Key Points
FI has 2 calcium-binding domains. Genetic variants and alanine mutations surrounding the calcium result in defective protein synthesis.
The present work provides substantial evidence for the role of calcium in FI and sheds new light on the molecular mechanism underlying FI variants.
Abstract
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a rare thrombotic microangiopathy. Genetic variants in complement proteins are found in ≈60% of patients. Of these patients, ≈15% carry mutations in complement factor I (CFI). Factor I (FI) is a multidomain serine protease that cleaves and thereby inactivates C3b and C4b in the presence of cofactor proteins. Crystal structures have shown that FI possesses 2 calcium-binding domains, low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) 1 and LDLRA2. Yet, the role of calcium in FI is unknown. We determined that 9 genetic variants identified in aHUS (N151S, G162D, G188A, V230E, A240G, G243R, C247G, A258T, and Q260D) cluster around the calcium-binding site of LDLRA1. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we established that the synthesis of all, except A258T, was impaired, implying defective protein folding, perhaps due to loss of calcium binding. To further explore this possibility, we generated 12 alanine mutants that coordinate with the calcium in LDLRA1 and LDLRA2 (K239A, D242A, I244A, D246A, D252A, E253A, Y276A, N279A, E281A, D283A, D289A, and D290A) and are expected to perturb calcium binding. Except for K239A and Y276A, none of the mutants was secreted. These observations suggest that calcium ions play key structural and functional roles in FI.
Introduction
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a rare thrombotic microangiopathy characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury.1 The major defect underlying the disease is a dysregulated complement system, most often arising from loss-of-function mutations in regulators (factor H [FH], factor I [FI], and CD46 [membrane cofactor protein {MCP}]).2,3 Less frequently, a gain-of-function mutation in one of the activators (C3 or factor B) is identified.4 Approximately 60% of patients with aHUS carry a rare variant in one of the complement proteins.1 However, most clinically identified variants have yet to be functionally characterized.
Genetic variants in complement factor I (CFI) have been reported in ≈15% of patients with aHUS.5,6 FI is a multidomain serine protease and a regulator of the alternative pathway of the complement system. It is composed of 2 polypeptide chains, heavy and light, connected by a disulfide bond (Figure 1A). The heavy chain is composed, from the N-terminal, of the FI membrane attack complex domain, 2 low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) domains, and a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain. The light chain hosts the catalytic serine protease domain containing the active site triad H380 (H57), D429 (D102), and S525 (S195). The crystal structures of FI show that these 2 chains come together to form a compact fold with many interactions at the interface.7,8 It is known that both chains are structurally and functionally important,9 yet exactly how the heavy chain influences the catalytic activity of the serine protease domain is unknown.
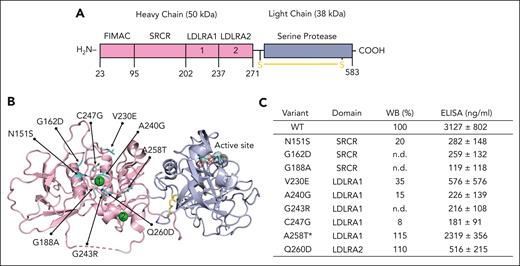
Genetic mutations surrounding the calcium in FI impair protein expression and function. (A) Linear structure of FI. FI is a multidomain glycoprotein composed of a heavy chain (50 kDa) and a light chain (38 kDa) held together by a disulfide bond (shown in yellow). The heavy chain is catalytically inactive and is composed of 4 domains (from the N-terminal) by the FI membrane attack complex (FIMAC) domain, a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain, and 2 low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) domains. A calcium ion (green sphere) is present in each LDLRA domain. The light chain hosts the active enzymatic site and folds into a canonical serine protease domain. (B) Mapping of 9 genetic variants (shown in cyan) on the 3-dimensional structure of FI reveals that they cluster around the calcium ion bound in LDLRA1. Note how the active site (dotted spheres) is located >40 Å away from the calcium-binding site, where the mutations cluster. (C) Table summarizing the location of each mutation and expression levels relative to wild-type (WT) measured by western blotting (WB) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The ELISA values represent mean ± SEM from at least 3 different transfections. ∗On comparison to WT FI, the proteolytic activity of variant A258T was defective with MCP. No defect was observed with FH or complement receptor 1 (CR1) as the cofactor protein (supplemental Figure 2). n.d., not detected.
Genetic mutations surrounding the calcium in FI impair protein expression and function. (A) Linear structure of FI. FI is a multidomain glycoprotein composed of a heavy chain (50 kDa) and a light chain (38 kDa) held together by a disulfide bond (shown in yellow). The heavy chain is catalytically inactive and is composed of 4 domains (from the N-terminal) by the FI membrane attack complex (FIMAC) domain, a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain, and 2 low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) domains. A calcium ion (green sphere) is present in each LDLRA domain. The light chain hosts the active enzymatic site and folds into a canonical serine protease domain. (B) Mapping of 9 genetic variants (shown in cyan) on the 3-dimensional structure of FI reveals that they cluster around the calcium ion bound in LDLRA1. Note how the active site (dotted spheres) is located >40 Å away from the calcium-binding site, where the mutations cluster. (C) Table summarizing the location of each mutation and expression levels relative to wild-type (WT) measured by western blotting (WB) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The ELISA values represent mean ± SEM from at least 3 different transfections. ∗On comparison to WT FI, the proteolytic activity of variant A258T was defective with MCP. No defect was observed with FH or complement receptor 1 (CR1) as the cofactor protein (supplemental Figure 2). n.d., not detected.
FI regulates complement activation by inactivating C3b and C4b through proteolytic cleavage (ie, cofactor activity).7-9 Because FI has an unusually low intrinsic activity, this regulatory function requires binding to “cofactor proteins”: FH, MCP (CD46), C4b-binding protein, or complement receptor 1 (CR1; CD35).10 FI also binds to 2 calcium ions, 1 in each LDLRA domain.7,8 Although it has been speculated that calcium plays a structural role,7,11 this hypothesis remains to be tested. In this report, genetic variants identified in patients with aHUS and alanine mutants produced in the laboratory provide functional evidence for the role of calcium ions in FI, thus shedding new light on the molecular mechanisms underlying FI activity in aHUS.
Study design
Proteins were transiently expressed in human embryonic kidney 293T cells (ATCC, Manassas, VA), as described.12 Levels of FI were determined on supernatant by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blotting (WB) using the validated monoclonal antibodies OX-21 (Invitrogen, ThermoFisher Scientific) and anti-FI(#1) (Quidel, San Diego, CA), respectively. Transfections, WBs, and ELISAs were performed at least 3 times for each variant. Plasma-purified FI served as an internal control. Cofactor assays were performed to assess the cleavage of human C3b by wild-type (WT) and FI variants in the presence of the cofactors FH, MCP, and CR1, as detailed previously.5,12,13 R programming language (CRAN, https://cran.r-project.org/) was employed for statistical computations. Pymol 2.4.0 (Schrodinger, LLC) was used for structural visualization. A detailed description of the methods is provided in the supplemental information (available on the Blood website).
Results and discussion
In recent years, crystal structures of FI unbound7 and bound to C3b and protein cofactors8 became available, offering an opportunity to better understand how mutations of FI might perturb their activity. By mapping the currently known genetic variants identified in patients with aHUS onto the structure of FI,8,14 we discovered that 9 of them (N151S, G162D, G188A, V230E, A240G, G243R, C247G, A258T, and Q260D) cluster around the calcium-binding site in the LDLRA1 domain (Figure 1B). To investigate further, the 9 genetic variants were transiently expressed in mammalian cells alongside the WT protein. Using WB, we found that 7 of the 9 variants had markedly reduced secretion (>80%) compared with the WT protein (Figure 1C). These included N151S, G162D, G188A, V230E, A240G, G243R, and C247G. WB of the lysates for these variants did not show intracellular accumulation of the protein, establishing that these variants result in a quantitative defect due to a lack of synthesis (supplemental Figure 1). The variants N151S, G162D, V230E, A240G, and C247G have been reported previously and have been demonstrated to have altered secretion.15-17 The variants A258T and Q260D were secreted normally.
In addition to WB, expression levels of FI were also measured by sandwich ELISA, a method that is commonly used in clinical laboratories. Although WT expressed at >3000 μg/mL, levels <600 μg/mL were measured for 8 variants, confirming poor expression (Figure 1C). Overall, we found a correlation between WB and ELISA, except for the variant Q260D, which was normal in WB but low in ELISA. The reason for this discrepancy is not clear, but we speculate that the variant Q260D might weaken the interaction between FI and the capture antibody used in ELISA, accounting for the difference in results compared with WT. Functional analysis for Q260D did not demonstrate a defect with cofactors FH, MCP, or CR1. The variant A258T, however, demonstrated defective activity with MCP but normal proteolytic activity in the presence of FH and CR1 (supplemental Figure 2).
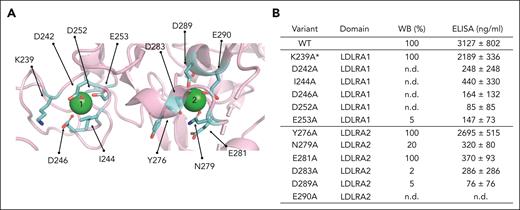
To substantiate these findings and further dissect the role of the 2 calcium-binding sites, we identified 12 amino acid residues that coordinate the 2 calcium ions (Figure 2A). These were K239, D242, I244, D246, D252, and E253 in LDLRA1 and Y276, N279, E281, D283, D289, and D290 in LDLRA2. Alanine mutagenesis was performed on all 12 residues. Of the 12 alanine substitutions, the secretion of 9 (D242A, I244A, D246A, D252A, E253A, N279A, D283A, D289A, and D290A) was markedly reduced (>80%) compared with WT, as measured by WB and ELISA (Figure 2B and supplemental Figure 3). Similar to Q260D, secretion of the variant E281A appeared to be normal by WB but low by ELISA. Finally, variants K239A and Y276A were secreted normally and in amounts comparable to WT. Evaluating the functional profile of K239A and Y276A, we found no defects for Y276A. By contrast, K239A had defective proteolytic activity with MCP, but not with FH and CR1 (supplemental Figure 4).
Alanine mutagenesis of residues in LDLRA1 and LDLRA2. (A) Side chain of residues (shown in cyan) surrounding the 2 calcium ions (green spheres) selected for the alanine mutagenesis studies. (B) Table summarizing the location of each mutation and expression levels relative to WT measured by WB and ELISA. The ELISA values represent mean ± SEM from at least 3 different transfections. ∗On comparison to WT FI, the proteolytic activity of variant K239A was defective with MCP, whereas no defect was observed with FH or CR1 as the cofactor protein (supplemental Figure 4). n.d., not detected.
Alanine mutagenesis of residues in LDLRA1 and LDLRA2. (A) Side chain of residues (shown in cyan) surrounding the 2 calcium ions (green spheres) selected for the alanine mutagenesis studies. (B) Table summarizing the location of each mutation and expression levels relative to WT measured by WB and ELISA. The ELISA values represent mean ± SEM from at least 3 different transfections. ∗On comparison to WT FI, the proteolytic activity of variant K239A was defective with MCP, whereas no defect was observed with FH or CR1 as the cofactor protein (supplemental Figure 4). n.d., not detected.
The present results thus demonstrate that genetic variants identified in patients with aHUS and alanine mutations surrounding the calcium-binding sites in the heavy chain of FI result in a defective phenotype, most commonly due to poor expression. This picture is consistent with the model that aHUS occurs due to a dysregulated complement system resulting from heterozygous mutations in complement regulators. When FI is involved, the present study now establishes that mutations in the heavy chain that sit in the LDLRA1 and LDLRA2 lead to a quantitative defect. Given that calcium is buried within the molecule in LDLRA1 and LDLRA2,7 we speculate that most of the mutations identified here negatively impact calcium binding to FI, resulting in a structurally defective protein that either fails to be synthesized or, when synthesized, is likely to be misfolded. These data thus reveal an important and unappreciated regulatory role of calcium in FI.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Massini Merzkani for help with statistical analysis and Dennis Hourcade for helpful suggestions during the preparation of the manuscript.
This work was partly supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (grant R01 HL150146) (N.P.); Barnes Jewish Hospital Foundation Fund; and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis (A.J.).
Authorship
Contribution: A.J., J.A., and N.P. conceived and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and interpreted results; Z.H. performed the experiments; A.J. drafted the manuscript; A.J. and N.P. drafted the figures; A.J., J.A., and N.P. edited the manuscript; and all authors approved the submitted version.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.J. serves on the scientific advisory boards of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease, and Novartis International AG; serves as a consultant for Chinook Therapeutics; and is a principal investigator for Apellis Pharmaceuticals. J.A. serves as a consultant for Kypha Inc, Q32BIO Inc, Celldex Therapeutics, Clinical Pharmacy Services, Kairos Bioconsulting LLC, Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Annexon Biosciences, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Broadwing Bio LLC, and Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Anuja Java, Washington University School of Medicine, 660 S Euclid Ave, Campus Box 8045, St. Louis, MO 63110; e-mail: ajava@wustl.edu; and Nicola Pozzi, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Edward A. Doisy Research Center, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, 1100 S Grand Blvd, St. Louis, MO 63104; e-mail: nicola.pozzi@health.slu.edu.
References
Author notes
Data for recombinant expression of CFI variants and complement functional assays are reported in the supplement. For any other original data, please contact ajava@wustl.edu.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal