Background: Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the most common indolent B-cell lymphoma, and its clinical behavior is heterogeneous. FL is sensitive to immunochemotherapy with anti-CD20 antibody, but characterized by a high rate of relapse and having a risk of histological transformation. Bendamustine + rituximab (BR) therapy is one of standard treatment options for both untreated and relapsed FL. There are several reports that 18[F]-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose(¹⁸F-FDG) PET-CT (PET) response after induction therapy can predict progression-free survival (PFS) in FL undergoing first-line immunochemotherapy. However, the significance of PET after second-line therapy has rarely been evaluated, especially in a prospective setting. Thus, we conducted a single arm prospective phase 2 study to compare 1-year (1-yr) PFS between patients with PET-positive and PET-negative at end-of-treatment (EOT) response assessment using standardized PET and CT after the BR therapy in patients with first relapsed or recurrent FL (UMIN000013756).
Method: The W-JHS NHL01 study is a prospective multicenter phase 2 trial, which included adult (≥20 years) patients with relapsed or recurrent FL (CD20 positive, grade 1-3a), ECOG-PS (≤2) and measurable lesion (CT minor axis >1.0cm). Patients had to have one prior regimen with chemotherapy and/or rituximab. Histologic transformation at recurrence was ineligible. Patients were treated with 6 cycles of BR (R 375 mg/m2 d1, B 90 mg/m2 d1-2, every 28 days). EOT PET within 1-2 months after last BR was evaluated, and assessments for progression were made using contrast enhanced CT scans at 12 and 18 months after the registration of this study and at physician's discretion thereafter. Standardized PET and contrast enhanced CT were evaluated centrally by independent expert radiologists and the PET positivity was defined by a residual ¹⁸F-FDG uptake score of 4 or greater (5-point scale). The efficacy of treatment was evaluated by CT scan according to Cheson 2007 criteria. The primary endpoint was 1-yr PFS. Key secondary endpoints were overall response rate (ORR), CR rate (CRR), 1-yr overall survival (OS).
Results: Between July 4, 2014 and Jan 24, 2017, 75 patients were enrolled, eight of whom were excluded from the analysis. Because 4 received fewer than 4 cycles of BR, 2 received with non-standardized PET and 2 had progression disease. Of the remaining 67 patients in the efficacy-evaluable population, median (range) age was 63 (47-83) and 27/67 (40%) were male. 60% of enrolled patients had received R-CHOP for first-line treatment. 60 (80%) patients received 6 cycles of BR. Among 67 patients, median follow-up of surviving patients was 23.9 months (12.2-45.1).
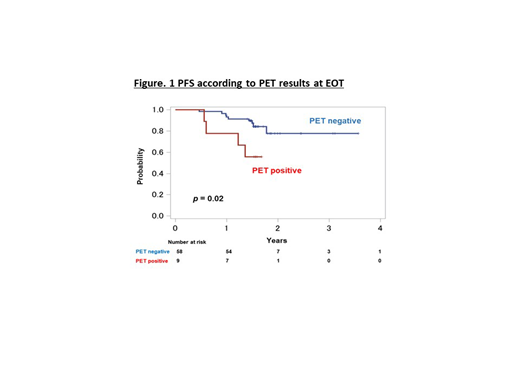
ORR of 67 patients was 97.0% (95%CI: 89.6-99.6%), CRR was 59.7% (95%CI: 47.1-71.5%). 1-yr PFS in 72 patients was 88.9% (95%CI:80.7-94.3%). 1-yr OS in all patients was 97.3% (95%CI:89.6-99.3%). The EOT PET positive rate after BR was 9/67 (13.4%). The prevalence according to 5-point scale was 3% in score 1, 70% in score 2, and 7.5% in score 3. 1-yr PFS was 77.8% [95% confidence interval (CI): 36.5- 93.9%] in EOT PET-positive group (n=9) and 93.1% (95% CI: 82.6-97.3%) in EOT PET-negative group (n=58), with a significantly favorable 1-yr PFS in patients with EOT PET-negative group (log-rank test: p = 0.02) (Figure 1). In addition, there was no statistically significant difference between 1-yr PFS and SUVmax after BR therapy. Standardized PET before BR was done in 29 patients. ΔSUV of ¹⁸F-FDG uptake was not significantly related with 1-yr PFS. And there were no significant relation between 1-yr PFS and FLIPI or FLIPI2.
The prevalence of grade 3 and 4 adverse events (AEs) was lymphopenia (77.3%), neutropenia (32%), leukopenia (30.7%), thrombocytopenia (4%), and anemia (1.3%). In non-hematologic AEs, there was each patient with appendicitis, herpes zoster, reactivation of HBV, nausea, general fatigue, acneiform eruption, hypernatremia, hyponatremia and hypocalcemia.
Conclusions: BR as a second-line treatment for FL was effective with high ORR of 97% and high 1-yr PFS of 88.9%. EOT PET could predict PFS in patients with relapsed/recurrent FL treated with BR.
Rai:Chugai: Speakers Bureau. Suzumiya:Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Chugai-Roche, Eisai, Takeda, Celltrion, SymBio, Astellas, Ono, AstraZeneca, Ootsuka, Taiho, Mundi, Dainihon-Sumitomo: Research Funding. Izutsu:Kyowa Kirin, Eisai, Takeda, MSD, Chugai, Nihon Medi-physics, Janssen, Ono, Abbvie, Dainihon Sumitomo, Bayer, Astra Zeneca, HUYA Japan, Novartis, Bristol-Byers Squibb, Mundi, Otsuka, Daiichi Sankyo, Astellas, Asahi Kasei: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy; Eisai, Symbio, Chugai, Zenyaku: Research Funding; Eisai, Chugai, Zenyaku: Honoraria; Chugai, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Astra Zeneca, Eisai, Symbio, Ono, Bayer, Solasia, Zenyaku, Incyte, Novartis, Sanofi, HUYA Bioscience, MSD, Astellas Amgen, Abbvie, ARIAD, Takeda, Pfizer: Research Funding. Nishikori:Eisai, Ono, Sumitomo Dainippon: Research Funding; Bristol Meyers Squibb, Janssen, MSD, Chugai, Eisai, Sumitomo Dainippon, Kyowa Kirin, Mundipharma, Takeda, Nippon Shinyaku, Ono, Pfizer: Honoraria. Shibayama:Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas, Teijin, MSD, Shionogi, Eisai, Sumitomo Dainippon, Taiho, Nippon Shinyaku: Research Funding; Takeda, Novartis, Janssen, Chugai, Eisai, Mundi Pharma, Ono, Otsuka, Kyowa Kirin, Sumitomo Dainippon, AstraZeneca, Avvie, DaiichiSankyo, Fujimoto, Nippon Shinyaku, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer: Honoraria. Maeda:Mundipharma Co Ltd.: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd.: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Research Funding. Yamauchi:Astellas, AbbVie: Consultancy; Pfizer, Chugai, Teijin, Solasia: Research Funding. Akashi:Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Astellas, Shionogi, Asahi Kasei, Chugai, Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Sumitomo Dainippon, Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy. Kanakura:Chugai, Eisai: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal