Background
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are chronic hematopoietic stem cell disorders, including polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), and primary myelofibrosis (MF). JAK2, MPL, and CALR mutations are considered as "driver mutations" and are directly implicated in the disease pathogenesis by activation of JAK/STAT signaling. However, some patients do not harbor any of these mutations. Since such triple-negative MPNs are very rare, no specific molecular markers were established to use for a precise differential diagnosis yet. So far, the introduction of next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies in research of myeloid neoplasms has provided valuable contributions on the identification of new molecular biomarkers, establishing more accurate risk rating and selection of more specific therapeutic interventions. This study aimed to identify, through targeted deep sequencing, specific genetic variants in patients with triple-negative MPNs.
Methods
We performed NGS targeted sequencing in 18 Brazilian triple-negative patients (11 MF and 7 ET). The median age at diagnosis was 64 years for primary myelofibrosis (range 42-78), and 52 years for essential thrombocythemia (range 19-79). In 14 cases, we used the Illumina TruSight Myeloid Panel covering 54 genes and in 4 cases we used a custom Sure Select Agilent panel containing more than 300 genes previously reported to be related to myeloid neoplasm. The inclusion criteria for variant filtering was quality score>30, read count>50, minor allele frequency<0.05, frameshift, nonsense, splice site and 5`UTR variants, and missense variants described as deleterious for at least three prediction softwares.
Results
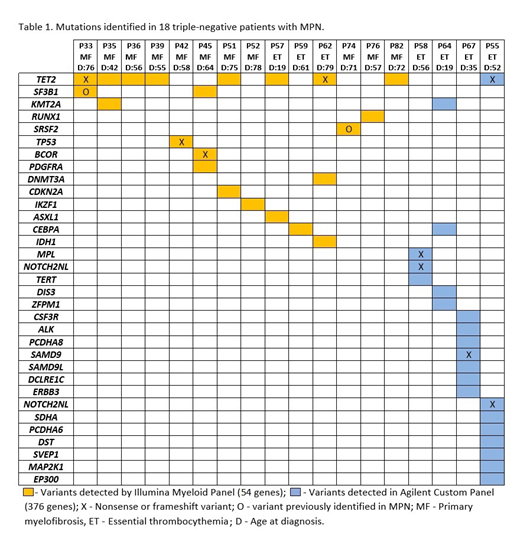
Possible pathogenic mutations were identified in 33 genes by Illumina and/or Agilent panels. Frameshift/nonsense or missense variants previously described as pathogenic correspond to 11 variants (Table 1). Out of these, mutations in TET2 were the most frequently identified (in 9/18 (50%) of the cases). In three MF patients with TET2 mutations no other considered pathogenic mutation was identified, indicating a possible role of TET2 as a driver gene. According to previous reports, the frequency of TET2 mutations in triple-negative MPNs patients were only 7%.
Phenotypically, in our triple-negative MPNs, 6/11 (54.5%) MF and 3/7 (42.9%) ET patients harbored TET2 mutations. Clinically, the adverse prognostic impact of TET2 mutations in MPN had not been consistently shown by previous studies.
In addition, mutations in SF3B1, CEBPA, and KMT2A genes were the second most frequent ones detected in 2/18 each (11%) of the patients, some of which were concomitant with TET2 mutations, suggesting additional clonal advantage due to these genetic events. Other potentially pathogenic variants were also detected is genes that have been reported to be related to other myeloid neoplasms (KMT2A, CDKN2A, TERT, DIS3, ZFPM1, PCDHA8, SAMD9, SAMD9L, DCLRE1C,ERBB3, SDHA, PCDHA6, SVEP1, MAP2K1 and EP300).
Conclusions
We have characterized the genomic alterations in 18 Brazilian patients with MPN triple-negative for either JAK2, CALR or MPL main mutations. Using a sensitive NGS platform, we identified significantly more frequent mutations in TET2 gene (in as many as a half of the cases) compared to JAK2, MPL, CALR mutation-positive MPN cases. We also uncovered mutations in genes not previously related with in MPN. Our novel findings call for further studies validating the frequencies, biological significance, and prognostic impacts of somatic mutations in triple-negative MPNs.
Ogawa:Qiagen Corporation: Patents & Royalties; RegCell Corporation: Equity Ownership; Kan Research Laboratory, Inc.: Consultancy; Asahi Genomics: Equity Ownership; ChordiaTherapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Dainippon-Sumitomo Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal