Abstract
It is shown that the tetraspanin CD9 has a complex pattern of distribution in hematopoietic cells and is heterogeneously expressed on human bone marrow CD34+ cells. CD34highCD38lowThy1+ primitive progenitors are contained in the population with intermediate CD9 expression, thus suggesting that CD9 expression may precede CD38 appearance. Cell sorting shows that colony-forming unit (CFU)-GEMM and CFU-GM are present in high proportions in this fraction and in the fraction with the lowest CD9 expression. Cells with the highest level of CD9 are committed to the B-lymphoid or megakaryocytic (MK) lineages, as shown by the co-expression of either CD19 or CD41/GPIIb and by their strong potential to give rise to CFU-MK. In liquid cultures, CD9highCD41neg cells give rise to cells with high CD41 expression as early as 2 days, and this was delayed by at least 3 to 4 days for the CD9mid cells; few CD41high cells could be detected in the CD9lowcell culture, even after 6 days. Antibody ligation of cell surface CD9 increased the number of human CFU-MK progenitors and reduced the production of CD41+ megakaryocytic cells in liquid culture. This was associated with a decreased expression of MK differentiation antigens and with an alteration of the membrane structure of MK cells. Altogether these data show a precise regulation of CD9 during hematopoiesis and suggest a role for this molecule in megakaryocytic differentiation, possibly by participation in membrane remodeling.
Introduction
The 24-kd CD9 antigen,1,2 a member of the tetraspanin superfamily,3,4 was originally identified on the surfaces of early B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells.5 Whereas further studies have extended its distribution to other types of leukemia, its expression remains predominant on B-lineage ALL and in promyelocytic M3 leukemia.6,7 This molecule is also expressed on various types of normal hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic tissues. In the peripheral blood, CD9 is highly expressed in basophils, eosinophils, and platelets, but not in erythrocytes.8
The function of CD9 is still unknown. Extensive studies have been performed in platelets that can be activated on the addition of CD9 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).9,10 However, this activation does not directly reflect the function of CD9 because it is mediated through FcγRII cross-linking by the mAbs.9,11 In contrast, FcγRII-independent effects of CD9 mAbs and the phenotype of CD9-transfected cells suggest the direct involvement of CD9 in basic cellular functions, such as proliferation, migration, and adhesion.4,12 Moreover, the recent description of CD9 knock-out mice has shown the crucial role of this molecule for sperm-egg fusion.13
Combining functional observations with biochemical data showing complex cell surface molecular associations has led to the hypothesis that tetraspanins may constitute a network of molecular interactions, the tetraspan web,14,15 and may function as surface organizers14 or facilitators.16 The organization of tetraspanins on the cell surface may allow the cross-talk of different types of surface molecules, whereas the functional properties of anti-tetraspanin mAbs might partially relate to the engagement of associated molecules. One of the molecules associated with CD9 is the integrin α4β1 (CD49d/VLA4),14,17,18 which is known to play a crucial role in hematopoiesis.19-21 Moreover, it was recently demonstrated that CD9 mAb inhibited the production of murine myeloid cells in a long-term bone marrow culture. However, in a soft-agar system, CD9 ligation did not alter the formation of granulomacrophage colonies.22 This suggested that the effect of CD9 mAb resulted from an alteration of interactions between myeloid progenitors and stromal cells that expressed CD9.23 Taken together, these results led us to investigate the possible role of CD9 in the regulation of human hematopoiesis.
Materials and methods
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies used were either conjugated (phycoerythrin [PE], fluorescein isothiocyanate [FITC], peridinin chlorophyll protein [PerCP], allophycocyanin [APC]) or unconjugated. The mAbs directed to CD13 (My-7 PE), CD14 (RM052 PE), CD19 (B4 FITC or PE), CD33 (D3HL60.251 PE), CD38 (T16 FITC), CD41/GPIIb (P2 PE), CD42a/GPIX (SZ1 FITC), CD42b/GPIb (SZ2 FITC), CD117/c-kit (95C3 PE), and GPA (11E4B-7-6 PE) were obtained from Coulter- Immunotech (Marseille, France). The mAbs directed to CD15 (Leu-M1 FITC), CD34 (8G12 FITC or PerCP), CD38 (HB7 PE), CD62P (AK-4 PE), CD90/Thy1 (5E10 PE), and HLA-DR (L243 PE) were purchased from Becton Dickinson/Pharmingen (San Jose, CA). Two mAbs directed to CD41 (5B12 PE) and CD61 (Y2/51 FITC) were from DAKO (Trappes, France). Other commercial mAbs were CLB-158 (CD7 PE; Ortho-Diagnostic, Raritan, NJ), 5B12 (CD41; Hemeris, Grenoble, France), and the rat anti-human CD9 mAb AL6 (Technopharma, Louvain, Belgium). The mouse anti-human CD9 mAb SYB-1 was biotinylated as previously reported.14 The secondary reagent for CD9 labeling was either a mouse-adsorbed goat anti-rat antibody (FITC; Southern Biotechnology Associates, Birmingham, AL) or streptavidin-APC (Becton Dickinson). As a negative control, each mAb was replaced by murine IgG of the same isotype.
Cell preparation
Normal bone marrow samples were collected on preservative-free heparin from patients undergoing hip prosthesis surgery, with the informed consent of the donors. Mononuclear cells were isolated by centrifugation on Ficoll-Hypaque (density, 1.077g/mL; Pharmacia, Orsay, France). Low-density mononuclear cells (LD cells) were washed several times in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1 mM EDTA to avoid platelet aggregation, resuspended at a concentration of 5 × 106 cells/mL in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, and incubated overnight in plastic culture flasks, at 37°C with 5% CO2 in air, to remove adherent cells.
Immunomagnetic purification of CD34+ cells
CD34+ cells were recovered from nonadherent LD cells by the immunomagnetic bead technique according to the description of the manufacturer (Isolation Kit CD34 MACS; Miltenyi Biotec, France). Briefly, nonspecific fixation was blocked with human immunoglobulin, and cells were labeled using a hapten-conjugated primary monoclonal anti-CD34 antibody (QBEND-10) and an anti-hapten antibody coupled to submicroscopic magnetic beads. The labeled cells were added to a sterile positive separation column (VS+; Miltenyi Biotech, Paris, France) placed in a magnetic field of the VarioMACS. CD34+ cells were flushed with PBS outside the column, removed from the magnetic field, and collected by centrifugation (700g). This purification procedure routinely yielded CD34+ cells that were more than 97% pure. Cell number and viability (greater than 97%) were assessed with a hemacytometer and trypan blue.
Cell immunostaining and flow cytometric analysis
Purified cells were stained with an mAb directed against the CD34 antigen (8G12 PE) and with fluorochrome-conjugated mAbs against other antigens to allow flow cytometric analysis or sorting of the cell subsets. Multiparameter analysis of the purified cells for cell surface antigen expression was performed as follows: 5 × 104cells were labeled with 10 μg/mL (saturating concentration) of conjugated mAbs at 4°C for 30 minutes in 40 μL PBS/2% bovine serum albumin and washed twice. In some experiments, a biotin-labeled mAb was used and revealed by streptavidin conjugated to APC. Immunostained cells were analyzed using 4-color Facscalibur (Becton Dickinson). For each sample, 104 to 105 events were acquired in list mode. In multiple stainings, adjustment of the crossover of fluorescence signals was obtained by compensation of the 2 single-stained samples to limit the superposition of fluorochrome emission spectra. Forward-scatter light (FS), side-scatter (SS), and 2 to 4 fluorescence signals were determined for each cell, stored in list mode data files, and analyzed with CellQuest (Becton Dickinson) or WinMDI software.
Cell sorting
Immunostained cells were sorted using a Coulter Elite flow cytometer (Coulter- Immunotech). For cell sorting, immunomagnetic-purified CD34+ cells were gated on (1) the FS/SS, excluding low FS/SS B-progenitor cells,24 (2) CD34 labeling, and (3) CD9 expression level, which was arbitrarily defined as CD9 low (25%), CD9 middle (40%), and CD9 high (25%) according to gates A, B, and C, respectively (in which CD41+ were excluded). Five percent of cells at the limits between these populations were excluded from the sorting. In some experiments, CD34+ cells were also sorted according to both CD9 and CD41 expression levels. Two gates were defined: gate D corresponded to CD41midCD9mid cells (6% to 8%), and gate E corresponded to CD41highCD9high cells (2% to 4%).
Progenitor colony assays
Total CD34+ cells and sorted subpopulations were cultured in methylcellulose medium to assess the growth of colony-forming unit–granulocyte macrophage, erythroid, and megakaryocytic (CFU-GEMM), CFU–granulocyte macrophage (GM), burst-forming unit–erythroid (BFU-E), and CFU–mastocytic (Mast). Two thousand purified cells were plated in 35-mm dishes (Becton Dickinson) in 1 mL Iscove modified Dulbecco medium (ICN) containing 1% methylcellulose (Fluka, Buchs, Switzerland), 30% selected fetal calf serum (Flow Lab), 1% bovine serum albumin (Sigma, St Louis, MO), 10−5 M 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma), 1% L-glutamine (GIBCO BRL), 1% antibiotic (Genzyme, Cergy St-Christophe, France), 2 U erythropoietin (EPO; Cilag, Italy), 10 ng stem cell factor (Amgen, Neuilly/Seine, France), 100 U IL-1β (Genzyme), 2.5 ng IL-3 (Sandoz, Basel, Switzerland), 1 ng IL-6 (Genzyme), 100 U GM-CSF (Sandoz), and 100 ng G-CSF (Dompe Biotechnology, Italy). We have previously established that such a cytokine combination was optimal for maximal colony formation from purified bone marrow CD34+cells.25 Duplicate cultures were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. CFU (50 or more cells) were scored using an inverted microscope, after 12 to 14 days of culture, on the basis of specific morphologic criteria.26
CFU megakaryocyte (CFU-MK) and BFU bipotent erythroid–megakaryocyte (BFU-E/MK) progenitors were assessed in collagen matrix by using the Easymega kit (Hemeris, Grenoble, France) according to the manufacturer's instructions.27,28 Briefly, 4 × 103 to 104 sorted CD34+cells were incubated in 1 mL serum-free Easymega medium supplemented by the following cytokines: 2.5 ng IL-3, 10 ng IL-6, and 50 ng thrombopoietin (Amgen). For BFU-E/MK assay, 2 U EPO was also added to the medium. In some experiments, purified CD34+ cells were incubated under similar semisolid culture conditions with or without a monoclonal anti-CD9 antibody (10 μg/mL) or an IgG1 isotype control (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK). Duplicate cultures were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The different types of colony were scored according to the criteria already described28 using an inverted microscope after 10 to 20 days of culture. Standard cytology staining (May-Grünwald-Giemsa) or immunocytochemistry with a CD41 mAb followed by APAAP staining was also performed for reliable and accurate identification of megakaryocytic colonies.
Megakaryocyte liquid culture
Short-term liquid cultures of human megakaryocytes were set up in duplicate wells (105 sorted cells/mL) using the same medium as for semisolid culture except for the presence of collagen. In some experiments, purified CD34+ cells were incubated in the presence of the SYB-1 CD9 mAb (10 μg/mL) or an IgG1 isotype control (R&D Systems). At various time-points of the culture, cells were harvested, counted, and labeled with mAbs directed against MK surface glycoproteins. Smears and pellets were also prepared for cytologic and ultrastructural studies. The final cell concentration was readjusted at 105 cells/mL with fresh medium containing the same mAbs.
Transmission electron microscopy
Culture cells were fixed at 4°C in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in PBS buffer for 30 minutes, washed twice in PBS, postfixed in 2% osmium tetroxide, dehydrated in graded ethanol, and embedded in epoxy resin. Thin sections (84 nm) were cut and examined with a JEOL 100C electron microscope, after uranyl acetate and lead citrate staining. At least 100 MK cells were examined under each set of culture conditions.
Statistical analysis
The significance of differences between groups was determined by Student t test for paired samples. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Distribution of the CD9 antigen on bone marrow low-density cells
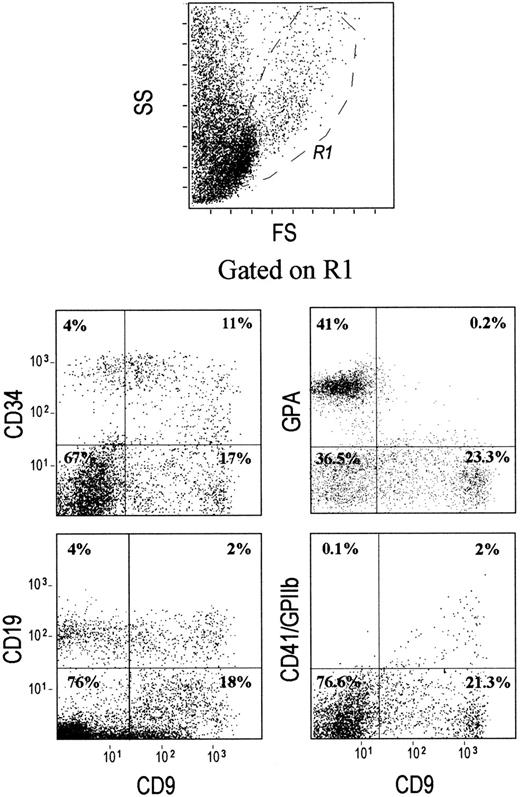
The expression of CD9 in bone marrow cells has not been accurately studied. Our results show that a minor proportion of bone marrow LD cells expresses CD9 at levels varying from negative/low to high (Figure1). Erythroid cells expressing the late differentiation marker, glycophorin A, are excluded from the CD9+ population. CD34+ cells heterogeneously express CD9 with an expression varying from low to high intensity. Interestingly, expression of the earliest megakaryocytic marker CD41 (GPIIb or integrin αIIb) is correlated with CD9 expression. All CD41high cells express high levels of CD9 antigen. The pattern of CD9 distribution in CD19+ cells (mainly B-lymphoid cells) is also heterogeneous (Figure 1). Multicolor analysis with an mAb recognizing surface immunoglobulins (sIg) allows the separation of CD19+ cells into sIg−CD9high and sIg+CD9neg/low populations (data not shown).
CD9 is expressed on CD34+, CD19+, and CD41+ cells, but not on GPA+ erythroid precursor cells.
Low-density cells were isolated from human bone marrow, stained with either CD34–PerCP-, CD19–PE-, CD41–PE-, or GPA-FITC-conjugated mAbs and were analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry. An R1 region was drawn by selecting the lymphomononuclear cells and was used for gating. The quads were set up on the isotype-matched controls dot plot. Plots shown are for one experiment representative of 10 performed using different low-density mononuclear bone marrow samples.
CD9 is expressed on CD34+, CD19+, and CD41+ cells, but not on GPA+ erythroid precursor cells.
Low-density cells were isolated from human bone marrow, stained with either CD34–PerCP-, CD19–PE-, CD41–PE-, or GPA-FITC-conjugated mAbs and were analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry. An R1 region was drawn by selecting the lymphomononuclear cells and was used for gating. The quads were set up on the isotype-matched controls dot plot. Plots shown are for one experiment representative of 10 performed using different low-density mononuclear bone marrow samples.
Antigenic characterization of the bone marrow CD34+cells according to CD9 expression
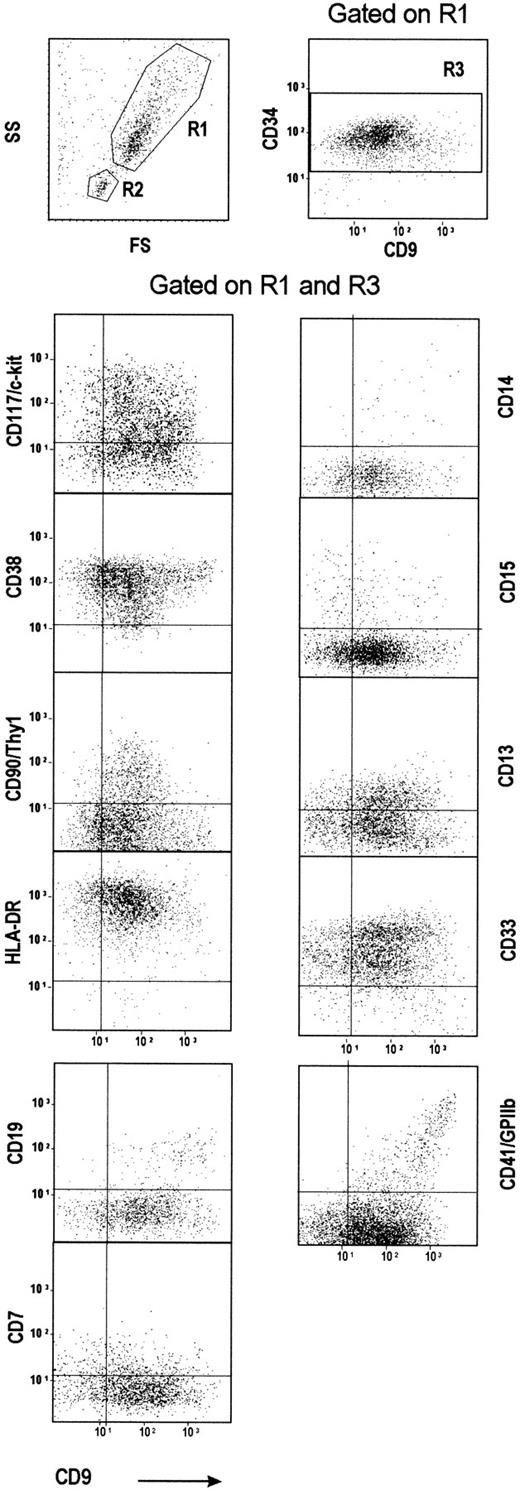
Phenotypic characterization of CD34+ cells in relation to the CD9 expression level was performed by multicolor fluorescence labeling using various lineage or differentiation-stage marker antibodies (Figure 2). As expected, the FS/SS plot showed 2 distinct CD34+ cell populations. The CD34 cells displaying the higher FS/SS value (gate R1) mainly included primitive and committed myeloid progenitors29 but few CD19+ cells. The other population, showing a lower FS/SS value (gate R2), was essentially composed of CD19+ pre-B cells (data not shown).24 In the bone marrow, the frequency of such a CD34+CD19+ cell subpopulation varied from one sample to another (10%-20%). In line with the results obtained on LD cells, when CD9/CD19 coexpression was analyzed either on R1 (Figure 2) or R2 populations (data not shown), most of the CD19+CD34+ cells expressed CD9 strongly.
Purified CD34+ cells with the highest CD9 expression are committed toward either B lymphoid (CD19+) or megakaryocytic (CD41+) lineages.
CD34+ cells were purified from human bone marrow, stained, and analyzed for the expression of CD9 and of various differentiation markers. Two gates were drawn by selecting either CD34+ cells with a high FS/SS value (R1 region) or CD34+ cells with a low FS/SS value (R2 region). A third region, R3, corresponding to CD34+ cells, was drawn on a second CD34-PerCP/CD9-APC dot plot gated on R1. The quads were set up on the isotype-matched controls dot plot. Plots shown are for one experiment representative of 10 performed using different CD34+ bone marrow samples.
Purified CD34+ cells with the highest CD9 expression are committed toward either B lymphoid (CD19+) or megakaryocytic (CD41+) lineages.
CD34+ cells were purified from human bone marrow, stained, and analyzed for the expression of CD9 and of various differentiation markers. Two gates were drawn by selecting either CD34+ cells with a high FS/SS value (R1 region) or CD34+ cells with a low FS/SS value (R2 region). A third region, R3, corresponding to CD34+ cells, was drawn on a second CD34-PerCP/CD9-APC dot plot gated on R1. The quads were set up on the isotype-matched controls dot plot. Plots shown are for one experiment representative of 10 performed using different CD34+ bone marrow samples.
We further studied the co-expression of CD9 with primitive and myeloid differentiation markers within the CD34+ population gated on the R1 plus R3 regions. Both CD38low 29 and HLA-DRlow 30 CD34+ populations have been reported to be enriched in primitive progenitor cells. The CD38/CD9 plot is triangular, indicating that the CD38low/neg cells are in the CD9mid population and suggesting that CD9 expression may precede CD38 appearance (Figure 2). The shape of the CD90(Thy1)/CD9 plot is reciprocal to the CD38/CD9 plot. The CD9/HLA-DR plot shows an even distribution of HLA-DR labeling according to CD9 expression, though a small fraction of the CD9mid cells, which contains the CD38low cells, expresses a reduced amount of HLA-DR (Figure 2).
Two different mAbs were used to detect CD41 on CD34+ cells. Few cells were labeled with mAb P2 (data not shown). In contrast, approximately 10% of cells were stained by the mAb 5B12. All the CD34+CD41+ cells were stained by the CD9 mAb. The correlation between CD9 and CD41 expression observed in LD cells was confirmed in CD34+-purified cells: CD41highcells express high levels of CD9 whereas CD41low cells are preferentially CD9mid (Figure 2). Platelet contamination was excluded by the absence of labeling with a CD42/GPIb mAb (data not shown). CD15, which is viewed as a myeloid differentiation marker,31 is heterogeneously and mainly expressed in the CD9low/mid cells. The distribution of the early myeloid markers, CD13 and CD33, is partly biphasic in CD34+ cells, with an even distribution of the 2 populations along the CD9 gradient. A small fraction of CD34+ cells expresses the monocytic marker CD14 with a heterogeneous distribution pattern according to CD9 labeling. CD7, which is expressed on primitive lympho-myeloid progenitors,31 is observed on few cells, mainly among the CD9low/mid cells.
Progenitor content according to CD9 expression
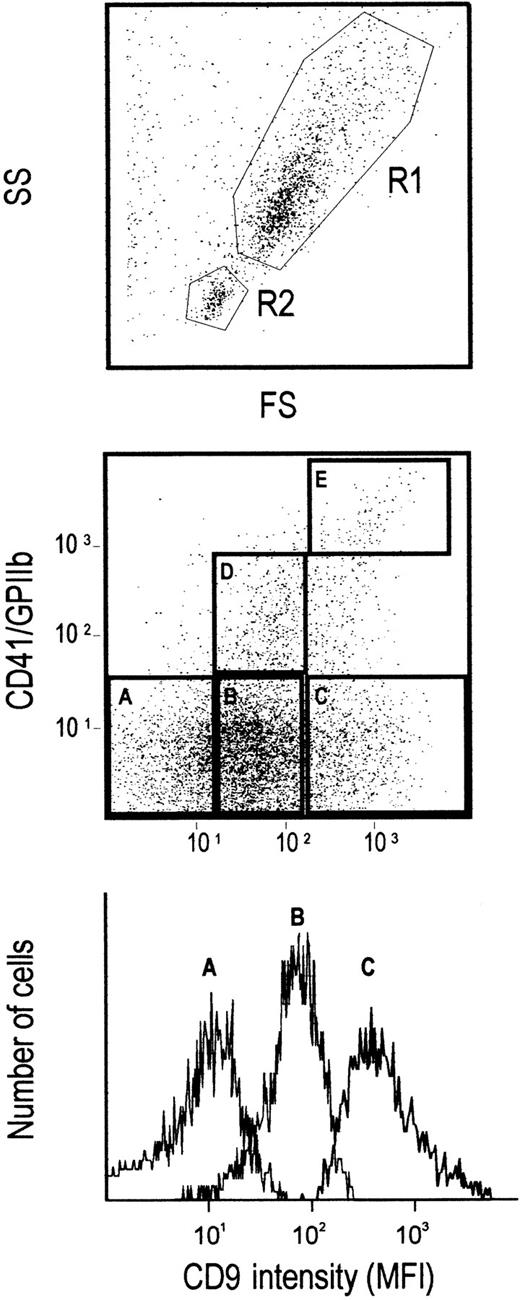
CD34+ cells (excluding the R2 low FS/SSC pre–B-cell population) were sorted according to their CD9 and CD41 expression levels (Figure 3). CD34+CD41neg bone marrow cells were sorted into CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9highsubpopulations according to gates defined in Figure 3 (gates A, B, C). Sorted cells were re-analyzed for CD9 expression and were cultured under semisolid or liquid conditions supplemented with various combinations of growth factors, as described in “Materials and methods.”
Cell sorting gates according to CD9 expression.
Purified bone marrow CD34+ cells were gated on the FS/SS high fraction (R1 region) excluding the R2 region, corresponding to the low FS/SS pre-B cell population. CD34+ cells were further sorted according to CD9 expression and excluding CD41+cells. Gates A, B, and C corresponded to the CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9high cell populations, respectively. In some experiments, CD9+CD41+cells were sorted according to CD41 expression; gates D and C corresponded to CD41mid/low and CD41high cells, respectively. The bottom histogram shows the CD9 expression in the A-, B-, and C-sorted populations.
Cell sorting gates according to CD9 expression.
Purified bone marrow CD34+ cells were gated on the FS/SS high fraction (R1 region) excluding the R2 region, corresponding to the low FS/SS pre-B cell population. CD34+ cells were further sorted according to CD9 expression and excluding CD41+cells. Gates A, B, and C corresponded to the CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9high cell populations, respectively. In some experiments, CD9+CD41+cells were sorted according to CD41 expression; gates D and C corresponded to CD41mid/low and CD41high cells, respectively. The bottom histogram shows the CD9 expression in the A-, B-, and C-sorted populations.
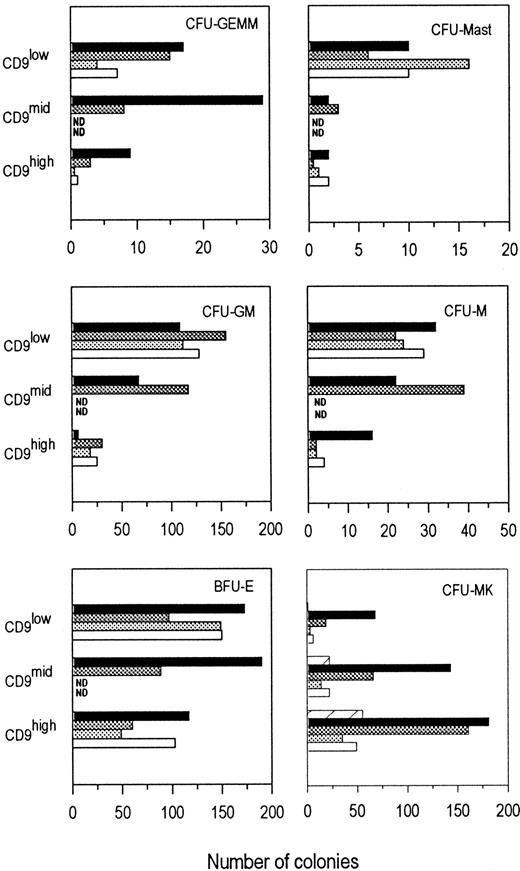
As shown in Figure 4, the CD9low fraction contained the highest proportion of CFU-mast. Pluripotent CFU-GEMM, CFU-GM, and CFU-M progenitors were preferentially found in the CD9low/mid fractions. Erythroid progenitors (BFU-E) were detected within the 3 fractions, with a slightly higher proportion in CD9low and CD9midpopulations. Furthermore, erythroid colonies present in the CD9low/mid fractions were larger than those in the CD9high factor (data not shown), suggesting that CD9low/mid fractions contained more primitive BFU-E. Interestingly, when cells from the CD9mid fraction were sorted according to their CD41 expression, the proportion of BFU-E was slightly higher in the CD41mid/low population than in the CD41neg population (250 ± 4 and 190 ± 9, respectively, for 2000 plated cells). CFU-GEMM were enriched in the CD41neg fraction compared to the CD41mid/lowpopulation (29 ± 2 and 9 ± 1 colonies, respectively, for 2000 plated cells).
Progenitor contents according to CD9 expression. CFU-MK frequency is increased in the CD34+CD9high and CD34+CD9mid cell fractions.
CD34+CD41neg bone marrow cells were sorted according to CD9 expression: CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9high (gates A, B, and C, respectively). Sorted cells were plated in duplicate or triplicate. For CFU-MK cultures, cells were plated at a density of 104 cells/mL in serum-free collagen culture. For the other myeloid progenitors (CFU-GEMM, BFU-E, CFU-GM, CFU-M, and CFU-Mast) assays, cells were plated at a density of 2000 cells/mL in methylcellulose culture. The growth factor cocktail used was adapted according to the type of progenitor cultures as described in “Materials and methods.” The histogram values represent the average number of colonies obtained per plate in one experiment; standard deviations between plates were less than 5%. Bars corresponded to 4 to 5 individual experiments using different CD34+ bone marrow samples. ND, not determined.
Progenitor contents according to CD9 expression. CFU-MK frequency is increased in the CD34+CD9high and CD34+CD9mid cell fractions.
CD34+CD41neg bone marrow cells were sorted according to CD9 expression: CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9high (gates A, B, and C, respectively). Sorted cells were plated in duplicate or triplicate. For CFU-MK cultures, cells were plated at a density of 104 cells/mL in serum-free collagen culture. For the other myeloid progenitors (CFU-GEMM, BFU-E, CFU-GM, CFU-M, and CFU-Mast) assays, cells were plated at a density of 2000 cells/mL in methylcellulose culture. The growth factor cocktail used was adapted according to the type of progenitor cultures as described in “Materials and methods.” The histogram values represent the average number of colonies obtained per plate in one experiment; standard deviations between plates were less than 5%. Bars corresponded to 4 to 5 individual experiments using different CD34+ bone marrow samples. ND, not determined.
CD9 expression and megakaryocytic lineage
In contrast to the other myeloid progenitors, when CD34+CD41− bone marrow cells were sorted into CD9low, CD9mid, and CD9highsubpopulations, CFU-MK were highly enriched in the CD9highpopulation (Figures 4, 5). Only a small proportion of CFU-MK was detected in the CD9low fraction, and an intermediate proportion was detected in the CD9midfraction. As indicated earlier, a small fraction of the CD34+CD9+ cells expresses the CD41 antigen. Therefore, we sorted CD9high and CD9mid cells according to their CD41 expression level (Figure 3). The proportion of CFU-MK was 4-fold higher in the CD9midCD41negfraction (gate B) than in the CD9midCD41mid/lowpopulation (gate D) (24 ± 2 and 6 ± 1, respectively, for 104 plated cells). In contrast, CD9highCD41high (gate E) only gave rise to a small number of differentiated megakaryocytic clusters.
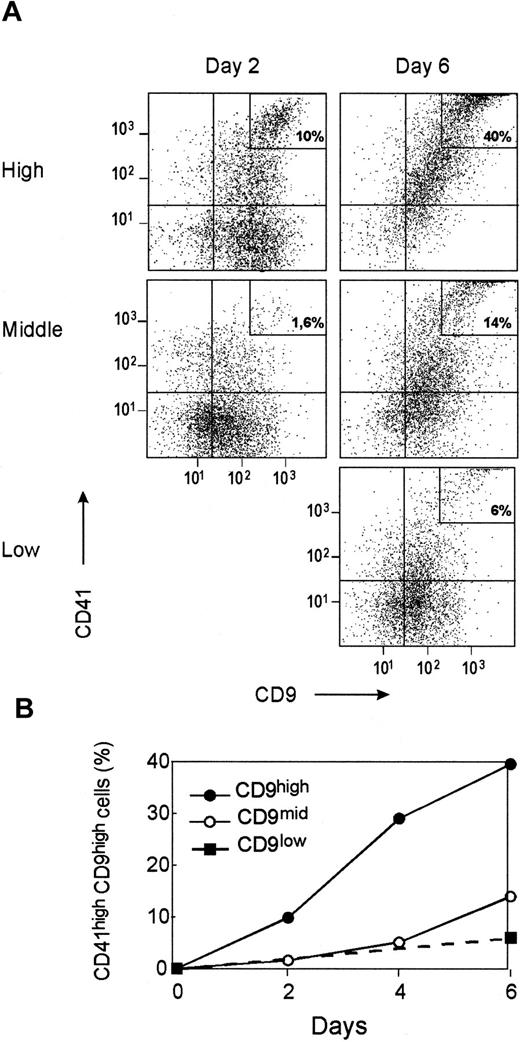
Kinetics of CD41 acquisition and CD9 modulation in megakaryocytic liquid cultures.
CD34+CD41neg cells were sorted according to CD9 expression, as shown in Figure 3, and were cultured for 6 days under megakaryocytic liquid conditions as described in “Materials and methods.” (A) Kinetics of CD9 and CD41 expression in CD34+ cell subpopulations sorted according to CD9 expression (CD9low, CD9mid, CD9high) during a 6-day culture. (B) Evolution of the percentage of CD41highCD9high cells in the different cell fractions during the culture. Plots and curves are for one experiment representative of the 4 performed using different CD34+ bone marrow samples.
Kinetics of CD41 acquisition and CD9 modulation in megakaryocytic liquid cultures.
CD34+CD41neg cells were sorted according to CD9 expression, as shown in Figure 3, and were cultured for 6 days under megakaryocytic liquid conditions as described in “Materials and methods.” (A) Kinetics of CD9 and CD41 expression in CD34+ cell subpopulations sorted according to CD9 expression (CD9low, CD9mid, CD9high) during a 6-day culture. (B) Evolution of the percentage of CD41highCD9high cells in the different cell fractions during the culture. Plots and curves are for one experiment representative of the 4 performed using different CD34+ bone marrow samples.
When EPO was added to these cultures, BFU-E/MK mainly arose from the differentiation of the CD9mid cells (21 ± 16 for 104 plated cells) compared to CD9high (7 ± 4 for 104 plated cells). Few BFU-E/MK were detected in the CD9low fraction and even then only in some experiments (data not shown).
To confirm that CD41negCD9mid or CD9high could give rise to differentiated megakaryocytes, we monitored the kinetics of CD41 acquisition and CD9 modulation in 1-week liquid cultures. Two days after seeding, the cells in the CD9high cell culture exhibited cytologic features of mature megakaryocytes, and 10% had high levels of both CD41 and CD9 (Figure5A-B). A similar evolution was observed in the CD9mid cell culture but was delayed by 3 to 4 days compared to the CD9high fraction. The CD9low population grew more slowly at the start of culture and, therefore, could not be analyzed by flow cytometry within the first 4 days. Few CD41high cells were detected in CD9low cells, even after 6 days of culture (Figure 5A-B).
Antibody ligation of CD9 alters MK cell production and modifies the membrane system during in vitro megakaryocytic differentiation
To address whether CD9 could be involved in MK differentiation, CD34+ cells were grown in liquid cultures, allowing the proliferation and differentiation of MK cells in the presence of CD9 mAb SYB-1 or of an isotype control.
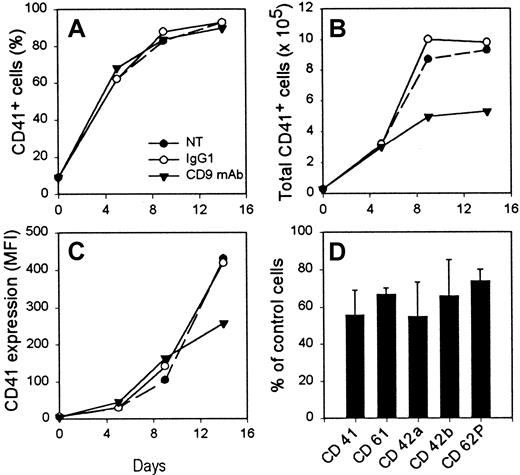
The addition of the CD9 mAb did not modify either the ploidy of the MK cells (data not shown) or the proportion of CD41+cells obtained during the culture. Actually, whether they were treated with mAbs or not, CD41+ cells represented 80% to 90% of the total number of cells on day 9 of the culture (Figure6A). In contrast, CD9 ligation greatly reduced the production of CD41+ cells because there were 50% fewer cells in the CD9 mAb-treated sample on day 9 of the culture (Figure 6B). Interestingly, these cells also showed a lower expression of early and late MK differentiation markers such as CD41, CD61, CD42a, CD42b, and CD62P (Figure 6C-D) compared to isotype-treated control cells.
CD9 mAb treatment reduces the production of MK cells from CD34+ cells in liquid culture.
Purified CD34+ cells were cultured for 16 days under megakaryocytic liquid culture conditions in the presence or absence of SYB-1 CD9 mAb or of an isotype control mAb. One experiment of 4 is shown. Percentage (A) and total number (B) of CD41+ cells determined at several time-points of the culture. (C) Level of CD41 expression at various time-points of the culture, expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (D) Variation of expression (MFI) of surface megakaryocytic markers in the presence of CD9 mAb compared to IgG1-treated cells on day 14 of the culture. NT, not treated.
CD9 mAb treatment reduces the production of MK cells from CD34+ cells in liquid culture.
Purified CD34+ cells were cultured for 16 days under megakaryocytic liquid culture conditions in the presence or absence of SYB-1 CD9 mAb or of an isotype control mAb. One experiment of 4 is shown. Percentage (A) and total number (B) of CD41+ cells determined at several time-points of the culture. (C) Level of CD41 expression at various time-points of the culture, expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (D) Variation of expression (MFI) of surface megakaryocytic markers in the presence of CD9 mAb compared to IgG1-treated cells on day 14 of the culture. NT, not treated.
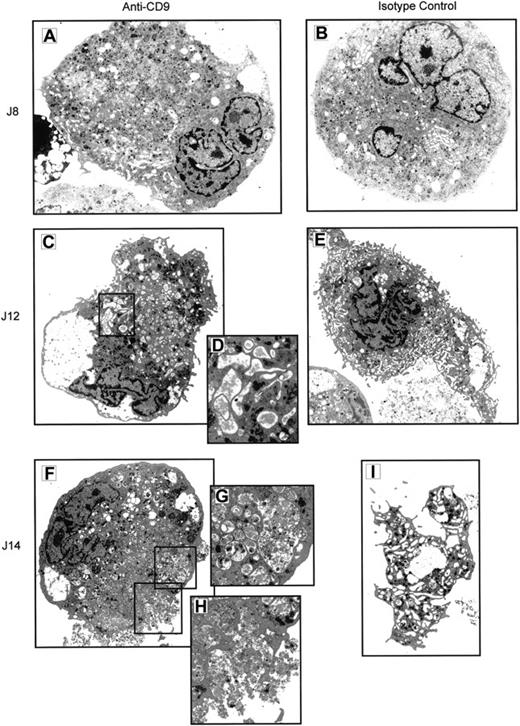
Electron microscope analysis of cells obtained after 8 to 14 days of culture confirmed that most of the cells, treated or not with a control mAb, had ultrastructural features typical of mature MKs.32 These cells had multilobed and indented nuclei, a well-developed and aligned demarcation membrane system, multivesicular bodies, and numerous specific MK granules (Figure7B). On days 12 to 14, formation (Figure7E) and shedding of proplatelets (Figure 7I) were frequently observed. When treated with the CD9 mAb, MK cells also had multilobed and indented nuclei (Figure 7A) but exhibited major cytoplasmic abnormalities. Indeed, whereas endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, and mitochondria did not show visible alterations, the plasma membrane system appeared to be deeply modified, especially on days 12 and 14 of the culture. The demarcation membrane system, with open cisternae, was not uniformly distributed throughout the cytoplasm (Figure 7A-C). Some of the cisternae contained abnormal fibrillar material (Figure 7D), and on day 14 few open cisternae were visible. Many multivesicular bodies containing vesicular, lamellar, and fibrillar material were observed on day 12. On day 14, the MK cytoplasm contained numerous heterogeneous multivesicular bodies and large vacuoles, probably resulting from the fusion of multivesicular bodies (Figure 7F-G). Final exocytosis of the vacuolar content was frequently observed at this time of culture (Figure 7H). Specific MK granules were seen on days 8 and 12 but were less numerous on day 14. Interestingly, proplatelet territories were never found in anti–CD9-treated cells, even on day 14.
Antibody ligation of CD9 alters the membrane structure and terminal maturation of MK cells in culture.
CD34+ cells were cultured for 14 days under MK conditions in the presence of CD9 mAb (A, C, D, F, G, H) or of isotype control (B, E, I) At different time-points (days 8, 12, 14), cells were harvested and analyzed by electron microscopy for ultrastructure. Isotype control cells displayed typical ultrastructural features of MKs: multilobed and indented nucleus (B), a well-developed and aligned demarcation membrane system (B, E), multivesicular bodies, numerous specific MK granules, formation (E), and shedding of proplatelets (I). CD9 mAb-treated cells also exhibited a multilobed and indented nucleus, but they showed major cytoplasmic abnormalities: demarcation membrane system heterogeneously distributed throughout the cytoplasm (A), some open cisternae containing a fibrillar material (D), numerous heterogenous multivesicular bodies (A, C, F, G), large vacuoles probably resulting from multivesicular body fusions (G), and exocytosis of the vacuolar content (H). Magnifications: × 2400 for C, E, F, I; × 3000 for A, B; × 6000 for D, G, H.
Antibody ligation of CD9 alters the membrane structure and terminal maturation of MK cells in culture.
CD34+ cells were cultured for 14 days under MK conditions in the presence of CD9 mAb (A, C, D, F, G, H) or of isotype control (B, E, I) At different time-points (days 8, 12, 14), cells were harvested and analyzed by electron microscopy for ultrastructure. Isotype control cells displayed typical ultrastructural features of MKs: multilobed and indented nucleus (B), a well-developed and aligned demarcation membrane system (B, E), multivesicular bodies, numerous specific MK granules, formation (E), and shedding of proplatelets (I). CD9 mAb-treated cells also exhibited a multilobed and indented nucleus, but they showed major cytoplasmic abnormalities: demarcation membrane system heterogeneously distributed throughout the cytoplasm (A), some open cisternae containing a fibrillar material (D), numerous heterogenous multivesicular bodies (A, C, F, G), large vacuoles probably resulting from multivesicular body fusions (G), and exocytosis of the vacuolar content (H). Magnifications: × 2400 for C, E, F, I; × 3000 for A, B; × 6000 for D, G, H.
Antibody ligation of CD9 increases the number of CFU-MK progenitors
The effect of CD9 ligation on the growth of human CFU-MK progenitors in semisolid medium was also studied. Because of individual variations in CFU-MK growth, we present individual data obtained from CD34+ cells isolated from 3 different bone marrow samples. Our results show that the addition of CD9 mAb to CD34+cells significantly increased the number of CFU-MK compared to control isotype IgG (Table 1).
CD9 ligation increases the number of CFU-MK from purified BM CD34+ cells
| Experiment . | Isotype control . | CD9 mAb . | Variation (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97 ± 1 | 137 ± 10* | + 42 |
| 2 | 76 ± 3 | 108 ± 15* | + 41 |
| 3 | 98 ± 11 | 137 ± 5* | + 39 |
| Experiment . | Isotype control . | CD9 mAb . | Variation (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97 ± 1 | 137 ± 10* | + 42 |
| 2 | 76 ± 3 | 108 ± 15* | + 41 |
| 3 | 98 ± 11 | 137 ± 5* | + 39 |
Cells were purified and plated in duplicate at a density of 104 cells/mL under human MK semisolid culture conditions in the presence of a CD9 mAb or an isotype control. Colonies were scored on day 10, and results are expressed as number of colonies (mean ± SD) in 3 independent experiments.
Significant difference from isotype control-treated cells (P < .005).
Discussion
The CD9 antigen belongs to the tetraspanin superfamily of surface molecules, which have been shown to play a role not only in cell migration or co-stimulation but also in the differentiation of non-hematopoietic and hematopoietic cells. CD9 has been shown to play a role in keratinocyte differentiation33 and in murine osteoclastic and myeloid differentiation.22-24Furthermore, the tetraspanin CD81 appears to be involved in murine thymocyte differentiation.35 However, to date, there is no evidence for the role of tetraspanins in human hematopoiesis. In this report, we have characterized the expression of CD9 in low-density mononuclear cells and in CD34+ progenitors purified from human bone marrow, and we have shown a precise regulation of CD9 expression along the megakaryocytic cell lineage. Furthermore, functional studies suggest a role for CD9 in megakaryopoiesis.
A minority of bone marrow LD cells expresses CD9. This is related to the fact that neutrophil precursors and erythroblasts,8,36which constitute the bulk of bone marrow nucleated cells, are CD9−. The expression of CD9 is correlated with that of CD41/GPIIb, the earliest megakaryocytic marker reported until now. High expression of CD9 was also found on CD34+CD10+CD19+ early B cells, which is consistent with its expression on early B-ALL cells.5
An important finding of the current study is that CD9 is expressed in nearly all CD34+ cells isolated from bone marrow; its range of expression varies from low to high levels. The combined use of multiple labeling with cell sorting and progenitor analysis points out the complex regulation of this molecule's expression during the early and late stages of hematopoietic differentiation. Because CD34++CD38lowCD90high cells are mainly contained in the CD9mid fraction, it is suggested that primitive progenitors are CD9mid. The presence of CFU-GEMM in the CD9low fraction may reflect a possible down-regulation of CD9 expression during the differentiation process from primitive to committed progenitors.
The early commitment of primitive progenitors toward erythro-megakaryocytic lineages is marked by an increase in CD9 expression, as supported by the fact that BFU-E/MK are mainly present in the CD9mid fractions. Later on, CD9 is lost upon erythroid differentiation, as shown by the lack of CD9 on GPA+ erythroid cells. In contrast, CD9 expression is increased within the megakaryocytic differentiation pathway, as demonstrated by a higher number of CFU-MK in the collagen matrix, and faster CD41+ cell production in liquid cultures arising from the CD9high cells, compared to CD9midand CD9low fractions. These results are in agreement with previous in vitro studies showing that during TPA treatment of K562 cells, a model for megakaryocytic differentiation, CD9 was up-regulated before the appearance of CD41/GPIIb.37
The relation between CD41 expression and the potential for multilineage hematopoietic differentiation has been addressed in several papers. Using single-cell38 or paired daughter cell cultures and immunolabeling,39 the erythro-megakaryocytic bipotentiality of the CD34+CD41+ cell subset has been reported.40 In the current study, sorted CD41high cells (2% of the CD34+ cells) had lost their erythroid potential and only formed clusters of mature megakaryocytic cells. However, the presence of BFU-E in the CD9midCD41mid fraction strengthened the hypothesis that CD41 can be weakly expressed at early stages of the erythro-megakaryocytic commitment.38,39 Interestingly, the presence of a low proportion of CFU-GEMM in the CD41mid/lowpopulation also supported the hypothesis that CD41 might be expressed on a fraction of pluripotent progenitors, as recently demonstrated in avians.41
The early increase in CD9 expression during in vivo and in vitro megakaryopoiesis suggested that the CD9 antigen might play a role in megakaryocytic differentiation, and antibody ligation of CD9 indeed altered the in vitro differentiation of human CD34+ cells into megakaryocytes. In the murine system, it has been suggested that CD9 is involved in osteoclastogenesis34 and in myelopoiesis.22 However, in these studies CD9, which is expressed on stromal cells, is thought to play an indirect role, possibly by modulating interactions between stromal cells, osteoclasts, and myeloid cells.23 In our study, the mechanism by which CD9 mAb altered in vitro CFU-MK formation was likely to be different because our culture system used freshly purified CD34+progenitor cells and did not rely on the presence of stromal cells.
Antibody ligation of CD9 inhibited the production of CD41+megakaryocytic cells in liquid cultures and altered terminal MK maturation. CD9 mAb treatment did not modify maturation of the nucleus, but it deeply altered the membrane structures of MK cells, such as demarcation membranes or heterogenous multivesicular body membranes, which appear to fuse with each other or with the plasma membrane. The lack of proplatelet formation in the presence of CD9 mAb and the reduced expression of surface MK markers likely result from these membrane alterations. Interestingly, it has been reported that CD9 and other tetraspanins are implicated in processes in which membranes are reorganized, especially in cell fusion. CD9 and CD81 mAbs were shown to inhibit and delay in vitro myotube formation, and overexpression of CD9 increased the formation of syncytia by myoblast-derived RD cells.42 Certain mAbs directed to tetraspanins were initially selected for their ability to inhibit the syncytia induced by different viruses.43-45 Finally, the strongest evidence that tetraspanins might be involved in membrane fusion comes from CD9 knock-out mice studies that have shown a crucial role for this molecule in sperm–egg fusion.13
In conclusion, our results showing the early up-regulation of CD9 on hematopoietic progenitors and the effect of CD9 mAb on megakaryocytic differentiation suggest that this tetraspanin plays a role in megakaryopoiesis, possibly by participating in the membrane remodeling process.
We thank Dr Masse for the continuous supply of bone marrow samples and Dr Bréard for the generous gift of mAb SYB-1. We thank Dr J. Breton-Gorius for her advice concerning the ultrastructure study of megakaryocytic cells.
Supported by Association Nouvelles Recherches Biomédicales, ARC nos. 1803 and 9203.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Marie-Caroline Le Bousse-Kerdilès, INSERM U268, Institut André LWOFF, Hôpital Paul Brousse, 14, Avenue Paul-Vaillant Couturier, 94800, Villejuif, France; e-mail:lebousse@infobiogen.fr.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal