TO THE EDITOR:
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) endow an autologous T-cell population with major histocompatibility complex–unrestricted killing activity against tumor antigens including CD19 or the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA). Neurologic toxicities ranging from confusion to severe cerebral edema are well described for CD19-directed CAR T cells and are denoted as immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).1 In BCMA-directed CAR T cells, the pivotal clinical trials for multiple myeloma suggest unique toxicities including parkinsonism-like symptoms.2,3 Because such therapies only recently gained commercial approval, real-world data remain scarce. We present our institutional experience on incidence, presentation, management, and outcome of neurotoxicities after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy.
With institutional review board approval, we retrospectively searched our institutional database at Massachusetts General Hospital for multiple myeloma treated with BCMA-directed CAR T cells between 2016 to 2023. Toxicities and outcome were evaluated within the 12 months after CAR T-cell transfusion. Relationships between categorical variables were analyzed using χ2-testing; and differences of continuous variables were assessed using the Student t test or the Mann-Whitney U test. Receiver operating characteristic curves estimated the prognostic ability of biomarkers. Survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank testing. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism software (version 9.5.0; significance level, P ≤ .05).
We identified 76 patients with multiple myeloma treated with BCMA-directed CAR T cells (Table 1), as previously reported in part.4 Patients were heavily pretreated (median prior therapies, 5.0; range, 1-11). Baseline symptoms were appreciated in 7 patients (9.2%) including mild confusion, tremors, radiculopathy, and expressive aphasia. No patient had evidence of central nervous system disease.
Characteristics of patients with multiple myeloma treated with BCMA-directed CAR T cells
| Neurotoxicity after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy . | No ICANS (%) . | ICANS grade 1-4 (%) . | Total (%) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall, n (%) | n = 45 | n = 31 | n = 76 | |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age at CAR T-cell transfusion (y) | 63.5 ± 1.3 | 65.5 ± 1.6 | 64.3 ± 1.0 | .346 |
| M:F ratio | 1:0.6 | 1:0.6 | 1:0.6 | .839 |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| ECOG at CAR T-cell transfusion (median, range) | 1 (0-3) | 1 (0-2) | 1 (0-3) | .566 |
| Presence of neurologic symptoms | 2 (4.4) | 5 (16.1) | 7 (9.2) | .083 |
| Disease entity | ||||
| IgG | 24 (53.3) | 14 (45.2) | 38 (50.0) | .613 |
| IgA | 8 (17.8) | 9 (29.0) | 17 (22.4) | |
| IgD | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Light chain | 11 (24.4) | 8 (25.8) | 19 (25.0) | |
| Nonsecretory | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Previous therapies | ||||
| Median therapy lines (median, range) | 5.0 (1-11) | 6.0 (1-10) | 5.0 (1-11) | .101 |
| Lenalidomide | 45 (100) | 29 (93.6) | 74 (97.4) | .994 |
| Bortezomib | 42 (93.3) | 30 (96.8) | 72 (94.7) | |
| Pomalidomide | 38 (84.4) | 27 (87.1) | 65 (85.5) | |
| Carfilzomib | 31 (68.9) | 22 (71.0) | 43 (56.6) | |
| Daratumumab | 24 (53.3) | 15 (48.4) | 39 (51.3) | |
| ASCT | 25 (55.6) | 20 (64.4) | 45 (59.2) | |
| Bridging | ||||
| Cyclophosphamide | 12 (26.7) | 8 (25.8) | 20 (26.3) | .377 |
| Bortezomib | 11 (24.4) | 5 (16.1) | 16 (21.1) | |
| Pomalidomide | 5 (11.1) | 8 (25.8) | 13 (17.1) | |
| Carfilzomib | 5 (11.1) | 7 (22.6) | 12 (15.8) | |
| None | 15 (33.3) | 9 (29.0) | 31 (40.8) | |
| Lymphodepletion | ||||
| Fludarabine/cyclophosphamide | 44 (97.8) | 31 (100) | 75 (98.7) | .403 |
| Cyclophosphamide alone | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Baseline laboratory findings | ||||
| CRP (mg/L) | 26.9 ± 6.5 | 34.6 ± 10.1 | 30.1 ± 5.6 | .275 |
| Ferritin (μg/L) | 1058 ± 264 | 1255 ± 345 | 1139 ± 210 | .481 |
| Platelets (103/μL) | 112 ± 9.3 | 100 ± 10.4 | 107 ± 7.0 | .396 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | .024 |
| LDH (U/L) | 245 ± 24 | 337 ± 143 | 283 ± 60 | .387 |
| CAR T-cell product | ||||
| Idecabtagene vicleucel | 22 (48.9) | 14 (45.2) | 36 (47.4) | .405 |
| Ciltacabtagene autoleucel | 2 (4.4) | 4 (12.9) | 6 (7.9) | |
| Others∗ | 21 (46.7) | 13 (41.9) | 34 (44.7) | |
| Vein-to-vein time (d) | 39.8 ± 1.5 | 39.4 ± 1.5 | 39.6 ± 1.1 | .545 |
| CD3+ cells per lymphocytes in peripheral blood (on day 7-31; %) | 84.3 ± 3.7 | 80.6 ± 4.9 | 82.8 ± 2.9 | .540 |
| CRS | ||||
| None | 6 (13.3) | 1 (3.2) | 7 (9.2) | .041 |
| Grade 1-2 | 39 (86.7) | 27 (87.1) | 66 (86.8) | |
| Grade 3-4 | 0 | 3 (9.7) | 3 (4.0) | |
| Anti-inflammatory therapy | ||||
| Tocilizumab | 22 (48.9) | 19 (61.3) | 41 (91.1) | .286 |
| Anakinra | 1 (2.2) | 9 (29.0) | 10 (13.2) | .001 |
| Dexamethasone | 10 (34.5) | 19 (65.2) | 29 (38.2) | .001 |
| Neurotoxicity after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy . | No ICANS (%) . | ICANS grade 1-4 (%) . | Total (%) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall, n (%) | n = 45 | n = 31 | n = 76 | |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age at CAR T-cell transfusion (y) | 63.5 ± 1.3 | 65.5 ± 1.6 | 64.3 ± 1.0 | .346 |
| M:F ratio | 1:0.6 | 1:0.6 | 1:0.6 | .839 |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| ECOG at CAR T-cell transfusion (median, range) | 1 (0-3) | 1 (0-2) | 1 (0-3) | .566 |
| Presence of neurologic symptoms | 2 (4.4) | 5 (16.1) | 7 (9.2) | .083 |
| Disease entity | ||||
| IgG | 24 (53.3) | 14 (45.2) | 38 (50.0) | .613 |
| IgA | 8 (17.8) | 9 (29.0) | 17 (22.4) | |
| IgD | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Light chain | 11 (24.4) | 8 (25.8) | 19 (25.0) | |
| Nonsecretory | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Previous therapies | ||||
| Median therapy lines (median, range) | 5.0 (1-11) | 6.0 (1-10) | 5.0 (1-11) | .101 |
| Lenalidomide | 45 (100) | 29 (93.6) | 74 (97.4) | .994 |
| Bortezomib | 42 (93.3) | 30 (96.8) | 72 (94.7) | |
| Pomalidomide | 38 (84.4) | 27 (87.1) | 65 (85.5) | |
| Carfilzomib | 31 (68.9) | 22 (71.0) | 43 (56.6) | |
| Daratumumab | 24 (53.3) | 15 (48.4) | 39 (51.3) | |
| ASCT | 25 (55.6) | 20 (64.4) | 45 (59.2) | |
| Bridging | ||||
| Cyclophosphamide | 12 (26.7) | 8 (25.8) | 20 (26.3) | .377 |
| Bortezomib | 11 (24.4) | 5 (16.1) | 16 (21.1) | |
| Pomalidomide | 5 (11.1) | 8 (25.8) | 13 (17.1) | |
| Carfilzomib | 5 (11.1) | 7 (22.6) | 12 (15.8) | |
| None | 15 (33.3) | 9 (29.0) | 31 (40.8) | |
| Lymphodepletion | ||||
| Fludarabine/cyclophosphamide | 44 (97.8) | 31 (100) | 75 (98.7) | .403 |
| Cyclophosphamide alone | 1 (2.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) | |
| Baseline laboratory findings | ||||
| CRP (mg/L) | 26.9 ± 6.5 | 34.6 ± 10.1 | 30.1 ± 5.6 | .275 |
| Ferritin (μg/L) | 1058 ± 264 | 1255 ± 345 | 1139 ± 210 | .481 |
| Platelets (103/μL) | 112 ± 9.3 | 100 ± 10.4 | 107 ± 7.0 | .396 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | .024 |
| LDH (U/L) | 245 ± 24 | 337 ± 143 | 283 ± 60 | .387 |
| CAR T-cell product | ||||
| Idecabtagene vicleucel | 22 (48.9) | 14 (45.2) | 36 (47.4) | .405 |
| Ciltacabtagene autoleucel | 2 (4.4) | 4 (12.9) | 6 (7.9) | |
| Others∗ | 21 (46.7) | 13 (41.9) | 34 (44.7) | |
| Vein-to-vein time (d) | 39.8 ± 1.5 | 39.4 ± 1.5 | 39.6 ± 1.1 | .545 |
| CD3+ cells per lymphocytes in peripheral blood (on day 7-31; %) | 84.3 ± 3.7 | 80.6 ± 4.9 | 82.8 ± 2.9 | .540 |
| CRS | ||||
| None | 6 (13.3) | 1 (3.2) | 7 (9.2) | .041 |
| Grade 1-2 | 39 (86.7) | 27 (87.1) | 66 (86.8) | |
| Grade 3-4 | 0 | 3 (9.7) | 3 (4.0) | |
| Anti-inflammatory therapy | ||||
| Tocilizumab | 22 (48.9) | 19 (61.3) | 41 (91.1) | .286 |
| Anakinra | 1 (2.2) | 9 (29.0) | 10 (13.2) | .001 |
| Dexamethasone | 10 (34.5) | 19 (65.2) | 29 (38.2) | .001 |
Characteristics are given for patients without neurotoxicity (n = 45), neurotoxicity (n = 31), and summarized for all cases (total; N = 76). Differences between the groups were analyzed using the unpaired Student t test (for parametric data) or the Mann-Whitney U test (for nonparametric data) for continuous variables; and categorical variables were assessed by the χ2-test. No correction for multiple testing was done. P values are given, and boldface indicates P ≤ .05.
ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CRP, C-reactive protein; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; F, female; Ig, immunoglobulin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; M, male.
Others: mainly CART-ddBCMA (NCT04155749), bb21217 (NCT03274219), and TriPRIL CAR T cells (NCT05020444).
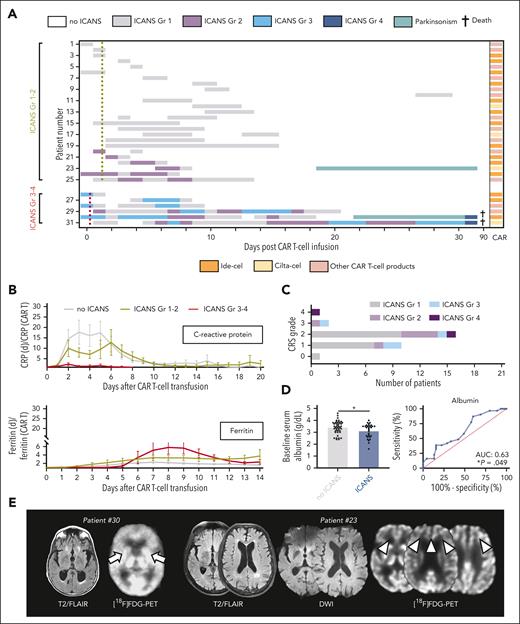
After BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy, 31 patients (40.8%) exhibited new neurologic symptoms, including 6 patients who developed severe symptoms (7.9%; Figure 1A). Mild ICANS (American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy grade 1-2) was characterized by headaches, expressive aphasia, and modest confusion. Severe ICANS (American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy grade 3-4) presented with substantial encephalopathy translating into profound confusion or impaired level of arousal (necessitating intubation in 1 patient with concurrent sepsis). ICANS was often accompanied by tremors or myoclonus. No neuropathies were observed. Median symptom onset was on day 3 (range, 0-27) for mild ICANS, and day 0 to 1 for severe ICANS (range, 0-4).
Toxicities and outcome after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. (A) Kinetics of neurotoxicity (ICANS) in each patient through 90 days after transfusion of BCMA-directed CAR T cells. Patients with mild ICANS (n = 25) and severe ICANS (n = 6) are depictured. Each row represents 1 patient, and the highest grade (Gr) of ICANS recorded on each day is color coded. Mean time to first fever of ≥38°C for patients with grade 1-2 ICANS (yellow dotted line) and grade 3-4 ICANS is indicated (red dotted line). The specific CAR T-cell product for each patient is also given. (B) Median ratio of the serum levels of the acute-phase proteins, C-reactive protein and ferritin, in relationship to serum levels at CAR T-cell transfusion. (C) Number of patients with each grade of CRS and ICANS. (D) Serum levels of albumin at CAR T-cell transfusion (left) and receiver operating characteristic curve for the prediction of ICANS of any grade by the serum levels of albumin (right). (E) Axial brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR; left panel each) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences (middle panel) of the patients with parkinsonism-like features after CAR T-cell transfusion. No specific acute MRI abnormalities are detected in either patient. On [18F]FDG-PET imaging (right panel each), basal ganglion hypometabolism (arrows) is demonstrated in 1 patient (patient #30) whereas the other individual shows frontal hypometabolism (arrowheads). (F) Distribution of best disease response in patients with and without ICANS. (G) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival after CAR T-cell transfusion for patients with (blue; n = 31) and without (gray; n = 45) ICANS. Points indicate patients who were deceased or censored, light shading indicates standard error of the mean. mOS, median overall survival.
Toxicities and outcome after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. (A) Kinetics of neurotoxicity (ICANS) in each patient through 90 days after transfusion of BCMA-directed CAR T cells. Patients with mild ICANS (n = 25) and severe ICANS (n = 6) are depictured. Each row represents 1 patient, and the highest grade (Gr) of ICANS recorded on each day is color coded. Mean time to first fever of ≥38°C for patients with grade 1-2 ICANS (yellow dotted line) and grade 3-4 ICANS is indicated (red dotted line). The specific CAR T-cell product for each patient is also given. (B) Median ratio of the serum levels of the acute-phase proteins, C-reactive protein and ferritin, in relationship to serum levels at CAR T-cell transfusion. (C) Number of patients with each grade of CRS and ICANS. (D) Serum levels of albumin at CAR T-cell transfusion (left) and receiver operating characteristic curve for the prediction of ICANS of any grade by the serum levels of albumin (right). (E) Axial brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR; left panel each) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences (middle panel) of the patients with parkinsonism-like features after CAR T-cell transfusion. No specific acute MRI abnormalities are detected in either patient. On [18F]FDG-PET imaging (right panel each), basal ganglion hypometabolism (arrows) is demonstrated in 1 patient (patient #30) whereas the other individual shows frontal hypometabolism (arrowheads). (F) Distribution of best disease response in patients with and without ICANS. (G) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival after CAR T-cell transfusion for patients with (blue; n = 31) and without (gray; n = 45) ICANS. Points indicate patients who were deceased or censored, light shading indicates standard error of the mean. mOS, median overall survival.
Although we did not observe a distinct serum profile of inflammatory markers (Figure 1B), there was a close association between systemic inflammation and ICANS, with virtually all patients with neurotoxicities demonstrating cytokine release syndrome (CRS; P = .041; Figure 1C). Fever ≥38°C as an early CRS sign trended to occur earlier among patients who developed severe ICANS (0.3 ± 0.4 vs 1.5 ± 0.2 days; P = .143). Lower albumin levels at CAR T-cell transfusion were seen among individuals with ICANS and may identify individuals at elevated risk (area under curve, 0.63; P = .049) (Figure 1D). Electroencephalography (EEG) was conducted in 5 patients with ICANS grade 1-2 and 5 patients with ICANS grade 3-4, and background slowing was often appreciated (grade 1-2: 60% [3/5] of EEGs; grade 3-4: 80% [4/5] of EEGs). No seizures were found, but generalized rhythmic delta activity was demonstrated in 1 patient with ICANS grade 2 and in 2 patients with ICANS grade 3. Antiepileptics did not substantially improve symptoms. Imaging was unrevealing. Management of mild ICANS included supportive care and the interlukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–antagonist tocilizumab for CRS. Severe ICANS was treated with high-dose steroids and the IL-1 receptor–antagonist anakinra. Neither myeloma subtypes, tocilizumab use, nor specific commercial CAR T-cell products were associated with ICANS occurrence or peculiar neurotoxicity kinetics. Two fatalities were encountered in the setting of concurrent sepsis.
After a full recovery of acute ICANS, 2 individuals (2.6%; 1 with high tumor burden and 1 with low tumor burden)3 presented with parkinsonism-like symptoms. One patient showed confusion and bradykinesia with increased muscle tone on day 22 after idecabtagene vicleucel; and [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) demonstrated bilateral hypometabolism in the basal ganglia, as previously described (Figure 1E).2 Symptoms worsened despite multimodal approaches (steroids, anakinra, and levodopa/carbidopa), and the patient finally deceased from bacterial and fungal sepsis. A second patient developed confusion, postural instability, mild tremor, and bradykinesia with hypomimia and hypophonia on day 19 after ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Frontal hypometabolism was displayed on [18F]FDG-PET; and flow cytometry of circulating lymphocytes 2 weeks after transfusion detected high rates of 99% CD3+ T cells. Confusion and bradykinesia improved within 2 weeks after dexamethasone (start: 10 mg every 6 hours; slowly tapered) and anakinra (100 mg every 12 hours; 10 days); and his postural stability fully recovered within 4 weeks after high-dose cyclophosphamide (2000 mg/m2, scheduled once) to decrease the number of circulating T cells.
Complete or partial disease response was noted in 63 patients (82.9%; including both patients with parkinsonism-like symptoms), and there were no response differences between patients with or without ICANS (P = .439; Figure 1F). Accordingly, ICANS was not associated with overall survival (hazard ratio for ICANS: 1.19; confidence interval [CI], 0.6-2.4; P = .628) at a median follow-up of 22 months (Figure 1G). This held true when we compared patients with severe ICANS with patients with mild ICANS. Thirteen individuals received a second CAR T-cell transfusion because of progressive disease. One patient with mild ICANS after the first CAR T-cell transfusion developed severe ICANS, whereas exclusively mild symptoms were observed among individuals without previous ICANS.
We found an ICANS rate of 41% after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell transfusion. This rate is higher than in the pivotal trials leading to commercial approval of BCMA-targeting CAR T cells.5-7 Our cohort included older patients with worse clinical performance, who may not have been eligible for treatment of prior clinical trials,5,7 and such clinical factors were shown to predispose for neurotoxicity.1,8 However, symptoms were generally mild and transient. Accordingly, the presence of ICANS did not alter survival in our cohort. Cautionary, we cannot rule out screening bias because our detailed review and daily neuro(-oncological) assessments yielded symptoms that would otherwise remain clinically silent. Consequently, the observed neurotoxicity frequency observed was also somewhat higher compared with previous real world–like studies.9,10 Patients with low serum albumin levels (potentially reflecting extensive disease or baseline inflammation)11 or high-grade CRS were at risk of ICANS. Importantly, repeated CAR T-cell transfusions appear to be without aggravated ICANS risk, but this warrants confirmation in larger cohorts.
Clinical ICANS symptoms predominantly included encephalopathy of varying degrees, and EEG abnormalities were often observed. Such findings were also made after CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy,1,12,13 supporting similar pathogenetic mechanisms. A close association between systemic inflammation characterized by early fever and high CRS rates was observed, arguing for systemic proinflammatory cytokines as a driver of ICANS.1,14 Cross-reactivity against brain mural cells could contribute to the higher ICANS rates after CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy.15
Notably, complex movement disorders reassembling parkinsonism may occur. On-target–off-tumor effects against BCMA+ cells in the basal ganglia were suggested as a mechanism.2,3 Considerable (CAR) T-cell expansion, effectiveness of cyclophosphamide against symptoms, and basal ganglion hypometabolism observed in our patients may support such a hypothesis. However, reversibility and frontal hypometabolism suggest additional pathomechanisms, which remain to be elucidated. Notably, we observed parkinsonism-like symptoms after both ciltacabtagene autoleucel and idecabtagene vicleucel. Whether different (experimental) CAR products carry different risk profiles is unclear as we were unable to present more detailed findings because of trial reporting restrictions. However, symptoms may be reversible; and optimal treatments, long-term outcome, and associations of parkinsonism-like symptoms with specific CAR T-cell products or CAR kinetics remain to be determined. Although no definitive conclusions can be made from our preliminary data, strategies to reduce the number of circulating CAR T cells (eg, cyclophosphamide) could play a role. Neuropathies reported by others were not observed in our study.5
Collectively, our results demonstrate an overall manageable neurotoxicity profile of BCMA-directed CAR T cells. Studies on treatment algorithms are warranted because severe acute neurotoxicities and delayed hypokinetic movement disorders may occur.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients and their families.
Authorship
Contribution: P.K. and J.D. were responsible for study concept and design; P.K., K.C.M., N.R., M.J.F., and J.D. collected data; P.K., K.C.M., A.J.Y., K.R., P.C.J., N.R., M.J.F., and J.D. were responsible for data analysis and interpretation; P.K. and J.D. reported statistics; P.K. and J.F. drafted the manuscript; and P.K., K.C.M., A.J.Y., K.R., P.C.J., N.R., M.J.F., and J.D. revised the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.J.Y. reports consulting for AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, GSK Janssen, Karyopharm, Oncopeptides Regeneron, Sanofi, and Takeda. K.R. reports research funding and travel support from Kite/Gilead; receives honoraria from Novartis; and provides consultancy and receives honoraria from BMS/Celgene. P.C.J. provides consulting for Seagen, ADC Therapeutics, and AstraZeneca; receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Medically Home. M.J.F. reports consulting for BMS, Novartis, Kite, Arcellx, Iovance, and Cytoagents. J.D. provides consulting for Amgen, Unum Therapeutics, and Novartis; and receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Philipp Karschnia, Division of Neuro-Oncology, Department of Neurosurgery, Ludwig Maximilian University Munich, Marchioninistr 15, 81377 Munich, Germany; e-mail: p.karschnia@med.uni-muenchen.de; and Jorg Dietrich, Division of Neuro-Oncology, Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Harvard Medical School, 55 Fruit St, Yawkey 9E, Boston, MA 02114; e-mail: dietrich.jorg@mgh.harvard.edu.
References
Author notes
∗M.J.F. and J.D. contributed equally to this work as joint senior authors.
On request from qualified investigators, anonymized data will be made available from the corresponding authors, Philipp Karschnia (p.karschnia@med.uni-muenchen.de) and Jorg Dietrich (dietrich.jorg@mgh.harvard.edu).
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.

![Toxicities and outcome after BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. (A) Kinetics of neurotoxicity (ICANS) in each patient through 90 days after transfusion of BCMA-directed CAR T cells. Patients with mild ICANS (n = 25) and severe ICANS (n = 6) are depictured. Each row represents 1 patient, and the highest grade (Gr) of ICANS recorded on each day is color coded. Mean time to first fever of ≥38°C for patients with grade 1-2 ICANS (yellow dotted line) and grade 3-4 ICANS is indicated (red dotted line). The specific CAR T-cell product for each patient is also given. (B) Median ratio of the serum levels of the acute-phase proteins, C-reactive protein and ferritin, in relationship to serum levels at CAR T-cell transfusion. (C) Number of patients with each grade of CRS and ICANS. (D) Serum levels of albumin at CAR T-cell transfusion (left) and receiver operating characteristic curve for the prediction of ICANS of any grade by the serum levels of albumin (right). (E) Axial brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR; left panel each) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences (middle panel) of the patients with parkinsonism-like features after CAR T-cell transfusion. No specific acute MRI abnormalities are detected in either patient. On [18F]FDG-PET imaging (right panel each), basal ganglion hypometabolism (arrows) is demonstrated in 1 patient (patient #30) whereas the other individual shows frontal hypometabolism (arrowheads). (F) Distribution of best disease response in patients with and without ICANS. (G) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival after CAR T-cell transfusion for patients with (blue; n = 31) and without (gray; n = 45) ICANS. Points indicate patients who were deceased or censored, light shading indicates standard error of the mean. mOS, median overall survival.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/14/10.1182_blood.2023020571/3/m_blood_bld-2023-020571-gr1b.jpeg?Expires=1769087923&Signature=L54hyfZgegebv5nbm2ihvwOa2nZVGZtNII~C8u1q4O-rhQb2W44z~v~GZOxsGkzVLMGraGDmrq92r7xxnFAbLruFRIKuXXCcTdSmqHZvgm-~mgaMudRCQlew-KPrlaE5tdmlT7UPbaB1Mm8kYMpwXHYsvL-HHvbMaG7UED7KaRX~Op0n1QwUwfY7RNj6av8fqpreClqdpI-aUUUexHRQ1CEzEIWhJ6o6qzmC72tYtx71gujap-DwbUWU4GPEx1wHvtExmtKwObnE-kg9X7PegD~SjkxWelw~sjtlYflzkR2CkZQgfVn50qy2G4U1bwSsSXX29JEaXKZf7MLi6UrxvA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal