Nowadays, patients with multiple myeloma (MM) have multiple choices of therapy including monoclonal antibodies, proteasome inhibitors, and immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs), whereas some patients still develop resistance to these drugs and require novel therapeutic modalities. Here, we focused on inhibition of HDAC and AKT to overcome drug resistance.
Lenalidomide (Len) selectively binds to cereblon (CRBN), which mediates recruitment of specific substrates like IKZF1 to E3 ubiquitin ligase and subsequent degradation, resulting in downregulation of IRF-4 and c-Myc. Then, we developed Len-resistant myeloma cells by RNAi-mediated downregulation of CRBN. Treatment of these cells with HDAC inhibitors reduced IKZF1 mRNA, suggesting potential efficacy of HDAC inhibitors against CRBN-low expressing or mutated MM. According to the integrated database for expression profile and disease prognosis (GenomicScape, http://www.genomicscape.com), higher expression of MICA was significantly associated with better overall survival in MM. MICA is an NK cell-activating ligand and plays an important role in ADCC. We observed that ADCC activity of both daratumumab and elotuzumab against MM cells was enhanced in the presence of HDAC inhibitors, which was compatible with our previous data that HDAC inhibitors upregulated MICA mRNA expression via inhibition of IKZF1 (ASH2018 abstract #4435). We also observed that HDAC inhibitors upregulated MICA mRNA in CRBN-deficient cells, suggesting promise of the combination of HDAC inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies against Len-resistant MM.
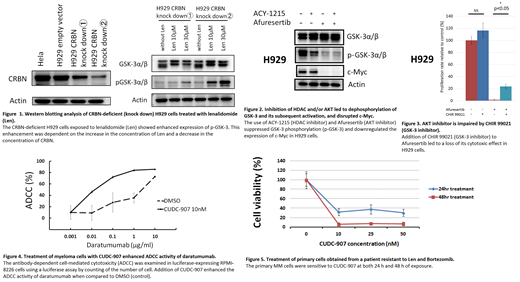
Len-resistance is also affected by phosphorylation status of GSK-3. PI3K/AKT pathway is frequently activated in MM cells, and AKT inactivates GSK-3 by direct phosphorylation, resulting in c-Myc stabilization. Enhanced phosphorylation of GSK-3 was observed in CRBN-deficient H929 cells after long-term culture with Len, and such a phosphorylation status of GSK-3 was correlated with less CRBN amount and higher Len concentration (Figure 1). Afuresertib, an AKT inhibitor, suppressed GSK-3 phosphorylation (p-GSK-3) with or without ACY-1215, an HDAC inhibitor, leading to a substantial decrease of c-Myc (Figure 2). On the other hand, CHIR 99021, a GSK-3 inhibitor, partially counteracted to cytotoxic effect of afuresertib on H929 cells (Figure 3). These results suggest that increased p-GSK-3 is involved in acquired Len-resistance, and that combined inhibition of HDAC and AKT can overcome Len-resistance through decreased p-GSK-3.
Furthermore, we examined the efficacy of CUDC-907, a dual HDAC and PI3K inhibitor. CUDC-907 had a cytotoxic effect on the MM cell lines including those had low CRBN expression. Bortezomib, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone resistant MM cell lines were also sensitive to CUDC-907. CUDC-907 upregulated MICA mRNA expression, but downregulated IKZF1 mRNA expression. Treatment of RPMI-8226 cells with CUDC-907 enhanced the ADCC activity of daratumumab (Figure 4). Furthermore, CUDC-907 was effective on primary MM cells which were resistant to bortezomib and Len (Figure 5).
Thus, dual inhibition of HDAC and AKT with or without monoclonal antibodies is a promising therapeutic approach to multi-drug resistant MM.
Imai:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Parmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Futami:Torii Pharmaceutical: Research Funding. Ri:Janssen Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Teijin Pharma: Research Funding. Yasui:TokioTHERA Holdings, Inc.: Equity Ownership. Iida:Teijin Pharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Research Funding; Chugai: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daichi Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding. Tojo:Torii Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; AMED: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal