplicate experiments is shown. (B) G-MDSCs as prophylaxis for murine BMF in C.B10 model. Ly6G+ G-MDSCs were isolated from C.B10 donor mice and injected into BMF mice at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cells) in the C.B10 model at the time of LN cell infusion. (C) Mice infused with G-MDSCs (n = 13) had significantly higher WBCs, RBCs, PLTs, and total BM cells, with decreased BM CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration, compared with control BMF mice (n = 10) when animals were analyzed at day 14. (D) Histology of sternal sections showed that G-MDSC administration improved BM cellularity. Images of the sternums are shown at ×20 magnification. Data are displayed as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
As prophylaxis, G-MDSCs attenuate BMF in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 model. (A) Suppression of T-cell proliferation in vitro by G-MDSCs. BM Ly6G+Ly6Clow (G-MDSCs), Ly6G+Ly6C−, and Ly6G−Ly6C+ cells from C.B10 mice were sorted by flow cytometry and added to CFSE-labeled LN cells from C57BL/6 (B6) mice at 1:1 ratio for 5 days after stimulation by PMA (50 ng/mL) with ionomycin (500 μM). A representative result of duplicate experiments is shown. (B) G-MDSCs as prophylaxis for murine BMF in C.B10 model. Ly6G+ G-MDSCs were isolated from C.B10 donor mice and injected into BMF mice at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cells) in the C.B10 model at the time of LN cell infusion. (C) Mice infused with G-MDSCs (n = 13) had significantly higher WBCs, RBCs, PLTs, and total BM cells, with decreased BM CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration, compared with control BMF mice (n = 10) when animals were analyzed at day 14. (D) Histology of sternal sections showed that G-MDSC administration improved BM cellularity. Images of the sternums are shown at ×20 magnification. Data are displayed as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
G-MDSCs from C.B10 donors attenuate BMF in the minor H–mismatched AA model
We then examined the role of G-MDSC in vivo in the minor H–mismatched AA model by injecting LN cells from B6 donors into sublethally irradiated C.B10 recipients. G-MDSCs enriched from the marrow of C.B10 donors were infused into AA mice at the time of LN cell injection as a prophylaxis (Figure 1B). Mice infused with G-MDSCs had much higher WBCs, RBCs, PLTs, and total BM cells, with decreased BM CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration at day 14, compared with BMF controls (Figure 1C). Sternal sections showed that G-MDSC administration improved BM cellularity (Figure 1D). These results indicated an active role of G-MDSCs in protecting BM cell targets from immune-mediated destruction. Furthermore, the preventive effects of G-MDSCs were apparent when donor and recipient differed by sex, as with infusion of G-MDSCs from male C.B10 donors into female recipients in the B6⇒C.B10 LN cell infusion AA model (supplemental Figure 2).
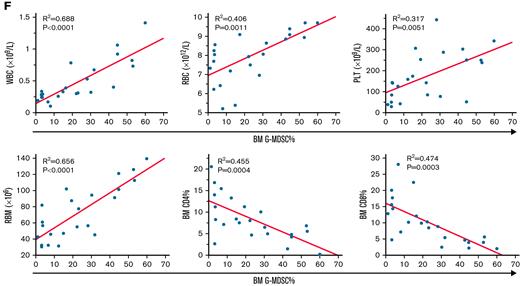
We next examined the therapeutic role of G-MDSCs in immune-mediated BMF by injecting G-MDSCs at day 3 after LN cell infusion in the same minor H–mismatched AA model (Figure 2A). Relative to BMF controls, G-MDSC–treated mice had increased WBCs, RBCs, HGB, PLTs, and total BM cells at day 14 after model initiation, relative to untreated BMF mice (Figure 2B). Thus, G-MDSCs effectively alleviated pancytopenia and BM hypoplasia when administrated as a cell therapy. G-MDSCs also suppressed both CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration into BM (Figure 2C), decreased Fas expression and Annexin V binding of residual BM cells (BM cells excluding T cells; Figure 2D), and suppressed intracellular levels of IFN-γ and TNF-α, and cell proliferation protein Ki67, in BM CD4 and CD8 T cells relative to control BMF mice (Figure 2E). By linear regression, G-MDSCs were positively correlated with WBC, RBC, PLT, and residual BM counts and negatively correlated with BM CD4 and CD8 T-cell frequencies (Figure 2F).
As therapy, G-MDSCs attenuate BMF in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 mice. (A) G-MDSCs were injected at day 3 after LN cell infusion in the C.B10 BMF model. (B) Relative to BMF controls, G-MDSC–treated mice (n = 12) had higher WBCs, RBCs, HGB, PLTs, and total BM cells at day 14 following model initiation relative to untreated BMF mice (n = 9). (C) G-MDSCs decreased CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration of BM. (D) G-MDSCs decreased Fas expression and Annexin V binding of residual BM cells (RBMs). (E) G-MDSCs suppressed intracellular levels of IFN-γ and TNF-α, as well as cell proliferation protein Ki67 in BM CD4 and CD8 T cells relative to BMF control mice. (F) The correlations of BM G-MDSCs with WBC, RBC, and PLT in peripheral blood and RBM, CD4% T cells, and CD8% T cells in the BM were analyzed by linear regression. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
As therapy, G-MDSCs attenuate BMF in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 mice. (A) G-MDSCs were injected at day 3 after LN cell infusion in the C.B10 BMF model. (B) Relative to BMF controls, G-MDSC–treated mice (n = 12) had higher WBCs, RBCs, HGB, PLTs, and total BM cells at day 14 following model initiation relative to untreated BMF mice (n = 9). (C) G-MDSCs decreased CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration of BM. (D) G-MDSCs decreased Fas expression and Annexin V binding of residual BM cells (RBMs). (E) G-MDSCs suppressed intracellular levels of IFN-γ and TNF-α, as well as cell proliferation protein Ki67 in BM CD4 and CD8 T cells relative to BMF control mice. (F) The correlations of BM G-MDSCs with WBC, RBC, and PLT in peripheral blood and RBM, CD4% T cells, and CD8% T cells in the BM were analyzed by linear regression. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
To investigate whether G-MDSCs improved WBC, RBC, PLT, and total BM counts directly rather than by suppressing T cells, we created an irradiation-mediated BM suppression model without LN cell infusion (Figure 3A). In this model, sublethal TBI caused decreased WBCs, NEUs, RBCs, and PLTs relative to normal mice without TBI (Figure 3B). Treatment with G-MDSCs improved WBCs and RBCs slightly, but increased NEUs and PLTs significantly, compared with TBI mice without G-MDSCs (Figure 3B). G-MDSCs treatment slightly increased total BM cells (Figure 3B) and the recovery of CD117+Sca-1+Lin− (KSL) cells (Figure 3C) and significantly increased the proportion and total number of myeloid progenitors (CD117+Scal-1−Lin−; Figure 3C). Thus, G-MDSCs not only suppressed T cell–mediated hematopoietic destruction in immune-mediated BMF but also preserved hematopoietic progenitor cells, especially myeloid progenitors, directly from irradiation-induced hematopoietic injury.
G-MDSCs improves hematopoiesis under irradiation-mediated BM suppression. (A) C.B10 mice were irradiated at 5 Gy (TBI, n = 6), some mice were treated with 10 × 106 C.B10 BM G-MDSCs/mouse IV (TBI+Ly6G cells, n = 9), normal C.B10 mice were included as normal controls (CON, n = 4). (B) Complete blood counts and total BM number were evaluated at 2 weeks after irradiation. (C) Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the BM. Flow cytometry plots were gated from Lin− cells. Frequency and absolute number of KSL (CD117+Sca-1+Lin−) and myeloid progenitor cells (MP, CD117+Sca-1−Lin−) are displayed. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
G-MDSCs improves hematopoiesis under irradiation-mediated BM suppression. (A) C.B10 mice were irradiated at 5 Gy (TBI, n = 6), some mice were treated with 10 × 106 C.B10 BM G-MDSCs/mouse IV (TBI+Ly6G cells, n = 9), normal C.B10 mice were included as normal controls (CON, n = 4). (B) Complete blood counts and total BM number were evaluated at 2 weeks after irradiation. (C) Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the BM. Flow cytometry plots were gated from Lin− cells. Frequency and absolute number of KSL (CD117+Sca-1+Lin−) and myeloid progenitor cells (MP, CD117+Sca-1−Lin−) are displayed. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
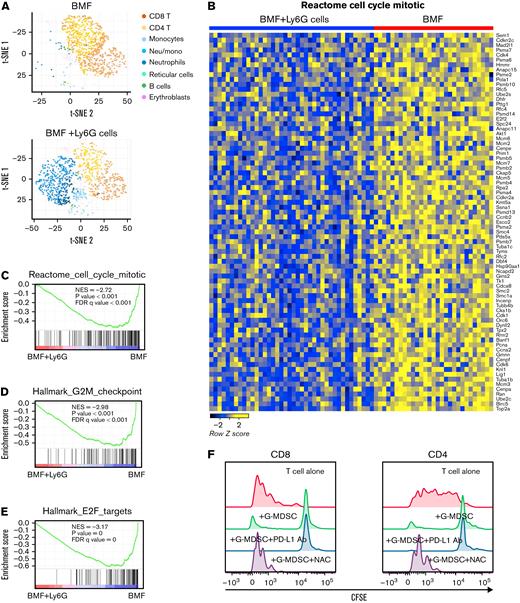
TotalSeq was applied to the therapy model of BMF to simultaneously detect surface proteins and mRNA expression at the single cell level among BM mononuclear cells. We observed increased proportions of myeloid cells and reduced proportions of T cells in BM cells from G-MDSC–treated mice, based on cell surface markers and marker genes (Figure 4A), consistent with flow cytometry results. In the BM infiltrated T-cell population, the most prominent change was decreased expression of genes related to cell cycle (Figure 4B-C), G2M checkpoint (Figure 4D; supplemental Figure 3A), and E2F targets (Figure 4E; supplemental Figure 3B) pathways in BM infiltrated T cells from G-MDSC–treated mice compared with BMF control mice, consistent with suppression of T-cell proliferation by G-MDSCs. Many genes were shared in these pathways (Figure 4B; supplemental Figure 3A-B) including Cdk1, Cdk4, Top2A, Mki67, and Ezh2. Top2A was the most suppressed gene. TOP2A and Ki67 are 2 common markers of cell proliferation.41,42 Of note, reduced gene expression of Mki67 detected by single-cell RNA sequencing (supplemental Figure 3A-B) was consistent with the decreased protein levels of Ki67 by flow cytometry (Figure 2E). Production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species is the main mechanism used by G-MDSCs to suppress T-cell proliferation.43 In our single cell RNA sequencing data, some genes involved in the ROS metabolic process including Arg2, Tspo, Rac1, and Hsp90aa were increased in non-T cells from G-MDSC–treated animal samples, suggesting this mechanism of action. When activated T cells were co-cultured with G-MDSCs in the presence or absence of ROS inhibitor N-acetylcysteine, inhibition of ROS production reversed G-MDSCs’ suppression of T-cell proliferation, whereas checkpoint blockade by PD-L1 antibody had no effect (Figure 4F). Our in vitro assay confirmed the involvement of the ROS pathway in G-MDSC–mediated T-cell suppression.
Surface proteins and mRNA expression at single cell level in whole BM mononuclear cells in therapy model detected by TotalSeq. (A) Increased proportion of myeloid cells and reduced proportion of T cells in the BM cells from G-MDSC–treated mice based on cell surface markers and marker genes of cell populations. (B) Heatmap of enriched genes in cell cycle pathway in BM infiltrated T cells from G-MDSC–treated mice compared with BMF control mice. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of differentially expressed genes in cell cycle (C), G2M checkpoint (D), and E2F targets (E) pathways in BM-infiltrated T cells from G-MSC–treated mice compared with BMF control mice. NES, normalized enrichment score; FDRq, false discovery rate q-value. (F) Involvement of reactive oxygen species pathway in G-MDSC–mediated suppression of T-cell proliferation. BM G-MDSCs obtained from C.B10 mice were added to CFSE-labeled LN cells from C57BL/6 (B6) mice at 2:1 ratio for 5 days after stimulation by PMA with ionomycin. N-acetylcysteine (1 mM) or anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (10 μg/mL) was added to detect the effects of reactive oxygen species inhibition and checkpoint blockade on T-cell proliferation. A representative result of duplicate experiments is shown.
Surface proteins and mRNA expression at single cell level in whole BM mononuclear cells in therapy model detected by TotalSeq. (A) Increased proportion of myeloid cells and reduced proportion of T cells in the BM cells from G-MDSC–treated mice based on cell surface markers and marker genes of cell populations. (B) Heatmap of enriched genes in cell cycle pathway in BM infiltrated T cells from G-MDSC–treated mice compared with BMF control mice. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of differentially expressed genes in cell cycle (C), G2M checkpoint (D), and E2F targets (E) pathways in BM-infiltrated T cells from G-MSC–treated mice compared with BMF control mice. NES, normalized enrichment score; FDRq, false discovery rate q-value. (F) Involvement of reactive oxygen species pathway in G-MDSC–mediated suppression of T-cell proliferation. BM G-MDSCs obtained from C.B10 mice were added to CFSE-labeled LN cells from C57BL/6 (B6) mice at 2:1 ratio for 5 days after stimulation by PMA with ionomycin. N-acetylcysteine (1 mM) or anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (10 μg/mL) was added to detect the effects of reactive oxygen species inhibition and checkpoint blockade on T-cell proliferation. A representative result of duplicate experiments is shown.
Eradication of host G-MDSCs accelerates BMF in the MHC-mismatched AA model
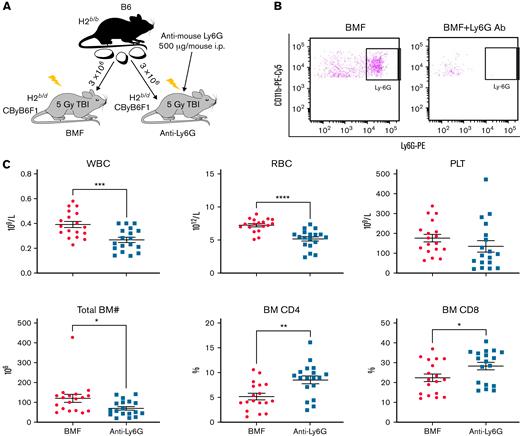
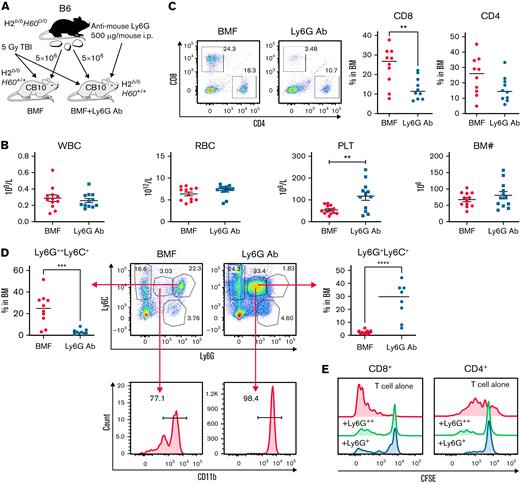
We further investigated the role of G-MDSCs in murine AA and BMF with antibody-mediated cell depletion. In the MHC-mismatched B6⇒CByB6F1 LN cell infusion AA model, recipient mice received intraperitoneal injection of anti-mouse Ly6G antibody to deplete G-MDSCs (Figure 5A). At day 13 after LN infusion, we confirmed by flow cytometry near total clearance of Ly6G+ cells in the BM of antibody-injected animals (Figure 5B). We observed worsened neutropenia, lymphopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and BM hypoplasia along with increased BM CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration in anti-Ly6G antibody-treated BMF mice compared with control BMF mice without antibody injection (Figure 5C). These results indicate that anti-Ly6G antibody facilitated T cell–mediated BM destruction through eradication of G-MDSCs in MHC-mismatched AA mice.
Anti-Ly6G Ab–mediated G-MDSC depletion accelerates BM damage in the MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 AA model. (A) LN cells extracted from B6 donor mice were injected into 5 Gy TBI pretreated CByB6F1 recipients. Some recipients also received intraperitoneal injection of anti-mouse Ly6G antibody at 500 μg/mouse to deplete G-MDSCs. (B) At 2 weeks, clearance of Ly6G+ cells in BM of antibody-injected animals was confirmed by flow cytometry. (C) At this time point, there was worse neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia in peripheral blood and BM hypoplasia in anti-Ly6G antibody–injected BMF mice (n = 18) than in control BMF mice without antibody injection (n = 18), as well as increased CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration in the BM. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
Anti-Ly6G Ab–mediated G-MDSC depletion accelerates BM damage in the MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 AA model. (A) LN cells extracted from B6 donor mice were injected into 5 Gy TBI pretreated CByB6F1 recipients. Some recipients also received intraperitoneal injection of anti-mouse Ly6G antibody at 500 μg/mouse to deplete G-MDSCs. (B) At 2 weeks, clearance of Ly6G+ cells in BM of antibody-injected animals was confirmed by flow cytometry. (C) At this time point, there was worse neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia in peripheral blood and BM hypoplasia in anti-Ly6G antibody–injected BMF mice (n = 18) than in control BMF mice without antibody injection (n = 18), as well as increased CD4 and CD8 T-cell infiltration in the BM. Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
Anti-Ly6G antibody mildly mitigates BMF in minor H–mismatched C.B10 recipients by expansion of an intermediate Ly6G population
We next injected the same 1A8 anti-Ly6G antibody into C.B10 mice in the B6⇒C.B10 LN cell infusion model (Figure 6A). Surprisingly, injection of the antibody improved PLTs and reduced BM CD8 T-cell frequency without change in total BM cell recovery, suggesting a mild protective role of anti-Ly6G antibody in this minor H–mismatched AA model (Figure 6B-C), which contrasted with the destructive effects of anti-Ly6G antibody in the MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 AA model (Figure 5). In these experiments, the discrepancy between the 2 models (MHC-mismatched B6⇒CByB6F1 vs minor H–mismatched B6⇒C.B10) appears to be due to differential G-MDSC modulation following anti-Ly6G antibody injection: in CByB6F1 animals, anti-Ly6G antibody treatment eradicated marrow G-MDSC (Figure 5B), but in the C.B10 model, anti-Ly6G antibody promoted generation of a new population of identical Ly6ClowCD11b+ phenotype, with intermediate Ly6G expression (Figure 6D). This intermediate Ly6G cell population was present in the BM after anti-Ly6G Ab injection in the C.B 10 model but not in the CByB6F1 model. When these intermediate Ly6G+ cells were isolated by microbeads and added to stimulated T cells to assay for immunosuppressive function in vitro, they suppressed the proliferation of both CD4 and CD8 T cells, similar to the Ly6Ghigh population (Figure 6E).
Anti-Ly6G Ab mediates intermediate Ly6G+cell expansion, resulting in mild attenuation of marrow failure in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 AA model. (A) Anti-Ly6G antibody was injected into a minor histocompatibility (minor-H)–mismatched C.B10 BMF model at the time of LN infusion. Anti-Ly6G antibody improved PLTs (B), reduced BM CD8 T-cell frequency (C) with no change in total BM cell recovery. (D) Anti-Ly6G antibody treatment promoted generation of a new Ly6ClowCD11b+ cell population with intermediate Ly6G expression. (E) Ly6G intermediate population showed similar immunosuppressive function as did G-MDSCs from normal control mice. The function assay was duplicated. BMF control group (n = 12), BMF+anti-Ly6G antibody group (n = 12). Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Anti-Ly6G Ab mediates intermediate Ly6G+cell expansion, resulting in mild attenuation of marrow failure in minor histocompatibility–mismatched C.B10 AA model. (A) Anti-Ly6G antibody was injected into a minor histocompatibility (minor-H)–mismatched C.B10 BMF model at the time of LN infusion. Anti-Ly6G antibody improved PLTs (B), reduced BM CD8 T-cell frequency (C) with no change in total BM cell recovery. (D) Anti-Ly6G antibody treatment promoted generation of a new Ly6ClowCD11b+ cell population with intermediate Ly6G expression. (E) Ly6G intermediate population showed similar immunosuppressive function as did G-MDSCs from normal control mice. The function assay was duplicated. BMF control group (n = 12), BMF+anti-Ly6G antibody group (n = 12). Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
G-MDSCs exert mild to no effect on attenuation of marrow failure in the MHC-mismatched AA model
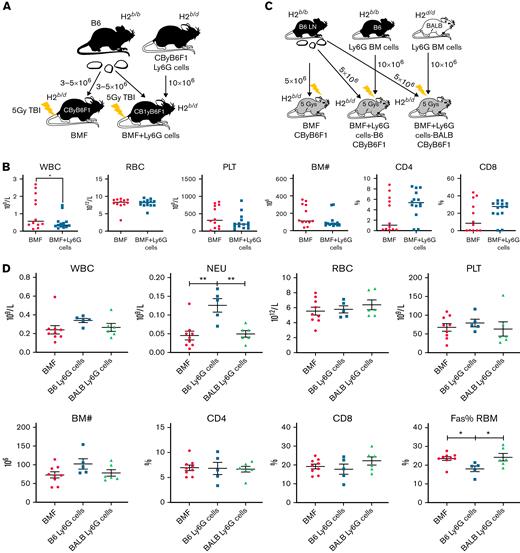
To determine whether the therapeutic efficacy of G-MDSCs in BMF occurred in a different strain combination, we enriched G-MDSCs from CByB6F1 donor mice and infused them into CByB6F1 recipients in the MHC-mismatched B6⇒CByB6F1 AA model at the time of B6 LN injection (Figure 7A). At day 14, G-MDSC–treated mice did not show improvement in pancytopenia or BM cellularity compared with control BMF mice, and BM T-cell infiltration appeared to be increased (Figure 7B). We speculated that failure of G-MDSCs to protect CByB6F1 recipient mice was due to the MHC disparity between B6 LN (H2b/b) and CByB6F1 G-MDSCs (H2b/d), which would stimulate a stronger immune response between host tissue and donor T cells. To test our hypothesis, we isolated G-MDSCs from BM of B6 (H2b/b) and BALB (H2d/d) donors and injected them into CByB6F1 recipient mice at the initiation of BMF (Figure 7C). At day 14, B6-derived G-MDSCs (of the same MHC as B6 LN)-treated mice had higher NEU counts and lower Fas expression in residual BM cells than did the other 2 groups, whereas BALB-derived G-MDSC–treated mice had worse blood counts and more T-cell infiltration in BM (Figure 7D). These results suggest that MHC disparity between G-MDSCs and effector T cells might, at least partly, affect the efficacy of G-MDSC–mediated immunosuppression.
G-MDSCs exert mild to no effect on attenuation of immune-mediated BMF in MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 recipients. (A) G-MDSC treatment of murine BMF in CByB6F1 model. BM G-MDSCs were isolated from CByB6F1 donor mice and were injected to MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 model at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cell) at the time of B6 mice-derived LN cell infusion. (B) G-MDSCs from CByB6F1 donor mice (n = 14) did not improve pancytopenia and BM cellularity compared with control BMF mice (n = 12), even increased T-cell infiltration in BM. (C) BM G-MDSCs were isolated from B6 or BALB donor mice and were injected into MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 model at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cells) at the time of B6-derived LN cell infusion. (D) B6-derived G-MDSCs (MHC-matched with B6 LN, n = 5) showed mild improvement of neutropenia and BM cellularity and decreased Fas expression in residual BM cells (RBM) in CByB6F1 recipient mice at day 14. BALB-derived G-MDSCs (MHC-mismatched with B6 LN, n = 6) did not show any improvement of BMF compared with control mice (n = 9). Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
G-MDSCs exert mild to no effect on attenuation of immune-mediated BMF in MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 recipients. (A) G-MDSC treatment of murine BMF in CByB6F1 model. BM G-MDSCs were isolated from CByB6F1 donor mice and were injected to MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 model at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cell) at the time of B6 mice-derived LN cell infusion. (B) G-MDSCs from CByB6F1 donor mice (n = 14) did not improve pancytopenia and BM cellularity compared with control BMF mice (n = 12), even increased T-cell infiltration in BM. (C) BM G-MDSCs were isolated from B6 or BALB donor mice and were injected into MHC-mismatched CByB6F1 model at 10 × 106 G-MDSCs/mouse (BMF+Ly6G cells) at the time of B6-derived LN cell infusion. (D) B6-derived G-MDSCs (MHC-matched with B6 LN, n = 5) showed mild improvement of neutropenia and BM cellularity and decreased Fas expression in residual BM cells (RBM) in CByB6F1 recipient mice at day 14. BALB-derived G-MDSCs (MHC-mismatched with B6 LN, n = 6) did not show any improvement of BMF compared with control mice (n = 9). Data are shown as means with standard errors. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
Discussion
To our knowledge, ours is the first study exploring G-MDSCs in a well-established murine model of immune-mediated BMF. We observed that G-MDSCs were effective in MHC-matched setting, but less so when MHC mismatched between donor and host animals.
The primary mechanism of T-cell suppression by G-MDSCs is production of ROS and reactive nitrogen species.43 We confirmed that inhibition of ROS reversed the suppressive effects of G-MDSCs on T-cell proliferation. Our single-cell RNA sequencing data demonstrate that G-MDSCs suppressed cell cycle, G2M checkpoint, and E2F pathways in T cells, the consequence of which was the inhibition of T-cell proliferation. Among genes decreased in expression, Cdk1 and Cdk4 are critical in controlling cell cycle and cell proliferation.44 The decreased expression of Top2A and Mki67 at the mRNA level and of Ki67 at protein level confirmed the suppression of T-cell proliferation by G-MDSCs. EZH2 promotes the survival of differentiated effector T cells through inhibition of numerous apoptosis pathways, including FAS, TNFR1, DR4, and MLK1 signaling.45 EZH2-deficient mice have decreased survival after intraperitoneal Toxoplasma gondii infection, associated with decreased IFN-γ–producing CD4+ T cells.46 These observations suggest that EZH2 is important in the generation of T effector cell responses in vivo, and the defects observed in EZH2-deficient mice attributable to decreased proliferation of EZH2 effector T cells. EZH2 was critical for the survival and proliferation of alloantigen reactive T cells and the development of GVHD in a MHC-mismatched B6 anti-BALB/C mouse model; IFN-γ–producing alloreactive T cells were significantly diminished in the absence of EZH2.47
Clearance of G-MDSCs with anti-Ly6G antibody facilitated T cell–mediated BM destruction in CByB6F1 mice in the MHC-mismatched AA model, further evidence of a protective effect of G-MDSCs. Efficient Ly6G+ cell eradication in CByB6F1 mice by 1A8 clone anti-Ly6G antibody is consistent with an early report in B6D2F1 mice, in which the 1A8 clone of anti-Ly6G antibody was introduced as an alternative to the anti–Gr-1 antibody (clone RB6-8C5) for specific depletion of neutrophils while preserving macrophages and other non-neutrophil Gr-1+ cells.48 In the C57BL/6⇒BALB/c allo-HCT transplantation models, however, injection of the same 1A8 anti-Ly6G antibody into BALB/c mice improved animal survival from GVHD responses in multiple experimental settings,32 similar to the observation in our minor H–mismatched AA model, in which anti-Ly6G antibody attenuated BM destruction. The protective effect of anti-Ly6G antibody in the minor H–mismatched setting was not the result of clearance of G-MDSCs but instead expansion of an intermediate Ly6G+ population. Despite differential effects on Ly6G+ cells at the same dose of anti-Ly6G antibody in C.B10 and CByB6F1 mice, observations from both models support a protective role of G-MDSCs, attenuating immune-mediated BMF.
The ineffectiveness of G-MDSCs in the MHC-mismatched AA model agrees with findings from earlier reports: when MDSCs are transferred to recipients of allogeneic donor hematopoietic grafts, they are exposed to the intense inflammatory environment associated with acute GVHD that directly undermines MDSC immunosuppressive activity.33 In another GVHD model, neutrophils in the ileum migrated to mesenteric LN, where they colocalized with T cells and presented antigen on MHC-II.11 In the AA and BMF model, MHC-II is also upregulated and co-localized with Fas on BM hematopoietic cells, which could potentiate apoptotic destruction of marrow targets.49 Although G-MDSC exerted different immunosuppressive activity in the minor H–mismatched and MHC-mismatched BMF models, whether MHC directly interferes with G-MDSC functionality needs further investigation. Of interest, G-MDSCs also acted directly to preserve HSPCs, especially myeloid progenitors, and augmented hematopoietic recovery after irradiation-induced hematopoietic injury. However, such direct action likely is insufficient to overcome MHC disparity in the MHC-mismatched BMF model.
We demonstrate the immunosuppressive role of G-MDSCs in attenuating immune-mediated AA in the MHC-matched C.B10 model, as occurs in other animal models of human autoimmune disease.21,50,51 B6⇒CByB6F1 LN cell infusion is a heterozygous MHC mismatch, in which B6 mice carry the H2b/b allele and CByB6F1 mice the H2b/d allele.7 This mismatch does not exist with B6⇒C.B10 LN cell infusion, as both B6 and C.B10 mice are MHC matched, displaying the same H2b/b allele.8 The immunogenicity of the B6⇒C.B10 LN cell infusion model arises from mismatch at multiple minor H antigens, H60 being dominant.52-55 Immune disparity between B6 and C.B10 mice also involves other minor antigens such as H4, H7, H13, and H28.56 The attenuation of marrow failure by infusion of male G-MDSCs into female C.B10 BMF recipients showed that G-MDSC immunosuppression could overcome Y antigen disparity.
In conclusion, G-MDSCs have an active role in protecting hematopoiesis from T cell mediated destruction when MHC is matched, but not when MHC is mismatched, in murine models of BMF: G-MDSC therapeutic efficacy is immune context-dependent.
Acknowledgments
Cell sorting was performed in the Flow Cytometry Core at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Single-cell sequencing was conducted in the DNA Sequencing Core of the NHLBI.
This study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Intramural Research Program.
Authorship
Contribution: J.C. and X.F. designed the study, performed experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; J.K., G.G.-M., N.A., A.L.M., and S.S. performed the experiments; Z.W., S.G., and S.B. performed single-cell RNAseq and analysis; and N.S.Y. designed the study and edited the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Xingmin Feng, Hematology Branch, NHLBI, National Institutes of Health, NIH Bldg. 10, CRC Rm. 3E-5216, 10 Center Dr., Bethesda, MD 20892; e-mail: fengx2@nhlbi.nih.gov.
References
Author notes
For sequencing data, readers may access dataset GSE193421. Please contact the corresponding author for other data sharing at fengx2@nhlbi.nih.gov.
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.