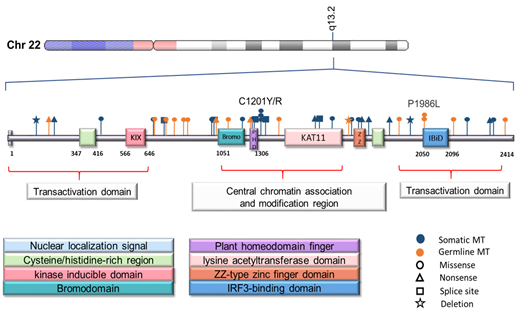
Systematic application of NGS has led to the discovery of a myriad of somatic mutations. One important class of genes affected by mutations in myeloid neoplasia (MN) is involved in epigenetic regulation either directly by modifying DNA or by enzymes modifying histones such as histone methyltranferases and demethylases (e.g., EZH2, MLL, UTX). This work focuses on mutations of EP300, a histone acetyl transferase. EP300 (22q13.2) encodes the adenovirus E1A associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein with lysine acetyltransferase activity as does its paralog CBP (16p13.3). Ablation of EP300 in mice results in embryonic lethality. Heterozygous germline EP300 mutations were described in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RBTS), a congenital neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by facial dysmorphology, distal limb abnormalities and mental retardation. In addition, RTBS patients appear to have a predisposition for childhood malignancies. Somatic EP300 mutations have been found in solid tumors and lymphoid neoplasia but have been less studied in MN.
We analyzed DNA sequencing results of 2382 MN patients [AML (n=1646), MDS (n=344), MDS/MPN (n=79), and MPN (n=31)]. Germline status of lesions was confirmed using skin-biopsy or CD3+ derived DNA, when such specimens were available. New nonsense, deletion, and exceedingly rare, individual, missense mutations (<0.01%, no reported homozygotes form in the control cohort), all of which were predicted to be deleterious by >4/6 applied scoring algorithms (CADD, PolyPhen2, SIFT, LRT, MutationAssesor and MutationTaster within Annovar) were included in downstream analyses. EP300 mutations were detected in 2% of patients (47/2382); 61% (28/46) were somatic and 39% (18/46) germline. Mutation types in somatic vs. germline were: missense (43 vs. 68%), nonsense (25 vs. 21%), splice site (14 vs. 0%), deletion (7 vs. 5%) and insertion (10 vs. 0%). No patients with hemizygous deletions were detected by SNP array. Median age of EP300 somatic and germline mutants were similar compared to EP300 wild type [63 (56-81) vs. 65 (29-79) vs. 65 (18/92) years]. For somatic EP300 mutants, 43% of cases (10/23) were characterized by normal and 22% complex cytogenetics without enrichment for -7/7q, del5q, del20q or +8. Of note, 67% of MDS patients (4/6) had a prior history of other malignancies treated with chemoimmunotherapy or radiation (lymphoma, prostate cancer).
Using VAF-based bioanalytic methods, we were able to roughly recapitulate the clonal architecture and identify founder lesions. We compared the expected vs. observed VAFs according to the corresponding variability in read counts and a stringent binomial distribution algorithm. EP300 mutations were more likely to be dominant lesions (62.5%) while 37% were subclonal. Serial sample analysis was performed; EP300 mutant subclones expanded during progression of the diseases suggesting a tumor suppressor function of EP300. In normal hematopoiesis, EP300 expression increases proportionally with myeloid precursors' maturation. We found that EP300 mRNA levels were significantly lower in AML patients vs. healthy controls (log2CPM: 7.92 vs. 8.27, P=.03; Beat AML).
One therapeutic approach would be to alleviate the effects of the mutations using HDACi. However, HDACi had equal sensitivity in EP300 mutant and WT cells in publicly available databases of drug sensitivity and also according to expression levels (low vs. high). Another alternative therapeutic approach is based on the potential synthetic lethality of a total loss of EP300 concluded from embryonic lethality in mice. Using in vitro proliferation assays we found that the HATi S7152 was more effective in growth inhibition (GI) in the EP300 mutant cells, Jurkat (M2118I) at 10 µM (GI: 84%) compared to EP300 wild type cells e.g., KG-1 (43%), K562 (54%), U937 (24%) and TF-1 (15%) at 10mM while NB-4 (L2393V) cells only reached a GI (27%) at 20µM.
In sum, we characterized for the first time the spectrum of somatic and germline EP300 mutations in MN and the possible therapeutic implications of using HATi to modulate EP300 activity.
Sekeres:Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Maciejewski:Alexion: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal