Abstract
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can kill target cells by the granule/exocytosis pathway or the Fas-mediated apoptosis pathway. The sensitivity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells to CTL-mediated apoptosis before and after CD40 activation was examined. Resting or CD40-activated CLL cells were found to be equally sensitive to class I–restricted CTL-mediated killing. Despite expressing CD95, the CD40-activated CLL target cells were found to be resistant to apoptosis induced by CH11, an IgM CD95 monoclonal antibody (mAb). Consistent with this, inhibitors of caspases, which are involved in the Fas-induced apoptotic pathway (eg, N-carbobenzoxy-Val-Ala-Asp fluoromethyl ketone [z-VAD-fmk]), were unable to block destruction of CLL target cells by CTL. In addition, preincubation of the effector T cells with the anti-Fas ligand mAb NOK-2 failed to inhibit their subsequent ability to kill CLL target cells. On the other hand, CTL activity was blocked by inhibitors of the granule exocytosis pathway such as ethylene-glyco-tetra-acetic acid or concanamycin A. These results indicate that CD40 activation does not impair the sensitivity of CLL cells to Fas-independent CTL-mediated apoptosis.
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a disease of mature B cells that are resistant to apoptosis. The majority of CLL lymphocytes are in the Go phase, and the small number of proliferating cells suggests that the accumulation of CLL B cells is due to their prolonged survival.1-3 Indeed, antiapoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family are overexpressed in CLL B cells and may contribute to the noted resistance of CLL cells to chemotherapy.3
CLL cells express CD40 and are sensitive to CD40 signaling caused by their interaction with cells that express CD154, the CD40 ligand. CD40 activation of leukemia cells induces expression of several immune accessory molecules including CD54 (intracellular adhesion molecule–1 [ICAM-1]), CD80 (B7), and CD86 (B7-2).4,5 CD40 activation also up-regulates expression of CD95 (Fas),5-7 a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family, which can trigger apoptosis when engaged by the Fas ligand or anti-Fas monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).8 However, it is controversial whether resting or CD40-activated CLL cells are sensitive to Fas-mediated apoptosis.6,7 9-12
In addition to the Fas-dependent pathway, however, cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can kill target cells by the granule exocytosis or perforin/granzyme pathway.13,14 In the granule-mediated apoptosis pathway, CTL effectors release the pore-forming protein perforin and homologous serine proteases (granzymes) from cytoplasmic granules onto target cells.15,16 Granzyme B (GrB) is the principal serine protease necessary for inducing target-cell apoptosis via the granule apoptosis pathway.17,18 This protease can cleave all caspases of the caspase cascade, with the exception of caspase-1.19 In addition to direct activation of caspases, recent evidence indicates that GrB also can induce cell death in a caspase-independent manner by direct and efficient cleavage of both noncaspase cytoplasmic proteins and nuclear apoptotic proteins such as DNA-dependent protein kinase and nuclear-mitotic-apparatus-protein.20-22
Conceivably, CLL cells stimulated via CD40 ligation may become more resistant to CTL-mediated killing. Several studies found that ligation of CD40 could inhibit fludarabine-induced apoptosis of CLL cells in vitro.7,10,23 CD40-activated CLL cells may also be more resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis than resting CLL cells.6,7 10 If such activated cells also resist perforin/GrB–mediated killing, then CD40-activated CLL B cells could be resistant to killing by CTL. The purpose of our study was to examine the relative sensitivity of cells to CTL-mediated cytotoxicity before and after CD40-induced cell activation.
Materials and methods
Reagents
We dissolved 40 mmol/L 3,3′ dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide (DiOC6) (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) as a stock solution in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and stored the solution at 4°C. Then 50 mmol/L z-VAD-fmk (N-carbobenzoxy-Val-Ala-Asp fluoromethyl ketone) (Kamiya Biochemical, Seattle, WA) was dissolved as a stock solution in DMSO and stored at −20°C. Cytochalasin B (Sigma Chemicals, St Louis, MO) was dissolved at 5 mg/mL DMSO and stored at 4°C.
We also used the following reagents (PharMingen, San Diego, CA, unless otherwise noted): the dye, PKH26-GL (Sigma); anti-Fas mAb CH-11 (PanVera, Madison, WI); anti-Fas ligand mAb NOK-2; fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated (FITC-conjugated) mAbs specific for CD3, CD16, CD80, or CD95; phycoerythrin-conjugated (PE-conjugated) mAbs specific for CD3, CD54, or CD86; allophycocyanin-conjugated (APC-conjugated) mAbs specific for CD4, CD19, or CD56; peridinin chlorophyl protein–conjugated (PerCp-conjugated) mAbs specific for CD8; and relevant fluorochrome-conjugated isotype control mAbs.
Cells
After informed consent, blood was obtained from patients satisfying diagnostic criteria for B-cell CLL.1 24 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by density centrifugation over Histopaque 1077 (Sigma). These cells typically were at least 95% positive for CD19 and CD5, as assessed by flow cytometry. CLL cells were viably frozen in fetal bovine serum (FBS) containing 10% DMSO and stored in liquid nitrogen. T cells were isolated from PBMCs of CLL patients and normal healthy donors by positive selection with anti–CD4- and anti–CD8-conjugated magnetic beads (Dynal, Lake Success, NY) per the manufacturer's instructions. Isolation of T cells by this method resulted in more than 95% CD3 T cells, as assessed by flow cytometry.
Human acute T-cell-leukemia cells, Jurkat, and human cervical carcinoma cells, HeLa cells (American Type Culture Collection, Bethesda, MD), were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (RPMI 1640) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mmol/L L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (RPMI10). A CD154-transfected HeLa cell line was generated by electroporation of an expression vector containing the full-length human CD154 into HeLa cells, followed by selection and cloning by limiting dilution in RPMI 10 containing 1 mg/mL G418 (Mediatech Inc, Herndon, VA). Immunoblot analysis confirmed that the CD154-transfected HeLa cells released soluble CD154 (sCD154) into the supernatant.25 To generate sCD154 supernatant for the stimulation of cells, the adherent CD154-transfected HeLa cells were grown to 70% confluence in serum-free lymphocyte medium (AIM-V, Gibco, Long Island, NY) supplemented with 2.5% FBS. The medium was harvested and centrifuged at 200g for 10 minutes to remove cells and debris and then frozen in aliquots at −20°C until use.
Generation of effector CTLs
Effector CTLs were generated as described.5 On day −2, CLL B cells were stimulated by coculture with CD154-HeLa or 5 ng/mL sCD154 in the presence of 10 ng/mL recombinant human interleukin-4 (rhIL-4) (PharMingen) for 48 hours. CD40-activated CLL cells were treated with 80 μg/mL mitomycin C (Sigma) at 37°C for 1 hour and washed 3 times in serum-free AIM-V. The cells were then plated in a 96-well U-bottom plate (Corning, Cambridge, MA) at 5 × 104 cells per well in 100 μL AIM-V, where they were kept until used as stimulator cells in a mixed-lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Purified normal T cells in AIM-V medium were added at 1 × 105 cells per well in a volume of 100 μL, for a final total volume per well of 200 μL, and the plates were incubated at 37°C, 5% carbon dioxide (CO2). After 5 days, the wells were supplemented with rhIL-2 (PharMingen) to a final concentration of 50 U/mL and cultured for an additional 3 days. On day 8, the cells were harvested, counted, and then returned for a second round of coculture with fresh CD40-activated stimulator cells. This cycle was completed a total of 3 times during 24 days, after which T cells were harvested for phenotypic analysis and/or use as effectors in CTL assays.
Flow cytometry
Cells were washed and suspended in staining medium consisting of RPMI 1640, 3% FBS, 0.05% sodium azide, and 1 μg/mL propidium iodide (PI) with saturating amounts of fluorochrome-conjugated mAbs. After 30 minutes at 4°C, the cells were washed with staining media and then analyzed by flow cytometry using a fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) (FACS-Calibur; Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). Dead cells stained with PI were excluded from the analyses. The relative expression of surface antigen is described as the mean fluorescence intensity ratio (MFIR). This value is calculated by taking the MFI of cells stained with a fluorochrome-conjugated antigen-specific mAb and dividing it by the MFI of cells stained with a fluorochrome-conjugated isotype-control mAb.
Fas-mediated apoptosis assay
Jurkat, resting CLL cells, and CD40-activated CLL cells were harvested, washed, and then suspended at 1 × 106 cells per mL. We plated 200 μL aliquots in U-bottom 96-well plates, and 500 ng/mL CH-11 mAbs (PanVera) were added. For some experiments, Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cells transfected to express human Fas-ligand (CHO-FasL) (provided by Dr Mark Cantwell, San Diego, CA) were used as effector cells at an effector/target (E/T) ratio of 5:1. At 4 hours, 3,3′ DiOC6 was added to a final concentration of 40 nmol/L for 15 minutes, and the cells were examined by flow cytometry. The proportion of cells undergoing Fas-mediated apoptosis was calculated by subtracting the percentage of DiOC6dull cells of control samples (spontaneous apoptosis) from that of DiOC6dull cells of cells incubated with the anti-Fas mAb. Cells undergoing apoptosis display dull DiOC6fluorescence and are termed DiOC6dull.
CTL assay
CLL target cells were cultured with CD154-HeLa transfectants, sCD154, or medium alone in 10 ng/mL of exogenous IL-4. Target cells were harvested, washed once in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and then suspended at 2.5 × 107 cells per mL in 200 μL Diluent C buffer from the PKH26-GL dye kit (Sigma). A 16 μmol/L dye PKH26 solution was prepared in 200 μL Diluent C buffer. An equal volume of the cell suspension and PKH26 solution was then mixed in a microfuge tube and kept at room temperature for 5 minutes. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 400 μL 1% bovine serum albumin–PBS (BSA-PBS) for an additional 1 minute. The cells were suspended in 13 mL RPMI 10 and then centrifuged at 200g for 10 minutes. The supernatant was removed, and the cells were washed twice again in AIM-V medium. PKH26-labeled target cells were then suspended at 2-4 × 105 cells per mL in AIM-V medium, and 100-μL aliquots were added to FACS tubes for the CTL assay. Effector cells (100 μL) at various concentrations were then mixed with target cells, and the tubes were centrifuged at 200g for 2 minutes and then incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. At this point, DiOC6 was added to each tube at a final concentration of 40 nmol/L, the cells were gently mixed to ensure equal staining, and the tubes were incubated for 15 minutes at 37°C prior to analysis by flow cytometry. In most cases, PKH26-negative effector cells were excluded from analysis, and 5000 PKH26-labeled target cells were collected per sample.
Where indicated, PKH26-labeled targets were incubated for 1 hour with 10 μg/mL of the major histocompatability complex (MHC) class I mAb W6/32 prior to culture alone or with effector CTLs.26 At hour 0 of the CTL assay, 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk, 10 μg/mL cytochalasin B, and 2 mmol/L ethyleneglycotetraacetic acid (EGTA) were added. For concanamycin A (CMA) inhibition, effector cells were incubated for 2 hours with 10 nmol/L CMA and washed twice prior to use in the CTL assay.
Results
CTL-mediated apoptosis of allogeneic resting and CD40-activated CLL target cells
To examine the sensitivity of cells to CTL-mediated apoptosis before and after CD40 activation, we generated allogeneic CTL from the blood T cells of unrelated healthy donors.5 For stimulator cells we used CD40-activated CLL B cells, which express high levels of immune accessory molecules such as CD54, CD80, CD86, and CD95 (data not shown). On average, 76% ± 4.6% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 4) of T cells stimulated in the allogeneic-mixed lymphocyte reaction against CD40-activated CLL cells were CD8+, and 20% ± 6.4% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 4) were CD4+. Less than 2% of these cells had a natural killer (NK) cell phenotype of CD3−/CD56+/CD16+(Figure 1A,B).
Phenotypic analysis of cell surface antigens on allogeneic CTLs.
CTL effectors were generated as described in “Materials and methods.” (A) The CD4/CD8 ratio in the effector T-cell population was determined by double staining with CD8-PerCP and CD4-APC. (B) The presence of CD56+/CD16+ NK cells was analyzed by double staining with CD16-FITC and CD56-APC. Data are representative of cell surface staining from at least 3 separate experiments in which CTLs were generated.
Phenotypic analysis of cell surface antigens on allogeneic CTLs.
CTL effectors were generated as described in “Materials and methods.” (A) The CD4/CD8 ratio in the effector T-cell population was determined by double staining with CD8-PerCP and CD4-APC. (B) The presence of CD56+/CD16+ NK cells was analyzed by double staining with CD16-FITC and CD56-APC. Data are representative of cell surface staining from at least 3 separate experiments in which CTLs were generated.
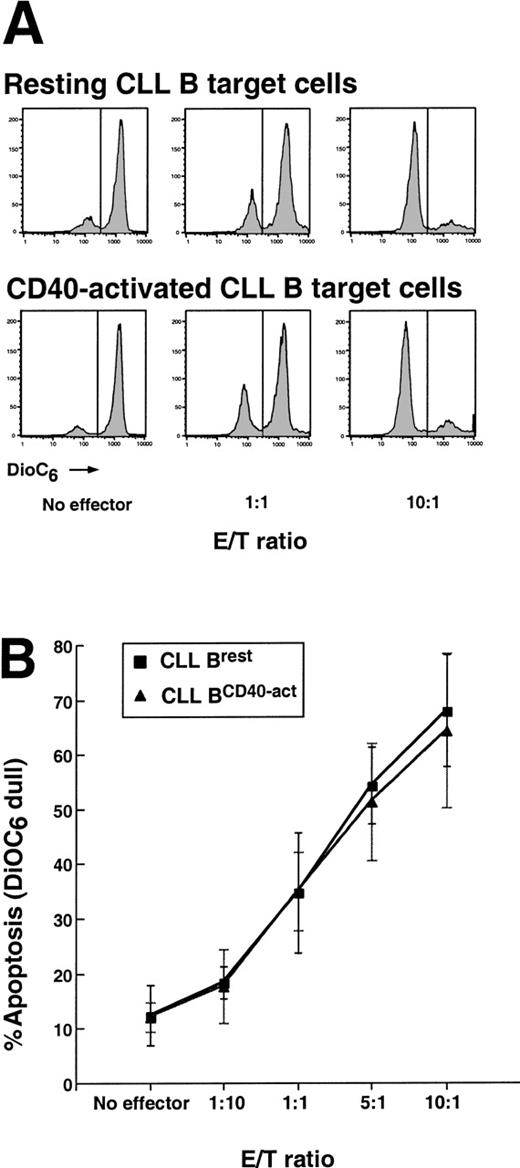
To distinguish effector cells from target cells, the CLL target cells were prelabeled with the cytoplasmic membrane dye PKH26, which displays red fluorescence when excited at 488 nm.27Effector cells were cocultured with PKH26-labeled target cells at E/T ratios of 10:1, 5:1, 1:1, and 1:10 for 4 hours. Cells were the stained with DiOC6 for 15 minutes prior to flow cytometric analysis. DiOC6 is a green fluorescent dye that monitors for changes in the inner mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), an event associated with cells undergoing apoptosis.27 28 Viable cells have high ΔΨm, display bright DiOC6 fluorescence, and are called DiOC6bright. As mentioned earlier, cells undergoing apoptosis display dull DiOC6 fluorescence and are termed DiOC6dull.
At an E/T ratio of 10:1, 68% ± 10% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 5) of the nonstimulated CLL cells or 64% ± 14% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 5) of the CD40-activated CLL cells underwent CTL-mediated apoptosis (Figure2A,B). In contrast, only 13% ± 4.9% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 5) of the nonstimulated B cells or 11% ± 2.6% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 5) of the CD40-activated B cells had detectable changes in ΔΨmwithout added effector cells over this same period. At each E/T ratio tested, the extent of CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting versus CD40-activated CLL B cells was the same (n = 5) (Figure 2A, B). We conclude that CD40-activated and resting CLL B cells are equally sensitive to allogeneic CTL-mediated killing.
Allogeneic CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting and CD40-activated CLL B cells.
(A) Fluorescence of PKH26/DiOC6–labeled target cells incubated with allogeneic effector T cells. CTL effectors were generated from normal human T cells and harvested for the CTL assay. Allogeneic CLL B target cells were mock or were CD40-stimulated for 48 hours, labeled with PKH26 to distinguish targets from effectors, and incubated with effectors at various E/T ratios for 4 hours. Cells were then stained with DiOC6 for 15 minutes prior to analysis by flow cytometry. DiOC6dull or apoptotic cells are represented by the area under each curve on the left side of each histogram. Data are from 1 experiment of 5 CTL assays. (B) The summary of CTL data from 5 separate experiments (mean plus or minus SD).
Allogeneic CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting and CD40-activated CLL B cells.
(A) Fluorescence of PKH26/DiOC6–labeled target cells incubated with allogeneic effector T cells. CTL effectors were generated from normal human T cells and harvested for the CTL assay. Allogeneic CLL B target cells were mock or were CD40-stimulated for 48 hours, labeled with PKH26 to distinguish targets from effectors, and incubated with effectors at various E/T ratios for 4 hours. Cells were then stained with DiOC6 for 15 minutes prior to analysis by flow cytometry. DiOC6dull or apoptotic cells are represented by the area under each curve on the left side of each histogram. Data are from 1 experiment of 5 CTL assays. (B) The summary of CTL data from 5 separate experiments (mean plus or minus SD).
To evaluate whether CTLs recognized CLL target cells via the CLL cell class I molecules of the MHC, we pretreated the CLL target cells with mAb W6/32, a mouse mAb specific for a nonpolymorphic epitope of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecules.26 When CLL target cells were incubated with 10 μg/mL W6/32 for 1 hour prior to their use in the CTL assay, CTL activity against both resting and CD40-activated CLL B cells was inhibited (Figure 3). The ability of W6/32 to block CTL cytotoxicity was observed in 4 separate experiments. Allogeneic CTL cells were cytotoxic only for the CLL B cells against which they were originally primed, as these cells did not manifest any cytotoxicity of leukemia cells from unrelated donors (data not shown).
Effect of blocking antibodies to MHC class I on CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells.
CLL target cells were preincubated with 10 μg/mL anti–MHC class I mAb W6/32 for 1 hour prior to initiation of the CTL assay. CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting (left) and CD40-activated (right) CLL B target cells with no pretreatment (darkened circles) or preincubated with W6/32 mAb (open circles) at an E/T ratio of 10:1. Data are representative of 1 out of 4 experiments performed with similar results.
Effect of blocking antibodies to MHC class I on CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells.
CLL target cells were preincubated with 10 μg/mL anti–MHC class I mAb W6/32 for 1 hour prior to initiation of the CTL assay. CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting (left) and CD40-activated (right) CLL B target cells with no pretreatment (darkened circles) or preincubated with W6/32 mAb (open circles) at an E/T ratio of 10:1. Data are representative of 1 out of 4 experiments performed with similar results.
Inhibitors of Fas-mediated apoptosis do not block CTL killing of CLL target cells
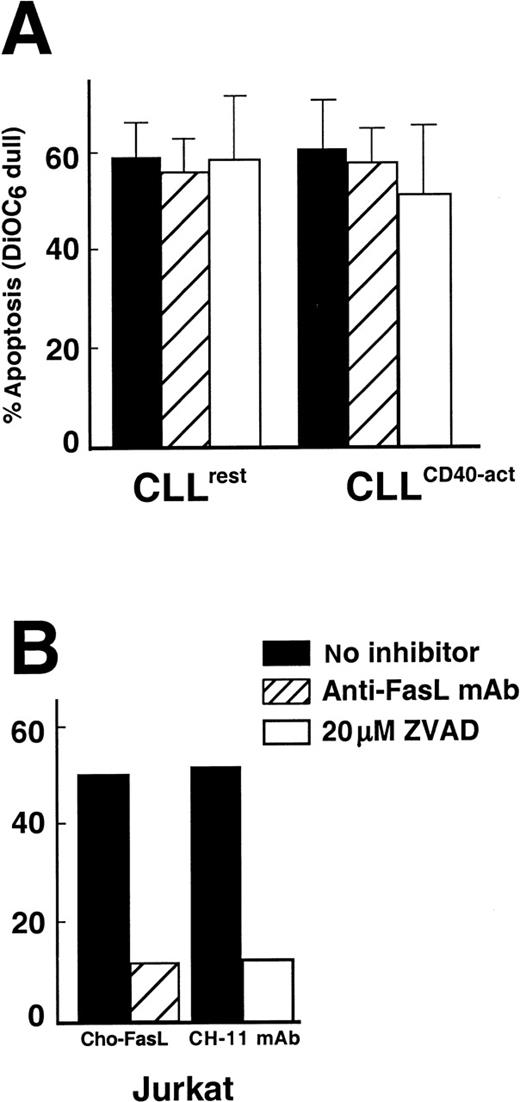
CTL assays were performed in the presence of the caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk. At an E/T ratio of 10:1, the average CTL-mediated apoptosis rate of resting CLL B cells was 59% ± 9% (mean plus or minus SD, n = 3) with 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk or 56% ± 14% (mean ± SD, n = 3) without z-VAD-fmk. The difference between treated versus nontreated groups was not significant (P = .6), and z-VAD-fmk did not have a significant effect on CTL-mediated apoptosis of CD40-activated B cells (P = .2) (Figure4A). In contrast, z-VAD-fmk was able to inhibit apoptosis of Jurkat cells induced by anti-Fas mAb (Figure 4B). We also pretreated effector cells for 45 minutes with a blocking concentration of the anti-Fas ligand mAb, NOK-2.29Pretreatment of the CHO-Fas ligand transfectants with NOK-2 inhibited Fas-mediated apoptosis of Jurkat cells. However, in 3 different experiments, pretreatment of CTL effectors had no effect on CTL-mediated apoptosis of either resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells (Figure 4A,B). Finally, the anti-Fas mAb CH-11 was unable to induce apoptosis of either resting or CD40-activated CLL cells, even at concentrations of 500 ng/mL (data not shown).
The effect of blocking antibody to FasL and a caspase inhibitor on CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells.
(A) CTL assays were performed as described in “Materials and methods” at an E/T ratio of 10:1, with 2 exceptions: (1) CTL effectors were preincubated for 45 minutes with MOPC21 control (black bars) or with NOK-2 anti-FasL mAb (hatched bars), or (2) the CTL assay was performed in the presence of 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk (open bars). Results are the mean plus or minus SD from 3 separate experiments. (B) CHO-FasL effector-mediated apoptosis of Jurkat cells in which effectors were either preincubated with MOPC21 control (black bar) or NOK-2 (hatched bar). Jurkat cells were also treated with anti-Fas mAb CH-11 for 4 hours in the absence (black bar) or presence (open bar) of 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk.
The effect of blocking antibody to FasL and a caspase inhibitor on CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells.
(A) CTL assays were performed as described in “Materials and methods” at an E/T ratio of 10:1, with 2 exceptions: (1) CTL effectors were preincubated for 45 minutes with MOPC21 control (black bars) or with NOK-2 anti-FasL mAb (hatched bars), or (2) the CTL assay was performed in the presence of 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk (open bars). Results are the mean plus or minus SD from 3 separate experiments. (B) CHO-FasL effector-mediated apoptosis of Jurkat cells in which effectors were either preincubated with MOPC21 control (black bar) or NOK-2 (hatched bar). Jurkat cells were also treated with anti-Fas mAb CH-11 for 4 hours in the absence (black bar) or presence (open bar) of 20 μmol/L z-VAD-fmk.
Allogeneic CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL target cells occurs via the granule exocytosis-mediated apoptosis pathway
Cytochalasin B, an inhibitor of E/T cell-conjugate formation, inhibited CTL cytotoxicity at an E/T ratio of 10:1 (data not shown). The granule exocytosis apoptosis pathway is calcium-dependent and can be inhibited with EGTA.14 The addition of 2 mmol/L EGTA completely inhibited CTL-mediated cytotoxicity of allogeneic CLL target cells (Figure 5). CMA selectively inhibits the granule exocytosis pathway by causing degradation of the pore-forming protein perforin.30 31 CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells was almost completely abrogated when the CTLs were pretreated with 10 nmol/L CMA for 2 hours prior to the assay (Figure5).
Effect of EGTA and CMA on CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting (left) and CD40-activated (right) CLL B cells.
A CTL assay was performed with (diagonal hatched bar) or without (black bar) 2 mmol/L EGTA, or CTL effectors were pretreated for 2 hours with 10 nmol/L CMA (open bars). CLL B target cells alone without effector cells (cross hatched bars). Data are the mean of 3 experiments plus or minus SD.
Effect of EGTA and CMA on CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting (left) and CD40-activated (right) CLL B cells.
A CTL assay was performed with (diagonal hatched bar) or without (black bar) 2 mmol/L EGTA, or CTL effectors were pretreated for 2 hours with 10 nmol/L CMA (open bars). CLL B target cells alone without effector cells (cross hatched bars). Data are the mean of 3 experiments plus or minus SD.
Discussion
We find that resting and CD40-activated CLL B cells are equally sensitive to MHC class I–restricted CTL-mediated apoptosis. In vitro priming of normal human T cells against CD40-activated CLL cells preferentially expanded CD8+ CTLs. Coculture of nonactivated or CD40-activated CLL B cells with allogeneic CTLs at an E/T ratio of 10:1 induced on average at least 60% apoptosis of both target cell populations in 5 separate experiments. Furthermore, with all E/T ratios tested, CLL B cells before and after CD40 activation were equally sensitive to CTL-mediated apoptosis.
CTL-mediated apoptosis of resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells did not occur through the FasL/Fas apoptosis pathway. First, the blocking antibody to FasL had no effect on CTL-mediated killing. In contrast, the anti-FasL blocking antibody completely inhibited CHO-FasL mediated apoptosis of Jurkat cells. Second, z-VAD-fmk, a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor that can block Fas-mediated apoptosis,32had no significant effect on CTL-mediated apoptosis of either resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells. Finally, we could not induce apoptosis of either resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells with anti-Fas mAb CH-11. Because of these results, we conclude that the CTL-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells does not occur via a Fas-dependent pathway.
These findings contrast with some reports indicating that CLL cells are susceptible to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Williams and colleagues,11 for example, recently reported that FasL-expressing effectors could induce apoptosis of nonactivated CLL cells from each of 8 patients studied. Moreover, 2 other groups reported that CD40 activation of CLL B cells actually increased the sensitivity of these cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis in 4 of 17 cases.6 12
Others, however, have found that CLL cells are resistant to Fas-mediated killing, particularly after CD40 ligation.6,7,9 10 Consistent with these reports, we were unable to induce either resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells to undergo apoptosis with anti-Fas mAb, despite the fact that CD40-activated CLL cells expressed high levels of Fas (CD95) (data not shown).
Resting and CD40-activated CLL B cells overexpress antiapoptotic factors such as Bcl-2 and the antiapoptotic protein, Mcl-1.3,7 Moreover, CD40 ligation on CLL B cells has been shown to enhance expression of Mcl-1 and FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP), a cytosolic protein that can compete with caspase-8/Fas-associated-death-domain-like IL-1β-converting enzyme (FLICE) for binding to the Fas-associated-death-domain (FADD)/mediator-of-receptor-induced toxicity-1 (MORT1) death domain.7,33 While it is not certain whether CD40 activation enhances the resistance to cytotoxic drugs in vivo, the enhanced expression of such antiapoptotic factors may explain in part the noted resistance of CD40-activated CLL cells to fludarabine-induced apoptosis in vitro.7,10 23
Nevertheless, we found that CD40-activated CLL cells are as sensitive as nonactivated leukemia cells to CTL-induced apoptosis. This is similar to findings reported for neoplastic B cells from patients with pre–acute lymphoblastic leukemia (pre-ALL) or follicular lymphoma (FL).34 35 We extended these findings to CLL and found that CTL-mediated apoptosis of both resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells was Fas-independent and mediated via the granule exocytosis pathway in an MHC class I restricted manner.
Consistent with this, we found that the Ca++ chelator EGTA effectively blocked CTL-mediated lysis of CLL target cells. The pore-forming action of perforin contained within CTL granules is Ca++–dependent.14,36 However, CTL killing via the Fas-dependent pathway is independent of exogenous Ca++.37,38 Finally, pretreatment of CTL effectors with CMA, which causes the degradation of perforin-containing lytic granules,30 31 also effectively inhibited CTL-mediated lysis of both resting and CD40-activated CLL target cells. Based on these data, we conclude that CTL-induced apoptosis of resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells is mediated by the granule exocytosis pathway.
There are several reasons why overexpression of antiapoptosis proteins does not prevent CTL-induced apoptosis of either resting or CD40-activated CLL cells. First, the effects of antiapoptotic proteins are likely cell-type specific, and there is no evidence that Bcl-2 family proteins inhibit granule- or GrB-mediated apoptosis of CLL B cells. Although overexpression of Bcl-2 is thought to be causal in chemoresistance of CLL B cells, a direct correlation between Bcl-2 expression levels and clinical response has not been found.3,39 Second, although Bcl-2 effectively blocks apoptosis induced by GrB, the predominant granzyme contained within CTL effector granules, Bcl-2 does not block cytotoxicity mediated by CTLs.21 40 This indicates that heretofore unknown granzymes or other proteases within effector granules may induce GrB-independent cell death. Presumably, these agents induce apoptosis of CLL B cells in a manner that is not affected by the antiapoptotic proteins overexpressed in resting or CD40-activated CLL B cells.
We and others have shown that CD40-activated CLL B cells can act in vitro as effective APCs and stimulate the production of CLL B cell-specific CTLs.5,41 These findings are relevant to clinical trials using CD40-activated CLL B cells as a vaccine to induce an antileukemia immune response in vivo. Results from a recently completed phase I protocol indicate that patients with CLL experience decreases in total lymphocyte counts and lymph node size following infusion with autologous CLL B cells that had been transfected to express the ligand for CD40 (CD154).42 As such, there can be apparent reduction in tumor mass even in the setting of CD40 activation. The finding that CLL B cells can be killed effectively by specific CTLs, even after CD40 activation, indicates that strategies which induce CLL-specific CTLs, either through gene transfer of CD1545 or allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation,43 may have therapeutic potential for patients with CLL.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs Laura Rassenti and Kazunori Kato for their helpful discussions and Esther Avery for her help in some of the flow cytometric analyses.
Supported by grants P01CA81534-02 and RO1CA49870-12 from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD.
Reprints:Thomas J. Kipps, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology, University of California at San Diego, 9500 Gilman Dr, La Jolla, CA 92092-0663; e-mail: tkipps@ucsd.edu.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.




This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal