Background: Measuring residual disease during the continuum of care is fundamental to oncology practice. In particular, minimal residual disease (MRD) assessments and trends over time can help inform clinical management, including change in treatment regimen or treatment discontinuation. In patients (pts) with plasma cell and lymphoid malignancies, next-generation sequencing (NGS)-MRD is a valuable tool for assessing MRD and depth of response to treatment. MRD status is strongly prognostic of time to relapse and overall survival in multiple myeloma (MM), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In this report, we summarize our 2-year experience with clinical implementation of NGS-MRD (clonoSEQ®) testing across a spectrum of plasma cell and lymphoid disease.
Methods: This retrospective analysis summarizes our experience using the NGS-MRD Assay (Adaptive Biotechnologies, Seattle, WA) in plasma cell and lymphoid malignancies. The assay uses multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and NGS to identify, characterize, and monitor unique disease-associated sequence rearrangements or clonotypes of immunoglobulin (Ig) IgH (V-J), IgH (D-J), IgK, and IgL receptor gene sequences, and translocated BCL1/IgH (J) and BCL2/IgH (J) sequences in DNA extracted from high disease burden diagnostic (ID) and post-treatment (MRD) samples. PCR amplification bias control ensures a quantitative read-out of the full B-cell receptor repertoire present in the ID sample and provides direct measure of tumor burden. Our study included pts with plasma cell and lymphoid malignancies, including MM, ALL, CLL, and MCL treated at the Moffitt Cancer Center between March 2017 and March 2019 who had provided at least an ID sample for NGS-MRD testing.
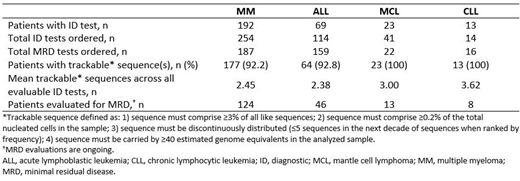
Results: A total of 423 ID tests using DNA from bone marrow (BM; n=407) or peripheral blood (PB; n=16) and 384 MRD tracking tests (BM, n=321; PB, n=63) were performed in 297 pts (Table). The median turnaround time from shipment arrival to assay initiation was 2.1 hours and from activation to report date was 7.1 days. For MM, ALL, MCL, and CLL, the numbers of tests ordered, calibration rates (defined as proportion of ID samples with trackable sequence[s]), and mean number of trackable sequences are shown in the Table. More ID tests were ordered than number of pts (range: 108-178%) due to multiple tests performed for each patient. Sequences analyzed for MRD tests included IgH, IgK/IgL, and T-cell receptors β and γ. The proportion of pts with detectable MRD is shown by indication in the Table.
In MM, autologous stem cell transplant (autoSCT)-eligible pts or those who achieved excellent initial responses but were transplant-ineligible, were primarily considered for NGS-MRD testing as part of standard of care. NGS-MRD testing was performed prior to autoSCT and post-SCT before initiation of maintenance therapy for prognostication. More than 90% of MM cases with successful NGS-MRD results had trackable clones. Negative NGS-MRD assured excellent disease control and supported the decision to discontinue therapy in some pts with significant toxicities.
In pts with ALL, treatment response after induction and/or consolidation guided decision-making for allogeneic (allo) SCT at first remission. MRD burden prior to alloSCT could potentially guide the decisions and timing on performing SCT or conditioning regimen intensity.
In pts with MCL, treatment response evaluated by NGS-MRD following 6 cycles of therapy was a decision point in a randomized trial of auto-transplant + rituximab vs rituximab alone (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03267433). MRD is also being used to guide the duration of rituximab maintenance therapy.
Updated data analysis for all indications, including CLL, is underway and will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusions: The NGS-MRD Assay is a highly sensitive diagnostic tool for the observation of deeper disease response to therapy in multiple specimen types and in various lymphoid and plasma cell malignancies. NGS-MRD may assist in therapeutic decision-making or prognostication. NGS-MRD is a sensitive and powerful prognostic tool available for the majority of pts, which will help our understanding of the role of MRD in clinical management of plasma cell and lymphoid malignancies.
Srivastava:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Employment, Equity Ownership. Lee:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Employment, Equity Ownership. Nishihori:Novartis: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding. Shah:AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria; Spectrum/Astrotech: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene/Juno: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria; Incyte: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Alsina:Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Baz:Merck: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Pinilla Ibarz:Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Sanofi: Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Teva: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Shain:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Research Funding; Sanofi Genzyme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal