Key Points
Endothelial KIT ligand deletion reduces systemic KIT ligand, precluding conclusions on role of endothelial niche expression of KIT ligand.
HSC homeostasis is regulated primarily by soluble rather than membrane KIT ligand expression in endothelial cells.
Abstract
A critical regulatory role of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) vascular niches in the bone marrow has been implicated to occur through endothelial niche cell expression of KIT ligand. However, endothelial-derived KIT ligand is expressed in both a soluble and membrane-bound form and not unique to bone marrow niches, and it is also systemically distributed through the circulatory system. Here, we confirm that upon deletion of both the soluble and membrane-bound forms of endothelial-derived KIT ligand, HSCs are reduced in mouse bone marrow. However, the deletion of endothelial-derived KIT ligand was also accompanied by reduced soluble KIT ligand levels in the blood, precluding any conclusion as to whether the reduction in HSC numbers reflects reduced endothelial expression of KIT ligand within HSC niches, elsewhere in the bone marrow, and/or systemic soluble KIT ligand produced by endothelial cells outside of the bone marrow. Notably, endothelial deletion, specifically of the membrane-bound form of KIT ligand, also reduced systemic levels of soluble KIT ligand, although with no effect on stem cell numbers, implicating an HSC regulatory role primarily of soluble rather than membrane KIT ligand expression in endothelial cells. In support of a role of systemic rather than local niche expression of soluble KIT ligand, HSCs were unaffected in KIT ligand deleted bones implanted into mice with normal systemic levels of soluble KIT ligand. Our findings highlight the need for more specific tools to unravel niche-specific roles of regulatory cues expressed in hematopoietic niche cells in the bone marrow.
Introduction
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), safeguarding life-long replenishment of all blood cell lineages, are tightly controlled by intrinsic and extrinsic cues.1 The concept that extrinsic HSC regulation is largely achieved locally within distinct HSC niches was proposed more than 4 decades ago.2 Developments facilitating identification, imaging, and cellular and molecular characterization of HSCs and their neighboring candidate niche cells have provided evidence of anatomical HSC niches in the bone marrow (BM).3-5 Although controversy remains regarding the exact cell types that constitute HSC niches,3-12 candidate HSC niches are vascularized3-5 and include endothelial cells (ECs).7 However, evidence for anatomical HSC niches does not in itself address whether the proposed niche cells have critical HSC-sustaining roles. Genetic experiments have been conducted to address this, including ablation of candidate niche cell types in the BM, resulting in phenotypes compatible with an HSC niche regulatory role for a number of cell types.6,8-11 However, this interpretation has been disputed3-5 because the observed HSC phenotypes may reflect systemic rather than niche cell-specific roles of ablated cell types and the soluble extrinsic regulators they produce, because the targeted cell types are not restricted to the BM or proposed HSC niches. Therefore, knocking out key regulatory molecules expressed in candidate BM HSC niche cells has been used as an alternative and potentially more specific approach to establish the direct regulatory roles of HSC niche cells.
KIT ligand (Kitl, also known as stem cell factor or steel factor) and its receptor KIT were initially discovered through the shared pleiotropic effects of germ line mutations in the Steel (Sl) and dominant-white spotting (W) locus, respectively, resulting in deficiencies in gametogenesis, melanogenesis, and hematopoiesis of different severity dependent on the type of mutation.13 In mice homozygous for the Sl mutation, resulting in the deletion of the Kitl coding sequences, a complete loss of KITL expression is observed, resulting in lethality late in gestation.14 Within the BM, where KITL is known to play a key role in the regulation of HSC numbers,1,3-5 ECs and leptin receptor positive perivascular stromal cells (LEPR+ PVCs) express the highest levels of Kitl.15 The identification of the membrane-bound expression of KITL (mKITL),16 which when membrane bound would probably require direct cell-cell contact between HSCs that express the receptor KIT and the BM niche cells that express mKITL, including ECs and PVCs,7,17 and the finding that Steel-Dickie (Sld) mutant mice that express only soluble KITL (sKITL) have a severe HSC defect,5,18,19 have been interpreted as evidence that mKITL acts locally in creating a BM HSC niche.5,7,20 Combined with the conditional deletion of Kitl (required for sKITL and mKITL expression) in ECs, resulting in reduced HSC numbers in the BM of adolescent as well as adult mice,7 this was interpreted as evidence for a perivascular HSC niche in the BM in which EC-derived mKITL regulates HSC maintenance.5 However, more recently we also demonstrated that circulating sKITL is drastically reduced in Sld mutant mice.21 Heterozygous germ line Kitl knockout mice display a reduction in HSC numbers7 and a corresponding gene dosage effect on the systemic sKITL levels.21 Because KITL is expressed by ECs outside and throughout the BM,22-24 this raised the alternative possibility that EC-derived KITL might sustain HSCs primarily through sKITL, potentially produced outside the HSC niche or even outside the BM, rather than through the proposed endothelial niche cell expression of mKITL.5,7 Herein, we pursued experiments to provide further insights into the regulatory roles of EC-derived systemic sKITL and EC niche–presented mKITL.
Methods
Mouse lines
Genetically modified mouse models used in the study are summarized in supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website. Mice allowing for the conditional deletion of Kitl (Kitltm2.1Sjm/J; Δ), encoding sKITL and mKITL, and KitlLEx7/LEx7 (LEx7) mice allowing for the conditional deletion of mKITL have been described.7,21 LEx7 mice had been backcrossed onto a C57BL/6 background for >5 generations. KitlΔEx7/ΔEx7 (ΔEx7) mice, with germ line deletion of mKitl, were generated by crossing LEx7 mice with CMV-Cretg/+ (B6.C-Tg[CMV-cre]1Cgn/J) mice.25 Conditional cell-specific deletion of mKitl was induced by crossing LEx7 mice with Tie2-Cretg/+ (B6.Cg-Tg[Tek-cre]1Ywa/J) mice (The Jackson Laboratory, stock 008863), LepRCre/+ (B6.129[Cg]-Leprtm2(cre)Rck/J) mice,7,26 or Amh-Cretg/+ (B6.FVB[129S]-Tg(Amh-cre)8815Reb/J) mice.27LepRCre/+ mice were identical to those previously used to study the role of KITL in hematopoiesis.7,28 The genotyping strategy used to distinguish Tie2-Cretg and LepRCre alleles (supplemental Figure 1) was identical to that in previous studies.7
Kitl-tdTomatotg/+ mice have been described,21 and Sl/+ (WC/ReJ KitlSl/J) mice29 were from The Jackson Laboratory (stock 000693). LEx7 mice,21Sl/+ mice,30 and LepRCre/+ mice7 were genotyped as previously described, whereas primers for genotyping ΔEx7, CMV-Cretg/+, Amh-Cretg/+, and Tie2-Cretg/+ mice are specified as follows: ΔEx7 forward primer 5′-CTTGCCTCGAGCCCTTAAT-3′ and ΔEx7 reverse primer 5′-GCCCTTAAGTGTGCCTTGTC-3′ (ΔEx7 <200 bp); CMV-Cretg/+ and Amh-Cretg/+ forward primer 5′-CGTTTTCTGAGCATACCTGGA-3′ and CMV-Cretg/+ and Amh-Cretg/+ reverse primer 5′-ATTCTCCCACCGTCAGTACG-3′ (Tg: 450 bp); Tie2-Cretg/+ forward primer 5′-CCTGTGCTCAGACAGAAATG-3′ and Tie2-Cretg/+ reverse primer 5′-GGCAAATTTTGGTGTACGGTC-3′ (Tg: ∼200 bp); and Kitl-tdTomatotg/+ forwardTomato primer 5′-CACCTCCCACAACGAGGACTACACC-3′, Kitl-tdTomatotg/+ forwardKitl-UTR primer 5′-GGGCTTCATTTGCTGTCTGTCACC-3′, and Kitl-tdTomatotg/+ reverseKitl primer 5′-TCTCACACCACGCCTGTCTCTCC-3′ (wild-type: 331 bp; Kitl-tdTomatotg/+: 588 bp).
All mice were maintained at the Biomedical Services animal facility, University of Oxford, in accordance with the United Kingdom Home Office regulations, and the procedures were performed under ethical license number 30/3103, approved by the Oxford University Clinical Medicine Ethical Review Committee.
Flow cytometry
Bones were processed by crushing in a mortar before counting the cellularity with a Sysmex cell counter. Mouse BM and spleen HSCs and myeloid progenitors and peripheral blood (PB) cell lineages were analyzed as described.31,32 Antibodies (supplemental Table 2) were titrated and specificity controlled based on simultaneous analysis of cell populations lacking expression of the antigens and/or by using isotype control antibodies from the same companies as those of specific antibodies. Dead cells were excluded using 7-amino-actinomycin D or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Stained cells were acquired on a BD LSRII or a BD LSRFortessa X-20 (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using FlowJo analysis software (TreeStar Inc).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Mouse PB serum samples were clotted for 2 hours and centrifuged for 20 minutes at 2000g. Bone extracellular fluid samples were collected, as previously described,33 from 1 mouse femur by removing distal epiphysis, followed by 1 minute centrifugation at 3000g, allowing for collection of BM fluid into 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes containing 50 μL phosphate-buffered saline. Collected cells were mixed by pipetting and centrifuged for 3 minutes at 300g, followed by the collection of supernatant. Isolated serum and BM fluid were assessed by KITL enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (R&D systems), as described.21 Optical density was measured on microplate reader (Molecular Devices-SpectraMaxM2e) set to 450 nm, with a wavelength correction of 570 nm. Concentration was extrapolated from a standard curve run for each individual experiment.
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
Two thousand cells were fluorescence-activated cell sorted directly into Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen), and RNA was isolated. Reverse transcription was performed using Superscript Vilo complementary DNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen). Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was performed with Taqman Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems): total Kitl, Mm00442972_m1; mKitl, Mm01232339_m1; and Hprt, Mm01545399_m1. Data were analyzed with ΔCt method, using housekeeping gene Hprt, or mean of housekeeping genes B2m, Gapdh, and Hprt, for normalization. Alternatively, 50 cells were sorted directly into CellsDirect 2X reaction mix with Taqman Gene Expression Assays. Samples were subjected to targeted complementary DNA amplification for 22 cycles, diluted 1:5 in Tris-EDTA buffer before multiplex qPCR analysis using the Biomark 96.96 Dynamic Array platform.34
Competitive BM transplantation
Functional assessment of HSC activity was performed through competitive long-term BM reconstitution experiments,31 the gold standard for assessing HSC activity.35 BM mononuclear cells (2 × 106) from CD45.2 donor mice were intravenously transplanted with unfractionated support/competitor CD45.1 BM cells (2 × 106) into lethally irradiated (split dosage of 500 cGy each) C57BL/6 (CD45.1) recipient mice (>8 weeks old). Flow cytometry analysis of CD45.1 and CD45.2 contribution to mature PB lineages and BM HSCs was performed 16 weeks after transplantation.31 For competitive transplantations with cells from femurs implanted under the kidney capsule, 5 × 106 donor cells (CD45.2) were transplanted together with 2.5 × 105 support BM CD45.1 cells into CD45.1 recipients.
Renal subcapsular bone transplantation assay
Wild-type, Kitl-tdTomatotg/+, and Sl/Sl embryos, on a CD45.2 background, were collected from pregnant mice at embryo day (E) 15.5, and femurs dissected under stereomicroscope. Both femurs from each embryo were surgically transplanted under the kidney capsule of 8- to 14-week-old wild-type mice with normal serum KITL levels, under anesthesia.36,37 CD45.1 recipients were used for evaluation of hematopoietic chimerism in transplanted bones, and CD45.2 recipients were used for evaluating HSC activity within kidney capsule–transplanted bones. Grafted bones were dissected from the kidney 3 to 4 weeks after transplantation, and the BM analyzed for cellularity, HSC and progenitor numbers, and long-term competitive repopulating ability.
Immunohistochemistry
Dissected testicles were cryo-embedded and sectioned (8-10 μm). Sections were fixed with methanol, blocked with protein (Dako), and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies. Stained sections were incubated with secondary antibodies for 2 hours and mounted with coverslips using ProLong Gold Antifade Reagent (Invitrogen). Antibodies used are shown in supplemental Table 2. Immunofluorescence data were acquired with a BioRad Radiance 2000 laser scanning confocal microscope or Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope. Images were analyzed using Fiji/ImageJ software with manual identification of spermatogonial precursor cells (SPCs) and KIT+ cells.
Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise specified, data sets were analyzed using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test to assess statistical significance.
Results
Endothelial KITL deletion results in reduced systemic KITL levels and HSC numbers
Using the same Tie2-Cretg (B6.Cg-Tg[Tek-cre]1Ywa/J) conditional targeting as in previous studies7 to delete the floxed Kitl (Kitltm2.1Sjm/J; Δ) allele (encoding mKITL and sKITL) in ECs of heterozygous Sl (WC/ReJ KitlSl/J) mice (Sl/Tie2Δ), we observed, as previously reported,7 a significant reduction (35%) in BM HSCs in Sl/Tie2Δ mice aged 4 weeks, as assessed by flow cytometry (Figure 1A-C), which was confirmed by a significant reduction in HSC long-term repopulating activity, as assessed by competitive transplantation (Figure 1D; supplemental Figure 2A-B). Sl/Tie2Δ mice also had a significant reduction in committed erythroid progenitor cells (Figure 1E; supplemental Figure 2C). However, and to our knowledge, not previously investigated, this was also accompanied by significantly reduced (39%) systemic levels of sKITL (Figure 1F; supplemental Table 3). Combined with the fact that KITL is produced by ECs in multiple other tissues and organs,22,23,38 this precludes the conclusion that maintenance of HSCs in BM is dependent on KITL produced by ECs within HSC niches5 or even ECs in the BM.
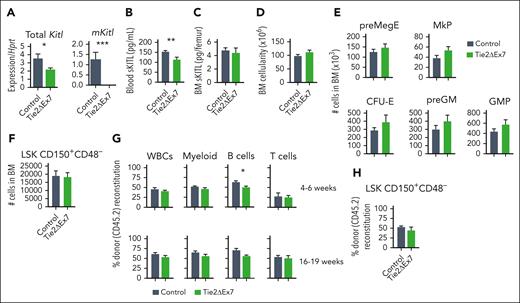
Endothelial Kitl deletion results in reduced HSC numbers and reduced systemic levels of sKITL. (A) Mean (± standard error of mean [SEM]) total BM mononuclear cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (B-C) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) profiles with gated cell populations as percentages of total BM cells (B) and mean (± SEM) Lineage–Sca1+KIT+ (LSK) CD150+CD48– HSC numbers (C) of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (D) Mean (± SEM) percent donor (CD45.2) contribution in total PB toward total white blood cells (WBCs), MAC1+GR1+ myeloid cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD4/CD8a+ T cells 6 and 16 weeks after competitive transplantation of Sl/+ (n = 3 donors) or Sl/Tie2Δ (5 donors) BM cells. (E) Mean (± SEM) numbers of pre–megakaryocyte-erythroid (preMegE), megakaryocyte (MkP), colony forming unit–erythroid (CFU-E), pre–granulocute-monocyte (preGM), and granulocyte-monocyte (GMP) progenitor cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (F) Mean (± SEM) blood serum sKITL levels determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) from 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 4) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (G-H) Mean (± SEM) total BM mononuclear cell (G) and LSK CD150+CD48– HSC (H) numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 5 per genotype). (I) Mean (± SEM) committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cell numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 4-5 per genotype). All data represent mean ± SEM, and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
Endothelial Kitl deletion results in reduced HSC numbers and reduced systemic levels of sKITL. (A) Mean (± standard error of mean [SEM]) total BM mononuclear cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (B-C) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) profiles with gated cell populations as percentages of total BM cells (B) and mean (± SEM) Lineage–Sca1+KIT+ (LSK) CD150+CD48– HSC numbers (C) of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (D) Mean (± SEM) percent donor (CD45.2) contribution in total PB toward total white blood cells (WBCs), MAC1+GR1+ myeloid cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD4/CD8a+ T cells 6 and 16 weeks after competitive transplantation of Sl/+ (n = 3 donors) or Sl/Tie2Δ (5 donors) BM cells. (E) Mean (± SEM) numbers of pre–megakaryocyte-erythroid (preMegE), megakaryocyte (MkP), colony forming unit–erythroid (CFU-E), pre–granulocute-monocyte (preGM), and granulocyte-monocyte (GMP) progenitor cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (F) Mean (± SEM) blood serum sKITL levels determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) from 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 4) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (G-H) Mean (± SEM) total BM mononuclear cell (G) and LSK CD150+CD48– HSC (H) numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 5 per genotype). (I) Mean (± SEM) committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cell numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 4-5 per genotype). All data represent mean ± SEM, and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
mKITL expressed by ECs is not critical for HSC maintenance in BM
We recently generated a novel mouse model allowing for the selective conditional depletion of mKITL.21 Here, we used this model to study the role of mKITL in steady-state HSC maintenance, because mKITL has been proposed to play an important local role in the regulation of HSCs in BM.5,18-20 Mice with germ line homozygous deletion of Kitl exon 7 (KitlΔEx7/ΔEx7; ΔEx7), encoding the transmembrane domain required for membrane localization of mKITL, were born at a reduced Mendelian ratio and with a white coat color (supplemental Figure 3A-B), characteristic of KITL deficiency. The BM of ΔEx7 mice had significantly reduced cellularity (P < .01) and 50%-reduced HSC numbers, although not reaching statistical significance (P = .06; Figure 1G-H; supplemental Figure 3C). Germ line deletion of mKITL also resulted in a reduction of several committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (Figure 1I). However, in addition to a complete loss of mKITL, we previously demonstrated a >60% reduction in systemic sKITL in ΔEx7 mice aged 3 weeks and also that circulating sKITL is drastically reduced in Sld mutant mice (supplemental Table 3),21 precluding any conclusion about the observed hematopoietic defects reflecting a niche or local role of mKITL in the BM.
In 4- to 6-week-old adolescent Tie2-Cretg/+;KitlLEx7/LEx7 (Tie2ΔEx7) mice, in which mKITL expression was specifically and efficiently deleted from ECs (Figure 2A; supplemental Figure 1), we also observed a significant (26%) reduction in circulating sKITL levels (Figure 2B; supplemental Table 3) but without any concomitant reduction of BM sKITL (Figure 2C; supplemental Table 4) and BM cellularity (Figure 2D), myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (Figure 2E), or phenotypically and functionally defined HSCs (Figure 2F-H; supplemental Figure 4).
mKITL expressed by ECs is required for sustaining systemic sKITL levels but not BM HSCs in adolescent mice. (A) qPCR analysis of Kitl messenger RNA (mRNA) levels using Kitl exon 2-3–spanning (measuring total Kitl mRNA) and exon 7-8–spanning (measuring mRNA generating mKITL) amplicons on FACS-purified BM ECs (CD45–TER119–CD31+) from 4- to 6-week-old Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 6) and wild-type littermate control mice (n = 13). Mean (± SEM) expression relative to Hprt is shown. (B) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the blood serum from 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 17) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 11) mice. The parametric Student t test was used for statistical analysis. (C) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the BM extracellular fluid from 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 10) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 4) mice. (D-F) Mean (± SEM) BM cellularity (D), number of committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (E) and LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs (F) from 2 femurs and 2 tibias from 4- to 5-week-old wild-type (control; n = 11) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 9) mice. No significant (P < .05) differences detected by either a parametric or nonparametric t test. (G-H) Percent CD45.2 contribution to total WBCs, MAC1+GR1+ myeloid cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD4/CD8a+ T cells in the blood at 4 to 6 and 16 to 19 weeks (G), and BM LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs at 16 to 19 weeks (H) after transplantation of BM from 5-week-old wild-type (control; n = 4) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5) CD45.2 mice, in competition with wild-type CD45.1 BM cells. Unless otherwise specified, all data represent mean ± SEM, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
mKITL expressed by ECs is required for sustaining systemic sKITL levels but not BM HSCs in adolescent mice. (A) qPCR analysis of Kitl messenger RNA (mRNA) levels using Kitl exon 2-3–spanning (measuring total Kitl mRNA) and exon 7-8–spanning (measuring mRNA generating mKITL) amplicons on FACS-purified BM ECs (CD45–TER119–CD31+) from 4- to 6-week-old Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 6) and wild-type littermate control mice (n = 13). Mean (± SEM) expression relative to Hprt is shown. (B) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the blood serum from 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 17) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 11) mice. The parametric Student t test was used for statistical analysis. (C) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the BM extracellular fluid from 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 10) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 4) mice. (D-F) Mean (± SEM) BM cellularity (D), number of committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (E) and LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs (F) from 2 femurs and 2 tibias from 4- to 5-week-old wild-type (control; n = 11) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 9) mice. No significant (P < .05) differences detected by either a parametric or nonparametric t test. (G-H) Percent CD45.2 contribution to total WBCs, MAC1+GR1+ myeloid cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD4/CD8a+ T cells in the blood at 4 to 6 and 16 to 19 weeks (G), and BM LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs at 16 to 19 weeks (H) after transplantation of BM from 5-week-old wild-type (control; n = 4) and Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5) CD45.2 mice, in competition with wild-type CD45.1 BM cells. Unless otherwise specified, all data represent mean ± SEM, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Although LepRCre-induced recombination in LEPR+ PVCs has been shown to be very inefficient in young mice,15LepRCre-induced targeting of a floxed Kitl allele (encoding mKITL and sKITL) was reported to result in significant reductions in HSCs in the BM of 1-month-old mice; however, Kitl expression was not investigated in targeted LEPR+ PVCs.7 In light of this, we investigated the impact of combined targeting of floxed mKitl alleles in ECs and LEPR+ PVCs on HSCs in the BM of 4- to 6-week-old mice by crossing the same LepRCre/+ (B6.129(Cg)-Leprtm2(cre)Rck/J) mice used in previous studies7 with Tie2ΔEx7 mice (supplemental Figure 1). Although mKitl expression was almost undetectable in ECs, no significant reduction in mKitl expression was observed in LEPR+ PVCs purified from the BM of Tie2-Cretg/+;LepRCreKitlLEx7/LEx7 (Tie2,LepRΔEx7) mice (supplemental Figure 5A-B), and the blood and BM sKITL levels were not significantly different compared with those in Tie2ΔEx7 mice (supplemental Figure 5C-D; supplemental Tables 3 and 4). With the exception of erythroid progenitors that were reduced in Tie2,LepRΔEx7 but not Tie2ΔEx7 mice, neither myeloid progenitors (supplemental Figure 5E-F) nor phenotypically or functionally defined HSCs were affected (supplemental Figures 4 and 5G-I). Furthermore, no significant differences in HSCs and multipotent progenitor populations were observed in the spleen from adolescent Tie2ΔEx7 or Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice (supplemental Figure 5J-L).
We next performed similar studies on adult (age, 13-15 weeks) Tie2ΔEx7 and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice, because adult mice have been shown to have a more pronounced reduction in HSCs upon conditional deletion of Kitl (encoding sKITL and mKITL) in ECs and PVCs.7 Similar to adolescent mice, mKitl was almost undetectable in ECs from the BM of Tie2ΔEx7 and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice (Figure 3A), and unlike in adolescent mice, a significant (59%) reduction was observed in mKitl expression in LEPR+ PVCs from the BM of Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice (Figure 3B). Moreover, a bigger drop in blood sKITL levels was observed in both Tie2ΔEx7 (40%) and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (43%) mice than in adolescent mice (Figure 3C; supplemental Table 3). Similar to young mice, sKITL levels were not reduced in the BM of Tie2ΔEx7 and rather significantly increased in Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice (Figure 3D; supplemental Table 4). However, similar to 4- to 6-week-old mice, no reduction in BM HSCs was observed (Figure 3E-F), and only megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor cells among the myelo-erythroid progenitors were significantly reduced in both Tie2ΔEx7 and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice (Figure 3G). In agreement with previous studies of targeted deletion of both mKITL and sKITL,7 a trend toward a higher number of spleen LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs was observed in Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice, whereas different multipotent progenitor cells were unaffected (supplemental Figure 6).
Endothelial expression of mKITL is required for sustaining normal levels of circulating sKITL but not BM HSCs in adult mice. (A-B) qPCR analysis of Kitl mRNA levels using Kitl exon 2-3–spanning (measuring total Kitl mRNA) and exon 7-8–spanning (measuring mRNA generating mKITL) amplicons in FACS-purified BM ECs (A) and LEPR+ PVCs (CD45–TER119–CD31–SCA1–LEPR+) (B) from 13- to 15-week-old Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5), Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 5-6) and wild-type littermate control (n = 3) mice. (C) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the blood serum from 13- to 15-week-old wild-type (control, n = 10), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 14) and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 14) mice. (D) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the BM extracellular fluid from 13- to 15-week- old wild-type (control, n = 3), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5), and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 5) mice. (E-G) Mean (± SEM) number (E) and frequency (F) of LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs, and number of committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (G) from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 13- to 15-week-old wild-type (control; n = 7), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 11), and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 8) mice. All data represent mean ± SEM, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Endothelial expression of mKITL is required for sustaining normal levels of circulating sKITL but not BM HSCs in adult mice. (A-B) qPCR analysis of Kitl mRNA levels using Kitl exon 2-3–spanning (measuring total Kitl mRNA) and exon 7-8–spanning (measuring mRNA generating mKITL) amplicons in FACS-purified BM ECs (A) and LEPR+ PVCs (CD45–TER119–CD31–SCA1–LEPR+) (B) from 13- to 15-week-old Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5), Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 5-6) and wild-type littermate control (n = 3) mice. (C) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the blood serum from 13- to 15-week-old wild-type (control, n = 10), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 14) and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 14) mice. (D) sKITL levels measured by ELISA in the BM extracellular fluid from 13- to 15-week- old wild-type (control, n = 3), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 5), and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 5) mice. (E-G) Mean (± SEM) number (E) and frequency (F) of LSK CD150+CD48– HSCs, and number of committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cells (G) from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 13- to 15-week-old wild-type (control; n = 7), Tie2ΔEx7 (n = 11), and Tie2,LepRΔEx7 (n = 8) mice. All data represent mean ± SEM, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Locally produced KITL is critical for sustaining BM erythroid progenitors but not HSCs
We next sought to investigate whether deletion of Kitl exclusively in BM would result in an HSC phenotype. Because no Cre lines delete Kitl expression exclusively and efficiently in the whole BM, we instead used an assay in which long bones from Sl/Sl mice (completely lacking expression of sKITL and mKITL) or wild-type mice were implanted under the kidney capsule of wild-type mice with normal expression of mKITL and sKITL (supplemental Figure 7A).
Because Sl/Sl embryos die late in gestation,13 we transplanted bones from E15.5 embryos. Previous studies implanting fetal Sl/Sl bones under the kidney capsule suggested that the number of LSK CD150+ cells were not reduced,36 but a more stringent, including functional, assessment of HSCs was not performed, and the prevalence of relevant niche cells and their expression of KITL was not investigated in the implanted bones. Hematopoiesis has been reported to not yet have colonized the BM at E15.539,40. Therefore, this approach would also ensure that any observed hematopoietic phenotype would not reflect a pretransplantation impact on HSCs because of the complete loss of KITL in all tissues of Sl/Sl embryos. However, because more recent studies suggested that rare HSCs reside in E15.5 fetal bones,41 we first assessed to what degree transplanted bones from E15.5 embryos upon harvesting were populated by HSCs already present in the E15.5 bones or by HSCs from the recipient by transplanting bones from CD45.2 embryos into CD45.1 recipients. In agreement with previous studies,36 analysis 3 weeks after bone transplantation revealed that all HSCs within both wild-type and Sl/Sl transplanted bones were from the recipient rather than transplanted bone (Figure 4A). Moreover, abundant ECs and LEPR+ PVCs were sustained in both wild-type and Sl/Sl transplanted bones, although at variable frequencies (Figure 4B). Transplanted bones from Kitl-tdTomato reporter mice21 showed high and comparable tdTomato expression with nontransplanted bones in LEPR+ PVCs, and in ECs, tdTomato expression was also sustained, although as expected,15 at lower levels than in LEPR+ PVCs (supplemental Figure 7B-C). In agreement with the Kitl-tdTomato data, LEPR+ PVCs purified from transplanted wild-type bones expressed comparable levels of Kitl with that of nontransplanted bones and no detectable Kitl levels in LEPR+ PVCs from transplanted Sl/Sl bones, demonstrating that LEPR+ PVCs were entirely derived from transplanted bones (Figure 4C). In ECs isolated from transplanted Sl/Sl bones, Kitl was reduced by 76% compared with transplanted wild-type bones (Figure 4C), demonstrating that the majority of ECs originate from the transplanted bone but also some ECs derived from the recipient, probably reflecting vascularization of the transplanted bones.36 Next, we phenotypically and functionally compared HSCs in transplanted bones from wild-type and Sl/Sl E15.5 embryos transplanted under the kidney capsule of wild-type mice (Figure 4D). No significant differences in BM HSCs were observed between transplanted wild-type and Sl/Sl bones, assessed phenotypically or functionally (Figure 4E-H). However, a large reduction in multiple stages of committed (Lin–SCA1–KIT+) progenitors was observed (Figure 4I), including multiple established32 stages of erythroid progenitors (Figure 4J-K), in agreement with the critical role of KITL in BM erythropoiesis.42 Collectively, these results support that systemically provided sKITL regulates HSC numbers in the BM and fail to support a critical role of local BM production of either mKITL or sKITL.
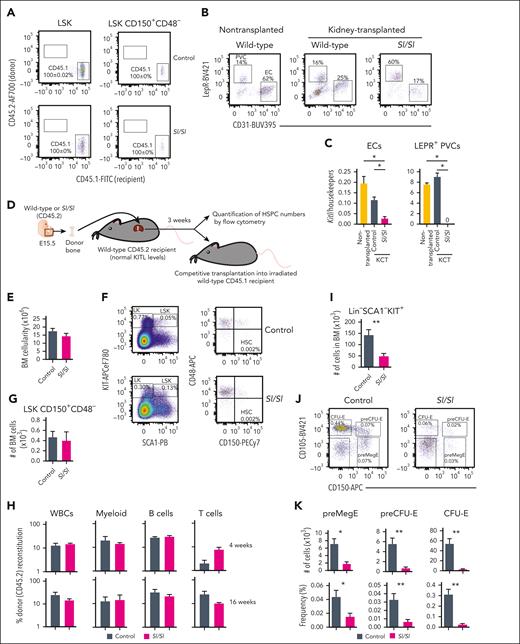
Evidence for a critical role of local BM KITL production for erythropoiesis but not HSCs. (A) Representative FACS profiles and mean (± SEM) percentage recipient CD45.1 reconstitution of LSK and LSK CD150+CD48– (HSCs) in kidney capsule–transplanted (CD45.2) E15.5 wild-type (control; n = 8) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) bones 3 weeks after transplantation. (B) Representative FACS plots showing the distribution of LEPR+ PVCs and CD31+ ECs after first gating as negative for the hematopoietic antigens CD45 and TER119 (CD45–TER119–) in the BM of a nontransplanted femur from 2.5-week-old wild-type mice (n = 5) and in E15.5 femur from wild-type (n = 8) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) embryos analyzed 3 to 4 weeks after transplantation under the kidney capsule of wild-type adult recipient mice. (C) Mean (± SEM) expression of total Kitl (Kitl exon 2-3 amplicon) relative to housekeeping genes (Hprt, B2m, and Gapdh) in ECs and LEPR+ PVCs isolated from femurs of 2.5-week-old wild-type mice (n = 5), and E15.5 femurs from wild-type (n = 5) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) embryos 3 to 4 weeks after kidney capsule transplantation (KCT). (D) Experimental design for evaluating impact on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) numbers within E15.5 wild-type or Sl/Sl (Kitl-deficient) bones transplanted into recipients with normal levels of KITL. (E) Mean (± SEM) BM cellularity of E15.5 femurs derived from CD45.2 wild-type (control) and Sl/Sl mice 3 weeks after transplantation under the kidney capsule of adult CD45.2 wild-type mice (n = 8 of each genotype). (F-G) Representative FACS profiles with gated cell populations as percentages of total BM cells (F) and mean (± SEM) LSK CD150+CD48– (HSC) numbers (G) per femur (n = 5 of each genotype). (H) Mean (± SEM) PB reconstitution 4 and 16 weeks after competitive transplantation of whole BM cells (CD45.2) from transplanted femurs from (E-G) in competition with wild-type CD45.1 BM cells into irradiated CD45.1 recipients. (I) Mean (± SEM) number of Lin–SCA1–KIT+ (LK) cells (including all committed progenitor cells) in transplanted femurs from panels D and E (n = 8 of each genotype). (J-K) Representative FACS profiles (J) and mean (± SEM) numbers (K, top row) and frequency (K, bottom) of distinct erythroid progenitor subsets in the BM of transplanted femurs from panels D and E (n = 8). All data represent mean ± SEM, and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
Evidence for a critical role of local BM KITL production for erythropoiesis but not HSCs. (A) Representative FACS profiles and mean (± SEM) percentage recipient CD45.1 reconstitution of LSK and LSK CD150+CD48– (HSCs) in kidney capsule–transplanted (CD45.2) E15.5 wild-type (control; n = 8) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) bones 3 weeks after transplantation. (B) Representative FACS plots showing the distribution of LEPR+ PVCs and CD31+ ECs after first gating as negative for the hematopoietic antigens CD45 and TER119 (CD45–TER119–) in the BM of a nontransplanted femur from 2.5-week-old wild-type mice (n = 5) and in E15.5 femur from wild-type (n = 8) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) embryos analyzed 3 to 4 weeks after transplantation under the kidney capsule of wild-type adult recipient mice. (C) Mean (± SEM) expression of total Kitl (Kitl exon 2-3 amplicon) relative to housekeeping genes (Hprt, B2m, and Gapdh) in ECs and LEPR+ PVCs isolated from femurs of 2.5-week-old wild-type mice (n = 5), and E15.5 femurs from wild-type (n = 5) and Sl/Sl (n = 4) embryos 3 to 4 weeks after kidney capsule transplantation (KCT). (D) Experimental design for evaluating impact on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) numbers within E15.5 wild-type or Sl/Sl (Kitl-deficient) bones transplanted into recipients with normal levels of KITL. (E) Mean (± SEM) BM cellularity of E15.5 femurs derived from CD45.2 wild-type (control) and Sl/Sl mice 3 weeks after transplantation under the kidney capsule of adult CD45.2 wild-type mice (n = 8 of each genotype). (F-G) Representative FACS profiles with gated cell populations as percentages of total BM cells (F) and mean (± SEM) LSK CD150+CD48– (HSC) numbers (G) per femur (n = 5 of each genotype). (H) Mean (± SEM) PB reconstitution 4 and 16 weeks after competitive transplantation of whole BM cells (CD45.2) from transplanted femurs from (E-G) in competition with wild-type CD45.1 BM cells into irradiated CD45.1 recipients. (I) Mean (± SEM) number of Lin–SCA1–KIT+ (LK) cells (including all committed progenitor cells) in transplanted femurs from panels D and E (n = 8 of each genotype). (J-K) Representative FACS profiles (J) and mean (± SEM) numbers (K, top row) and frequency (K, bottom) of distinct erythroid progenitor subsets in the BM of transplanted femurs from panels D and E (n = 8). All data represent mean ± SEM, and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.
Critical role of mKITL in the testis
To determine whether the observed requirement for sKITL, rather than mKITL, for HSCs in the BM might reflect a more general dependence on sKITL rather than mKITL, we investigated whether mKITL might be important for sustaining KIT+ SPCs in the testis,43 because Sertoli cells that act as niche cells for KIT+ SPCs appear to be highly specific for the testis. In agreement with previous studies, KIT+ SPCs were localized in close proximity to β3-tubulin–positive Sertoli cells in the testis of 4-week-old wild-type mice (Figure 5A). A recent study demonstrated that the combined deletion of sKITL and mKITL in Sertoli cells results in reduced numbers of KIT+ SPCs, but neither the relative role of sKITL and mKITL nor the potential effects on systemic sKITL expression were investigated.44 We, therefore, specifically ablated mKITL expression in Sertoli cells by generating Amh-Cretg/+ (B6.FVB(129S)-Tg(Amh-cre)8815Reb/J);KitlLEx7/LEx7 (AmhΔEx7) mice.45 Immunostaining with a mKITL specific antibody showed efficient elimination of mKITL in Sertoli cells but not in VE-cadherin–positive ECs from testes of AmhΔEx7 mice (Figure 5B). This was achieved without affecting the systemic levels of sKITL (Figure 5C; supplemental Table 3). Although BM HSC numbers and thymopoiesis were unaffected (supplemental Figure 8A-D), a significant reduction of both KIT+ SPCs and testis size was observed (Figure 5D-E; supplemental Figure 8E-F). Deletion of Kitl exon 7 in Sertoli cells was also accompanied by a significant increase in GFRA1+ spermatogonial stem cells that do not express KIT (Figure 5D-E).46 Therefore, in contrast to HSCs, KIT+ SPCs cannot be sustained by systemic sKITL and require mKITL presented by a specific niche cell type, Sertoli cells, for their maintenance and expansion in the testis.
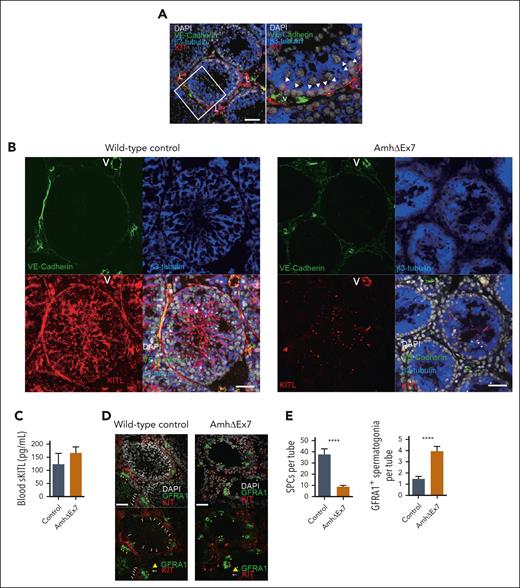
mKITL expression in Sertoli cells is critical for maintenance of Kit+ SPCs in testis. (A) Immunostaining for KIT (red), VE-cadherin (endothelium; green), β3-tubulin (Sertoli cells; blue), counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (nuclear stain; gray) in 4-week-old wild-type mouse testes. Representative of 12 sections from 3 separate mice. Arrow heads: KIT+ spermatogonial precursors adjacent to β3-tubulin+ Sertoli cells. Scale bar represents 50μm. (B) Immunostaining against cytoplasmic domain of mKITL (red), VE-cadherin (green), β3-tubulin (blue), counterstained with DAPI (gray) in 4-week-old AmhΔEx7 and wild-type mouse testes. Representative of 4 to 7 mice of each genotype. Scale bars represent 50μm. (C) Mean (± SEM) blood serum sKITL levels in 4-week old wild-type (control; n = 3) and AmhΔEx7 (n = 7) mice. (D) Immunostaining for KIT (red) and GFRA1 (green), counterstained with DAPI (gray) in 4-week-old wild-type control and AmhΔEx7 mouse testes. White arrows: KIT+ SPCs; yellow arrowhead: GFRA1+ spermatogonia. Representative of 15 mice of each genotype. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (E) Mean (± SEM) KIT+ SPCs and GFRA1+ cells per seminiferous tubule in 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 19) and AmhΔEx7 (n = 30) testes (mean ± SEM). More than or equal to 50 round cross sections of seminiferous tubules were counted per genotype. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test for multiple comparisons was used to assess statistical significance. ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. L, KIT+ Leydig cells; V, blood vessel.
mKITL expression in Sertoli cells is critical for maintenance of Kit+ SPCs in testis. (A) Immunostaining for KIT (red), VE-cadherin (endothelium; green), β3-tubulin (Sertoli cells; blue), counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (nuclear stain; gray) in 4-week-old wild-type mouse testes. Representative of 12 sections from 3 separate mice. Arrow heads: KIT+ spermatogonial precursors adjacent to β3-tubulin+ Sertoli cells. Scale bar represents 50μm. (B) Immunostaining against cytoplasmic domain of mKITL (red), VE-cadherin (green), β3-tubulin (blue), counterstained with DAPI (gray) in 4-week-old AmhΔEx7 and wild-type mouse testes. Representative of 4 to 7 mice of each genotype. Scale bars represent 50μm. (C) Mean (± SEM) blood serum sKITL levels in 4-week old wild-type (control; n = 3) and AmhΔEx7 (n = 7) mice. (D) Immunostaining for KIT (red) and GFRA1 (green), counterstained with DAPI (gray) in 4-week-old wild-type control and AmhΔEx7 mouse testes. White arrows: KIT+ SPCs; yellow arrowhead: GFRA1+ spermatogonia. Representative of 15 mice of each genotype. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (E) Mean (± SEM) KIT+ SPCs and GFRA1+ cells per seminiferous tubule in 4-week-old wild-type (control; n = 19) and AmhΔEx7 (n = 30) testes (mean ± SEM). More than or equal to 50 round cross sections of seminiferous tubules were counted per genotype. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test for multiple comparisons was used to assess statistical significance. ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. L, KIT+ Leydig cells; V, blood vessel.
Discussion
Our findings illuminate the challenges of unraveling the role of specific niche cell types in regulating HSCs residing in BM. In previous studies, specific deletion of Kitl (encoding sKITL and mKITL) in ECs resulted in perturbed maintenance of HSCs in BM.7 This, combined with the observation that Sld mutant mice that express sKITL but not mKITL have a severe HSC defect,5,18,19 led to the conclusion that ECs promote HSC maintenance through the synthesis of KITL in a perivascular HSC niche.5 However, more recently, we showed that both Sld mutant mice and mice with targeted germ line deletion of mKitl also have severely reduced systemic levels of sKITL.21 Not previously investigated, we established here that endothelial-specific deletion of Kitl, or only mKitl, is also accompanied by significant reductions in systemic sKITL. Despite reduction in the systemic sKITL levels, we failed to observe significantly reduced HSC numbers in the BM of adolescent and adult mice, with complete endothelial deletion of mKitl, as well as in adult mice in which mKitl was deleted in both ECs and LEPR+ PVCs. In another recent study, the targeted deletion of mKitl in ECs in newborn mice was accompanied by a reduction in HSCs, but the effect on systemic sKITL levels was not investigated.15 Our findings highlight that any finding implicating an EC niche role of mKITL will be limited by the endothelial deletion of mKitl also reducing circulating sKITL levels, and by sKITL and mKITL being expressed by ECs elsewhere in the BM as well as in most other tissues and organs.
Our findings fail to support an important HSC regulatory role for mKITL expressed by ECs in BM niches, as previously suggested,5,7 and are more compatible with BM HSC homeostasis being primarily dependent on the availability of endothelial sKITL, potentially produced by ECs outside HSC niches or even outside the BM. Similar to previous studies, LepRCre was inefficient in reducing mKitl expression in LEPR+ PVCs, particularly in adolescent mice, limiting the interpretation of our findings in Tie2,LepRΔEx7 mice failing to support an HSC regulatory role in the BM of mKITL expressed by LEPR+ PVCs. However, and in agreement with previous studies,36 this was also supported by the lack of an HSC phenotype in Sl/Sl (compared with that in wild-type) bones with intact LEPR+ PVCs, with no Kitl expression, and ECs, with severely reduced expression, when implanted in wild-type mice with normal circulating sKITL levels. Although these experiments also are compatible with HSC homeostasis in the BM being more dependent on systemic sKITL levels than on local BM expression of either mKITL or sKITL, it is important to emphasize that hematopoiesis in kidney capsule–implanted fetal bones are unlikely to reflect normal steady-state hematopoiesis. In contrast to HSCs, erythroid progenitors, known to also be highly KITL dependent,42 were reduced in the same kidney capsule–transplanted Sl/Sl bones.
How mKITL expression enhances systemic sKITL levels remains unclear. A possible mechanism is through the shedding of mKITL into circulation or binding of mKITL to KIT receptors, enhancing the level of circulating sKITL. Another observation made in our studies was that despite of the significantly reduced systemic levels of sKITL in Tie2ΔEx7 mice, sKITL levels in BM were unaffected, and in Tie2,LeprΔEx7 mice, these levels were even above normal levels. Although the identity and location (within HSC niches or elsewhere inside or outside the BM) of the cells responsible for this compensatory correction of sKITL levels in BM remain to be established, this study further supports a role of sKITL to reduce the impact of reduced sKITL levels in the circulation and/or local mKITL expression on HSC numbers in BM.
Although it is important to emphasize that our findings do not rule out an HSC niche role of endothelial expression of either sKITL or mKITL, they demonstrate that previous genetic models and data fall short of providing strong evidence for the proposed HSC regulatory role of KITL specifically synthesized by ECs in perivascular BM niches for HSCs.5,7 Most importantly, our studies highlight the hurdles that must be overcome to establish in a more definitive manner the regulatory roles of specific HSC niche cells and extrinsic cues in the BM. To date, to our knowledge, no proposed candidate HSC niche cells or regulators have been convincingly shown to be unique to the proposed anatomical HSC niches or BM, nor have any tools been developed to genetically modify candidate niche cells in a niche-specific or even BM-specific manner. Herein, the specific depletion of mKITL in Sertoli cells in the testis, reproducing the KIT+ sperm cell precursor deficiency of KITL-deficient mice,43 without affecting circulating sKITL levels, illustrates how a highly specific deletion of mKITL expression in a niche cell population (specific to the testis) can establish the identity of a distinct niche cell and its role in the local regulation of a distinct stem/progenitor cell, through mKITL expression in this case. A similar niche role for mKITL has also been suggested for KIT+ thymic progenitors.21 Although the tightly regulated number of HSCs and other findings are consistent with the importance of distinct BM HSC niches, more unequivocal insights into the identity and functional roles of such niches await application of more specific genetic approaches.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sean Morrison for sharing the Kitltm2.1Sjm/J mice and for critical input on these studies, Peter Besmer for providing the antibody against the intracellular region of KITL, the Medical Research Council Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine (MRC WIMM) Flow Cytometry core facility for assistance with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (supported by the MRC Human Immunology Unit, MRC Molecular Haematology Unit [MC_UU_12009], The National Institute for Health and Care Research Oxford BRC, and the John Fell Fund [131/030 and 101/517]), and the University of Oxford Biomedical Services for assistance with managing the mouse strains.
This work was supported by the MRC United Kingdom (G0801073 and MC_UU_12009/5 [S.E.W.J.] and MC_UU_12009/7 [C.N.]), Kay Kendall Leukaemia Fund (S.E.W.J. and T.C.L.), the Swedish Research Council (538-2013-8995 [S.E.W.J.] and 2015-03561 [P.S.W.]), the Knut och Alice Wallenberg Foundation (KAW 2016.0105 [S.E.W.J.] and KAW 2015.0195 [P.S.W.]), StratRegen KI (S.E.W.J.), and Wellcome Trust Sir Henry Dale Fellowship (T.C.L.) (210424/Z/18/Z).
Authorship
Contribution: S.E.W.J. and C.N. conceptualized the project; S.M., R.F., T.C.L., J.C., P.S.W., F.A., T.S., A.J.M., C.N., and S.E.W.J. designed the experiments; S.M., R.F., T.C.L., T.M., J.C., H.B., M.B., R.N., and B.W. performed the experiments; S.M., R.F., T.C.L., P.S.W., C.N., and S.E.W.J. wrote the manuscript; and all authors analyzed the experiments, examined and had the opportunity to edit the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Sten Eirik W. Jacobsen, Department of Medicine Huddinge, Hematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory, Center for Hematology and Regenerative Medicine, Box 285, 17177 Stockholm, Sweden; e-mail: sten.eirik.jacobsen@ki.se; and Claus Nerlov, Stem Cell Biology, Medical Research Council Molecular Haematology Unit at the University of Oxford, MRC Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, Oxford OX3 9DS, United Kingdom; e-mail: claus.nerlov@imm.ox.ac.uk.
References
Author notes
∗S.M., R.F., T.C.L., J.C., and P.S.W. contributed equally to the work.
†C.N. and S.E.W.J. contributed equally to the work.
All data are available within manuscript or on request from the corresponding author, Sten Eirik W. Jacobsen (sten.eirik.jacobsen@ki.se).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![Endothelial Kitl deletion results in reduced HSC numbers and reduced systemic levels of sKITL. (A) Mean (± standard error of mean [SEM]) total BM mononuclear cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (B-C) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) profiles with gated cell populations as percentages of total BM cells (B) and mean (± SEM) Lineage–Sca1+KIT+ (LSK) CD150+CD48– HSC numbers (C) of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (D) Mean (± SEM) percent donor (CD45.2) contribution in total PB toward total white blood cells (WBCs), MAC1+GR1+ myeloid cells, CD19+ B cells, and CD4/CD8a+ T cells 6 and 16 weeks after competitive transplantation of Sl/+ (n = 3 donors) or Sl/Tie2Δ (5 donors) BM cells. (E) Mean (± SEM) numbers of pre–megakaryocyte-erythroid (preMegE), megakaryocyte (MkP), colony forming unit–erythroid (CFU-E), pre–granulocute-monocyte (preGM), and granulocyte-monocyte (GMP) progenitor cells from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 3) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (F) Mean (± SEM) blood serum sKITL levels determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) from 4-week-old Sl/+ (n = 4) and Sl/Tie2Δ (n = 5) mice. (G-H) Mean (± SEM) total BM mononuclear cell (G) and LSK CD150+CD48– HSC (H) numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 5 per genotype). (I) Mean (± SEM) committed myelo-erythroid progenitor cell numbers from 2 femurs and 2 tibias of 3-week-old ΔEx7 and wild-type littermate controls (n = 4-5 per genotype). All data represent mean ± SEM, and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to assess statistical significance. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/19/10.1182_blood.2022019018/3/m_blood_bld-2022-019018-gr1.jpeg?Expires=1769164498&Signature=4dQltvZGvdlt4p6fdyN-8eNIAxqRsxdXjGBGn2MLug3-6zDysx2SUO0copR8i3B7QvLLZztyM1D-iybLBLVpmKrPFKEt4YhBsNLc-bpDV75FKxX2V7HCUPPR2dUgKcgWhuGq6qtxwKApdm3oCt9faQX5~-X28wQygYEiCbqm8u3TYPdlY08wPpjYsu1BdmcFrxoCN~qgmTjY6IG~WQKednqY9SajZ13El-OS1L62g-hgL26~jgf6UVn2CHzWLLWWcc3hK2pDfRrpYoySzAO5SCkg9oj4UN0Tha8ELOjCE2nuTfm0MTMURT8pBl8eqX1J~vbq1u~ITD7sH-lKBm~OTw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal