Abstract
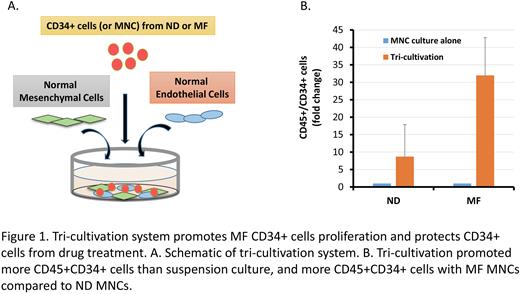
Although the importance of the interplay between myelofibrosis (MF) hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPC) and microenvironmental cells (MC) has been conjectured, direct evidence that such interactions contribute to MF HSPC predominance has not been extensively studied due to the absence of a model system. The components of the MF tumor microenvironment (TME) include non-mutated mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial cells (ECs) thought to be activated by their interaction with MF hematopoietic cells. We developed a tricultivation system (TCS) to recapitulate MF HSPC/TME interactions (Fig. 1A) which involves culturing MF or normal donor (ND) mononuclear cells (MNCs) with normal MSCs and ECs for 6 days. Enumerating the numbers of MF or ND HSPC generated and comparing them to those generated in suspension cultures (SC), we found that the number of ND CD45+CD34+ cells generated in the TCS was 4x greater than that generated in SC (Fig. 1B). By contrast, 20x more MF CD45+CD34+ cells were generated in the TCS (Fig. 1B). We also observed a 10x increase in the numbers of JAK2V617F+ colonies that were assayed from the CD34+ cells in the TCS. These findings reflect the importance of the human TME on MF HSPC.
To identify the transcriptional changes that contribute to the more profound expansion of MF as compared to ND CD45+CD34+ cells in the TCS, we performed bulk RNAseq on purified CD34+ cells from either NDs or MF patients before or after co-cultivation with normal ECs and MSCs. We identified 237 differentially expressed genes (DEG) between the ND and MF CD34+ cells. Many of the 157 gene transcripts upregulated in MF CD34+ are also increased in other cancers, promoting cell proliferation and tumor invasion (FAM22B, EYA2, ALDH1A2, TNFSF18, TCIM). Progressive downregulation of p53 activity is hypothesized to play a role in MF progression. LIN28B, known to block translation of p53, was upregulated (3.7E+12x, padj=8.1E-30) in primary MF CD34+ cells. TWIST1 was also upregulated (3.9E+3x, padj=4.9E-4), and has been shown to be induced by STAT signaling and the HIF1a-NFkB axis. TWIST1 hinders key posttranslational modifications of p53 and facilitates HDM2-mediated degradation. The transcriptome of MF CD34+ cells differed from that of ND CD34+ cells following incubation in the TCS due to the persistence of the increased upregulation of LIN28B (2.8E+3x, padj=5.2E-8).
HDM2 antagonist (HDM2a) therapy is currently being evaluated to treat MF patients with wild type TP53. Upregulation of HDM2 and downregulation of p53 leads to upregulation of NFkB resulting in increased production of proinflammatory cytokines by hematopoietic cells and MSCs. BET inhibitor (BETi) studies have implicated BRD4 in activating NFkB. IL8 and VEGF protein levels were increased in supernatants of MF MNC TCS. BETi therapy decreased NFkB activation in MF CD34+ cells and MSCs, and the level of cytokines by 30%. HDM2a and BETi co-treatment decreased cytokine levels by 50%. HDM2a therapy in both TCS and SC resulted in reduced JAK2V617F+ colonies, but the absolute number that persisted in the TCS was 7x greater than that in SC. Treatment with BETi decreased JAK2V617F+ colonies by 25% in the TCS but by 75% in SC. HDM2a combined with BETi decreased JAK2V617F+ colonies by 95% in TCS. These data indicate the MF TME contributes to resistance of MF CD34+ cells to HDM2a therapy which can be overcome by addition of a BETi.
HDM2a therapy of ND CD34+ cells following TCS culture upregulated a total of 8 genes (padj<0.01) including HMD2 (6.5x), the HDM2 target POLH (2.0x), as well as the p53 targets MIR34AHG (5.6x) and SESN1 (3.6x). HDM2a therapy of MF CD34+ cells in the TCS induced 19 DEGs (padj<0.01) including HDM2 (10.7x), POLH (3.0x), MIR34AHG (5.3x) and SESN1 (4.8x). Other up-regulated genes include p21 (6.4x) and PUMA (5.3x), and XPC (3.8x) that has known p53 dependent and independent functions These data indicate that the TME promotes the predominance of MF as compared to ND progenitors which we attribute to increased transcripts of genes that downregulate p53 activity prior to and following incubation in the TCS. Although HDM2a therapy activates numerous events downstream of p53 in the TCS the reduction of mutated colonies was less. This TME-mediated resistance to HDM2a therapy was eliminated by the co-administration of a BETi which likely downregulates NFκB activity and the elaboration of pro-survival cytokines.
Disclosures
Hoffman:Ionis: Consultancy; Repare: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Silence Therapeutics: Consultancy; Scholar Rock: Research Funding; Abbvie: Other: Chair DSMB, Research Funding; Turning Point: Research Funding; Protagonist Therapeutics: Consultancy; Novartis: Other: Chair DSMB.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal