Abstract
The chemokine stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and its unique receptor, CXCR4, are required for normal cardiovascular development, but a critical role for SDF-1 in postnatal vascular remodeling and the mechanisms underlying SDF-1/CXCR-4 vasculogenesis are unclear. Here we show that SDF-1 is expressed by the vascular endothelium from selected healthy and tumor tissues. In vitro, primary endothelial cells constitutively express SDF-1 that is detected in the cytoplasm, on the cell surface, and in the culture supernatant. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) increase SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells. In functional studies, pertussis toxin and antibodies to SDF-1 or CXCR-4 disrupt extracellular matrix-dependent endothelial cell tube formation in vitro. This morphogenic process is associated with time-dependent modulation of surface CXCR-4 expression that changes from being diffuse to being polarized and subsequently lost. In vivo, pertussis toxin and neutralizing antibodies directed at SDF-1 inhibit growth factor–dependent neovascularization. These results indicate that SDF-1/CXCR-4 identifies VEGF- and bFGF-regulated autocrine signaling systems that are essential regulators of endothelial cell morphogenesis and angiogenesis.
Introduction
The chemokine stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and its receptor CXCR-4 are required for normal development of the nervous, hematopoietic, and cardiovascular systems. Mice with targeted deletions of the SDF-1 or the CXCR-4 gene generally die in utero with defects primarily involving neuron migration in the cerebellum, formation of the ventricular septum in the heart, and generation of large vessels supplying the gastrointestinal tract.1-4 They also display defects in B-cell lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis.1-4 After birth, SDF-1 is expressed by stromal cells from several tissues,5,6dendritic cells, endothelial cells and pericytes from normal skin,7 osteoblasts and endothelial cells from the bone marrow,8 and astrocytes and neurons from the brain.9 Studies in vitro have shown that SDF-1 is chemotactic for cells that express the CXCR-4 receptor, including CD34+ hematopoietic cells, monocytes, and lymphocytes, and can promote the transendothelial migration of CD34+ cells and other cells.10-14 Tumor cell migration to characteristic metastatic sites may reflect SDF-1–induced motility of CXCR4-expressing tumor cells.15-17 At high concentrations, SDF-1 exerted selective repulsion of subpopulations of T cells.18 Through complex interactions with adhesion molecules, SDF-1 can promote the attachment of T lymphocytes and CD34+ cells to the vascular endothelium.19-21In vivo, SDF-1 and CXCR-4 have been shown to regulate the retention of CD34+ hematopoietic cells to the bone marrow and to play a role in facilitating stem cell survival and engraftment.22-25
A critical role for SDF-1 and CXCR-4 in vasculogenesis and angiogenic remodeling during development was deduced by the defective formation of large vessels supplying the gastrointestinal tract in mice lacking CXCR-4.2,3 In the mutant embryos, large vessels arising from the lesser curvature of the stomach were absent, and the mesenteries contained arteries and veins of reduced size that often failed to form appropriately paired branches. During normal embryonic development, CXCR-4 is strongly expressed in endothelial cells of blood vessels from the mesentery, the stomach, and the intestinal wall.3
Studies in humans show that vascular endothelial cells from adult bone marrow and skin express SDF-13,7,8,26 and that vascular endothelial cells generally express CXCR-4.27-29 However, little is known about patterns of SDF-1 expression in the vascular endothelium, the factors that regulate its expression by endothelial cells, and what role endothelial cell–derived SDF-1 might play. Because a number of mechanisms that mediate pathologic blood vessel formation in the adult resemble those during embryogenesis, we looked for a potential role of SDF-1 and CXCR-4 as regulators of vascular remodeling.
Materials and methods
Cells and cell cultures
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), prepared from umbilical cord by 0.1% collagenase II (Worthington Biochemical, Freehold, NJ) digestion, were propagated through passage 5 in M199 (Gibco-BRL, Grand Island, NY) culture medium with 20% newborn calf serum (Sigma Chemical, St Louis, MO), 5% human AB serum, 1.6 mML-glutamine (Gibco-BRL), 50 mg/mL porcine heparin (Sigma), 50 μg/mL ascorbate (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ), 15 mM HEPES buffer (Calbiochem-Behring, La Jolla, CA), and 15 μg/mL endothelial cell growth supplement (a crude extract of bovine neural tissue containing basic fibroblast growth factor [bFGF] and acidic FGF; Sigma).30 Human microvascular endothelial cells (Cascade Biologics, Portland, OR) were propagated according to the manufacturer's instructions. HS-5 human stromal cells and Daudi Burkitt lymphoma line (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were cultured in 10% RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco-BRL) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Biofluids, Rockville, MD). Human T cells were derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Growth factors, chemokines, antibodies, and reagents
Recombinant (Escherichia coli–derived) purified human SDF-1α, monoclonal antihuman–mouse SDF-1 antibody (IgG1, clone 79018.111), mouse IgG1 isotype control (hybridoma clone 11711.11), monoclonal anti–SDF-1 neutralizing antibody (IgG1 clone 79014.111), goat IgG antihuman SDF-1 antibody, biotinylated goat antihuman SDF-1α antibody, mouse IgG2A antihuman CXCR-4 monoclonal antibody (clone12G5), mouse IgG2A isotype control (hybridoma clone 20102.1), and monoclonal mouse IgG2B antihuman CXCR-4 antibody (hybridoma clone 44716.111) were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Antivimentin (clone VIM 3B4) was from Boehringer Mannheim (Indianapolis, IN). Control goat IgG was from Cappell ICN Pharmaceuticals (Aurora, OH). Rabbit antihuman SDF-1 antigen affinity-purified polyclonal antibody and recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF A) were from PeproTech (Rocky Hill, NJ). Affinity-purified goat anti-actin antibodies were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated affinity purified F(ab')2 fragment goat antimouse IgG (H+L) was from Jackson Immuno Research (West Grove, PA). Alexa Fluor 568–conjugated goat antimouse IgG F(ab')2 fragment was from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). Peroxidase-linked, donkey antirabbit IgG antibody was from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Piscataway, NJ). Phalloidin–FITC and pertussis toxin (PTX) were from Sigma Chemical.
RNA preparation and reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction analysis
Total RNA was extracted using TRI Reagent (Molecular Research Center, Cincinnati, OH). Semiquantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was carried out essentially as described.31 cDNA was synthesized from 2 μg total RNA using SuperScript pre-amplification system (Gibco-BRL). The amount of cDNA used for each amplification reaction was based on the results of PCR for GAPDH showing equivalent amounts of product amplified from all samples. The number of amplification cycles was determined experimentally for each primer pair to fit the linear part of the sigmoid curve, reflecting the relationship between the number of amplification cycles and the amount of PCR product. RT-PCR assay detection of quantitative differences in mRNA for each gene product was established by serial dilutions of input cDNA used in PCR assays. Amplification was performed in a 50-μL reaction mixture using 5 μL cDNA, platinum Taq DNA polymerase (Gibco-BRL), 1 μL dNTP mixture (10 mM; Gibco-BRL), and specific SDF-1 primers at appropriate annealing temperatures. SDF-1α and β, SDF-1 α/β, and GAPDH were amplified for 30, 30, and 28 cycles, respectively. PCR products were separated on 1.8% agarose gel (NuSieve agarose; FMC, Rockland, ME). Primer sequences and predicted sizes of the amplified product were as follows:
hSDF-1α/β, 5′ ATGCCCATGCCGATTCTTCG, 3′ TGTCTGTTGTTGTTCTTCAGCC, 120 bp; hSDF-1α, 5′ TGCCTTCACCTCCTCTTTCAAAC, 3′ AGCAGGGGGACCATTACACATC, 332 bp; hSDF-1β, 5′ ATGCCCATGCCGATTCTTCG, 3′ TAGGCTTTGCCCAGGTTGACTG, 635 bp; G3PDH, 5′ GCCACCCAGAAGACTGTGGATGGC, 3′ CATGTAGGCCATGAGGTCCACCAC, 446 bp.
Endothelial cell membrane preparations
Cell membranes were prepared essentially as previously described.32 Briefly, cells (in 10 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.6, and 0.5 mM MgCl2) were homogenized in a Dounce homogenizer and were incubated on ice for 20 to 30 minutes. Homogenates were equilibrated to 150 mM NaCl and were spun at 1780g for 10 minutes. Supernatants were centrifuged for 45 minutes at 100 000g, and the pellets were suspended in cold Triton lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris HCl, 300 mM NaCl, pH 7.6, 0.5% Triton-x100, and protease inhibitors (Complete, Mini; Roche, Mannheim, Germany). After another centrifugation at 14 000g for 30 minutes, supernatants were collected and used as a source of cell membranes.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot analysis
Cell lysates from 1 × 106 cells were solubilized in tricine sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer (Novex, San Diego, CA), boiled, and run through 10% to 20% tricine gels (Novex). After transfer, Immobilon-P membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA) were incubated overnight with rabbit antihuman SDF-1 antibody (0.5 μg/mL); bound antibody was detected with affinity-purified, peroxidase-linked, donkey antirabbit IgG antibody (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) and a chemiluminescence detection system (ECL kit; Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). Relative protein expression levels were estimated by membrane rehybridization with goat anti-actin antibody.
Immunofluorescence microscopy
Culture wells (24-well plates; Costar, Corning, NY) were coated with gelatin (200 μL) or glass chamber slides (2-well; Lab-Tech, Naperville, IL) were coated with 250 μL Matrigel (Becton Dickinson Labware, Bedford, MA), blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4) for 1 hour, and seeded with HUVECs (10 000-50 000 cells/mL). After incubation, HUVECs were washed, fixed with 1% to 3.5% formaldehyde, and stained. Primary antibodies (1:50 dilution mouse anti–SDF-1 monoclonal antibody, clone 79018.111 or 1:100 dilution mouse anti–CXCR-4 monoclonal antibody, clone 44716.111; R&D Systems) were incubated for 45 minutes at 4°C. FITC-conjugated F(ab')2 fragment goat antimouse IgG (Jackson Immuno Research) or goat antimouse Alexa 568–conjugated IgG (Molecular Probes) was added to visualize SDF-1 and CXCR4, respectively. Slides were washed, mounted (fluorescence mounting medium; DAKO, Carpinteria, CA), and examined using a Zeiss Axiophot microscope (Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with a Roper Scientific CCD camera (Tucson, AZ). Images were imported into Adobe Photoshop. Intracytoplasmic F-actin immunofluorescence was performed on HUVECs grown on Matrigel as described above, fixed with 1% formaldehyde, and permeabilized with 0.1% saponin PBS, pH 7.5, for 10 minutes at room temperature. F-actin was detected by staining with phalloidin-FITC (4 × 10−7 M; Sigma) for 30 minutes at room temperature. For confocal microscopy, fluorescent cells were examined with an epifluorescence microscope (Optiphot; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a confocal system (MRC-1024; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). Sequential excitation at 568 nm and 488 nm was provided by a 15-mW krypton–argon laser (American Laser, Salt Lake City, UT). Red fluorescence and green fluorescence were collected using photomultiplier tubes with 598/40 and 522/32 emission filters, respectively. After sequential excitation, images were merged and processed using LaserSharp (Bio-Rad Laboratories) software.
Flow cytometry
HUVECs were detached with 2 mM EDTA in PBS, washed twice with ice-cold binding buffer (RPMI 1640, 20 mM HEPES, 1% BSA), blocked with mouse IgG1 isotype control for 30 minutes at 1 μg/mL, and incubated (5 × 105/mL in 100 μL PBS–0.1%BSA) with murine monoclonal anti–SDF-1 (5 μg/mL for 45 minutes at 4°C; R&D Systems). After they were washed, cells were incubated with FITC-labeled goat antimouse F(ab′)2 fragment for 30 minutes at 4°C. Intracytoplasmic expression of SDF-1 was tested after cell permeabilization with 0.1% saponin. As a control for permeabilization, cells were stained with mAb to vimentin (Boehringer, Mannheim). Data were collected from 5 × 103 viable cells using a FACScalibur cytofluorometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) and analyzed using CELLQuest software (Becton Dickinson). Background fluorescence was assessed through staining with isotype-matched antibodies.
Immunohistochemistry
Tissue sections were retrieved from files of the Laboratory of Pathology, National Cancer Institute. Samples were fixed in formalin and were paraffin embedded. Antigens were retrieved after steaming the sections in citrate buffer (10 mM), pH 6.0, and 0.01% Tween for 30 minutes. After blocking with 3% goat serum for 15 minutes, the sections were incubated with mouse monoclonal anti–SDF-1 antibody (clone 79018.111, dilution 1:50; R&D Systems) or mouse monoclonal antihuman CD31 antibody (dilution 1:20; DAKO) overnight at room temperature. Bound antibody was detected with a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody formulation for recognition of rabbit and mouse immunoglobulins (Ventana Medical System, Tucson, AZ). After the addition of an avidin–horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate, the enzyme complex was visualized with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrachloride and copper sulfate.
SDF-1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Plates (Immulon IB; Dynex Technologies, Chantilly, VA) were coated overnight at 4°C with mouse monoclonal antibody against SDF-1 (10 μg/mL, clone 79018.111; R&D Systems) in carbonate buffer (pH 9.8), washed, and blocked (Superblock; Pierce, Rockford, IL). SDF-1 protein standard (11 000-24 300 pg/mL; R&D Systems) or test samples were added in triplicate to wells in PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 and were incubated for 2 hours at room temperature. After washing, biotinylated goat antihuman SDF-1α antibody was added (100 μL/well; 200 ng/mL) in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.4) containing 0.05% Tween 20 and 0.1% BSA) and was incubated for 2 hours at room temperature. After washing, streptavidin HRP (1:200 dilution in Tris-HCl buffer containing 0.05% Tween 20 and 0.1% BSA, 100 μL/well; R&D Systems) was added and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. After washing, TMB (tetramethyl benzidine) peroxidase substrate solution (KPL, Gaithersburg, MD) was added (100 μL/well) followed by stop solution (1 M H2SO4). Plates were read at 450 nm with correction at 630 nm. The concentration of SDF-1 in test samples was calculated from absorbance values in relation to the standard curve using SOFTmax PRO software. The assay was found to be specific for SDF-1 and to have a lower limit of assay sensitivity of approximately 10 pg/mL SDF-1.
Matrigel tube formation assay
The assay was carried out essentially as previously described.33 34 Multiwell dishes (48-well plates) or glass-chamber slides (2-well chambers) were coated with 200 to 250 μL Matrigel (Collaborative; BD PharMingen, San Diego, CA) at 4°C and were incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. HUVECs (10-30 000 cells/mL) were added to the Matrigel-coated wells in complete culture medium. Neutralizing antibodies against SDF-1 (goat IgG antihuman SDF-1; R&D Systems), CXCR-4 (mouse monoclonal antihuman CXCR-4; clone 44716.111; R&D Systems), or isotype-matched control antibodies were added at 10 μg/mL; PTX was added at 200 ng/mL. After 1 to 18 hours of incubation, cells were photographed under phase-contrast microscopy, and images were imported into Adobe Photoshop. Tubes were examined at low-power magnification (×5). At least 10 fields were examined per well; each experimental condition was tested in triplicate.
In vivo Matrigel angiogenesis assay
The in vivo Matrigel angiogenesis assay was performed as described previously.35 An aliquot (0.5 mL) of Matrigel (Becton Dickinson Labware), either alone or with the desired additives, was injected subcutaneously into the mid-abdominal region of female BALB/c athymic mice 6 to 8 weeks old. Additives included murine bFGF (150 ng/mL; R&D Biosystems), murine VEGF (150 ng/mL; PeproTech), PTX (100 ng/mL), control murine IgG1 (200 μg/mL), or monoclonal anti–SDF-1 neutralizing antibody (200 μg/mL). There were 6 to 8 mice per group. Mice that received PTX within the Matrigel also received intravenous inoculations of PTX (200 ng/mouse) on days 0 and 1. After 7 days, the animals were killed, and Matrigel plugs were removed, fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin solution (Sigma Chemical), and embedded in paraffin. Tissues were sectioned (5-μm thick), and slides were stained with Masson trichrome (American Histolabs, Gaithersburg, MD). Quantitative analysis of angiogenesis was performed using IPLab software (BioVision Technologies, Exton, PA). The results are expressed as the mean (SEM) area (expressed in μm2) occupied by cells within a Matrigel field measuring 1.0 × 106μm2.
Results
SDF-1 expression in vascular endothelium from human tissues
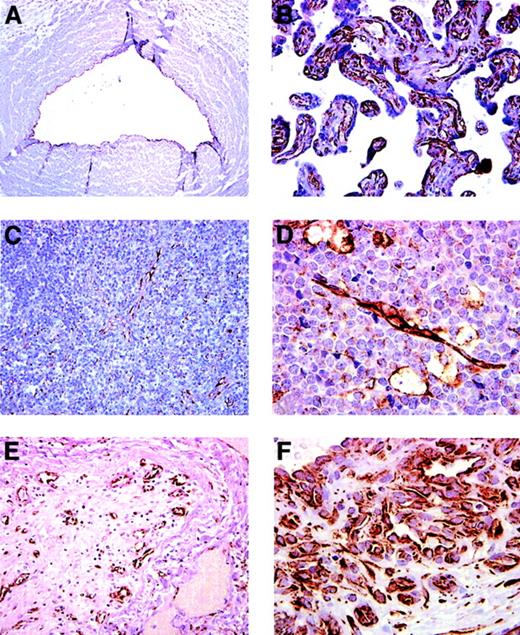
To evaluate SDF-1 expression in the normal human vascular endothelium, different tissues were tested for SDF-1 by immunohistochemistry. The vascular endothelium was identified morphologically as the inner lining of vascular channels containing red blood cells or by expression of the endothelial cell marker CD31. We confirmed7,8 the presence of SDF-1 in endothelial cells lining blood capillaries in the bone marrow and the skin (not shown). Additionally, we found the endothelium lining the umbilical vein (Figure 1A), the chorionic villi (Figure1B) and the high endothelial venules in the lymph node (Figure 1C) to be positive for SDF-1. By contrast, the vascular endothelium in capillaries from kidneys, brain, skeletal muscle, lung, and liver was SDF-1 negative (not shown). The endothelium lining arterioles and arteries in many tissues, including the skin, lung, small intestine, liver, and umbilical cord, stained positive for SDF-1 (not shown). Whereas blood capillaries within the normal brain tissue stained consistently negative for SDF-1, we confirmed36 that blood vessels within glioblastoma multiforme and proximal to infarcted brain tissue were positive for this chemokine (not shown). In addition, capillary blood vessels within Burkitt lymphoma tissue (Figure 1D) and those arising within an occluded vessel, presumably as a result of recanalization (Figure 1E), stained intensely positive for SDF-1. Endothelium lining blood channels within a lobular capillary hemangioma was also positive for SDF-1 (Figure 1). Thus, SDF-1 is constitutively expressed in the normal vascular endothelium lining blood capillaries and arteries from several organs. SDF-1 is also expressed in capillary blood vessels arising presumably from neovascularization of certain tumors and ischemic tissue, suggesting that SDF-1 expression could be induced in endothelial cells during new vessel formation.
SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells lining capillary vessels revealed by immunohistochemical staining.
(A) Umbilical vein: the endothelium lining the vein stains positive for SDF-1. (B) Placenta: capillaries and blood vessels within chorionic villi are positive for SDF-1. (C) Lymph node: SDF-1 staining marks high endothelial venules within T-cell areas. Isolated cells identified morphologically as macrophages–dendritic cells are positive for SDF-1. (D) Lymph node: endothelium and scattered macrophages within Burkitt lymphoma stain positive for SDF-1. (E) Lung: a medium-size occluded vessel (within an area of organizing pneumonia) with evidence of recanalization displays SDF-1–positive endothelium lining the newly formed intraluminal vessels. (F) Skin: the typical lobular capillary network of a pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma) and small capillaries lined by prominent endothelial cells are positive for SDF-1. Original magnification, ×40.
SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells lining capillary vessels revealed by immunohistochemical staining.
(A) Umbilical vein: the endothelium lining the vein stains positive for SDF-1. (B) Placenta: capillaries and blood vessels within chorionic villi are positive for SDF-1. (C) Lymph node: SDF-1 staining marks high endothelial venules within T-cell areas. Isolated cells identified morphologically as macrophages–dendritic cells are positive for SDF-1. (D) Lymph node: endothelium and scattered macrophages within Burkitt lymphoma stain positive for SDF-1. (E) Lung: a medium-size occluded vessel (within an area of organizing pneumonia) with evidence of recanalization displays SDF-1–positive endothelium lining the newly formed intraluminal vessels. (F) Skin: the typical lobular capillary network of a pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma) and small capillaries lined by prominent endothelial cells are positive for SDF-1. Original magnification, ×40.
SDF-1 expression and regulation in endothelial cell cultures
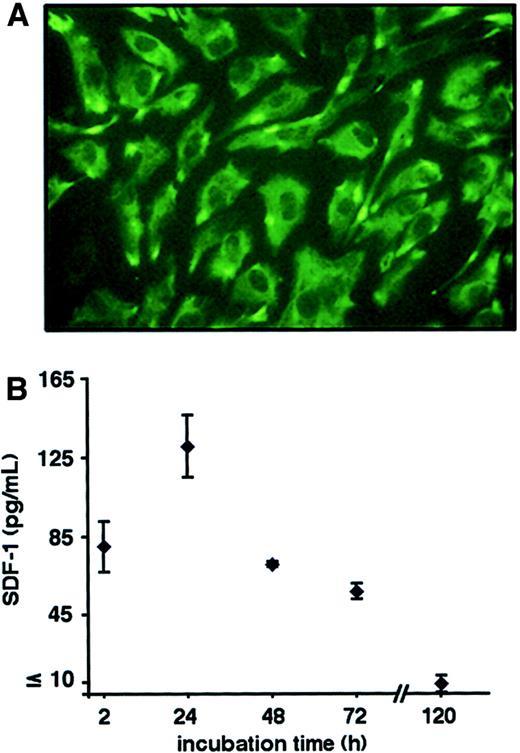
We used the endothelium lining the umbilical vein that stained positive for SDF-1 (Figure 1) as a source of primary human endothelial cells (HUVECs). By passage 2, 95% of the cells were positive for the endothelial cell marker CD31, as assessed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis (not shown). By immunofluorescence microscopy (Figure 2A), most HUVECs expressed SDF-1. The expression of SDF-1 continued seemingly unchanged in HUVECs propagated in vitro for at least 5 passages; later passages were not examined. Because SDF-1 does not contain retention signals to the endoplasmic reticulum,37 we looked for SDF-1 in the conditioned medium from HUVECs. Using a specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), SDF-1 was detected in culture supernatants of HUVECs incubated for 2 to 120 hours (Figure 2B). We examined whether SDF-1 is present on the endothelial cell surface. Membrane-associated SDF-1 was demonstrated by a specific ELISA applied to membrane protein extracts from HUVECs but not from control Daudi calls (Table1). Total cell extracts from HUVECs, but not human peripheral blood T cells, were also positive for SDF-1 (Table1). These experiments indicated that SDF-1 is expressed in endothelial cells and is released into the extracellular compartment.
Primary cultures of endothelial cells express SDF-1.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of HUVECs grown on gelatin-coated wells. Cells were fixed with 3.5% formaldehyde and stained with a murine monoclonal anti–SDF-1 antibody (IgG1, clone 79018.111). Antibody binding was revealed by FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibodies. Control staining with mouse IgG1 (hybridoma clone 11711.11) and FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibodies was negative (not shown). (B) SDF-1 detected in the supernatant of HUVECs measured by specific ELISA. Cells (3 × 104/mL) plated on Matrigel-coated chamber slides were incubated for the indicated time intervals. Results reflect the means (± SD) of 3 independent HUVEC cultures. Assay sensitivity for SDF-1 was calculated at approximately 10 pg/mL.
Primary cultures of endothelial cells express SDF-1.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of HUVECs grown on gelatin-coated wells. Cells were fixed with 3.5% formaldehyde and stained with a murine monoclonal anti–SDF-1 antibody (IgG1, clone 79018.111). Antibody binding was revealed by FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibodies. Control staining with mouse IgG1 (hybridoma clone 11711.11) and FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibodies was negative (not shown). (B) SDF-1 detected in the supernatant of HUVECs measured by specific ELISA. Cells (3 × 104/mL) plated on Matrigel-coated chamber slides were incubated for the indicated time intervals. Results reflect the means (± SD) of 3 independent HUVEC cultures. Assay sensitivity for SDF-1 was calculated at approximately 10 pg/mL.
SDF-1 expression in HUVECs
| Test sample . | Total protein (ng ± SD) . | SDF-1 (ng ± SD) . |
|---|---|---|
| HUVEC membrane | 25.0 × 106 ± 77.2 | 10.36 ± 0.2 |
| HUVEC cell lysate | 38.0 × 104 ± 20.7 | 1.58 ± 0.1 |
| Daudi cell membrane | 18.5 × 106 ± 23.0 | ND |
| T-lymphocyte cell lysate | 7.5 × 106 ± 37.6 | ND |
| Test sample . | Total protein (ng ± SD) . | SDF-1 (ng ± SD) . |
|---|---|---|
| HUVEC membrane | 25.0 × 106 ± 77.2 | 10.36 ± 0.2 |
| HUVEC cell lysate | 38.0 × 104 ± 20.7 | 1.58 ± 0.1 |
| Daudi cell membrane | 18.5 × 106 ± 23.0 | ND |
| T-lymphocyte cell lysate | 7.5 × 106 ± 37.6 | ND |
Cell membrane preparations derived from approximately 107 cells and cell lysates derived from approximately 2 × 106 cells were tested for SDF-1 content by specific ELISA. Data represent the means of triplicate determinations (± SD).
ND indicates not detected.
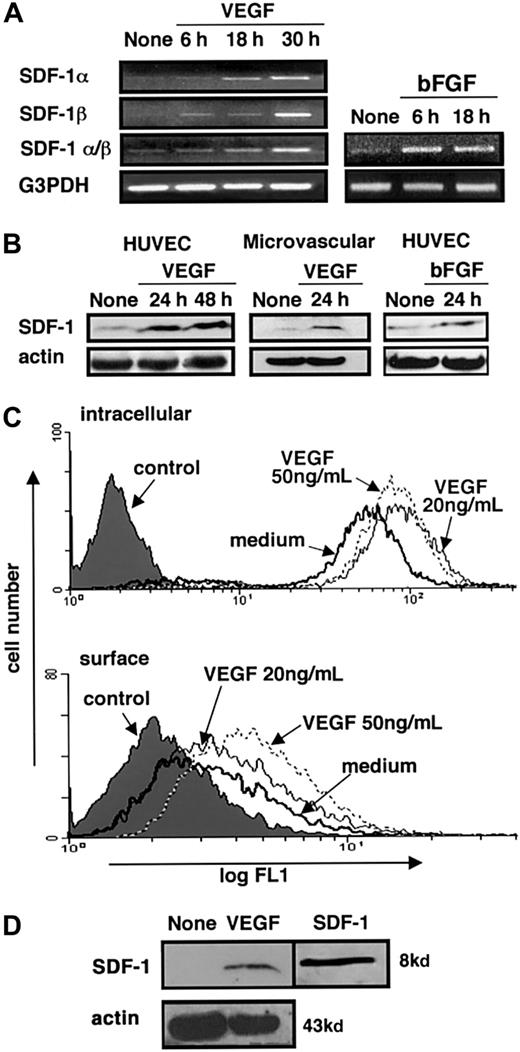
Immunohistochemical study results presented above (Figure 1) raised the possibility that SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells might increase during neovascularization. Because VEGF and FGF are known to stimulate new vessel formation,38-40 we tested for SDF-1 expression in VEGF- or bFGF-treated HUVECs. First HUVECs were starved of endothelial cell growth supplement for 20 to 24 hours, and then they were cultured for 6, 18, or 30 hours in medium alone or in medium supplemented with human VEGF (50 ng/mL) or bFGF (25 ng/mL). Using semiquantitative RT-PCR, the mRNAs for SDF-1α and SDF-1β were found to be more abundant in HUVECs cultured with VEGF or bFGF than in medium alone. Stimulation of SDF-1 mRNA by VEGF and bFGF was time dependent (Figure 3A). Through immunoblotting with specific antibodies, SDF-1 protein was detected in cell lysates of HUVECs and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. After 24- or 48-hour culture with human VEGF or bFGF, levels of SDF-1 protein were more abundant (Figure 3B). By FACS analysis, surface and intracellular SDF-1 was detected in HUVECs cultured in medium alone. After 24-hour culture with human VEGF (20 or 50 ng/mL), the fluorescence intensity for surface and intracellular SDF-1 was increased (Figure 3C). These effects of VEGF were dose dependent and were not detected at VEGF concentrations of 5 ng/mL (not shown). Regulation of SDF-1 surface expression was also documented by immunoblotting. As shown (Figure 3D), SDF-1 was detected by specific antibodies in endothelial cell membrane preparations purified from HUVECs cultured for 24 hours with VEGF (50 ng/mL). Under these experimental conditions, SDF-1 was not detected in membrane preparations from HUVECs cultured in medium alone (Figure 3). These results provide evidence that SDF-1 is expressed in endothelial cells propagated in vitro and that VEGF and bFGF can further induce SDF-1 expression in these cells.
SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells and regulation by VEGF.
HUVECs or human dermal microvascular endothelial cells were first starved of growth supplements by incubation in medium alone for 20 to 24 hours and then cultured in medium alone or in medium supplemented with VEGF. At the indicated time points, total RNA was extracted, and cell lysates or membrane extracts were prepared. (A) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of SDF-1α and β expression in HUVECs cultured in medium alone, with VEGF (50 ng/mL), or with bFGF (25 ng/mL) for the indicated time periods. RNA preparations were tested by parallel RT-PCR amplification for G3PDH. (B) Western blot analysis of SDF-1 expression in HUVECs cultured in medium alone, with VEGF (50 ng/mL), or bFGF (25 ng/mL) and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells cultured with medium alone or VEGF (50 ng/mL) detected by affinity-purified rabbit antihuman SDF-1α antibodies. Loading accuracy was tested by membrane reprobing with antibodies to actin. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of surface and intracellular SDF-1 expression in HUVECs cultured for 24 hours in medium alone or with VEGF (20 or 50 ng/mL). Cells were stained with either a murine monoclonal antihuman–mouse SDF-1 antibody (IgG1, clone 79018.111) or isotype-matched control antibody (hybridoma clone 44716.14) followed by an FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibody. (D) Western blot analysis of SDF-1 expression in membrane preparations of HUVECs cultured for 24 hours in medium alone or with VEGF (50 ng/mL) detected by rabbit anti–SDF-1 antibodies. Loading accuracy was verified by reprobing the membranes with anti-actin antibodies. Recombinant SDF-1 (5 ng) was run in parallel.
SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells and regulation by VEGF.
HUVECs or human dermal microvascular endothelial cells were first starved of growth supplements by incubation in medium alone for 20 to 24 hours and then cultured in medium alone or in medium supplemented with VEGF. At the indicated time points, total RNA was extracted, and cell lysates or membrane extracts were prepared. (A) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of SDF-1α and β expression in HUVECs cultured in medium alone, with VEGF (50 ng/mL), or with bFGF (25 ng/mL) for the indicated time periods. RNA preparations were tested by parallel RT-PCR amplification for G3PDH. (B) Western blot analysis of SDF-1 expression in HUVECs cultured in medium alone, with VEGF (50 ng/mL), or bFGF (25 ng/mL) and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells cultured with medium alone or VEGF (50 ng/mL) detected by affinity-purified rabbit antihuman SDF-1α antibodies. Loading accuracy was tested by membrane reprobing with antibodies to actin. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of surface and intracellular SDF-1 expression in HUVECs cultured for 24 hours in medium alone or with VEGF (20 or 50 ng/mL). Cells were stained with either a murine monoclonal antihuman–mouse SDF-1 antibody (IgG1, clone 79018.111) or isotype-matched control antibody (hybridoma clone 44716.14) followed by an FITC-labeled goat antimouse IgG antibody. (D) Western blot analysis of SDF-1 expression in membrane preparations of HUVECs cultured for 24 hours in medium alone or with VEGF (50 ng/mL) detected by rabbit anti–SDF-1 antibodies. Loading accuracy was verified by reprobing the membranes with anti-actin antibodies. Recombinant SDF-1 (5 ng) was run in parallel.
Endothelial cell–derived SDF-1 regulates ECM-dependent tube formation
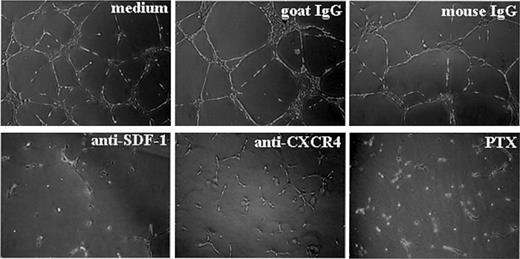
Previously, the SDF-1 receptor CXCR-4 was consistently detected on endothelial cells, and VEGF and bFGF were shown to enhance its expression.27,29 We have shown above that endothelial cells can express SDF-1 more abundantly after exposure to VEGF or bFGF. Therefore, we examined potential functions of SDF-1 and CXCR-4, both expressed by endothelial cells. We tested the effects of blocking antibodies directed at SDF-1 or CXCR-4 in an in vitro morphogenesis assay in which endothelial cells plated on extracellular matrix preparations, such as Matrigel, assemble into capillarylike structures.33,41,42 Though it relies only on the interactions of endothelial cells with extracellular matrix, this assay recapitulates several aspects of new vessel formation, including endothelial cell migration, attachment, and differentiation.33 Neutralizing antibodies against SDF-1 or CXCR-4 added to HUVECs at the time of cell plating on Matrigel prevented the formation of characteristic tubular structures assembled in a branching reticular network after 16-hour incubation with medium alone or with control antibodies. In the presence of neutralizing SDF-1 or CXCR-4 antibodies, HUVECs appeared isolated or assembled in clumps of rounded cells or short, thick cords attached to the Matrigel surface (Figure 4). A similar effect was produced by the addition of PTX to endothelial cells at the time of culture on Matrigel-coated plates (Figure 4). PTX can block Giprotein–mediated CXCR-4 signaling through ADP ribosylation of the α subunit of Gi proteins.43 This failure of HUVECs to undergo characteristic morphogenic changes on Matrigel was not attributable to interference with HUVEC attachment to Matrigel by PTX or the antibodies to CXCR-4 or SDF-1 (not shown). As judged by trypan blue staining, HUVECs were mostly viable after 18-hour exposure to PTX or to antibodies against SDF-1 or CXCR-4.
SDF-1/CXCR-4 regulation of ECM-dependent tube formation by endothelial cells.
HUVECs (30 × 104) were plated on Matrigel-coated, 48-well plates and were incubated for 16 hours in medium alone, with PTX, or with antibodies (neutralizing goat IgG antihuman SDF-1; control goat IgG; neutralizing murine monoclonal antihuman CXCR4 IgG2A, clone12G5; or control murine IgG2A, hybridoma 20102.1; all at 10 μg/mL). Images reflect tube formation after 16-hour incubation detected by phase-contrast microscopy (original magnification, ×5). Representative results from 4 experiments.
SDF-1/CXCR-4 regulation of ECM-dependent tube formation by endothelial cells.
HUVECs (30 × 104) were plated on Matrigel-coated, 48-well plates and were incubated for 16 hours in medium alone, with PTX, or with antibodies (neutralizing goat IgG antihuman SDF-1; control goat IgG; neutralizing murine monoclonal antihuman CXCR4 IgG2A, clone12G5; or control murine IgG2A, hybridoma 20102.1; all at 10 μg/mL). Images reflect tube formation after 16-hour incubation detected by phase-contrast microscopy (original magnification, ×5). Representative results from 4 experiments.
When applied to already-formed HUVEC tubules, antibodies to SDF-1 or to CXCR-4 were ineffective at disrupting the preformed structures (not shown). When added 1 hour after initial HUVEC plating on Matrigel-coated plates, PTX and antibodies to SDF-1 or CXCR-4 disrupted the tube formation detected 18 hours after plating. Later additions (2.5 hours after HUVEC plating) of PTX or antibodies to SDF-1 or CXCR-4 were increasingly less effective at disrupting tube formation. These results provide evidence that SDF-1 and CXCR-4 mediate critical signaling for endothelial cell assembly into tubular structures on extracellular matrix.
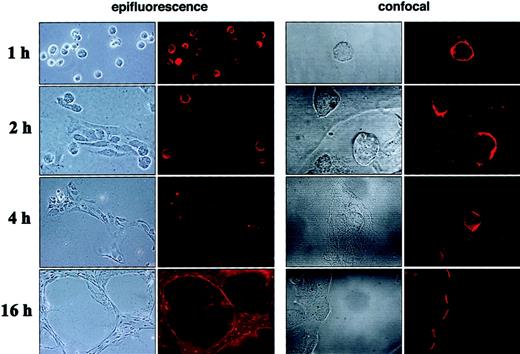
ECM-induced regulation of CXCR-4 expression in endothelial cells
Time-course experiments (Figure5) revealed that 1 hour after dispersion on Matrigel, HUVECs were mostly attached and remained as single cells forming only loose aggregates of rounded cells. At this time, CXCR-4 was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy on most (88%) HUVECs. As seen more clearly by confocal microscopy, CXCR-4 was generally uniformly distributed along the endothelial cell surface. After 2-hour incubation on Matrigel, HUVECs were found as aggregates of various shapes and as single cells. Many cells within the clumps had changed morphology from rounded to elongated. At this 2-hour time-point, only 18% of the cells continued to express CXCR-4, which was detected on the cell surface mostly with a polar distribution. The directional polarity of cells was different even within cells proximal to each other. After 4-hour incubation, most endothelial cells appeared to be part of cordlike structures spanning the Matrigel surface, and most cells became elongated. At this time, CXCR-4–positive staining was minimal and resided in rare (approximately 2%), often round, cells not included in cordlike structures. At the 16-hour time point, when HUVECs were distributed in a tight network of interconnecting tubular structures, CXCR-4 staining uniformly marked the outer margins of the tubular network and, to a lower degree, some cells residing within the cords.
Time-dependent changes of CXCR-4 expression and localization during ECM-dependent endothelial cell tube formation.
HUVECs (10 × 103) were plated on Matrigel-coated, glass chamber slides (2-well) and were incubated at 37°C for 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours. After incubation, cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde and examined unstained with a phase-contrast microscope or stained for CXCR-4 with a murine monoclonal antihuman CXCR4 antibody (IgG2B, clone 44716.111) followed by Alexa 568–conjugated goat antimouse IgG, and they were examined with an epifluorescence microscope with or without a confocal system. Representative images from phase-contrast microscopy showed different stages of HUVEC migration and assembly into tubular structures at 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours. Parallel changes in levels and distribution of CXCR-4 surface expression on HUVEC detected by epifluorescence (original magnification, ×20 all time points except ×10 at 16-hour time point) and confocal microscopy (original magnification, ×60).
Time-dependent changes of CXCR-4 expression and localization during ECM-dependent endothelial cell tube formation.
HUVECs (10 × 103) were plated on Matrigel-coated, glass chamber slides (2-well) and were incubated at 37°C for 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours. After incubation, cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde and examined unstained with a phase-contrast microscope or stained for CXCR-4 with a murine monoclonal antihuman CXCR4 antibody (IgG2B, clone 44716.111) followed by Alexa 568–conjugated goat antimouse IgG, and they were examined with an epifluorescence microscope with or without a confocal system. Representative images from phase-contrast microscopy showed different stages of HUVEC migration and assembly into tubular structures at 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours. Parallel changes in levels and distribution of CXCR-4 surface expression on HUVEC detected by epifluorescence (original magnification, ×20 all time points except ×10 at 16-hour time point) and confocal microscopy (original magnification, ×60).
Although surface CXCR-4 expression was reduced in HUVECs incubated for 2 hours on Matrigel, intracellular CXCR-4 staining was present in virtually all HUVECs after 2-hour incubation on Matrigel (at this time point, less than 20% of cells expressed surface CXCR-4). In addition, there was a rapid loss of SDF-1 surface expression in HUVECs (whereas virtually all cells were SDF-1 positive by surface immunofluorescence 1 hour after plating on Matrigel, only 12% of cells were positive after 1.5 hours) and SDF-1 accumulation in the conditioned medium. Initially undetectable (less than 10 pg/mL) in the 1-hour culture supernatant of HUVECs plated on Matrigel (not shown), SDF-1 was detected at later time points (Figure 2B).
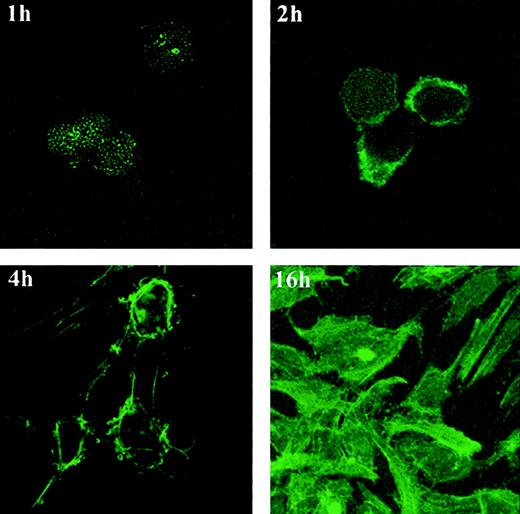
Previous studies have documented that chemokine receptor–ligand interactions can trigger intracellular actin polymerization required for cell motility.10 15 Because ECM-dependent morphogenic change in endothelial cells was accompanied by CXCR-4 modulation and was blocked by neutralizing antibodies to SDF-1 or CXCR-4, we looked for intracellular actin polymerization during this process. Staining for filamentous actin (F-actin) and examination by confocal microscopy revealed characteristic time-dependent changes in HUVECs plated on Matrigel (Figure 6). HUVECs stained minimally for F-actin 1 hour after plating on Matrigel. By 2 hours, many cells had acquired F-actin staining focally along the periphery and displayed membrane blebs extending from these positive areas. At the 4-hour time point, thin stress fibers connecting irregularly shaped endothelial cells stained positive for F-actin, as did focal areas in which the filaments appeared to be anchored to the cells. By 16 hours, a vigorous network of intensely staining fibers marked the tubular structures covering the Matrigel surface (Figure 6).
F-acting expression and distribution in HUVECs undergoing tube formation on Matrigel.
HUVECs (10 × 103) incubated on Matrigel-coated glass chamber slides at 37°C for 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours were stained with phalloidin–FITC and were photographed under confocal microscopy (original magnification, ×60 at all time points except ×20 at 16-hour time point).
F-acting expression and distribution in HUVECs undergoing tube formation on Matrigel.
HUVECs (10 × 103) incubated on Matrigel-coated glass chamber slides at 37°C for 1, 2, 4, and 16 hours were stained with phalloidin–FITC and were photographed under confocal microscopy (original magnification, ×60 at all time points except ×20 at 16-hour time point).
Contribution of endogenous SDF-1 function to growth factor–induced angiogenesis in vivo
The experiments described above provided evidence that CXCR-4 signaling induced by endothelial cell–derived SDF-1 is critical to endothelial cell assembly into tubular structures on ECM. Given that tube formation on ECM is believed to reflect an endothelial cell morphogenic process that recapitulates in vitro some of the events occurring during new vessel formation in vivo, we examined whether neutralization of endogenous SDF-1 or interference with Gisignaling disrupts angiogenesis. An in vivo Matrigel-based assay was used to evaluate the effects of neutralizing antibodies directed at SDF-1 and of PTX on growth factor–induced angiogenesis. In this assay, bFGF and VEGF promoted Matrigel invasion by endothelial cells identified as von Willebrand factor–positive cells and the formation of vascular structures containing red cells within the Matrigel.44 PTX dose and regimen administered systemically to the mice (200 ng/mouse intravenously on days 0 and 1) were selected on the basis of previous studies showing effective reduction of endogenous Gi protein signaling and minimal toxicity to the animals.45 Microscopic evaluation of the Matrigel plugs, removed from the animals after 7 days and processed for histology, revealed that PTX treatment and SDF-1 neutralization reduced markedly the cell infiltration of plugs impregnated with bFGF and VEGF. Digital analysis of the Matrigel area occupied by cells revealed that PTX treatment reduced growth factor–induced neovascularization by approximately 84% to 86% (Table 2). In addition, neutralizing antibodies against SDF-1 reduced neovascularization induced by bFGF plus VEGF by approximately 68%, whereas control IgG had a minimal effect. These results provide evidence that endogenous SDF-1 function plays a critical role in the regulation of growth factor–induced angiogenesis.
Contribution of endogenous SDF-1 function to growth factor–induced angiogenesis in vivo
| Addition to Matrigel . | Mean surface area (SEM) occupied by cells (μm2/106 μm2) . |
|---|---|
| None | 2 041 (178) |
| PTX | 3 845 (339) |
| bFGF | 21 476 (1 582) |
| VEGF | 12 719 (1 748) |
| bFGF + VEGF | 20 717 (1 584) |
| bFGF + PTX | 3 340 (409) |
| VEGF + PTX | 2 345 (152) |
| bFGF + VEGF + PTX | 2 859 (164) |
| bFGF + VEGF + control IgG | 21 978 (962) |
| bFGF + VEGF + anti–SDF-1 | 6 675 (350) |
| Addition to Matrigel . | Mean surface area (SEM) occupied by cells (μm2/106 μm2) . |
|---|---|
| None | 2 041 (178) |
| PTX | 3 845 (339) |
| bFGF | 21 476 (1 582) |
| VEGF | 12 719 (1 748) |
| bFGF + VEGF | 20 717 (1 584) |
| bFGF + PTX | 3 340 (409) |
| VEGF + PTX | 2 345 (152) |
| bFGF + VEGF + PTX | 2 859 (164) |
| bFGF + VEGF + control IgG | 21 978 (962) |
| bFGF + VEGF + anti–SDF-1 | 6 675 (350) |
Mice were injected subcutaneously with 0.5 mL Matrigel alone, Matrigel with PTX (100 ng/mL), Matrigel plus bFGF (150 ng/mL) with or without PTX (100 ng/mL), Matrigel plus murine VEGF (150 ng/mL) with or without PTX (100 ng/mL), Matrigel plus bFGF (150 ng/mL) plus VEGF (150 ng/mL) with or without PTX (100 ng/mL), Matrigel plus bFGF (150 ng/mL) plus VEGF (150 ng/mL) with or without control murine IgG1(hybridoma 11711, 200 μg/mL) or Matrigel plus bFGF (150 ng/mL) plus VEGF (150 ng/mL) with or without neutralizing monoclonal anti–SDF-1 antibody (clone 79014.111, 200 μg/mL). Mice that received PTX with Matrigel were also injected intravenously with PTX (200 ng/mouse) on days 0 and 1. Plugs were removed after 7 days, and histologic sections were stained by Masson trichrome. Results reflect the mean surface area (expressed in μm2) occupied by cells within a surface area of 106 μm2. Nonoverlapping fields covering the entire plug were scanned; there were 12 to 16 plug sections per group. Surface areas were measured by semi-automated digital analysis.
Discussion
One of the fundamental features of the vascular system is that it consists of a highly heterogeneous and nonuniform branching structure. During vascular development and subsequently during remodeling of the existing vasculature, the spatial distribution and the directionality of branches originating from the vascular tree are nonuniform. This polarity of the vascular network is exemplified by the left–right asymmetry of the vascular system, by the specification of arterial and venous channels, and by the variable 3-dimensional spatial orientation of vessels generated in the course of angiogenic responses.46 47
Recently, factors were identified that regulate new vessel formation during vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, including members of the VEGF, angiopoietin, and ephrin families and their receptors.48-50 In addition to these factors, which are specific to the vascular endothelium, many others that are not vascular endothelium specific are required for or contribute to blood vessel formation, including members of the transforming growth factor-β, FGF, and platelet-derived growth factor families.46,48,49However, insight into the molecular basis for vascular heterogeneity and polarity is only beginning to emerge. In particular, little is known about the spatial cues that guide endothelial cells into a correct 3-dimensional network of branching vessels. It has been proposed that ephrin-B2 and its receptor, EphB4, play a critical role in the establishment of the arterial or venous identity in the developing vasculature.51 In zebrafish, a candidate gene responsible for gridlock, a patterning defect resembling coarctation of the aorta has been identified.52 Angiopoietin-1 and the orphan receptor TIE1, in combination, were shown to be critical for the development of the right-hand side, but not for the left-hand side, venous system.47 Furthermore, an essential role for SDF-1 and CXCR-4 in vascular development was suggested by genetic disruption of CXCR-4, which was associated with a failure to form large vessels supplying the gastrointestinal tract.3 22
In this report, we show that SDF-1 is detected in the normal adult vascular endothelium in a number of tissues. We also show that SDF-1 appears to be induced in endothelium undergoing vascular remodeling in the context of tumor angiogenesis and vessel recanalization. This suggested a role for VEGF as an in vivo regulator of SDF-1 expression in endothelial cells. Experiments in vitro, described here, document endothelial cell expression of SDF-1 and its stimulation by VEGF and bFGF. Because previous studies had shown that CXCR4 is constitutively expressed in the normal vascular endothelium,7,36 a result confirmed here, the potential functional relevance of endothelial cells expression of SDF-1 and CXCR-4 was examined. We show that the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR-4 critically regulate ECM-dependent endothelial cell branching morphogenesis. When either SDF-1 or CXCR-4 were neutralized by antibodies or the activation of Giprotein–linked signaling pathways was inactivated by PTX, endothelial cells failed to appropriately migrate and assemble into tubular structures on Matrigel substrate. ECM-dependent assembly of endothelial cells into tubular structures was associated with time-dependent modifications of CXCR-4 expression that changed from being diffuse to the endothelial cell surface to being polarized and subsequently down-modulated. These changing patterns of CXCR-4 expression temporally correlated with SDF-1 release from endothelial cells, intracellular actin polymerization, and endothelial cell movement and assembly into a network of tubular structures. Given that SDF-1 and its receptor are expressed by endothelial cells and are induced by VEGF (here and Pablos et al,7 Gupta et al,27 Salcedo et al,29 Rempel et al36), we conclude that SDF-1 and CXCR-4 define an autocrine signaling system that is exploited during new vessel formation. Indeed, new vessel formation induced in vivo by VEGF and bFGF was markedly reduced by PTX that blocks Gi signaling and by specific neutralizing antibodies directed at SDF-1. By regulating endothelial cell assembly into tubelike structures, endogenous SDF-1–CXCR4 may provide critical signals directing vascular remodeling and neovascularization.
Based on current knowledge about the factors and events underlying new vessel formation,46,49 vasodilation involving nitric oxide and increased vascular leakage induced by VEGF are early events in the process, followed by vessel destabilization by Ang2 and matrix degradation by proteinases and other enzymes. Once loosened from contact with other endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and matrix, endothelial cells proliferate in response to VEGF and other angiogenic factors. Subsequently, proliferating endothelial cells migrate to distant sites, spread, and assemble into a correct pattern of 3-dimensional networks of solid cords that subsequently acquire a lumen. The results presented here suggest that SDF-1/CXCR-4 is a signaling system that regulates specific steps in the process of new vessel formation. SDF-1 molecules released by or presented on endothelial cells would create local chemokine gradients or local chemokine accumulation dictating directional responses of endothelial cells. Type of movement, chemotaxis, chemokinesis, or movement away from the chemokine would critically depend on CXCR-4 receptor occupancy, G-protein local concentration, and activation of signaling pathways.53 54 As a consequence of this autocrine regulatory pathway, endothelial cells would move, spread, and join with each other, steps required for subsequent formation of a structured network of branching vessels.
Previously, hepatocyte growth factor–scatter factor,55angiomotin,56 and collagen XVIII NC1 region34have been reported to variously stimulate endothelial cell motility. Numerous functional characteristics distinguish SDF-1/CXCR-4 from these mitogenic factors. Hepatocyte growth factor–scatter factor was characterized as a growth factor that promotes urokinase production,33 but SDF-1 does not promote endothelial cell proliferation.29 Angiomotin, a recently identified angiostatin-binding protein, promoted endothelial cell motility once transfected into the cells, an activity that was specifically inhibited by angiostatin.56 However, the role of naturally expressed angiomotin remains undefined, and, unlike CXCR4, angiomotin does not appear to act as a typical surface receptor because it lacks a signal peptide and a transmembrane domain. Collagen XVIII NC1 stimulated migration of cells away from already-formed tubular structures,34 whereas SDF-1/CXCR4 was inactive once endothelial cells formed tubular structures. Additionally, SDF-1/CXCR4 is unique among regulators of endothelial cell motility and tube formation in that both ligand and receptor are expressed by endothelial cells and are regulated by VEGF and bFGF. Thus, SDF-1/CXCR-4 defines a growth factor–regulated signaling system in endothelial cells that mediates critical steps in vascular remodeling.
We thank Susan Garfield for confocal microscopy, Ricardo Dreyfuss for photomicroscopy, Michelle Riconscente for help with the illustrations, and Drs Josh Farber, Michael Norcross, Carol Parent, and Hynda Kleinman for helpful discussions.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Ombretta Salvucci, Experimental Transplantation and Immunology Branch, National Cancer Institute, Bldg 10, Rm 12N226, MSC 1907, Bethesda, MD 20892; e-mail: salvucco@mail.nih.gov.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal