Background
Hydroxyurea (HU) is used to treat sickle cell disease (SCD) in part because of its ability to increase hemoglobin F (HbF) concentration, but the mechanism by which HU induces HbF, and the low or lack of HbF response in a fraction of the patient remains unclear.
HU causes myelo-suppression and induces stress hematopoiesis, which is associated with increase production of HbF. Earlier research has shown that HbF levels in SCD patients are inversely correlated with reticulocytes, which can be secondary to: 1) HbF-induced decreased hemolysis with less needs for red blood cell (RBC) production, and 2) Myelo-suppression. It has also been shown that the number of CD34+ cells is generally lower in HU treated patients, but the overall response of the hematopoietic system in relationship to HbF has not been characterized. Here, we prospectively isolated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from HU-treated SCD patients and characterize their hematopoietic and HbF responses.
Methods
Peripheral blood (PB) was collected from 19 HbSS who had been HU for >3 years and from 12 healthy controls. Frozen mono-nuclear cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using CD49f, 90 45Ra, 123, 235a, 38, 34, 33 and lineage antibodies. The number of 49f+ long-term Hematopoietic Stem Cells (LT-HSC), Multipotent Progenitors (MPPs), Common Myeloid Progenitors (CMPs), Megakaryocyte-Erythroid Progenitors (MEPs), and Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors (GMPs) per uL of blood or per CD34+ cells was then quantified.
Results
The percentages of reticulocytes per uL of blood were found to correlate positively with the concentration per uL of blood of all stem and progenitor cell populations tested (CD34 (R2 = 0.6583), LT-HSC (R2 = 0.3532), MPP (R2 = 0.2603), CMP (R2 = 0.5889), MEP (R2 = 0.2411), and GMP (R2 = 0.6911)).
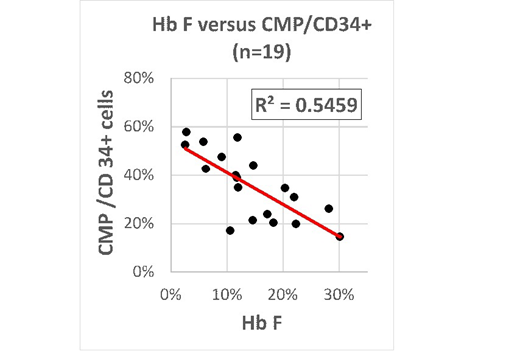
Statistically significant (p<0.05) inverse correlations were also observed between HbF levels and the number of CD34+/uL ( R2 = 0.2931), and the number of CMP/uL (R2 = 0.3732). Normalization of the data to the number of circulating CD34+ cells revealed that there was a strong inverse correlation between HbF levels and the percentage of circulating CMPs (R2 = 0.5424), and importantly, that this correlation was specific to the CMP population since Hb F did not correlates with any of the other HSPC populations analyzed .
Analysis of the PB of 12 healthy individuals revealed that, as in SCD patients, the percentage of CMPs varied between < 10% and >60% of the total circulating CD34+ cells. Further analysis revealed that the CMP percentages in both SCD and healthy controls appeared characteristics of each individual tested since the measurements were remarkably correlated (R2 >0.7) when they were repeated on blood samples collected at intervals of two-weeks or one-year.
Discussion
The positive correlation between the reticulocyte and HSPC populations that we observed was previously unreported and suggests that, in first approximation, the reticulocytes could serve as a proxy for the levels of circulating HSPCs which could help assess the degree of bone marrow suppression in compliant non-responding HU-treated patients.
We identified an inverse correlation between percentages of HbF and circulating CMPs in HU-treated SCD patients that is specific to these progenitors. The specificity of the correlation suggests that the major mechanism for the correlation is unlikely to be differential mobilization of CMPs to the PB since inducing mobilization generally affect all HSPCs. A depletion of the CMPs in the bone marrow of high Hb F responders is therefore a more likely mechanism. A possible mechanism for the correlation is that HU acts directly on CMPs by accelerating their differentiation leading to the relative depletion of these progenitors in high F individuals, and initiating the reprogramming of gene expression that ultimately results in high level of gamma-globin expression.
Alternatively, the similar range of variability in the percentage of CMPs in HU-treated SCD patients and in healthy individuals never exposed to HU, and the observation that the percentage of circulating CMP seem to be an intrinsic characteristic of each individual suggest that the percentage of circulating CMPs might be a genetically determined marker associated with the ability to produce HbF in response to HU therapy, rather than being a consequence of the treatment.
Minniti:Doris Duke Foundation: Research Funding. Manwani:Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; GBT: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal