Background
There are many factors associated with early mortality after CABG, including postoperative thrombocytopenia (Kertai, 2016). Many factors during CABG surgery, such as administration of heparin or cardio pulmonary bypass during surgery are related to thrombocyte count reduction (Hamid, Akhtar, Naqvi, & Ahsan, 2017; Arepally, 2017). However, it is possible for a post-CABG patient to suffer a significant thrombocyte reduction without reaching the thrombocytopenic state (thrombocyte count <150000/µL). Up to this time, there is still lack of study about association between thrombocyte reduction after surgery and 30-day mortality in patients undergo CABG. This study aim to determine cut off point for postoperative thrombocyte reduction as a predictor of 30-day mortality after CABG surgery.
Method
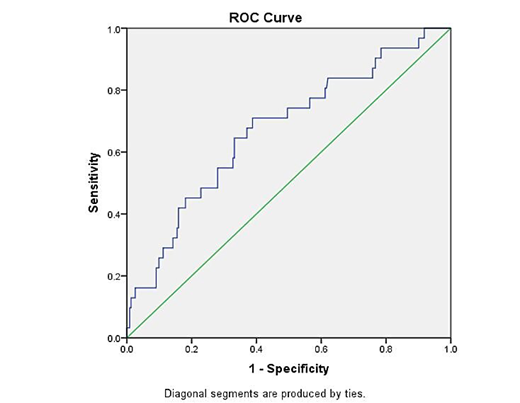
This is a retrospective cohort study using medical record of 263 adult patients who underwent CABG surgery in dr. Ciptomangunkusumo National Hospital on 2012-2015. Thrombocyte reduction was determined by substracting preoperative thrombocyte count from postoperative thrombocyte count. Receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis between percentage of thrombocyte reduction and 30-day mortality after surgery was done to obtain the sensitivity and specificity value of a particular degree of thrombocyte reduction. Cut off point was obtained from intersection between sensitivity and specificity value.
Result
Thirty-day mortality rate after CABG surgery in this study was 11.9%. Cut off point obtained from ROC analysis was 30% with area under the curve (AUC) 0.671. The sensitivity of this cut off point to predict early mortality after CABG surgery was 64.5%, while the specificity was 64.7%
Conclusion
Thrombocyte reduction more than or equal to 30% can be used as a predictor of 30-day mortality after CABG surgery.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal