Abstract
Background:
TP53 mutations occur in 10-20% of patients with AML, constitute high-risk disease as per ELN criteria, and confer poorer prognosis. Venetoclax combination therapies and CPX-351 were recently approved for AML treatment and lead to improved outcomes in subsets of high-risk AML, however the most effective approach for treatment of TP53-mutated (m) AML remains unclear. In this study we explored the clinical outcome of TP53m AML patients treated over the last 8 years as novel therapies have been introduced to our therapeutic armamentarium.
Methods:
We conducted a multicenter observational study in collaboration with 4 U.S. academic centers and analyzed clinical characteristics and outcome of 174 TP53m AML patients diagnosed between March 2013 and February 2021. Mutation analysis was performed on bone marrow specimens using 42, 49, 199, or 400 gene targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) panels. Patients with an initial diagnosis of AML were divided into 4 groups (GP) based on the progressive use of novel therapies in clinical trials and their approvals as AML induction therapy during different time periods: 2013-2017 (GP1, n= 37), 2018-2019 (GP2, n= 53), 2019-2020 (GP3, n= 48) and 2020-2021 (GP4, n= 36) to analyze difference in outcome.
Results:
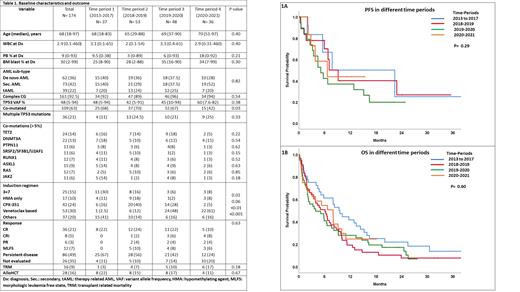
Baseline characteristics were not significantly different across different GP, as shown in Table 1. Median age of patients was 68 (range [R], 18-83), 65 (R, 29-88), 69 (R, 37-90) and 70 (R, 51-97) years in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.40). The percentage of patients with de novo AML/secondary AML/therapy-related AML in GP1-4 was 40/40/20, 36/29/24, 37.5/37.5/25 and 28/52/20, respectively (p=0.82). The proportion of patients with complex cytogenetics (CG) was 92%, 89%, 96% and 94% in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.54). The median TP53m variant allele frequency (VAF) was 48% (range [R], 5-94), 42% (R, 5-91), 45% (R, 10-94) and 60% (R, 8-82) in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.38). Four (11%), 13 (24.5%), 10 (21%) and 9 (25%) patients had multiple TP53 mutations in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.33).
The proportion of patients who received 3+7 (30%, 16%, 6% & 8%; p=0.01), HMA only (11%, 18%, 2% & 8%; p=0.06), venetoclax-based (2.5%, 12%, 48%, & 61%; p <0.01) and CPX-351 induction (16%, 40%, 28% & 5%; p<0.001) were varied in GP1-4, respectively. The rate of CR/CRi was 22%, 26%, 28% and 18% in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.63). Treatment related mortality during induction was observed in 3%, 7%, 10% and 17% of patients in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.18). Overall, 28 (16%) patients received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHCT) after induction/consolidation: 22%, 15%, 17% and 11% in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.67). In subset analysis, there was no difference in the rate of CR/CRi with venetoclax-based regimens vs. others (39% vs 61%, p=0.18) or with CPX-351 vs. others (25% vs 75%, p=0.84).
The median progression-free survival was 7.7, 7.0, 5.1 and 6.6 months in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.60, Fig 1A). The median overall survival (OS) was 9.4, 6.1, 4.0 and 8.0 months in GP1-4, respectively (p=0.29, Fig 1B). In univariate analysis for OS, achievement of CR/CRi (p<0.001) and alloHCT in CR1 (p<0.001) associated with favorable outcome, whereas complex CG (p=0.01) and primary refractory disease (p<0.001) associated with poor outcome. Multiple TP53 mutations (p=0.73), concurrent ASXL1m (p=0.86), extra-medullary disease (p=0.92), ≥ 3 non-TP53m mutations (p=0.72), TP53m VAF ≥ 40% vs. < 40% (p=0.25), induction with CPX-351 vs. others (p=0.59) or venetoclax-based regimen vs. others (p=0.14) did not show significance for favorable or poor OS in univariate analysis. In multivariable analysis, alloHCT in CR1 (hazard ratio [HR]=0.28, 95% CI: 0.15-0.53; p=0.001) retained an association with favorable OS and complex CG (HR 4.23, 95%CI: 1.79-10.0; p=0.001) retained an association with dismal OS.
Conclusion:
We present the largest experience with TP53m AML patients analyzed by NGS. Although outcomes were almost universally dismal, alloHCT appears to improve the long-term survival in a subset of these patients. Effective therapies are warranted to successfully bridge patients to alloHCT and to prolong survival for transplant ineligible patients.
Badar: Pfizer Hematology-Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Litzow: Omeros: Other: Advisory Board; Pluristem: Research Funding; Actinium: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Jazz: Other: Advisory Board; AbbVie: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Biosight: Other: Data monitoring committee. Shallis: Curis: Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Goldberg: Celularity: Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aprea: Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding; DAVA Oncology: Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Research Funding; Prelude Therapeutics: Research Funding; Aptose: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Atallah: BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Foran: revolution medicine: Honoraria; gamida: Honoraria; bms: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria; novartis: Honoraria; takeda: Research Funding; kura: Research Funding; h3bioscience: Research Funding; OncLive: Honoraria; servier: Honoraria; aptose: Research Funding; actinium: Research Funding; abbvie: Research Funding; trillium: Research Funding; sanofi aventis: Honoraria; certara: Honoraria; syros: Honoraria; taiho: Honoraria; boehringer ingelheim: Research Funding; aprea: Research Funding; sellas: Research Funding; stemline: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal