Fourteen patients with PML/RAR-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) were given salvage therapy at the time of first molecular relapse. All patients had achieved first molecular remission after the AIDA protocol (all-trans retinoic acid [ATRA] + idarubicin) and were being prospectively monitored by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Molecular relapse was defined as reappearance of RT-PCR–positivity for the PML/RAR fusion (sensitivity 10−4) in 2 successive marrow samples collected during postconsolidation monitoring. The median duration of first molecular remission was 7.5 months (range, 2 to 25). Salvage therapy consisted of oral ATRA for 30 days followed by 4 daily courses of chemotherapy (CHT) with cytarabine 1 g/m2/d and mitoxantrone 6 mg/m2/d. Second molecular remission was obtained in 12 of 14 patients (86%). Seven of these 12 attained molecular remission after ATRA alone. Of the 2 patients who persisted PCR+ after CHT, 1 died in remission and 1 progressed to hematologic relapse. Of 12 patients PCR−, 8 received consolidation with autologous bone marrow transplantation (ABMT), and 4 received ATRA-containing maintenance. Ten patients in this group are in sustained second molecular remission at a median time of 9.5+ months (range, 4 to 22+) and 2 underwent hematologic relapse 6 and 13 months, respectively, after transient second molecular remission. The 2-year Kaplan and Meier survival estimate from time of relapse was 92% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 61% to 98%) in this series, and 44% (95% CI: 35% to 52%) in a previous series of 37 patients who received the same treatment at the time of hematologic recurrence (P < .05, by log-rank test). This study suggests that early administration of salvage therapy is advantageous in APL and represents the first experience on therapy of molecular relapse in acute leukemia.
ACUTE PROMYELOCYTIC leukemia (APL) is characterized by a specific chromosome translocation t(15;17) and a unique response to the differentiating agent all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). Although combined treatment with anthracycline-based chemotherapy and ATRA induces long-lasting remission and potential cure in up to 70% of newly diagnosed patients, early death during induction and occurrence of relapse still represent the major obstacles to final cure in this disease.1-4
At the molecular level, the t(15;17) results in a hybrid PML/RARα gene, which is readily identified by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Besides allowing a more rapid and refined diagnosis, this test has proven useful for minimal residual disease monitoring during follow-up.5-7 Using conventional RT-PCR assays with sensitivity between 103 and 104, several investigators have shown that detection of residual PML/RARα transcript during remission predicts subsequent hematologic relapse.8-15 This was confirmed in a recently reported study of the GIMEMA group (Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche Maligne dell’ Adulto) in which patients enrolled in the AIDA (all-trans retinoic acid + idarubicin) trial were prospectively monitored at preestablished time intervals.16
As a result of these findings, our group elected to anticipate salvage therapy in those patients who, at any time after front-line induction and consolidation, showed conversion from PCR− to PCR+ for PML/RARα while remaining in hematologic remission. We report here a clinical and laboratory study on an initial series of 14 APL patients treated at the time of first molecular relapse.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients and previous therapy.
Fourteen patients with PML/RARα-positive APL who were given salvage therapy at the time of first molecular relapse are included in this study. All cases were initially enrolled for front-line therapy in the GIMEMA trial AIDA17 and were prospectively monitored by RT-PCR of PML/RARα at the following preestablished time intervals: every 2 to 3 months during the first year, every 4 months during the second and third year, and every 6 months thereafter. Median age was 39.5 years (range, 19 to 65), median white blood cell (WBC) count was 5.4 × 109/L (range, 0.6 to 165.7). As to the type of PML/RARα fusion detected at diagnosis, 9 patients showed a bcr3 and 5 patients a bcr1 PML/RARα isoform. According to the AIDA study design,17 after the end of consolidation, 12 patients were randomized to receive some type of maintenance, and 2 patients to no further therapy. In the former group, 5 patients were assigned to ATRA-containing maintenance (ATRA alone in 1 case and ATRA plus methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine chemotherapy in 4 cases), and 7 patients to chemotherapy alone. Detailed doses and schedules of maintenance treatments are reported elsewhere.17 The median duration of first molecular remission was 7.5 months (range, 2 to 25 months).
Criteria for molecular relapse.
In patients showing no evidence of disease at the morphologic analysis, molecular relapse was defined as the conversion from PCR− to PCR+ for PML/RARα detected in 2 successive postconsolidation bone marrow (BM) samples collected 2 to 4 weeks apart. The practice of confirming PCR positivity in a separate BM sample before administering salvage therapy was established by our group based on 2 considerations: (1) transient PCR positivity not resulting in clinical recurrence had been detected, although very rarely, in our series (unpublished observations); (2) this practice represents a further cautionary step, which may allow to rule out false positivity due to contamination of the first sample. Patients who converted to PCR+ while in morphological remission in the BM, but showed simultaneous overt disease in the central nervous system (CNS) or other extramedullary sites, are not included in this study.
RT-PCR of PML/RARα.
Sequential BM samples were collected in each patient at established time intervals for identification of molecular relapse and to assess response at the PCR level during and after salvage treatment. Mononuclear cells from BM aspirates were prepared locally at the participating institutions in the Italian multicenter AIDA study and suspended in a 4-mol/L guanidium thiocyanate (GTC) solution as reported.16,17 Cryopreserved GTC samples were sent in dry ice to 1 of 2 referral molecular biology laboratories (Hematology, University “La Sapienza” of Rome and Clinica Pediatrica, University of Milano-Monza). Reagents and experimental conditions for RT-PCR of PML/RARα, sensitivity level of the reaction, and interlaboratory quality control experiments to assess results reproducibility have been reported elsewhere.16 17
Therapy for molecular relapse.
After confirmation of molecular relapse, all patients received as reinduction ATRA 45 mg/m2/d by mouth for 30 days. This was followed, after 1 week of rest, by cytosine arabinoside 1 g/m2 days 1 through 4 (intravenous [IV] infusion over 6 hours) and 3 hours after the end of cytosine arabinoside, mitoxantrone 6 mg/m2 days 1 through 4 by IV bolus. Patients who converted to PCR− were consolidated with unpurged autologous BM transplantation (ABMT). BM harvest was collected at the time of second molecular remission. In 6 patients, the conditioning regimen was based on the BAVC protocol (carmustine [BCNU], cytarabine [Ara-C], amsacrine [m-AMSA], and etoposide [VP16]),18 while patients no. 2 and 7 received busulfan and cyclophosphamide according to the schedule reported by Tutschka et al.19 Patients not eligible for ABMT after reinduction were given maintenance therapy with intermittent ATRA, methotrexate, and 6-mercaptopurine, as reported.17Survival was calculated from the time of molecular relapse according to the Kaplan and Meier life tables.20
RESULTS
Response to reinduction treatment.
Response to therapy was assessed by molecular analysis of BM samples collected after ATRA alone, after chemotherapy, and at various time points after ABMT and/or during follow-up. All samples used for molecular studies were blindly analyzed in parallel by light microscopy to confirm the status of hematologic remission. ATRA was always administered on an outpatient basis and no relevant side effects were recorded during this treatment. After reinduction with ATRA alone, 7 patients (50%) tested PCR− for the PML/RARα hybrid. After completing chemotherapy with cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone, 12 of 14 (86%) tested PCR−, while 2 (14%) persisted PCR+ and in hematologic remission. The results of serial RT-PCR analyses are shown in Table 1.
Patients’ Outcome After Salvage Therapy
| Patient No. . | Duration of 1st Molecular Remission . | PML/RARα PCR After Salvage Therapy . | ABMT . | Duration of 2nd Molecular Remission . | Outcome . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-ATRA . | Post-CHT . | BM Harvest . | |||||
| 1 | 11 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 22+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 2 | 11 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 17+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 3 | 12 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 16+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 4 | 2 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 13 | Hematologic relapse at 13 mo; 3rd molecular remission with ATRA/MTZ/AraC |
| 5 | 11 | Neg | Neg | ND | ND | 11+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 6 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | ND | 10+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 7 | 7 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 9+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 8 | 9 | Pos | Neg | ND | ND | 8+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 9 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 7+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 10 | 4 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 6+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 11 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 6 | Hematologic relapse at 8 mo; patient is presently receiving As2O3 therapy |
| 12 | 25 | Pos | Neg | Neg | ND | 4+ | A & W in 2nd hematologic remission |
| 13 | 2 | Pos | Pos | ND | ND | — | Hematologic relapse at 10 mo; 2nd hematologic remission after As2O3 |
| 14 | 8 | Pos | Pos | ND | ND | — | Hemorrhagic death in remission |
| Patient No. . | Duration of 1st Molecular Remission . | PML/RARα PCR After Salvage Therapy . | ABMT . | Duration of 2nd Molecular Remission . | Outcome . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-ATRA . | Post-CHT . | BM Harvest . | |||||
| 1 | 11 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 22+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 2 | 11 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 17+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 3 | 12 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 16+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 4 | 2 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 13 | Hematologic relapse at 13 mo; 3rd molecular remission with ATRA/MTZ/AraC |
| 5 | 11 | Neg | Neg | ND | ND | 11+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 6 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | ND | 10+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 7 | 7 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 9+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 8 | 9 | Pos | Neg | ND | ND | 8+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 9 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 7+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 10 | 4 | Pos | Neg | Neg | Yes | 6+ | A & W in 2nd molecular remission |
| 11 | 3 | Neg | Neg | Neg | Yes | 6 | Hematologic relapse at 8 mo; patient is presently receiving As2O3 therapy |
| 12 | 25 | Pos | Neg | Neg | ND | 4+ | A & W in 2nd hematologic remission |
| 13 | 2 | Pos | Pos | ND | ND | — | Hematologic relapse at 10 mo; 2nd hematologic remission after As2O3 |
| 14 | 8 | Pos | Pos | ND | ND | — | Hemorrhagic death in remission |
Abbreviations: ABMT, autologous bone marrow transplantation; ND, not done; A & W, alive and well; CHT, chemotherapy.
Clinical and molecular outcome.
Of the 2 patients persistently PCR+ after reinduction, 1 (no. 14) died of intracranial hemorrhage during postchemotherapy aplasia and 1 (no. 13) had hematologic relapse 10 months later, despite receiving additional chemotherapy. This latter patient is presently in second hematologic (PCR+) remission after 1 cycle of IV arsenic trioxide (kindly supplied by PolaRx Inc, New York, NY). In the group of patients PCR− after reinduction, 2 patients (nos. 5 and 8) showed prolonged BM hypoplasia, which was complicated by pulmonary infection in 1 case. These 2 patients as well as patients no. 6 (ABMT refusal) and 12 (on waiting list for ABMT, not yet performed due to logistic problems), were given after reinduction maintenance treatment with ATRA, methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine as reported.17 The remaining 8 patients who experienced no significant toxic effects after salvage treatment underwent unpurged ABMT at a median time interval of 2 months (range, 1 to 5 months) from the achievement of second molecular remission. RT-PCR analysis confirmed in all cases absence of PCR-amplifiable PML/RARα transcripts in the BM harvest. No major toxic effects were recorded during and after ABMT procedures.
Ten patients (no. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 12 in Table 1) have remained in sustained second molecular remission for a median time of 9.5+ months (range, 4 to 22+). This group included 6 of the 8 autografted and all the 4 nonautografted patients. Two patients (no. 4 and 11), both in the ABMT group, had hematologic relapse at 13 and 8 months from the achievement of second molecular remission. In case no. 4, overt disease recurrence was not predicted by RT-PCR monitoring, which yielded persistently negative results up to 2 months before relapse. This patient underwent second hematologic remission with oral ATRA and third molecular remission after cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone chemotherapy. In case no. 11, hematologic relapse was preceded by a PCR+ test performed 2 months earlier (Table1). This patient was resistant to further therapy with ATRA and is currently receiving arsenic trioxide.
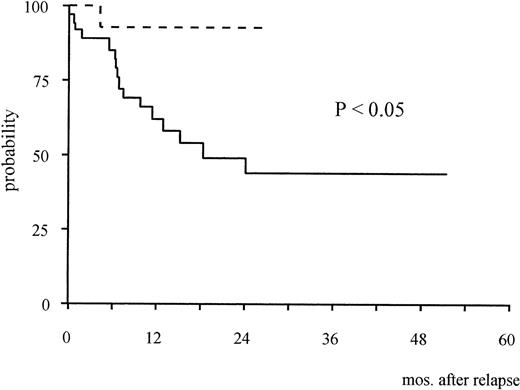
The 2-year Kaplan-Meier estimate of survival from the time of first molecular relapse was 92% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 61% to 98%). This was compared with survival of 37 patients enrolled in the AIDA study who were treated with the same reinduction approach at the time of hematologic recurrence (historical controls). In this latter group, median age was 35.3 years (range, 9.5 to 73.8), median WBC count at presentation was 2.3 × 109/L (range, 0.3 to 85.5) and median duration of first hematologic remission was 12.2 months (range, 5.2 to 29.1). The median duration of first molecular remission was 6 months (range, 2 to 23) in 23 patients of the historical group who were adequately monitored during follow-up; hematologic relapse was preceded by a positive PML/RARα test in 20 of these 23 cases. The 2-year estimate survival from the time of hematologic relapse for the historical series was 44% (95% CI: 35% to 52%). The difference with survival of the 14 patients treated for molecular relapse was statistically significant (P < .05, Fig 1).
Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival from relapse in patients treated at the time of molecular relapse (dotted line) and in the historical series of patients treated for hematologic relapse (continuous line).
Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival from relapse in patients treated at the time of molecular relapse (dotted line) and in the historical series of patients treated for hematologic relapse (continuous line).
DISCUSSION
The availability of a disease-specific and PCR-detectable molecular marker has recently allowed a more refined assessment of response to treatment and relapse risk in patients with APL. As a consequence, several investigators have adopted the term molecular remission, corresponding to therapy-induced conversion to PCR−for the PML/RARα in the BM, as a more advanced therapeutic goal in this disease.17,21-24 On the other hand, a number of monitoring studies have shown that reappearance during hematologic remission of PCR+ cells almost invariably predicts recurrence of overt disease.8-15 After confirmation of this in a prospective monitoring study,16 we started considering as having molecular relapse those patients who converted from PCR− to PCR+ during hematologic remission and decided to early administer salvage treatment in such cases.
It must be emphasized that such clinical correlations have been established using relatively insensitive PML/RARα PCR assays (capable of detecting beween 10−3 and 10−4positive cells). By contrast, the use of techniques characterized by greater sensitivity, including amplification of the reciprocal RARα/PML hybrid, have yielded prognostically less informative results, due to the detection of residual transcripts in some patients in long-term remission.25
The present study has 2 main weaknesses, which prevent us from drawing firm conclusions on the advantage of anticipating salvage treatment in APL. First, our series includes a small number of patients whose follow-up is relatively short. In addition, it was quite difficult for us to find an adequate control group, such that a historical series of patients treated with the same approach had to be used to compare survival. Indeed, given the high risk of early mortality in APL patients with overt disease, we considered unethical comparing early versus delayed therapeutic intervention in a randomized study, even though we realize that this would be the best methodologic approach to test this issue. Despite the above limitations, this study represents, to the best of our knowledge, the first report on the treatment of molecular recurrence in acute leukemia, and we believe that it contains some interesting preliminary observations.
Early therapy of relapse, ie, intervening on a minimal tumor burden, minimizes the most serious disease- and treatment-related risks of APL, such as hemorrhagic death and the life-threatening ATRA syndrome. All patients in the present study could be treated on an outpatient setting for ATRA administration with no toxic effects being recorded. Subsequent chemotherapy, however, was associated with important toxicity in 3 cases, including 1 death in remission, which occurred during marrow aplasia.
Second, most patients in this series had aggressive disease, as indicated by the initial median WBC count (5.4 × 109/L), and by first molecular remission duration, which was ≤12 months in 13 of 14 and extremely short (≤6 months) in 6 of 14 cases (Table 1). In addition, they all relapsed at the molecular level after having received optimal front-line therapy including simultaneous ATRA and anthracycline-containing chemotherapy, the only exception being patient no. 2 who could not complete the programmed induction schedule due to ATRA toxicity. This notwithstanding, a status of second molecular remission could be achieved in 86% of patients. Furthermore, half of the patients showed conversion to PCR− after ATRA alone, a phenomenon that is only occasionally observed in patients receiving ATRA for clinically overt disease.8,10 Recently, Grimwade et al26 also reported the achievement of molecular remission in 2 patients who received ATRA as therapy for minimal residual disease.
Given the relative insensitivity of the RT-PCR assay used, it is presumable that the molecular remissions observed after ATRA alone reflect the reduction of tumor burden below the PCR detection threshold, rather than eradication of leukemia. For that reason, we decided to adopt as treatment for molecularly relapsed APL the same intensive approach used by our group for patients in hematologic relapse. In this latter subset, we recently reported the achievement of prolonged second molecular remission with ATRA followed by chemotherapy and ABMT for patients with PCR− BM.27However, all 4 patients who could not receive ABMT in the present study had prolonged second molecular remission; thus, the advantage of using ABMT in addition to ATRA and chemotherapy remains unclear.
Due to heterogeneity of potentially relevant prognostic factors (eg, age, WBC count, PML/RARα isoform, type of maintenance and first molecular remission duration), we were unable to do a pair-matched comparative analysis between patients treated for molecular and hematologic relapse. However, patients in the historical control group had a significantly worse survival compared with those treated for molecular relapse. In particular, 16 of 37 (43%) patients have died in the former group, compared with 1 of 14 (7%) in the molecular relapse category (Fig 1). Our results in patients treated for first hematologic relapse are in line with those of the MRC group, who recently reported a remission rate of 65% and 50% and 2-year survival rates of 44% and 43% for patients relapsing at the hematologic level after chemotherapy plus short or extended ATRA, respectively.28
While our preliminary observations suggest a benefit in anticipating salvage therapy in APL, it is difficult to establish which is the best treatment approach for minimal disease recurrence. Recent observations with arsenic trioxide (As2O3) indicate that this agent is more potent than ATRA for inducing molecular remission.21 Although long-term results of As2O3 are not yet available, its use in the particular setting of molecular relapse might be encouraged. However, due to the relative infrequency of relapses in this disease, comparative (ie, phase III) studies aimed at evaluating different approaches will most likely require collaborative efforts at the multiinstitutional or even multinational level.
Supported by grants from ROMAIL (Associazione Italiana contro le Leucemie, sez. di Roma), AIRC (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro), and Fondazione Tettamanti (Monza).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
Author notes
Address reprint requests to Francesco Lo Coco, MD, Dipartimento di Biotecnologie Cellulari ed Ematologia, Università “La Sapienza” Via Benevento 6, 00161 Rome, Italy; e-mail:lococo@bce.med.uniroma1.it.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal