Introduction: Cytopenias are a leading cause of ruxolitinib (RUX) discontinuation for patients (pts) with myelofibrosis (MF). Though RUX 5 mg BID is recommended for pts with platelet (PLT) counts of 50 to <100 × 109/L, this regimen can increase risk of thrombocytopenia with minimal benefit on splenomegaly or symptom burden. Fedratinib (FEDR) is an oral, selective inhibitor with activity against wild-type and mutant JAK2 that was assessed as first-line MF treatment (Tx) in the placebo (PBO)-controlled, phase III JAKARTA study, and as post-RUX Tx in the single-arm, phase II JAKARTA2 study. Here we report the efficacy and safety of FEDR 400 mg QD in JAKARTA and JAKARTA2 pts with baseline (BL) PLT counts of <100 × 109/L ("<100") or ≥100 × 109/L ("≥100").
Methods: JAKARTA and JAKARTA2 enrolled adult pts with intermediate- or high-risk MF, PLT counts ≥50 × 109/L, and ECOG PS scores ≤2. These analyses include pts in both studies who received FEDR 400 mg QD (starting dose), and JAKARTA pts randomized to PBO. Outcomes are also assessed for a subgroup of JAKARTA2 pts who met new, more stringent criteria for RUX relapsed/refractory (R/R) or intolerant ("Stringent Criteria Cohort"). RUX R/R required ≥3 mo RUX Tx with an initial response followed by spleen regrowth or suboptimal response; RUX intolerance required ≥28 d of RUX Tx with development of RBC transfusion requirement or grade ≥3 cytopenias, hematoma, or hemorrhage.
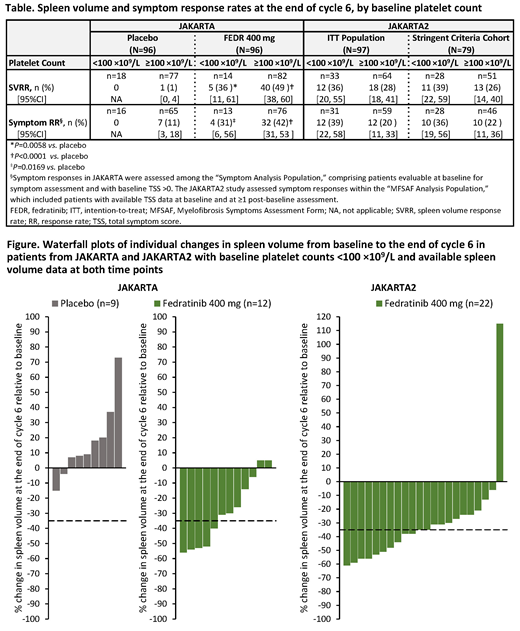
Endpoints of this analysis were spleen volume response rate (SVRR; the proportion of pts who achieved ≥35% spleen volume reductions) and symptom response rate (RR; ≥50% reduction in total symptom score [TSS] on the modified Myelofibrosis Symptom Assessment Form [MFSAF] from BL to end of cycle 6 [EOC6]). SVRR analyses were intention-to-treat (ITT); pts missing data at EOC6 were considered nonresponders.
Results: In JAKARTA, the overall SVRR at EOC6 in the FEDR 400 mg and PBO arms was 47% and 1%, respectively (P<0.0001); median duration of spleen volume response with FEDR was 18.2 mo. In all, 14/96 pts (15%) in the FEDR arm and 18/96 pts (19%) in the PBO arm had BL PLT counts <100. SVRRs with FEDR and PBO in pts with BL PLT counts <100 (Figure) were 36% and 0%, respectively (Table). SVRR and symptom RR with FEDR and PBO in pts with BL PLT counts <100 were similar to those in pts with BL PLT counts ≥100 (Table).
In the BL PLT <100 group, median exposure to FEDR 400 mg and PBO at EOC6 was 24 wks and median FEDR relative dose intensity was >99%. At EOC6, rates of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia (preferred term) for all pts in the JAKARTA FEDR 400 mg and PBO arms were 5% and 6%, respectively; in the subgroup of pts with BL PLT counts <100, rates were also similar between Tx arms (FEDR, 29%; PBO, 22%). Grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia events in the FEDR 400 mg arm led to dose modifications in 1% of pts and permanent Tx discontinuation in 2% of pts, all of whom had BL PLT counts <100.
In JAKARTA2, median prior RUX Tx duration for all pts (N=97) was 10.7 mo. SVRR overall was 31% (Figure) and symptom RR was 27%. Median duration of spleen volume response was not reached at study termination. Among pts with BL PLT counts <100 (n=33), SVRR was 36% and symptom RR was 39% (Table). In the Stringent Criteria Cohort (n=79), SVRR for pts with BL PLT counts <100 (n=28) was 39% and symptom RR was 36%. In both the ITT Population and the Stringent Criteria Cohort, SVRR and symptom RR were comparable between pts with BL PLT counts <100 and those with BL PLT counts ≥100 (n=64; Table).
Median duration of FEDR Tx in pts with BL PLT counts <100 was 27 wks (range 1-79) and in pts with BL PLT counts ≥100 was 22 wks (1-71). 91% of pts with BL PLT counts <100 and 97% with BL PLT counts ≥100 received ≥80% of their intended FEDR dose. Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally similar between PLT groups at EOC6, except for a higher frequency of expected grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia among pts with BL PLT counts <100 (49% vs. 8% in the BL PLT ≥100 group). Among all pts in JAKARTA2, grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia events led to dose modification in 4 pts (3 pts with BL PLT counts <100) and Tx discontinuation in 2 pts (1 pt with BL PLT count <100).
Conclusion: Pts with MF who entered JAKARTA or JAKARTA2 with PLT counts <100 × 109/L achieved similar spleen volume and symptom RRs with FEDR, whether used as first-line therapy, as pts with BL PLT counts ≥100 × 109/L. FEDR was generally well tolerated in pts with very low PLT counts at BL. FEDR is a promising new Tx option for pts with MF and low PLT counts who might otherwise receive suboptimal Tx.
Harrison:Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; AOP: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CTI: Speakers Bureau; Promedior: Honoraria; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Sierra Oncology: Honoraria; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau. Schaap:Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Vannucchi:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CTI: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; ITALFARMACO: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Kiladjian:AOP Orphan: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy. Passamonti:Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Zweegman:Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Talpaz:BMS: Consultancy; Stemline: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Travel; Incyte: Research Funding; Constellation: Research Funding; Asana: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; CTI: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Samus: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding. Verstovsek:Incyte: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Genetech: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sierra Oncology: Research Funding; Pharma Essentia: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Ital Pharma: Research Funding; Protaganist Therapeutics: Research Funding; Constellation: Consultancy; Pragmatist: Consultancy. Rose:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Zhang:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Berry:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Brownstein:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Mesa:AbbVie: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding; AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses; CTI: Research Funding; Galena Biopharma: Consultancy; Shire: Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy; LaJolla: Consultancy; PharmaEssentia: Research Funding; Genotech: Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses; Baxalta: Consultancy; Promedior: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Sierra Oncology: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Samus: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal