Background: Navitoclax (Nav) is a small-molecule inhibitor of several antiapoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) family proteins, including BCL-xL, BCL2, and BCL-W. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that when administered alone, Nav can effectively induce apoptosis in various types of cancerous cells, including those isolated from patients (pts) with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Ruxolitinib (Rux), a potent Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor, can durably improve symptoms, splenomegaly, and overall survival in pts with myelofibrosis (MF) and is approved for the treatment of pts with primary MF in many countries, including Japan and Taiwan. However, pts can develop resistance to Rux, which may be overcome by the addition of Nav to a combination therapy regimen. An ongoing phase 2 study (NCT03222609) is assessing the safety and efficacy of Nav + Rux combination therapy in pts with MF, and a phase 1 study (NCT04041050) is evaluating the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of Nav monotherapy in Japanese pts with MPNs in part 1 and Nav + Rux combination therapy in Japanese and Taiwanese pts with MF in part 2. Herein we report the currently available results of this phase 1 study, the first to assess Nav treatment in Japanese and Taiwanese pts with MPNs including MF, polycythemia vera (PV), or essential thrombocythemia (ET).
Methods: This phase 1, multicenter, open-label study enrolled pts ≥20 years of age with diagnosis of MPNs: MF, PV, or ET per World Health Organization classification. Eligible pts for part 1 of this study had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1 and were unable to tolerate/declined standard therapy or had MPNs that were unresponsive to standard therapy. Pts received Nav monotherapy at a starting dose of 50 mg orally once per day (QD) with a stepwise dose increase every ≥7 days to a maximum of 300 mg QD on the basis of tolerability. Per protocol, pts could receive treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or the end of clinical benefit. Primary safety objectives included assessing the number of pts with dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) within 28 days of Nav initiation and the number of pts with adverse events (AEs) throughout the study. DLTs included: grade (G)≥2 bleeding associated with low platelet counts of any G; bleeding requiring platelet transfusion; unexpected G≥2 toxicity requiring dose modification or delay of ≥1 week attributable to Nav; and all other G≥3 AEs considered related to Nav (exceptions: G3/4 leukopenia, G3 neutropenia, G4 neutropenia <7 days, G3/4 lymphopenia, G3 thrombocytopenia, G4 thrombocytopenia <7 days, or G3 nausea, vomiting, and/or diarrhea unless unresponsive to treatment).
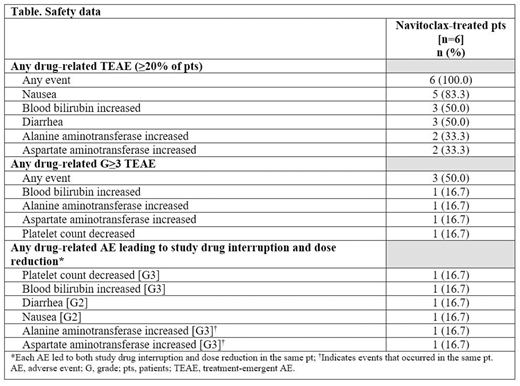
Results: As of May 2020, 6 female Japanese pts (median age: 62.5 years [range 41-79]) were enrolled in part 1 of this phase 1 study and diagnosed with the following: post-PV MF (n=1), post-ET MF (n=1), PV (n=2), and ET (n=2). All pts had received ≥1 prior therapy. Safety data are presented in the Table. The treatment duration for all 6 pts was between 4.6-24.7 weeks as of this cutoff, and all 6 pts were able to receive the maximum 300-mg dose of Nav, with no DLTs reported in any pts. No pts experienced a G≥4 AE during this period. Only 1 of 6 pts experienced a serious AE (SAE); this pt was discontinued and removed from the study on day 52 due to an SAE of epilepsy considered unrelated to Nav treatment. Five of 6 pts experienced a drug-related AE that led to study drug interruption and dose reduction, and all 5 pts remained on study and continued treatment. The current/most recent dose of Nav for all pts (excluding the pt who discontinued) was between 200-300 mg QD. No deaths were reported.
Conclusions: Nav monotherapy had a tolerable safety profile in Japanese pts with MPNs enrolled in part 1 of this phase 1 study, with no DLTs reported. No clinically meaningful differences in safety were detected in this study compared with previous Nav monotherapy studies for hematologic malignancies. Preliminary PK and efficacy analyses for Part 1 are in progress, and Part 2 is ongoing with results to be reported in the presentation.
Shibayama:Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Celgene, Ono, Takeda, AbbVie, Eisai, Novartis, Janssen, Chugai, Astellas, Teijin, MSD, Shionogi, Sumitomo Dainippon, Taiho, Nippon Shinyaku: Research Funding; Takeda, Novartis, Janssen, Ono, Chugai, Eisai, Kyowa Kirin, Sumitomo Dainippon, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, Fujimoto, Nippon Shinyaku, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Otsuka, Mundipharma: Honoraria. Tanaka:Novartis Pharma KK, Celgene K.K: Speakers Bureau. Yeh:Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astex: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hsiao:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Nuthalapati:AbbVie: Current Employment, Other: may own stock. Ono:AbbVie: Current Employment, Other: may own stock. Uehara:AbbVie: Current Employment, Other: may own stock. Okubo:AbbVie: Current Employment, Other: may own stock. Komatsu:Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., PharmaEssentia Japan KK, AbbVie GK, Celgene KK, Novartis Pharma KK, Shire Japan KK, Japan Tobacco Inc: Consultancy; Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Novartis Pharma KK, Shire Japan KK: Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Other: member of safety assessment committee in M13-834 clinical trial.; PPMX: Consultancy, Research Funding; Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd.: Patents & Royalties: PCT/JP2020/008434, Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shire Japan KK, Novartis Pharma KK, PharmaEssentia Japan KK, Fuso Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd., Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutica: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal