Background: Regulatory T cells (Treg), a well defined suppressor cell population with the phenotype of CD4+CD25+CD127- FoxP3+ are emerging as a promising adoptive therapy for a diverse subset of autoimmune diseases and inflammatory disorders. Specificlaly, cord blood (CB) Tregs have been shown to be superior to peripheral blood (PB) Tregs in their function and stability. Here, we define a novel subset of CB Tregs CD4+CD8+CD25+CD127- FoxP3+ that is not very well defined in the PB population and explore its' differentiation characteristics.
Method: Tregs were isolated from CB or PB as described previously and cultured in the presence of CD3/28 beads and IL-2. On the day of harvest, cells were further sorted for CD8+ cell population and labelled as CD8+CD4+ (double positive CB Tregs: DP) and the leftover fraction as CD8-CD4+ (single positive CB Tregs: SP). Cells fractions were analyzed using flow cytometry and for cytokine assay, cells were activated (5 hours) with 1X Cell Stimulation Cocktail with Golgi inhibitors and stained for IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17, IL-10 or TGFβ1 as per manufacturer's instructions. Additional cytokine assay was performed on the culture supernatants. DNA methylation assay was performed for the TSDR region as per manufacturer's instructions. Single cell RNAseq was performed at Albert Einstein Hospital and analyzed at Methodist Hospital. A threshold for original counts were applied to all four conditions, i.e. only transcripts with original counts>10 in all four. This step reduced the number of genes from 34626 to 16628; subsequently stringent cutoffs pairs showed two sets of genes- 1) Fold change>1.5, p-value<0.1, and 2) Fold change<2/3, p-value<0.1, this led to 73 rows, all with defined transcript names. Enrichment analysis using ConsensusPathDB for the above two gene sets were run to identify all pathways with at least one member-gene overlapping with either list, and the enrichment p-value for the pathway<0.1.
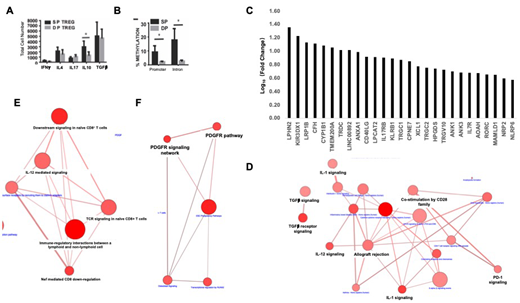
Result: We cultured the Tregs isolated from CB or PB for 14 days and no evidence of a DP Tregs (0) was seen in PB as compared to a clearly defined DP Treg (8-26%) population in CB cultures. No differences were seen between the SP and DP CB Tregs in terms of the markers for mechanisms of suppression (FoxP3,Helios,CD39 ), homing (PSGL1, CLA, CD62L, CD49d), TGF-beta signaling (LAP, TGF-beta, GARP) and T cell signaling (LAG23, PD1, Icos, Tim3, CTLA-4, GITR). DP CBTregs consisted of a significantly higher expression of CCR4hiCXCR3hiCD95hipopulation. DP CB Tregs demonstrated a significantly higher IL-10 secretion compared to SP CB Tregs (Fig 1A) which correlated with the level of IL-10 secreted in the cell cuture supernatant (data not shown). While the degree of suppression of the proliferating conventional T cells was similar by the DP and SP CB Tregs (data not shown), a significantly higher demethylation of FoxP3 promoter and first intron region was observed in the DP vs SP CB Treg population (n=3) (Fig 1B). A total of 337 pathways were identified from Up-406 gene set, 80 of these pathways had enrichment p-value<0.05 and q-value<0.25 (Fig 1C). The Top 10 pathways enriched with members of Up-406 genes include (Fig 1D): TGF-β Receptor Signaling; Interleukin-10 signaling; Inflammatory bowel disease; IL12 signaling mediated by STAT4. A total of 158 pathways were identified from Down-314 gene set, 19 of these pathways had enrichment p-value<0.05 and q-value<0.25. The Top 10 pathways enriched with Down-314 genes included Immuno-regulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell; ESC Pluripotency Pathways; Downstream signaling in naive CD8+ T cells; PDGF receptor signaling network; Nef Mediated CD8 Down-regulation (Fig E, F).
Conclusion: We have identified a novel double positive CD4+CD8+ CB Treg population. Additional experiments for evaluating suppressor mechanism in addition to IL-10 secretion are ongoing.
Verma:Stelexis: Equity Ownership, Honoraria; Acceleron: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding. Iyer:Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Parmar:Cellenkos Inc.: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal