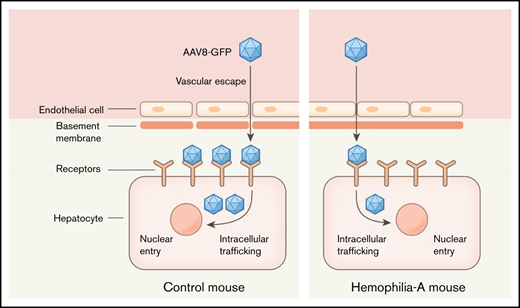
Abstract
Hemophilia A is an inherited bleeding disorder caused by defective or deficient coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) activity. Until recently, the only treatment for prevention of bleeding involved IV administration of FVIII. Gene therapy with adeno-associated vectors (AAVs) has shown some efficacy in patients with hemophilia A. However, limitations persist due to AAV-induced cellular stress, immunogenicity, and reduced durability of gene expression. Herein, we examined the efficacy of liver-directed gene transfer in FVIII knock-out mice by AAV8-GFP. Surprisingly, compared with control mice, FVIII knockout (F8TKO) mice showed significant delay in AAV8-GFP transfer in the liver. We found that the delay in liver-directed gene transfer in F8TKO mice was associated with absence of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (LSEC) fenestration, which led to aberrant expression of several sinusoidal endothelial proteins, causing increased capillarization and decreased permeability of LSECs. This is the first study to link impaired liver-directed gene transfer to liver-endothelium maladaptive structural changes associated with FVIII deficiency in mice.
Key Points
FVIII knockout mice manifest delayed AAV8-mediated gene transduction in the liver.
The delayed liver-directed gene transduction in FVIII knockout mice is associated with loss of sinusoidal endothelial fenestration.
Introduction
Hemophilia A is an X-linked recessive bleeding disorder caused by defective or deficient coagulation factor VIII (FVIII).1,2 Affected individuals are at risk for spontaneous bleeding into joints, which can lead to persistent arthropathy.1,3 Current therapy primarily relies on the administration of exogenous FVIII, which is inconvenient, does not fully prevent breakthrough bleeding, and fosters the development of inhibitor alloantibodies.1 Recent advancements in liver-directed gene transfer suggest that gene therapy can be a potential cure for hemophilia A.4,5 Adeno-associated virus (AAV) -based liver-directed gene therapy is the current approach in hemophilia A,6 and various clinical trials to assess the efficacy and safety of gene therapy in patients are now in progress.4,7,8 The enormous size of the FVIII coding sequence and the suboptimal synthesis of FVIII protein post–gene therapy are 2 persistent challenges of gene therapy approaches.5,9 Moreover, immunogenicity of recombinant FVIII10 and FVIII overexpression eliciting a cellular stress response are other major concerns.11 The FVIII total knockout (F8TKO) mouse is an ideal model for evaluating novel hemophilia A gene therapies.12 AAV-mediated FVIII gene transduction is effective, although with a transient response in F8TKO mice.13 In this study, we evaluated the stability and efficacy of a liver-driven gene transfer approach in F8TKO mice14 using a recombinant AAV8 vector. We used green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a model gene for transduction because of its small size and lack of known adverse effects in the liver. Interestingly, when compared with littermate control mice, liver-directed gene transfer was significantly delayed in F8TKO animals. Remarkably, the delay in liver-directed gene transfer in F8TKO mice was associated with an absence of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (LSEC) fenestration, which can lead to altered expression of major endothelial proteins, causing increased capillarization and decreased permeability of LSECs.
Methods
Animals
FVIII total knockout mice (F8TKO) on C57BL/6J background were a generous gift from Pete Lollar. For these studies, we used F8TKO male mice14 and age-matched unaffected littermate controls, heterozygous females generated by crossing homozygous F8TKO mice with C57BL/6J mice. AAV8–thyroid-binding globulin (TBG)-GFP was obtained from Vector Biolabs. Four-week-old F8TKO male mice were given an intraperitoneal (IP) injection of 1 × 1012 genome copies of AAV8–TBG-GFP. Twelve-week-old F8TKO null mice were given a single intravascular injection of 5 × 1011 genome copies of AAV8–TBG-GFP per mouse. A second line of FVIII-KO, B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J strain and littermate controls were obtained from Jackson Laboratory. Twelve-week-old B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J mice and controls were given a single intravascular injection of 5 × 1011 genome copies of AAV8–TBG-GFP. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee at the University of Pittsburgh.
SEM and transmission electron microscopy
For scanning electron micrography (SEM), whole liver was perfused and fixed in glutaraldehyde. The surgical and perfusion techniques have been described previously.15 Slides were examined with a JEM-1011 transmission electron microscope at 80 kV.
Liver intravital imaging
The surgical procedure has already been published in detail.15 Texas red (TXR)-dextran (200 g) or AF488-anti-CD31 (100 g) was used as intravascular fluorescent dyes. A Nikon MPE-multiphoton excitation microscope was used for microscopy at the Center for Biological Imaging at the University of Pittsburgh.
Statistical analysis
All comparisons between the 2 groups were deemed statistically significant by an unpaired, 2-tailed Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .01). Additional methods used in this study are standard and are described in the supplemental data.
Results and discussion
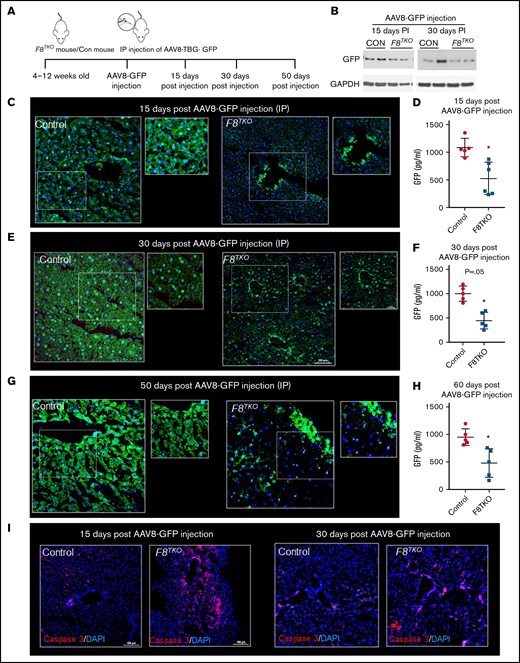
To examine the efficacy, stability, and safety of AAV-mediated liver-directed gene transfer in F8TKO mice, AAV8–TBG-GFP was administered IP, and GFP expression was analyzed in the liver 15 and 30 days postinjection (Figure 1A-B). Previously, we showed that AAV8–TBG-GFP (at a dose of 1 × 1012 genome copies) can successfully transfer to the liver within 10 to 12 days.16 Surprisingly, immunofluorescence (Figure 1C) of GFP at day 15 postinjection revealed significantly fewer GFP+ cells in the liver of F8TKO compared with control mice. Only large hepatic veins contained GFP+ cells in the F8TKO liver (Figure 1C). Whole-liver enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) also indicated that GFP expression in the liver was significantly lower in F8TKO compared with control mice (Figure 1D). Similar to the 15-day timepoint, we identified fewer GFP+ cells in F8TKO liver 30 days postinjection (Figure 1E). On day 30, however, the total percentage of GFP+ cells was higher than on day 15 (Figure 1E-F; supplemental Figure 1A), but it remained significantly lower when compared with control mice. Notably, we still found GFP staining in the large hepatic veins in F8TKO mice that was not present in control liver at day 30 postinjection (Figure 1E). Finally, the reduced GFP expression was confirmed using a Western blot assay, which revealed consistently low GFP protein expression in F8TKO liver compared with controls on days 15 and 30 postinjection (Figure 1B). Consistent with IP injection, IV injection, even at a lower dose, resulted in a similar delay in GFP transduction in F8TKO animals at 8 weeks as seen by both immunofluorescence (Figure 1G), ELISA (Figure 1H), and western blot assays (supplemental Figure 1F). Identical to F8TKO mice, a second strain of FVIII-deficient mice (B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J) exhibited a similar delay in AAV8-GFP transduction compared with control mice at 8 weeks following IV administration of AAV8-GFP (supplemental Figure 1C-E).
AAV8-driven liver-directed gene transfer is significantly delayed in hemophilia A mice. (A) Schematic showing delivery of AAV8–TBG-GFP to hemophilia A (F8TKO) or control (unaffected littermate heterozygous) mouse. (B) Western blot analysis of GFP in control and F8TKO mice after 15- and 30-days post–AAV8-GFP administration (IP). (C) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 15 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IP). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (D) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO at 15 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .04). (E) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 30 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IP). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (F) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO 30 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .06). (G) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 60 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IV). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (H) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO at 60 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .07). (I) Immunofluorescence for caspase-3 showed an increased accumulation in F8TKO mouse liver 15- and 30-days post–AAV8-GFP administration, which was not seen in matched control liver. All control mice used were unaffected littermate heterozygoes mice.
AAV8-driven liver-directed gene transfer is significantly delayed in hemophilia A mice. (A) Schematic showing delivery of AAV8–TBG-GFP to hemophilia A (F8TKO) or control (unaffected littermate heterozygous) mouse. (B) Western blot analysis of GFP in control and F8TKO mice after 15- and 30-days post–AAV8-GFP administration (IP). (C) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 15 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IP). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (D) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO at 15 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .04). (E) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 30 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IP). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (F) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO 30 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .06). (G) Immunofluorescence of GFP staining in control and F8TKO mice 60 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (IV). The dotted regions are zoomed in as inset. (H) ELISA assay of total liver GFP amount in control and F8TKO at 60 days post–AAV8-GFP injection (P = .07). (I) Immunofluorescence for caspase-3 showed an increased accumulation in F8TKO mouse liver 15- and 30-days post–AAV8-GFP administration, which was not seen in matched control liver. All control mice used were unaffected littermate heterozygoes mice.
The recombinant AAV8-vector efficiently transduces target tissues by passing across17 the permeable barrier of endothelial cells.18 We hypothesized that the reduced GFP transduction in F8TKO mice was due to endothelial cell death upon AAV8 administration. Supporting our hypothesis, caspase-3 staining revealed significant enrichment in the liver of F8TKO mice compared with control mice after AAV8-GFP administration at both the 15- and 30-day timepoints (Figure 1I). To further confirm apoptosis of LSECs, we next used liver intravital imaging to visualize LSECs in F8TKO mice at baseline and upon AAV8-GFP administration. TXR-dextran (red) and AF488–anti-CD31 antibody (green) were IV administered to visualize hepatic blood flow and LSECs, respectively. At baseline, both control and F8TKO mice showed normal blood flow and enriched expression of AF488–anti-CD31 (Figure 2A). However, there were fewer AF488–anti-CD31+endothelial cells in F8TKO than control mice at day 15 post–AAV8-GFP treatment (Figure 2A), suggestive of apoptosis of LSECs in F8TKO mice post–AAV8-GFP administration.
F8TKO mice show defenestrated vascularized LSEC with decreased permeability. (A) Liver intravital imaging of control and F8TKO liver at baseline and 15 days post–AAV8-GFP administration injected with TXR-dextran and AF488-anti-CD31. (B) SEM images show LSEC fenestrae are significantly less in a representative F8TKO mouse as compared with a control mouse. (C) SEM images show LSEC fenestrae are significantly less in a representative B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J mouse as compared with a control mouse. (D) Quantification of pore grouping and total number of fenestrae per field of view in the liver of control B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J and F8TKO mice. (E) Heatmap consisting of qRT-PCR analysis of endothelial-specific genes (CD31, VEGF, ICAM1, stabilin2, ID1, Gata4, and Ehd3) in control and F8TKO mice liver. (F) Western blot analysis of VEGF and CD31 in control and F8TKO mice at baseline. Immunofluorescence for PECAM (G) and LYVE-1 (H) showed an increased accumulation in F8TKO mouse liver tissue at baseline, which was not seen in age-matched control liver. All control mice used were unaffected littermate heterozygoes mice.
F8TKO mice show defenestrated vascularized LSEC with decreased permeability. (A) Liver intravital imaging of control and F8TKO liver at baseline and 15 days post–AAV8-GFP administration injected with TXR-dextran and AF488-anti-CD31. (B) SEM images show LSEC fenestrae are significantly less in a representative F8TKO mouse as compared with a control mouse. (C) SEM images show LSEC fenestrae are significantly less in a representative B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J mouse as compared with a control mouse. (D) Quantification of pore grouping and total number of fenestrae per field of view in the liver of control B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J and F8TKO mice. (E) Heatmap consisting of qRT-PCR analysis of endothelial-specific genes (CD31, VEGF, ICAM1, stabilin2, ID1, Gata4, and Ehd3) in control and F8TKO mice liver. (F) Western blot analysis of VEGF and CD31 in control and F8TKO mice at baseline. Immunofluorescence for PECAM (G) and LYVE-1 (H) showed an increased accumulation in F8TKO mouse liver tissue at baseline, which was not seen in age-matched control liver. All control mice used were unaffected littermate heterozygoes mice.
We hypothesized that the reduced GFP transduction and increased apoptosis of LSECs in F8TKO mice were caused by endogenous endothelial structural changes that prevented molecule passage to the liver.19 To gain access to the liver parenchyma, liver-directed molecules typically pass through fenestrae present in LSECs.17,20 As the diameter of LSEC fenestrations is smaller than the resolution of standard light microscopy, we used SEM to visualize them. As shown in Figure 2B-D, the endothelial fenestration in the liver of F8TKO and B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J mice was dramatically reduced compared with control mouse liver. Furthermore, grouping of fenestrae and overall pore size were also reduced in F8TKO mice as well as B6; 129S-F8tm1Kaz/J mice (Figure 2B,D). The absence of fenestrae has been associated with LSEC capillarization, which promotes basement membrane formation while decreasing permeability.21,22 There was significant upregulation of LSEC markers associated with capillarization, including CD31, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), ICAM1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1), stabilin2, ID1 (Inhibitor of DNA Binding-1), Gata4, and Ehd3 (EH Domain Containing-3) in F8TKO mice by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot (Figure 2E-F; supplemental Figure 1G). qRT-PCR also confirmed the upregulation of basement membrane markers collagen types I (α1), III (α1), and α-smooth muscle actin in the liver of F8TKO mice (supplemental Figure 1D). Finally, immunostaining for the LSEC markers PECAM and LYVE1 demonstrated increased LSCE capillarization in F8TKO mice. As a result of the morphological modification of those cells, staining for both Lyve1 and PECAM (Figure 2G-H) was enhanced throughout the liver tissue, suggestive of increased LSEC capillarization. Our current study is the first to highlight endothelial maladaptive structural changes in FVIII-deficient mice and their deleterious impact on the efficacy of liver-directed gene transfer. Indeed, abnormal endothelial function was recently recognized in patients with hemophilia.23 Our current findings will inspire future investigations looking at the molecular mechanism underlying loss of endothelial fenestration associated with FVIII deficiency and whether or how this possibly could be affecting liver gene therapy in hemophilia.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pete Lollar at Emory University for providing breeding pairs of F8TKO mice, and Mark T. Gladwin for useful suggestions on our preliminary data.
This work was supported by VMI pilot grant P3HVB, National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases grant K01NIH-NIDDK125617, ASH Junior Faculty Scholar Award (T.P.-S.), NIH, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grants R01HL128297 (P.S.), R01HL141080 (P.S.), R01HL124021 (S.Y.C.), and HL122596 (S.Y.C.); American Heart Association (AHA) grant 18TPA34170588 (P.S.); AHA predoctoral fellowship 19PRE34430188 (R.V.); AHA postdoctoral fellowship AHA828786 (T.W.K.). This work was also supported by the Bayer Hemophilia Award (P.S.); the AHA grant 18EIA33900027 (S.Y.C.); and in part by Health Resources & Services Administration HRSA H30MC2450-04-00 to the Vascular Medicine Institute from the Hemophilia Center of Western Pennsylvania (P.S., T.P.-S.) and by Vitalant (P.S.).
Authorship
Contribution: T.P.-S. conceived and designed the study; T.W.K., R.V., E.-M.J., S.G., S.A., J.F., and T.P.-S. acquired the data; T.P.-S. analyzed and interpreted the data; E.T. and O.K. oversaw breeding the F8TKO mice; J.F. conducted the SEM imaging; T.B. provided reagent; R.K.D. performed experiments; T.P.-S. drafted the manuscript; E.M.N., M.V.R., and P.S. critically reviewed and edited the manuscript; D.B.S., S.C.W., S.Y.C., E.M.N., and P.S. provided technical and material support; E.M.-J. and T.W.K. performed the statistical analysis; and T.P.-S. and P.S. obtained funding.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: P.S. is a recipient of 2021 Basic Sciences Research Award from Bayer Hemophilia Award Program (BHAP) of Bayer Corp and funding (not relevant to the current study) as a part of sponsored research agreements with CSL Behring Inc, IHP Therapeutics, and Novartis AG. S.Y.C. has served as a consultant for Acceleron Pharma and United Therapeutics; is a director, officer, and shareholder in Synhale Therapeutics; and has held research grants from Actelion, Bayer, and Pfizer. M.V.R. receives research funding from Sanofi, BioMarin, SPARK, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals USA and serves on advisory boards of Sanofi, BioMarin, SPARK, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals USA. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Tirthadipa Pradhan-Sundd, Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Vascular Medicine Institute, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, 200 Lothrop Street, Pittsburgh, PA 15261; e-mail: tip9@pitt.edu.
References
Author notes
Requests for data sharing may be submitted to Tirthadipa Pradhan-Sundd (tip9@pitt.edu.).
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.