Key Points
Melanocortin fusion protein protects fibrinogen and prevents TIC in a rat model of polytrauma with hemorrhagic shock.
IL-6–activated monocytes can induce oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen in a mitochondrial superoxide–dependent fashion.
Abstract
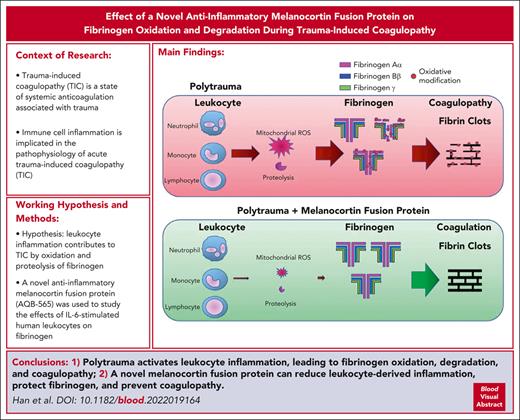
Immune cell inflammation is implicated in the pathophysiology of acute trauma-induced coagulopathy (TIC). We hypothesized that leukocyte inflammation contributes to TIC through the oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen. To test this hypothesis, antioxidants and a novel anti-inflammatory melanocortin fusion protein (AQB-565) were used to study the effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6)–stimulated human leukocytes on fibrinogen using single-cell imaging flow cytometry and multiplex fluorescent western blotting. We also studied the effects of AQB-565 on fibrinogen using an in vivo rat trauma model of native TIC. IL-6 induced cellular inflammation and mitochondrial superoxide production in human monocytes, causing fibrinogen oxidation and degradation in vitro. Antioxidants suppressing mitochondrial superoxide reduced oxidative stress and inflammation and protected fibrinogen. AQB-565 decreased inflammation, inhibited mitochondrial superoxide, and protected fibrinogen in vitro. Trauma with hemorrhagic shock increased IL-6 and other proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, selectively oxidized and degraded fibrinogen, and induced TIC in rats in vivo. AQB-565, given at the onset of hemorrhage, blocked inflammation, protected fibrinogen from oxidation and degradation, and prevented TIC. Leukocyte activation contributes to TIC through the oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen, which involves mitochondrial superoxide and cellular inflammation. Suppression of inflammation by activation of melanocortin pathways may be a novel approach for the prevention and treatment of TIC.
Introduction
Polytrauma is defined as a multisystem injury including bones, soft tissue, and multiple organ systems and is associated with hemorrhagic shock, increased morbidity, and mortality.1-4 Major tissue injury and hemorrhagic shock also contribute to trauma-induced coagulopathy (TIC), a state of systemic anticoagulation associated with trauma that profoundly increases early bleeding mortality.1,5 Inflammation is also increased with polytrauma. The landmark Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury “glue grant” research program examined the leukocyte genetic response to severe blunt injury with multisystem injury consistent with polytrauma.6 Remarkably, over 80% of the human leukocyte genome was significantly affected, with the greatest changes taking place within 12 hours of injury in genes involved with innate immunity and inflammation.
Endothelial and leukocyte-derived proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines have been implicated in inflammatory and coagulation responses to both sepsis and trauma.7-12 Yet, the pathways connecting cellular inflammation with coagulation after acute polytrauma remain undefined. Previously, we demonstrated key associations between lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-derived neutrophil and monocyte activation and the hemostatic protein fibrinogen, whereas leukocyte activation appeared to oxidatively prime fibrinogen for degradation during sterile inflammation.13
Fibrinogen is a blood hemostatic protein composed of pairs of trimers (Aα, Bβ, and γ) and is cleaved and polymerized into fibrin mesh, providing the structural support of the hemostatic thrombus.14-16 Functional fibrinogen concentration in the blood is rapidly decreased after severe injury and is strongly associated with TIC and increased mortality.5,10,17-19 Fibrinogen is also the most susceptible major plasma protein to oxidative modification.20 Specific oxidative modifications are linked to changes in fibrin polymerization, clot structure, and susceptibility to fibrinolysis.21-23 We previously demonstrated that fibrinogen is both depleted and selectively oxidized in human patients with trauma and TIC.21,24 However, pathways involved in inflammation-induced fibrinogen modifications and their potential role in TIC remain unclear.
Melanocortins are a family of anti-inflammatory peptides, including adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and α-, β-, and γ-melanocyte–stimulating hormones (α-, β-, γ-MSHs).25,26 Melanocortins mediate anti-inflammatory effects that act through diverse pathways. They act peripherally to suppress activation of NFκB, affecting cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E, and reactive oxygen species (ROS).27-30 Melanocortin peptides can protect against ischemia and reperfusion injuries,31 and they have shown therapeutic effects in preclinical and clinical studies of hemorrhage and shock and for acute injuries to vital organ systems, including the brain.27-29,31-39 However, no individual melanocortin peptide binds to all 5 melanocortin receptors (MCR1-5) and thus would not be expected to provide broad-based anti-inflammatory effects that may affect cytokines and the inflammatory storm associated with severe trauma and TIC.
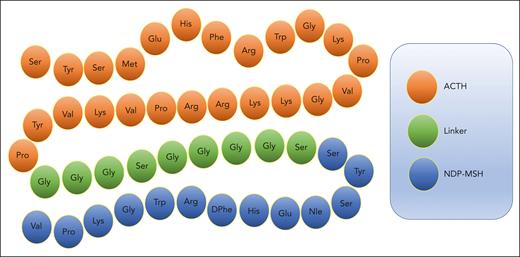
To overcome this limitation, we proposed to test a novel melanocortin fusion protein formed from 2 of the most potent and broad-acting melanocortins, ACTH and α-MSH, to create the linear polypeptide AQB-565 (Aequus Biopharma, Seattle, WA) (Figure 1). AQB-565 was more effective than either ACTH or α-MSH alone in inhibiting a wide range of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines and significantly reducing the infiltration of neutrophils to sites of inflammation when tested in a preclinical model of acute gout.40 AQB-565 also demonstrated central nervous system activity by reducing seizure activity in a preclinical model of infantile spasms.25 Although melanocortins have been well studied in many elements of trauma and hemorrhagic shock, there is little information on the role of broad-based melanocortin pathway activation in trauma-induced inflammation and coagulopathy.
Amino acid sequence of melanocortin fusion protein AQB-565. ACTH is linked at the N-terminal to NDP-MSH via a peptide linker to create AQB-565, which is 47 amino acids in length.
Amino acid sequence of melanocortin fusion protein AQB-565. ACTH is linked at the N-terminal to NDP-MSH via a peptide linker to create AQB-565, which is 47 amino acids in length.
Here, we aimed to investigate mechanisms governing the interactions between leukocyte activation, fibrinogen, and TIC in vitro and evaluate the presence of these pathways in vivo using a rat model of native TIC. Single-cell imaging flow cytometry revealed that interleukin-6 (IL-6)–stimulated monocytes predominantly provoked oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen that required mitochondrial superoxide generation. Mitochondrial superoxide from monocytes also mediates NFκB transactivation and endogenous monocyte TNFα secretion. Rat polytrauma with hemorrhagic shock was associated with increased cytokine production, including IL-6, and the development of TIC. Antioxidants targeting mitochondrial superoxide and AQB-565 displayed activity against inflammation, oxidation, and TIC both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
Rat polytrauma coagulopathy model
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River) were traumatized, as described previously10 and in the supplemental Methods; available on the Blood website. Polytrauma-induced rats were given either AQB-565, saline control, or the antifibrinolytic tranexamic acid (TXA). TXA was chosen because it is currently the only drug found useful to improve survival in human patients with trauma experiencing significant injury and blood loss, and it also has more general anti-inflammatory properties.41 The dose of AQB-565 was decided according to previous observations, which showed potent anti-inflammatory and central nervous system activity in preclinical rat models.28,40
Multiplex cytokine, PT, aPTT, and fibrinogen measurements
Cytokines and chemokines, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and fibrinogen concentrations in plasma from polytrauma-induced rats treated with saline or AQB-565 were measured as described in the supplemental Methods.
OxyBlot and multiplex fluorescent western blot analysis
Fibrinogen Aα, Bβ, and γ and the extent of oxidative modification of these isoforms from plasma of polytrauma-induced rats treated with saline or AQB-565 or culture-conditioned media from human leukocytes were detected by multiplex fluorescent western blot and using the OxyBlot protein oxidation detection kit (Millipore) as described in the supplemental Methods.
Flow cytometry analysis
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes were identified from peripheral blood cells of rats and healthy human donors after red blood cells (RBC) were lysed using high-dimensional immunophenotyping (supplemental Figure 5), as described previously13,42 and in the Supplemental Methods. To determine the inflammatory status of RBC-lysed leukocytes in polytrauma-induced rats with or without AQB-565 and human IL-6–stimulated leukocytes treated with various antioxidants, including TXA and AQB-565, single-cell flow imaging for NFκB and TNFα was performed, as described in the supplemental Methods. Various sources of ROS were also measured from RBC-lysed leukocytes as described in the supplemental Methods (supplemental Figure 8A).
Clottability measurement
Statistics
Details about statistics are described in the supplemental Methods.
Results
Polytrauma induces inflammation, causes oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen, and induces TIC in a rat model
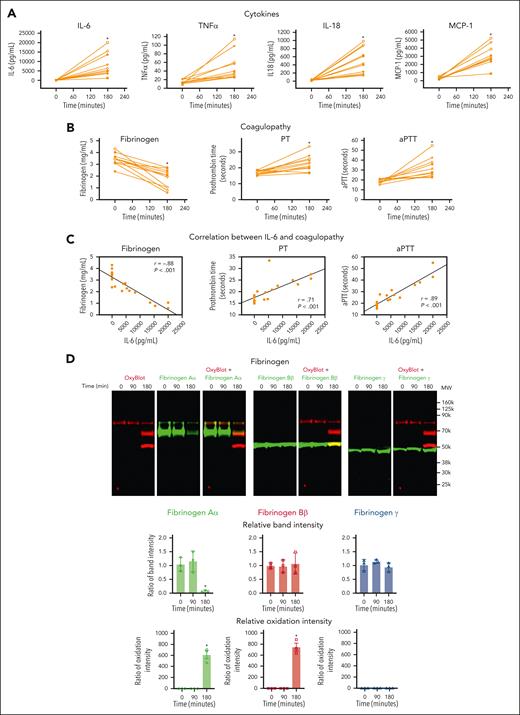
To assess the effect of polytrauma on inflammation and coagulation in vivo, we induced rat polytrauma by liver and small intestine crush with femoral fracture and blood withdrawal to induce hemorrhagic shock, followed by fluid resuscitation.10 Although cytokines and chemokines are involved in both hypercoagulability and hypocoagulability,10,12,44,45 we concurrently measured a 13-cytokine panel in plasma (Figure 2A). RBC, TNFα, MCP-1, and IL-18 were significantly increased during hemorrhagic shock (Figure 2A). IL-6 demonstrated the greatest increase and was steeply increased at 180 minutes of shock, whereas TNFα showed a steady yet limited increase over time (supplemental Figure 1).
Polytrauma induces inflammation, leading to oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen and causing coagulopathy in rats. Plasma was collected at the indicated time points from polytrauma-induced male rats (n = 11). (A) Cytokines were measured from plasma at the indicated time points by multiplex cytokine (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17, IL-18, IL-33, GM-CSF, MCP-1, CXCL1, IFNγ, and TNFα) analysis kit (n = 11, mean ± SEM). ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Fibrinogen, PT, and aPTT were measured using Ceveron alpha. ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (C) Relationships between IL-6 and fibrinogen, PT or aPTT, were determined by linear regression analysis using Pearson correlation coefficient. (D) Plasma was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Ratio of a specific band intensity were measured using Image Studio and plotted on the right panel. ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; INF, interferon; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Polytrauma induces inflammation, leading to oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen and causing coagulopathy in rats. Plasma was collected at the indicated time points from polytrauma-induced male rats (n = 11). (A) Cytokines were measured from plasma at the indicated time points by multiplex cytokine (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17, IL-18, IL-33, GM-CSF, MCP-1, CXCL1, IFNγ, and TNFα) analysis kit (n = 11, mean ± SEM). ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Fibrinogen, PT, and aPTT were measured using Ceveron alpha. ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (C) Relationships between IL-6 and fibrinogen, PT or aPTT, were determined by linear regression analysis using Pearson correlation coefficient. (D) Plasma was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Ratio of a specific band intensity were measured using Image Studio and plotted on the right panel. ∗P < .05 vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; INF, interferon; SEM, standard error of the mean.
TIC was confirmed to be present at 180 minutes of shock by a significantly increased PT (mean ± standard error of the mean, 16.78 ± 0.38 vs 22.85 ± 0.23 seconds), an increased aPTT (18.67 ± 0.57 vs 32.21 ± 0.23 seconds), and decreased fibrinogen (3.40 ± 0.15 vs 1.78 ± 0.23 g/L) (Figure 2B). These coagulation parameters were also very strongly correlated with proinflammatory cytokines, IL-6, TNFα, MCP-1, and IL-18 (Figure 2C; supplemental Figure 2).
To determine the specific effects of polytrauma-induced inflammation on fibrinogen, we performed multiplex fluorescent western blots for carbonyl band staining using OxyBlot (red band) and individual fibrinogen Aα, Bβ, and γ chains using subunit-specific antibodies (green band) to determine which fibrinogen chains were affected (Figure 2D). Fibrinogen remained intact and was not oxidized up to 90 minutes of shock. However, after 180 minutes, the fibrinogen Aα-chain became oxidized and was degraded. In addition, fibrinogen Bβ-chain was oxidized but not degraded at 180 minutes (Figure 2D). Fibrinogen γ-chain was resistant to both oxidation and degradation regardless of exposure (Figure 2D). Because we used monoclonal antibodies for detecting fibrinogen chains and there is a possibility that a single epitope against a specific fibrinogen chain could be masked by oxidative modification of amino acids, we repeated western blots using polyclonal antibodies for fibrinogen chains (supplemental Figure 3). The results were similar, where fibrinogen Aα-chain was oxidized and degraded, whereas fibrinogen Bβ-chain was oxidized but not degraded, and fibrinogen γ-chain was resistant to both oxidation and degradation.
Because fibrinogen Aα-chain was degraded in polytrauma-induced rats, we then tested whether the antifibrinolytic drug TXA could prevent this degradation in vivo. However, TXA failed to prevent degradation of the fibrinogen Aα-chain and had no effect on fibrinogen oxidation (supplemental Figure 4).
In summary, after 180 minutes of hemorrhagic shock, the rat polytrauma model demonstrated increased proinflammatory cytokines, including profoundly increased IL-6, which was associated with a coagulopathy consistent with TIC and selective oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen Aα and Bβ chains.
Melanocortin fusion protein, AQB-565, attenuates inflammation, protects fibrinogen from oxidation and proteolysis, and prevents TIC in the rat polytrauma model
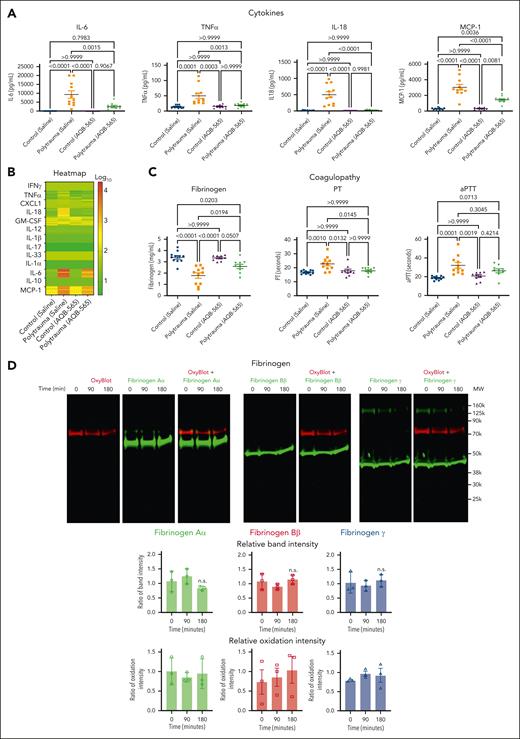
The anti-inflammatory AQB-565 was tested as a single intravenous dose given at the onset of hemorrhagic shock. AQB-565 attenuated increases in proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, after 90 minutes of shock (Figure 3A; supplemental Figure 5). PT and fibrinogen concentrations were restored with AQB-565, but aPTT was not different with AQB-565 compared with saline control (Figure 3B). AQB-565 also prevented the oxidation of fibrinogen and protected against the degradation of fibrinogen Aα (Figure 3C). These differences could not be attributed to differences in systemic blood pressure or the degree of metabolic shock between groups, as these parameters were not affected by AQB-565 (supplemental Figure 6).
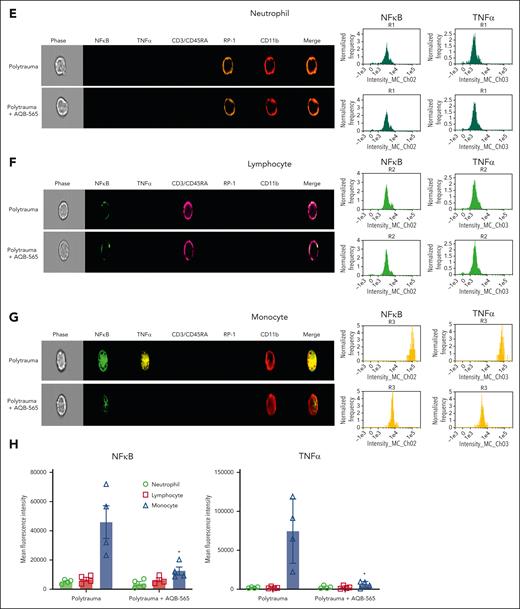
Melanocortin fusion protein, AQB-565, attenuates cytokines release, oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen, and prevents coagulopathy in polytrauma rats. Polytrauma-induced rats were injected with saline (control, n = 11) or AQB-565 (treatment, n = 9) as described in methods. (A) Cytokines were measured from plasma at 180 minutes by multiplex cytokine analysis kit (mean ± SEM). P value showing in each relevant comparison. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Heatmap of individual cytokines were plotted by the logarithm with base of 10. Scale bar with color change of green to red shown on the right panel. (C) Fibrinogen, PT, and aPTT were measured using Ceveron alpha (mean ± SEM). P value showing in each relevant comparison. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (D) Plasma was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Ratio of a specific band intensity were measured using Image Studio and plotted on the right panel with mean ± SEM). n.s. vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (E-H) RBC-lysed leukocytes were obtained from polytrauma-induced rat injected with saline (control, n = 3) or AQB-565 (treatment, n = 3). NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα production was visualized and analyzed using a single-cell imaging flow cytometry in neutrophils (E), lymphocytes (F), and monocytes (G). Quantitative histograms are shown on the right panel of each row. (H) Quantitative results are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .05 vs polytrauma. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. n.s., not significant. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Melanocortin fusion protein, AQB-565, attenuates cytokines release, oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen, and prevents coagulopathy in polytrauma rats. Polytrauma-induced rats were injected with saline (control, n = 11) or AQB-565 (treatment, n = 9) as described in methods. (A) Cytokines were measured from plasma at 180 minutes by multiplex cytokine analysis kit (mean ± SEM). P value showing in each relevant comparison. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Heatmap of individual cytokines were plotted by the logarithm with base of 10. Scale bar with color change of green to red shown on the right panel. (C) Fibrinogen, PT, and aPTT were measured using Ceveron alpha (mean ± SEM). P value showing in each relevant comparison. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (D) Plasma was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Ratio of a specific band intensity were measured using Image Studio and plotted on the right panel with mean ± SEM). n.s. vs 0 minute. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (E-H) RBC-lysed leukocytes were obtained from polytrauma-induced rat injected with saline (control, n = 3) or AQB-565 (treatment, n = 3). NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα production was visualized and analyzed using a single-cell imaging flow cytometry in neutrophils (E), lymphocytes (F), and monocytes (G). Quantitative histograms are shown on the right panel of each row. (H) Quantitative results are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .05 vs polytrauma. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. n.s., not significant. SEM, standard error of the mean.
We then examined if AQB-565 could also dampen inflammatory activation of peripheral rat leukocytes in vivo during polytrauma. After identifying neutrophil, lymphocyte, and monocyte populations in the blood (supplemental Figure 7), we measured nuclear NFκB translocation and resulting intracellular TNFα expression using a single-cell imaging flow cytometer. Neutrophils were stained with both RP-1 and CD11b antibodies (brown and red, fifth and sixth columns), lymphocytes were stained with CD3/CD45RA antibodies (pink, fourth column), and monocytes were stained using a CD11b antibody (red, sixth column) in Figure 3E-G. NFκB translocation into the nucleus was detected using a NFκB p65 antibody (green, second column). Intracellular TNFα expression was detected using a TNFα antibody (yellow, third column). Polytrauma did not induce inflammation, as indicated by NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα expression in neutrophils (Figure 3E). In lymphocytes (Figure 3F), minimal NFκB translocation was detected during polytrauma (first row) that was not inhibited by AQB-565 (second row). However, polytrauma did induce NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα expression in monocytes (first row, Figure 3G), which were substantially reduced by AQB-565 (second row).
In summary, polytrauma in rats provoked signal transduction and proinflammatory gene expression in monocytes that was attenuated by AQB-565, thus protecting fibrinogen from oxidative modification, degradation, and TIC in vivo.
Mitochondrial superoxide is generated from monocytes in IL-6–stimulated human leukocytes in vitro, and antioxidants, NAC and Mito-Tempo, and anti-inflammatory drug, AQB-565, block ROS generation
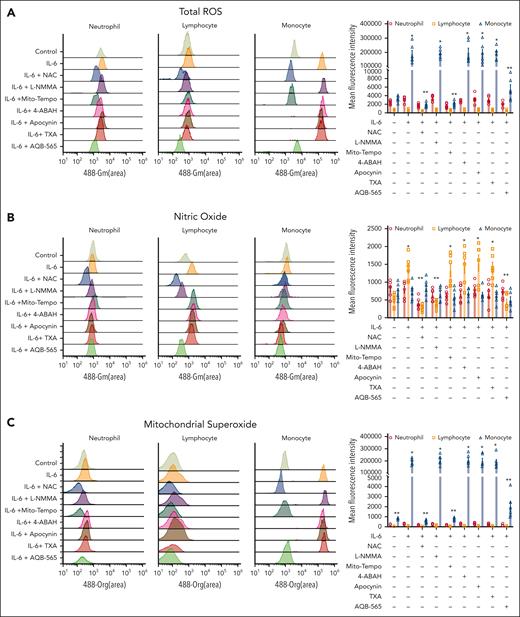
Oxidative stress can be generated as various molecular forms from various cellular sources.46,47 Leukocytes in the peripheral vascular system can also be potential cellular source for creating ROS during polytrauma. These oxidants can both modify blood proteins directly and regulate inflammatory signaling pathways. To identify potential pathophysiological oxidants and their molecular and cellular sources during polytrauma-induced inflammation, we incubated human leukocytes with IL-6 in vitro. We chose to activate leukocytes using IL-6 because it was steeply and profoundly increased in vivo and positively correlated with clot formation parameters (Figure 2; supplemental Figure I). High-dimensional immunophenotyping was performed to identify the cellular source of ROS (supplemental Figure 8). In addition, to determine the molecular source of ROS generation, we specified ROS using a fluorescence-based assay in identified neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes. Total ROS were generated primarily from monocytes, whereas there was no significant overall increase from neutrophils or lymphocytes (Figure 4A). Lymphocytes generated only a small amount of NO as a molecular source of ROS (Figure 4B). More specifically, mitochondrial superoxide was generated to the greatest extent from monocytes but not from either neutrophils or lymphocytes (Figure 4C).
Oxidative stress is generated in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes and caused by mitochondria-derived superoxide originated from monocytes. RBC-lysed human leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were activated by IL-6 (10 ng/mL) and incubated with indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors (NAC; a pan antioxidant, L-NMMA; an antioxidant for NOS, Mito-Tempo; an antioxidant for mitochondrial superoxide, 4-ABAH; an antioxidant for MPO, apocynin; an antioxidant for NOX, TXA; an inhibitor of plasminogen activation, AQB-565; anti-inflammatory drug) as described in supplemental Methods and supplemental Figure 8A for 3 hours. Total ROS (A), nitric oxide (NO)(B), and mitochondrial superoxide (C) were measured as described in methods. Each panel is representative of 6 independent experiments. Results in right panel of each row are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .001 vs control, ANOVA, and Bonferroni post hoc test. MPO, myeloperoxidase; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Oxidative stress is generated in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes and caused by mitochondria-derived superoxide originated from monocytes. RBC-lysed human leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were activated by IL-6 (10 ng/mL) and incubated with indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors (NAC; a pan antioxidant, L-NMMA; an antioxidant for NOS, Mito-Tempo; an antioxidant for mitochondrial superoxide, 4-ABAH; an antioxidant for MPO, apocynin; an antioxidant for NOX, TXA; an inhibitor of plasminogen activation, AQB-565; anti-inflammatory drug) as described in supplemental Methods and supplemental Figure 8A for 3 hours. Total ROS (A), nitric oxide (NO)(B), and mitochondrial superoxide (C) were measured as described in methods. Each panel is representative of 6 independent experiments. Results in right panel of each row are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .001 vs control, ANOVA, and Bonferroni post hoc test. MPO, myeloperoxidase; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; SEM, standard error of the mean.
The primary source of overall oxidative stress was then identified using the selective inhibition of ROS by antioxidants. Total ROS generation was not changed significantly by all antioxidants in neutrophils and lymphocytes (Figure 4A). In contrast, total ROS was inhibited by NAC and Mito-Tempo in monocytes (Figure 4A). Antioxidants against NADPH oxidase (NOX)-derived ROS showed no inhibition of ROS generation in all leukocyte cell types (Figure 4A). Specific inhibition of NO by NG-methyl-l-arginine acetate salt (L-NMMA) had minimal effects on overall ROS generation for all cell types (Figure 4B). These results identify mitochondrial superoxide generated primarily by monocytes as the primary molecular source of ROS generation in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes.
We then tested the effects of TXA and the anti-inflammatory melanocortin fusion protein AQB-565 on ROS generation by IL-6–stimulated leukocytes. TXA is a synthetic lysine analog that blocks the enzymatic cleavage of fibrinogen and fibrin and is currently used clinically for the treatment of bleeding patients with trauma.48,49 TXA did not block ROS generation in any leukocyte cell type (Figure 4). Interestingly, AQB-565 inhibited total ROS generation and mitochondrial superoxide generation in monocytes and NO generation in lymphocytes (Figure 4).
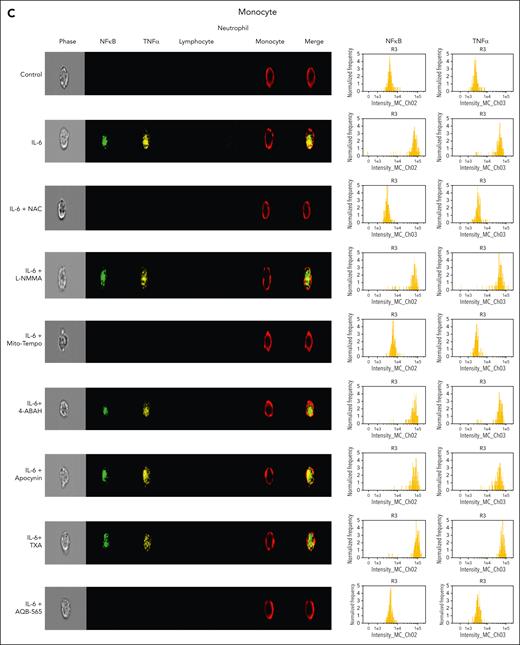
IL-6–induced intracellular signal transduction is inhibited by antioxidants and AQB-565 in human leukocytes
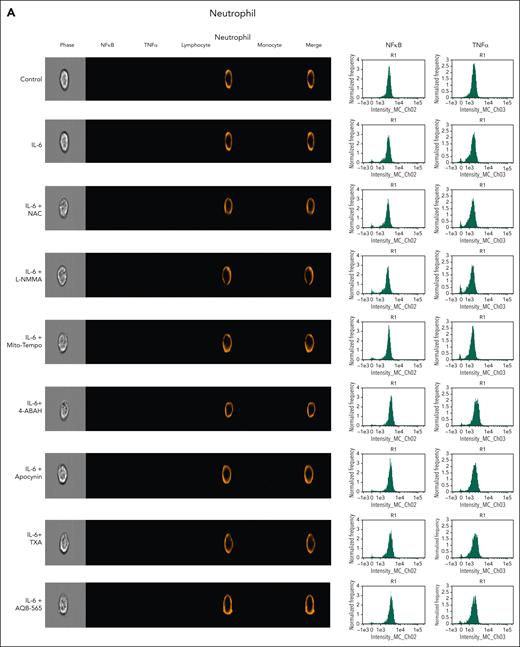
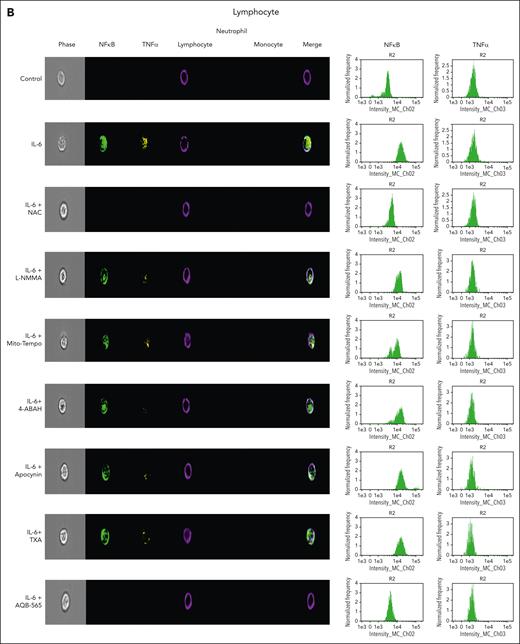
To investigate intracellular leukocyte signal transduction pathways as a component of cellular ROS generation, we measured nuclear NFκB translocation and resulting intracellular TNFα expression using a single-cell imaging flow cytometer. In addition, we used targeted antioxidants, antifibrinolytics, and AQB-565 to examine this secondary intracellular signaling transduction pathway. Neutrophils were stained with a CD16b antibody (brown, fifth column), lymphocytes were stained with CD3/19 antibodies (purple, fourth column), and monocytes were stained using a CD14 antibody (red, sixth column) in Figure 5A-C. NFκB translocation into the nucleus in response to IL-6 simulation was detected using a NFκB p65 antibody (green, second column). Intracellular TNFα expression was detected using a TNFα antibody (yellow, third column). Neither signal transduction nor proinflammatory gene expression was induced in neutrophils by IL-6 stimulation in Figure 5A. In lymphocytes (Figure 5B), NFκB translocation and minimal TNFα expression were found after IL-6 exposure (second row) that were inhibited by NAC and AQB-565 (third and ninth rows, respectively), but were unaffected by L-NMMA, Mito-Tempo, 4-amino-benzoic acid, hydrazide (4-ABAH), apocynin, and TXA (fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, and eighth rows, respectively). However, there were substantial increases in NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα expression in monocytes (Figure 5C) after IL-6 treatment (second row) that were inhibited by NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565 (third, fifth, and ninth rows). L-NMMA, 4-ABAH, apocynin, and TXA did not inhibit these changes in monocytes (fourth, sixth, seventh, and eighth rows). These data imply that mitochondrial superoxide from monocytes triggers intracellular signal transduction and proinflammatory gene expression in response to IL-6 stimulation.
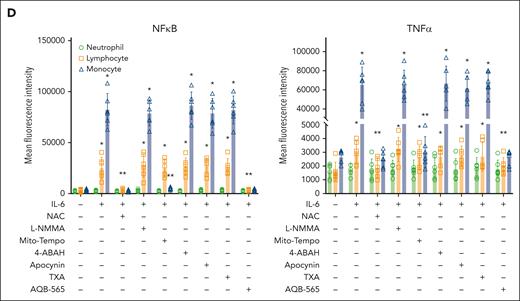
NFκB translocation and TNFα production are mainly induced in monocytes among IL-6–stimulated leukocytes and inhibited by NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in Figure 4 for 3 hours. NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα production was visualized and analyzed using a single-cell imaging flow cytometry in neutrophils (A), lymphocytes (B), and monocytes (C). Quantitative histograms are shown on the right panel of each row. (D) Quantitative results are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .001 vs control, ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. SEM, standard error of the mean.
NFκB translocation and TNFα production are mainly induced in monocytes among IL-6–stimulated leukocytes and inhibited by NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in Figure 4 for 3 hours. NFκB translocation and intracellular TNFα production was visualized and analyzed using a single-cell imaging flow cytometry in neutrophils (A), lymphocytes (B), and monocytes (C). Quantitative histograms are shown on the right panel of each row. (D) Quantitative results are plotted as the mean fluorescent intensity of each sample on the vertical axis with mean ± SEM. ∗P < .001 vs control, ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. SEM, standard error of the mean.
Fibrinogen is oxidized and degraded by IL-6–stimulated human leukocytes in vitro
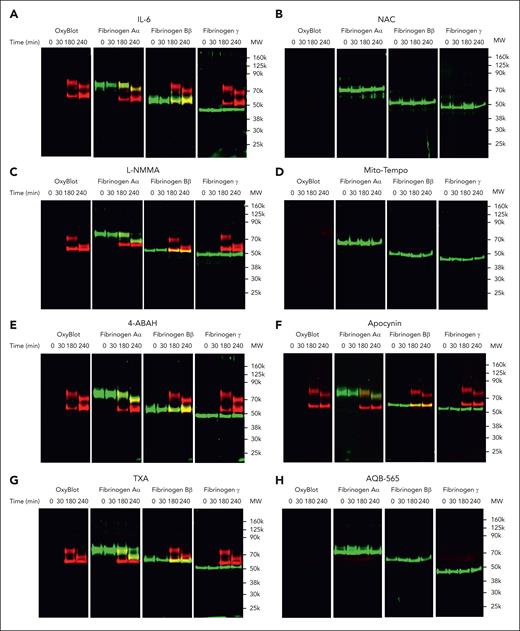
We next used multiplex fluorescent western blots to determine if fibrinogen oxidation and degradation occurred in the presence of IL-6–stimulated leukocytes (Figure 6). Fibrinogen Aα- and Bβ-chains (green band) became oxidized within 180 minutes of exposure to activated leukocytes (red band) in Figure 6A. In addition, fibrinogen Aα-chain was fragmented, whereas fibrinogen Bβ- and γ-chains remained intact at 240 minutes (green band, Figure 6A; supplemental Figure 9). Fibrinogen γ-chain remained resistant to oxidation and degradation by 240 minutes (green band, Figure 6A). These data indicate that activated human leukocytes can directly oxidize and degrade fibrinogen.
NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565-inhibitable ROS are responsible for oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with fibrinogen (4 mg/mL) and indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in supplemental Methods; supplemental Figure 8B for indicated time periods. (A-H) Conditioned medium was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data images are representative of 4 independent experiments.
NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565-inhibitable ROS are responsible for oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with fibrinogen (4 mg/mL) and indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in supplemental Methods; supplemental Figure 8B for indicated time periods. (A-H) Conditioned medium was analyzed by OxyBlot and immunoblotting using fibrinogen Aα-, Bβ-, and γ-specific antibodies. Data images are representative of 4 independent experiments.
We then asked whether antioxidants, such as TXA or AQB-565, could affect monocyte-derived oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen. We observed that NAC and Mito-Tempo completely blocked fibrinogen oxidation and degradation (Figure 6B,D; supplemental Figure 9), and L-NMMA, 4-ABAH, and apocynin did not prevent fibrinogen oxidation or degradation (Figure 6C,E-F; supplemental Figure 9). Interestingly, TXA did not inhibit oxidation but somewhat delayed proteolysis of fibrinogen Aα (Figure 6G; supplemental Figure 9). AQB-565 inhibited both the oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen (Figure 6G; supplemental Figure 9). These results suggest that antioxidant and anti-inflammatory treatments could specifically block activated monocyte-induced oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen in vitro.
Our results showed that oxidation followed by fragmentation of fibrinogen Aα happened sequentially. However, fragmentation of fibrinogen Aα could also be caused by extensive oxidation rather than enzymatic proteolysis. To clarify, IL-6–stimulated leukocytes incubated with fibrinogen were coincubated with a cell-culturable global proteinase inhibitor cocktail, which inhibited serine, cysteine, aspartic protease and aminopeptidases, and fibrinogen. The inhibitor cocktail inhibited the fragmentation of fibrinogen Aα (supplemental Figure 10). Moreover, SDS-PAGE of incubations without inhibitors detected the migration of a 10 kDa protein fragment likely to represent the proteolyzed fibrinogen Aα-chain fragment. These results suggest that proteolysis derived from stimulated leukocytes is the cause of fibrinogen degradation rather than oxidation.
Monocyte-originated inflammation leads to fibrinogen dysfunction
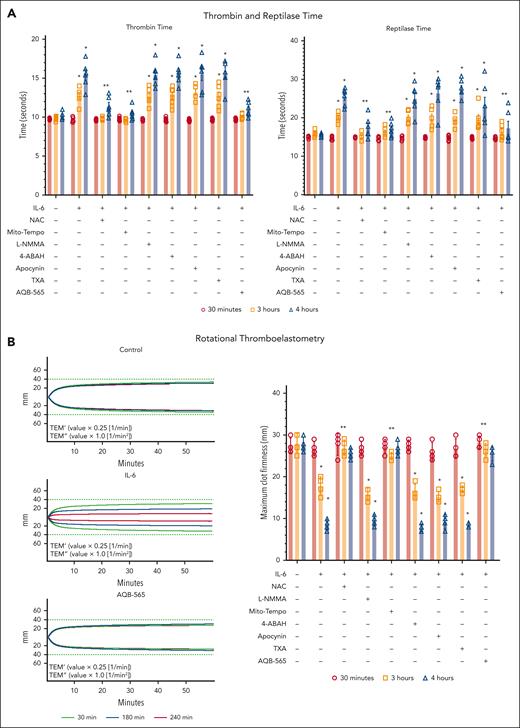
We next used thrombin time and reptilase time assays and the ROTEM assay to investigate the functional implications of fibrinogen oxidation and degradation associated with human leukocyte activation. Fibrin polymerization was impaired as demonstrated by an increase in both thrombin and reptilase times and a decrease in ROTEM maximum clot firmness (MCF) when fibrinogen was incubated with IL-6–stimulated leukocytes after 3 hours (Figure 7; supplemental Figure 11). Western blots revealed that thrombin and reptilase time increased and MCF decreased after oxidation, yet before significant fibrinogen degradation (Figure 6). Consistent with prior experiments using the antioxidants, NAC and Mito-Tempo could restore thrombin and reptilase times and MCF to normal ranges. In addition, TXA could neither prevent the prolongation of thrombin and reptilase times nor rescue MCF. AQB-565 attenuated increases in thrombin and reptilase times and restored MCF consistent with its conferred protection from fibrinogen oxidation and degradation. Collectively, these results imply that mitochondrial superoxide from monocytes can induce both the direct oxidation of fibrinogen and its subsequent degradation. Fibrinogen oxidation can also contribute directly to coagulopathy, and rapid fibrinogen Aα-chain fragmentation is not inhibited by TXA, whereas both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory treatment with AQB-565 targeting mitochondrial superoxide restored fibrinogen form and function by preventing its oxidation and degradation.
NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565 alleviate the delay of thrombin and reptilase time and thinning of MCF from conditioned media at 3 and 4 hours in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with fibrinogen, indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in supplemental Methods; supplemental Figure 8B for indicated time periods. Conditioned medium was analyzed for thrombin and reptilase time (A, n = 6, mean ± SEM) and ROTEM as described in supplemental Methods (B, n = 4, mean ± SEM). ∗P < .001 vs control. ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Representative rotational thromboelastograms are overlaid with the conditioned media at 30 (green color), 180 (blue color), and 240 (red color) minutes. Quantitative results are plotted as MCF value on the right panel. ∗P < .001 vs control. ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. SEM, standard error of the mean; MCF, maximal clot firmness.
NAC, Mito-Tempo, and AQB-565 alleviate the delay of thrombin and reptilase time and thinning of MCF from conditioned media at 3 and 4 hours in IL-6–stimulated leukocytes. IL-6–stimulated RBC-lysed leukocytes from healthy donors (n = 6) were incubated with fibrinogen, indicated various antioxidants and inhibitors as described in supplemental Methods; supplemental Figure 8B for indicated time periods. Conditioned medium was analyzed for thrombin and reptilase time (A, n = 6, mean ± SEM) and ROTEM as described in supplemental Methods (B, n = 4, mean ± SEM). ∗P < .001 vs control. ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (B) Representative rotational thromboelastograms are overlaid with the conditioned media at 30 (green color), 180 (blue color), and 240 (red color) minutes. Quantitative results are plotted as MCF value on the right panel. ∗P < .001 vs control. ∗∗P < .001 vs IL-6. ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. SEM, standard error of the mean; MCF, maximal clot firmness.
Discussion
Our results implicate blood inflammation as an important contributor to TIC, which is mediated by fibrinogen. Elucidated pathways include cytokine-induced leukocyte activation, the generation of mitochondrial superoxide, and the associated oxidation and degradation of fibrinogen. Furthermore, early anti-inflammatory and antioxidant treatment could mitigate coagulopathy, whereas antifibrinolytic therapy could not.
In this model, there appeared to be a distinct proinflammatory phenotype associated with polytrauma and hemorrhagic shock that was associated with a profound elevation of IL-6 on or around 3 hours after injury. Other published rodent models demonstrated a similar increase of IL-6 at 3 hours after polytrauma, which was preceded by a maximal increase of TNFα at 1 hour and its subsequent decrease by 2 hours.10 For TNFα, the timing of measurement appears to be important, and it is possible that our current sampling protocol missed an earlier maximal spike of TNFα taking place before 90 minutes after injury. In contrast, previous work using LPS to induce sterile inflammation in a similar rodent model differed by inducing TNFα and IL-6 increases several fold greater than the current polytrauma model.13 LPS stimulation also activated leukocytes more broadly, including both neutrophils and monocytes, when compared with IL-6 stimulation.13 Our results align with known proinflammatory cytokine storm taking place in human leukocytes studied from patients with trauma after injury.6 These findings are also important because there is evidence that cytokines are associated with coagulopathy after injury in humans. Schöchl and colleagues found that IL-6 was increased in those patients with trauma with TIC and that IL-6 concentration was useful as a predictor of massive blood product transfusion.50 Interestingly, thromboelastometry revealed significantly decreased functional measures of fibrin polymerization associated with increased IL-6 in their cohort, supporting a similar relationship between inflammation and fibrinogen dysfunction in humans.50 Future studies investigating the role of IL-6 on TIC using neutralizing antibodies are necessary.
We found that in vitro stimulation of human leukocytes using IL-6 induced monocyte mitochondrial superoxide, fibrinogen Aα and Bβ chain oxidation, and selective fibrinogen Aα-chain fragmentation. These changes could be inhibited by early anti-inflammatory treatment using AQB-565 and select antioxidants but could not be inhibited using TXA. Similar results were found in vivo using AQB-565 as an early anti-inflammatory therapy in the rat polytrauma model by protecting fibrinogen and preventing TIC. Importantly, the fibrinogen Aα-chain is also oxidized in emergency department patients with trauma who have TIC compared with those without trauma.24 We found that the primary effect of TXA was to delay degradation of fibrinogen, which did not prevent prolongation of thrombin or reptilase times and decreased MCF as measures of fibrin polymerization. These results suggest that there may be an important role for inflammation-induced coagulopathy that involves oxidative stress taking place early after trauma and before significant proteolysis. Further focused characterization of the effects of oxidation on fibrin structure and function is warranted.
We showed that fibrinogen Aα-chain was degraded in the polytrauma-induced rat model and fragmented with I-L6–stimulated leukocytes. Adding a protease inhibitor cocktail preserved the fibrinogen chains, suggesting that proteolytic enzymes were responsible. Future studies that identify the specific proteases secreted by polytrauma-stimulated leukocytes are needed. The culprit enzymes could be identified using targeted protease inhibitors such as serine, cysteine, aspartic protease, and aminopeptidases or using end point peptide sequencing to identify cleaved sites in fibrinogen Aα fragments via degradomics.
We predominantly detected oxidative modification of fibrinogen both in vivo and in vitro using OxyBlot. In all in vitro experiments, fibrinogen solution was incubated with cultured leukocytes. Therefore, the relative concentration of fibrinogen relative to secreted proteins likely accounted for the lack of other significant OxyBlot staining on the gels. In vivo, fibrinogen was also the only band stained by OxyBlot. This result is likely due to plasma fibrinogen being much more susceptible to oxidative modification compared with the other major plasma proteins.20 In addition, endogenous antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione may provide a degree of protection for other proteins less susceptible to oxidation, thus reducing their oxidation to below the level of detection for the assay.
We showed that fibrinogen Aα and Bβ were very susceptible to oxidative modification and proteolysis, whereas fibrinogen γ remained resistant. The preference for oxidation and degradation may be due to a combination of the composition of the amino acids of these fibrinogen chains and their relative hydration state. Fibrinogen α and β subunits are enriched with basic amino acids like histidine, lysine, and arginine, which are more easily oxidized and are targets for many proteases, whereas fibrinogen γ is composed of more acidic amino acids like aspartate and glutamate, which are relatively more resistant to oxidation and proteolysis. Hydration may also contribute to the relative resistance to oxidation and proteolysis of the individual fibrinogen chains. The alpha-C domain has an ordered structure that is connected via a less ordered and flexible connector region composed of a series of repeat sequences.51 Thus, the increased flexibility of the alpha-C region increases hydration and promotes access by oxidants and proteolytic enzymes, whereas other susceptible amino acids of the β and γ chains tend to be more buried within coil-coil regions.
Antioxidants have been extensively studied as treatments for critical illness and injury while focusing on sepsis. Clinical trials using high doses of vitamin C have reported mixed results.52-56 However, there is some evidence that high-dose antioxidant vitamin cocktails may reduce hospital length of stay, organ failure, and mortality for patients with trauma admitted to intensive care.57,58 These therapies were tested many hours or days after hospital arrival, and there is currently no human evidence available to support the efficacy of antioxidant therapy when given more acutely. Here, the broad-based antioxidant NAC was found to protect against both fibrinogen oxidation and degradation. NAC could be a promising drug candidate for treating coagulopathy because it is inexpensive and can be administered both orally and intravenously. However, there is also evidence that NAC induces anticoagulation and platelet inhibition, so its use in bleeding situations such as trauma may not be possible.59-61 New antioxidant therapeutics may be needed to test during the first moments after a severe traumatic injury.
Drugs targeting inflammation by blocking individual cytokines have been tested as treatments for sepsis with mixed results.62-64 However, the inflammatory response to severe injury is quite broad-based. Differences in the overall magnitude of the cytokine response differentiate trauma survival and outcomes better than changes in individual cytokines or inflammatory pathways.6 We found that AQB-565, a melanocortin fusion protein having wide anti-inflammatory activity, did successfully prevent cytokine increase, oxidation, and TIC in vivo after polytrauma. ACTH and α-MSH, are the only 2 melanocortins that have received Food and Drug administration approval and are used to treat patients: (1) ACTH to treat a range of autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions,65 and (2) an analog of α-MSH to treat a rare inflammatory skin condition, erythropoietic porphyria.66 Our chosen dose of AQB-565, 1 mg per kg in the rat, is equivalent to 0.16 mg/kg in a human. This equates to a human dose of ∼10 mg using allometric scaling.67 AQB-565 is made by a standard peptide manufacturing process. The cost to make this amount of material would be less than $5. The only melanocortins approved by the Food and Drug Administration are Acthar Gel and Scenesse. Acthar gel is an adrenocorticotropic hormone and is dosed at 80 to 160 units, which is equivalent to approximately 1 to 2 mg/kg. A dose of Scenesse (afamelanotide), which is an analog of alpha-MSH, is 16 mg/kg. If translated as expected, the dosage required to achieve therapeutic effects of AQB-565 would be much lower, and potentially safer, than current melanocortin therapies.
Importantly, to our knowledge, this study demonstrates for the first time that melanocortins have potent therapeutic effects on coagulopathy and that these effects are linked to their anti-inflammatory effects. A randomized controlled trial of hydrocortisone focusing on pulmonary outcomes for intubated patients with trauma found a significant reduction in ventilator days and pneumonia with hydrocortisone treatment.68 However, anti-inflammatory therapies have not been tested in the critical moments after severe trauma, when bleeding mortality is highest.
In conclusion, polytrauma induces inflammation and oxidative stress, causing the oxidation and proteolysis of fibrinogen and TIC. Mitochondrial superoxide from monocytes causing fibrinogen oxidation followed by degradation constitutes an important pathway linking inflammation to TIC. Selective antioxidants and administration of the novel melanocortin fusion protein AQB-565 attenuated inflammation and prevented TIC by restoring fibrinogen coagulability. The observations reported here may have implications for using melanocortins to treat many other serious acute conditions in which both coagulopathy and inflammation are present. Further studies are needed to determine the therapeutic potential of AQB-565 in treating polytrauma and TIC.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by US Department of Defense grant W81XWH-18-DMRDP-PTCRA (to N.J.W.).
Authorship
Contribution: N.J.W., R.B., and S.A.S. conceived the project and obtained funding; C.Y.H., X.W., K.M.R., J.C.B., and A.E.S.J. conducted the experiments; C.Y.H., S.A.S., and N.J.W. designed the experiments, supervised the work, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; and all authors contributed to and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.J.W. has received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the US Department of Defense, is a shareholder in Stasys Medical Corp, and is a consultant to Velico Medical Corp. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Nathan J. White, Department of Emergency Medicine, Harborview Medical Center, Box 359702, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98104; e-mail: whiten4@uw.edu.
References
Author notes
Data and protocols will be available from the corresponding author, Nathan J. White (whiten4@uw.edu), upon reasonable request.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal