Background
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) conducted in populations of European ancestry (EA) have identified and confirmed 23 germline susceptibility loci for multiple myeloma (MM). The effect sizes of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at these loci are small, therefore combining them into a single summary measure, known as a polygenic risk score (PRS), may provide a more meaningful risk factor. We have previously shown a PRS comprised of the 23 SNPs for MM contributes to increased risk of MM, with a 2.7-fold increase for highest vs. lowest PRS quintiles. Whether the MM-PRS is also associated with overall survival (OS) in MM cases has not been evaluated. We examined the association between MM-PRS and OS in two EA studies.
Methods
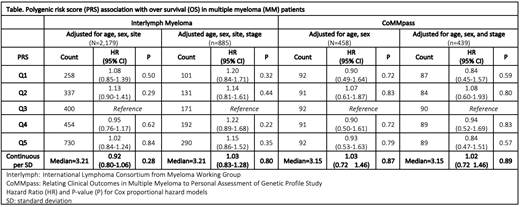
The first study consisted of 2,179 EA MM cases from ten studies included in the Multiple Myeloma Working Group within the International Lymphoma Consortium (InterLymph). Cases were diagnosed between 1970 and 2015 and genotyped using multiple platforms (Oncoarray, Affymetrix, Human660W-quad Beadchip, and Illumina arrays); 885 cases also had stage [based on International Staging System (ISS)] available. Each of the GWAS was subjected to rigorous standard quality control independently (prior to imputation via the Michigan imputation server based on the Haplotype Reference Consortium (HRC). The second study consisted of 515 newly diagnosed EA MM cases from CoMMpass (Relating Clinical Outcomes in Multiple Myeloma to Personal Assessment of Genetic Profile), diagnosed from 2011-2013, who had whole genome sequencing (WGS) performed on germline DNA. The WGS data was used to call common germline genetic variants through the Mayo Clinic bioinformatics pipeline. Briefly, genetic variants were detected with GenomeGPS, aligned to the hg19 reference genome, called using the GATK (V3.6) Haplotype Caller, and merged for multiple-sample joint calling. To reduce the false positive variants, variant quality score recalibration (VQSR) was applied for both SNPs and INDELs. After quality control, 458 EA samples remained. Follow-up was available for both studies and consisted of time from MM diagnosis date until death or date of last known follow-up. The PRS was constructed from the 23 MM SNPs using the published per allele odds ratio associated with MM risk. The published log odds ratios for each SNP were multiplied by the number of risk alleles (0, 1, 2) for the corresponding SNP, and summed, resulting in a unique score per person. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazard models were used to assess the association between PRS with MM OS considering two models: 1) adjusted for age, sex, study and 2) additional adjustment by stage (ISS). Hazard ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated. The PRS was evaluated both as a continuous variable, per standard deviation (SD), and as a categorical variable (quintiles).
Results
MM cases (N=2,179) in the InterLymph study were 59% male and 41% female and the median age was 61.0 years (26-90 years). Median follow-up time was 57.2 months (1.0-509.0 months) with 868 reported deaths. MM cases with stage information available consisted of 20% stage I (n=178), 53% stage II (n=466), and 27% stage III (n=241). No association was observed between PRS and OS in MM patients regardless of adjustment for stage (continuous PRS (HR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.83-1.28, P=0.80) or by quintile PRS (p>0.05)) (Table). The CoMMpass EA MM cases (n=458) had similar distributions for sex (61% male and 39% females) but were slightly older 65 years (27-93 years) and had shorter follow-up time (median=39.75 months (0.13-77.2)) with 117 deaths. Stage was available for 96% of CoMMpass cases including 36% stage I (n=159), 33% stage II (n=146), and 31% stage III (n=134). We also observed no association of PRS and OS in the CoMMpass study (HR=1.02, 95% CI: 0.72 -1.46, P= 0.89), adjusted for age, sex, and stage (Table).
Discussion
A PRS score for MM risk is not associated with OS for MM cases in two EA populations. Given that prior studies have shown association of genetic variation with MM survival, efforts to identify additional loci associated with OS or MM specific survival are warranted. Future studies should also consider germline variants impact on molecular subtypes, specific therapies, and outcomes.
Kumar:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal